CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (4): 1841-1851.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240693
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tianzi CAI1( ), Haifeng ZHANG1, Haidan LIN2, Zilong ZHANG1, Pengyu ZHOU1, Bolin WANG1(
), Haifeng ZHANG1, Haidan LIN2, Zilong ZHANG1, Pengyu ZHOU1, Bolin WANG1( ), Xiaonian LI3(
), Xiaonian LI3( )
)
Received:2024-06-21
Revised:2024-10-24
Online:2025-05-12
Published:2025-04-25
Contact:
Bolin WANG, Xiaonian LI
蔡天姿1( ), 张海丰1, 林海丹2, 张子龙1, 周鹏宇1, 王柏林1(
), 张海丰1, 林海丹2, 张子龙1, 周鹏宇1, 王柏林1( ), 李小年3(
), 李小年3( )
)
通讯作者:
王柏林,李小年
作者简介:蔡天姿(1999—),女,硕士研究生,czltz2584@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Tianzi CAI, Haifeng ZHANG, Haidan LIN, Zilong ZHANG, Pengyu ZHOU, Bolin WANG, Xiaonian LI. A density functional theory study on the sensing of dissolved gases CO and CO2 in transformer oil using boron-doped nitrogen-based graphene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1841-1851.
蔡天姿, 张海丰, 林海丹, 张子龙, 周鹏宇, 王柏林, 李小年. 硼掺杂氮基石墨烯检测变压器油中溶解气体CO和CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1841-1851.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
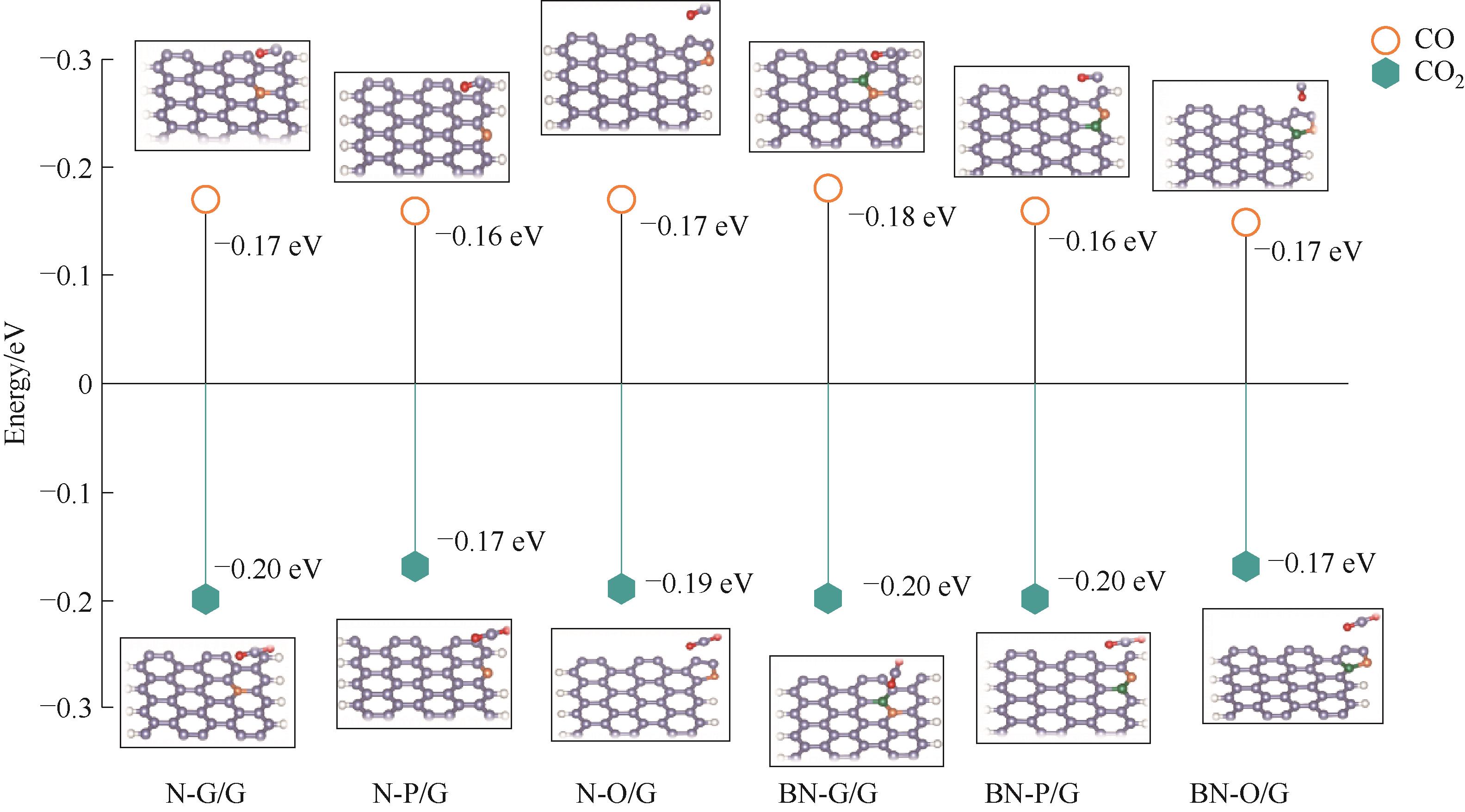
Fig.3 Optimal configuration diagrams and adsorption energies of CO and CO2 gases on various heteroatom-doped graphene nanoribbon systems (purple: C; yellow: N; green: B; red: O; white: H)
| Structure | Bond length/Å | D/Å | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C | B—C | B—N | N—C | CO | CO2 | |
| G | 1.421 | |||||
| N-G/G | 1.429 | 1.406 | 3.229(O—N) | 3.102(O—N) | ||
| BN-G/G | 1.428 | 1.498 | 1.441 | 1.410 | 3.447(O—B) | 3.672(O—B) |
| N-P/G | 1.445 | 1.364 | 3.695(O—N) | 3.621(O—N) | ||
| BN-P/G | 1.464 | 1.538 | 1.416 | 1.346 | 3.767(O—B) | 3.632(O—B) |
| N-O/G | 1.436 | 1.398 | 3.677(O—N) | 3.766(O—N) | ||
| BN-O/G | 1.446 | 1.476 | 1.357 | 1.402 | 3.440(O—B) | 3.475(O—B) |
Table 1 Bond lengths and distances of CO and CO2 gases adsorbed onto the surface of various heteroatom-doped graphene nanoribbon systems
| Structure | Bond length/Å | D/Å | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C | B—C | B—N | N—C | CO | CO2 | |
| G | 1.421 | |||||
| N-G/G | 1.429 | 1.406 | 3.229(O—N) | 3.102(O—N) | ||
| BN-G/G | 1.428 | 1.498 | 1.441 | 1.410 | 3.447(O—B) | 3.672(O—B) |
| N-P/G | 1.445 | 1.364 | 3.695(O—N) | 3.621(O—N) | ||
| BN-P/G | 1.464 | 1.538 | 1.416 | 1.346 | 3.767(O—B) | 3.632(O—B) |
| N-O/G | 1.436 | 1.398 | 3.677(O—N) | 3.766(O—N) | ||
| BN-O/G | 1.446 | 1.476 | 1.357 | 1.402 | 3.440(O—B) | 3.475(O—B) |
| Structure | Transfer electron/e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | B | C | O1 | O2 | CO | CO2 | |
| CO/BN-G/G | -1.498 | +1.885 | +1.059 | -1.072 | -0.013 | ||
| CO/BN-O/G | -1.467 | +1.913 | +1.073 | -1.085 | -0.012 | ||
| CO2/BN-G/G | -1.490 | +1.881 | +2.076 | -1.060 | -1.023 | -0.009 | |
| CO2/BN-O/G | -1.480 | +1.948 | +2.087 | -1.050 | -1.047 | -0.008 | |
Table 2 Charge transfer quantities for CO and CO2 adsorption on BN-G/G and BN-O/G
| Structure | Transfer electron/e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | B | C | O1 | O2 | CO | CO2 | |
| CO/BN-G/G | -1.498 | +1.885 | +1.059 | -1.072 | -0.013 | ||
| CO/BN-O/G | -1.467 | +1.913 | +1.073 | -1.085 | -0.012 | ||
| CO2/BN-G/G | -1.490 | +1.881 | +2.076 | -1.060 | -1.023 | -0.009 | |
