CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2559-2568.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241497
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yiyun ZHANG1( ), Hengzhi CHEN1(
), Hengzhi CHEN1( ), Yang LI1, Chang'an MU1, Quanhai WANG2
), Yang LI1, Chang'an MU1, Quanhai WANG2
Received:2024-12-24
Revised:2025-02-04
Online:2025-07-09
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Hengzhi CHEN
张亿韵1( ), 陈恒志1(
), 陈恒志1( ), 李洋1, 慕长安1, 王泉海2
), 李洋1, 慕长安1, 王泉海2
通讯作者:
陈恒志
作者简介:张亿韵(2002—),女,硕士研究生,202418131194@stu.cqu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yiyun ZHANG, Hengzhi CHEN, Yang LI, Chang'an MU, Quanhai WANG. Effects of turbulence on radial gas diffusion in binary particle fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2559-2568.
张亿韵, 陈恒志, 李洋, 慕长安, 王泉海. 湍流对双组分颗粒流化床气体径向扩散的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2559-2568.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 颗粒 | 密度/(kg/m3) | 粒径范围/μm | 平均粒径/μm | 最小流化速度/(m/s) | Geldart分类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
硅胶 玻璃珠 | 750 2500 | 425~880 425~880 | 652 652 | 0.22 0.41 | B B |
Table 1 Physical properties of particles used in this work
| 颗粒 | 密度/(kg/m3) | 粒径范围/μm | 平均粒径/μm | 最小流化速度/(m/s) | Geldart分类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
硅胶 玻璃珠 | 750 2500 | 425~880 425~880 | 652 652 | 0.22 0.41 | B B |
| Flow field | Unsteady |
|---|---|
| Pressure-velocity coupling | Phase Couple SIMPLE |
| Discretization | Second-order upwind |
| Solid pressure | Lun et al |
| Radial distribution | Lun et al |
| Granular temperature | Algebraic |
| Granular viscosity | Gidaspow |
| Granular bulk visosity | Lun et al |
| Frictional viscosity | Schaeffer |
| Frictional pressure | Based-KTGF |
| Angle of internal friction | 30.0° |
| Time step size | 5×10-4 s |
| Mesh size | 2 mm×5 mm |
Table 2 Modeling parameters in bubbling fluidized bed
| Flow field | Unsteady |
|---|---|
| Pressure-velocity coupling | Phase Couple SIMPLE |
| Discretization | Second-order upwind |
| Solid pressure | Lun et al |
| Radial distribution | Lun et al |
| Granular temperature | Algebraic |
| Granular viscosity | Gidaspow |
| Granular bulk visosity | Lun et al |
| Frictional viscosity | Schaeffer |
| Frictional pressure | Based-KTGF |
| Angle of internal friction | 30.0° |
| Time step size | 5×10-4 s |
| Mesh size | 2 mm×5 mm |
| Case | Cμ | C1 | C2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03 | 1.84 | 1.42 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 1.64 | 1.62 |
| 3 | 0.09 | 1.44 | 1.92 |
| 4 | 0.12 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
Table 3 Constants of standard k-ε turbulence model
| Case | Cμ | C1 | C2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03 | 1.84 | 1.42 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 1.64 | 1.62 |
| 3 | 0.09 | 1.44 | 1.92 |
| 4 | 0.12 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