| CO2/BN-O/G | -1.480 | +1.948 | +2.087 | -1.050 | -1.047 | -0.008 | |
| 1 | Ni J M, Yang B Q, Jia F F, et al. Theoretical investigation of the sensing mechanism of the pure graphene and Al,B,N,P doped mono-vacancy graphene-based methane[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2018, 710: 221-225. |
| 2 | Skorupska M, Ilnicka A, Lukaszewicz J P. Modified graphene foam as a high-performance catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. RSC Advances, 2023, 13(36): 25437-25442. |
| 3 | Gui Y G, Xu L N, Ding Z Y, et al. Co, Rh decorated GaNNTs for online monitoring of characteristic decomposition products in oil-immersed transformer[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 561: 150072. |
| 4 | Zhang J, Wang Y Q, Wei Z, et al. Ni-decorated ZnO monolayer for sensing CO and HCHO in dry-type transformers: a first-principles theory[J]. Chemosensors, 2022, 10(8): 307. |
| 5 | Yuan T, Fu C, Gong Y J, et al. First-principles insights into Cu-decorated GaN monolayers for sensing CO and HCHO in dry-type transformers[J].ACS Omega, 2021, 6(29): 19127-19133. |
| 6 | Simões A N, Lustosa G M M M, de Souza Morita E, et al. Room-temperature SnO2-based sensor with Pd-nanoparticles for real-time detection of CO dissolved gas in transformer oil[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2024, 311: 128576. |
| 7 | Li Z, Zhang Q R, Wang Z T, et al. A highly sensitive low-pressure TDLAS sensor for detecting dissolved CO and CO2 in transformer insulating oil[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 174: 110622. |
| 8 | Zeng Q L, Wang L H, Zhu H, et al. Estimating daily concentrations of near-surface CO, NO2, and O3 simultaneously over China based on spatiotemporal multi-task transformer model[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2024, 316: 120193. |
| 9 | Gui Y G, Liu Z C, Ji C, et al. Adsorption behavior of metal oxides (CuO, NiO, Ag2O) modified GeSe monolayer towards dissolved gases (CO, CH4, C2H2, C2H4) in transformer oil[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2022, 112: 134-145. |
| 10 | Wang H M, Wu H L, Cui H. First-principles screening in Cu-embedded PtSe2 monolayer as a potential gas sensor upon CO and HCHO in dry-type transformers[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2022, 1209: 113586. |
| 11 | Cui H, Jia P F, Peng X Y, et al. Adsorption and sensing of CO and C2H2 by S-defected SnS2 monolayer for DGA in transformer oil: a DFT study[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 249: 123006. |
| 12 | Xie R J, Lu J B, Wang J. High performance room temperature CO gas sensor based on CuO/ TiO2/N-MWCNTs ternary nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2024, 131: 248-256. |
| 13 | Wu H, Fang J, Yuan S, et al. Exploration on the application of copper oxide particles doped janus ZrSSe in detecting dissolved gases in oil-immersed transformers: a DFT study[J]. Materials Today Chemistry, 2024, 38: 102038. |
| 14 | He T, Liu H C, Zhang J, et al. DFT study on the adsorption and sensing properties of dissolved gases (H2, CO and CH4) in transformer oil on PdO-doped In2O3 (110) surfaces[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2023, 832: 140865. |
| 15 | Zhao P P, Tang M C, Zhang D Z. Adsorption of dissolved gas molecules in the transformer oil on metal (Ag, Rh, Sb)-doped PdSe2 momlayer: a first-principles study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 600: 154054. |
| 16 | Chen Z W, Zhang X X, Xiong H, et al. Dissolved gas analysis in transformer oil using Pt-doped WSe2 monolayer based on first principles method[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 72012-72019. |
| 17 | Zhang Y S, Yan S C, Zhu Y W. Gas-sensing properties of Ti, Zr, V, and Nb-modified Ti3C2O2 for decomposed gases in locomotive electric transformers: a DFT study[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2024, 53(8): 3548-3558. |
| 18 | Zhang B S, Zhang J Q, Huang Y, et al. Burning process and fire characteristics of transformer oil[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2020, 139(3): 1839-1848. |
| 19 | Saeid M, Zeinoddini-Meymand H, Kamel S, et al. Interaction of transformer oil parameters on each other and on transformer health index using curve estimation regression method[J]. International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 2022, 2022: 7548533. |
| 20 | Prasojo R A, Diwyacitta K, Suwarno, et al. Transformer paper expected life estimation using ANFIS based on oil characteristics and dissolved gases (case study: Indonesian transformers)[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(8): 1135. |
| 21 | Jia L F, Chen J X, Cui X S, et al. Gas sensing mechanism and adsorption properties of C2H4 and CO molecules on the Ag3-HfSe2 monolayer: a first-principle study[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 911170. |
| 22 | Cui H, Chen D C, Zhang Y, et al. Dissolved gas analysis in transformer oil using Pd catalyst decorated MoSe2 monolayer: a first-principles theory[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2019, 20: e0094. |
| 23 | Qiao H, Zhang X B, Wang P, et al. Metal oxide decorated GeTe monolayer as promising materials for dissolved gases in transformer oil[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2024, 31(2): 904-911. |
| 24 | Zeng T T, Ma D L, Gui Y G. Gas-sensitive performance study of metal (Au, Pd, Pt)/ZnO heterojunction gas sensors for dissolved gases in transformer oil[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(18): 9819-9830. |
| 25 | Xu Z L. Ni-decorated PtS2 monolayer as a strain-modulated and outstanding sensor upon dissolved gases in transformer oil: a first-principles study[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(6): 6090-6098. |
| 26 | Zheng H B, Yang E C, Wu S Y, et al. Investigation on formation mechanisms of carbon oxides during thermal aging of cellulosic insulating paper[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2022, 29(4): 1226-1233. |
| 27 | Zhao P P, Li T T, Zhang D Z. Adsorption of dissolved gas molecules in the transformer oil on silver-modified (002) planes of molybdenum diselenide monolayer: a DFT study[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2021, 33(48): 485201. |
| 28 | Wang X R, Gui Y G, Ding Z Y, et al. Density functional theory study of Pd, Pt, and Au modified GeSe for adsorption and sensing of dissolved gases in transformer oil[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2022, 31: 101994. |
| 29 | Qian G C, Hu J, Wang S, et al. Adsorption and sensing properties of dissolved gas in oil on Cr-doped InN monolayer: a density functional theory study[J]. Chemosensors, 2022, 10(1): 30. |
| 30 | Mu L, Chen D C, Cui H. Single Pd atom embedded Janus HfSeTe as promising sensor for dissolved gas detection in transformer oil: a density functional theory study[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2022, 35: 102398. |
| 31 | Jung Mi H, Kwak M, Ahn J, et al. Highly sensitive and selective acetylene CuO/ZnO heterostructure sensors through electrospinning at lean O2 concentration for transformer diagnosis[J]. ACS Sensors, 2024, 9(1): 217-227. |
| 32 | Mann S, Mudahar I, Sharma H, et al. Lattice thermal conductivity of pure and doped (B, N) graphene[J]. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(9): 095003. |
| 33 | Siburian R, Sebayang K, Supeno M, et al. Effect of N-doped graphene for properties of Pt/N-doped graphene catalyst[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2017, 2(3): 1188-1195. |
| 34 | 张芳芳, 韩敏, 赵娟, 等. 单空缺石墨烯负载的Pd单原子催化剂上NO还原的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1382-1391. |
| Zhang F F, Han M, Zhao J, et al. DFT study on reduction of NO over Pd atom anchored on single-vacancy graphene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1382-1391. | |
| 35 | Gao Q Q. A DFT study of the ORR on M-N3 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, or Cu) co-doped graphene with moiety-patched defects[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(5): 2453-2465. |
| 36 | Jo W K, Jin Y J. 2D graphene-assisted low-cost metal (Ag, Cu, Fe, or Ni)-doped TiO2 nanowire architectures for enhanced hydrogen generation[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 765: 106-112. |
| 37 | Singla M, Sharma D, Jaggi N. Effect of transition metal (Cu and Pt) doping/co-doping on hydrogen gas sensing capability of graphene: a DFT study[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(29): 16188-16201. |
| 38 | 马生贵, 田博文, 周雨薇, 等. 氮掺杂Stone-Wales缺陷石墨烯吸附H2S的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. |
| Ma S G, Tian B W, Zhou Y W, et al. DFT study of adsorption of H2S on N-doped Stone-Wales defected graphene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. | |
| 39 | Gui Y G, Peng X, Liu K, et al. Adsorption of C2H2, CH4 and CO on Mn-doped graphene: atomic, electronic, and gas-sensing properties[J]. Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2020, 119: 113959. |
| 40 | Zhao C J, Wu H R. A first-principles study on the interaction of biogas with noble metal (Rh, Pt, Pd) decorated nitrogen doped graphene as a gas sensor: a DFT study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 435: 1199-1212. |
| 41 | Zheng Z Q, Wang H L. Different elements doped graphene sensor for CO2 greenhouse gases detection: the DFT study[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2019, 721: 33-37. |
| 42 | Avramov P V, Kudin K N, Scuseria G E. Single wall carbon nanotubes density of states: comparison of experiment and theory[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2003, 370(5/6): 597-601. |
| 43 | Yue Y X, Zuo F M, Wang B L, et al. Highly efficient catalyst for 1,1,2-trichloroethane dehydrochlorination via BN3 frustrated Lewis acid-base pairs[J]. Nano Research, 2024, 17(6): 4773-4781. |
| [1] | Weijie ZHANG, Jiawen HE, Yiming ZHANG, Deli LI, Guangya HU, Xiao CAI, Jinhua WANG, Zuohua HUANG. Effects of fuel stratification on flow field and flame structure of multi-stage swirling methane combustion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1754-1764. |
| [2] | Cong QI, Linfei YUE. Heat transfer characteristics of interwoven network minichannel heat sinks [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1534-1544. |
| [3] | Rui SUN, Junfeng WANG, Haojie XU, Bufa LI, Yaxian XU. Research progress on heat transfer enhancement mechanism of spray cooling technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1404-1421. |
| [4] | Mengqi SHI, Huan WANG, Shoujuan WANG, Yuebin XI, Fangong KONG. Research progress of lignin-based polyporous carbon in lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1463-1483. |
| [5] | Yihao JIN, Junxin LUO, Zhangmao HU, Wei WANG, Qian YIN. Experimental investigation on hydrophilic functionalized MgSO4/expanded vermiculite composites for water adsorption and heat storage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1852-1862. |
| [6] | Zhaoxue ZHANG, Zhengyu LI, Wenhui CUI, Qian WANG, Zhiping WANG, Linghui GONG. Research on cascade recovery and utilization of cold energy in liquid hydrogen energy storage based on liquid neon - liquid nitrogen [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1731-1741. |
| [7] | Fazheng WANG, Lin SUI, Weili XIONG. TTPA-LSTM soft sensor modeling for multi-sampling rate data [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1635-1646. |
| [8] | Junde ZHAO, Aiguo ZHOU, Yanlin CHEN, Jiale ZHENG, Tianshu GE. Current status of energy consumption of adsorption CO2 direct air capture [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1375-1390. |
| [9] | Yingdong ZHAO, Peijun JI, Riyao CONG, Haichao FU, Jialong ZHANG, Pengzhong CHEN, Xiaojun PENG. Preparation and high-resolution lithography study of organic tin photoresists containing acrylates [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1820-1830. |
| [10] | Guanglei WANG, Xiaoling LIU, Zhen XU, Lin LI. Performances of gas-water direct contact heat exchange for compressed air energy storage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1595-1603. |
| [11] | Haiqian ZHAO, Fang CHEN, Tao CHEN, Jianwei GUO, Wenjing LIN, Chufen YANG. Folate-modified pH-responsive copolymer mixed micelles for anticancer drug delivery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1702-1710. |
| [12] | Di WU, Shipeng LIU, Wenwei WANG, Jiuchun JIANG, Xiaoguang YANG. Recent advances in the influence of mechanical pressure on the performance of lithium metal batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1422-1431. |
| [13] | Lu LIU, Kai WAN, Wenyue WANG, Tai WANG, Jiancheng TANG, Shaoheng WANG. Study on orthohydrogen and parahydrogen conversion coupled flow and heat transfer based on helium expansion refrigeration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1513-1522. |
| [14] | Xiaokun WANG, Zelin LIAO, Junliang WU, Xingyu CHEN, Yifei YU, Gaohong HE, Xiujuan ZHANG. Preparation and performance evaluation of LDH-PTFPMS/PEI composite membrane for improving blood compatibility and CO2 transfer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1800-1808. |
| [15] | Shuli LIU, Wenhao ZHOU, Shaoliang ZHANG, Yongliang SHEN. Heat release performance of direct absorption/storage solar collector [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1722-1730. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||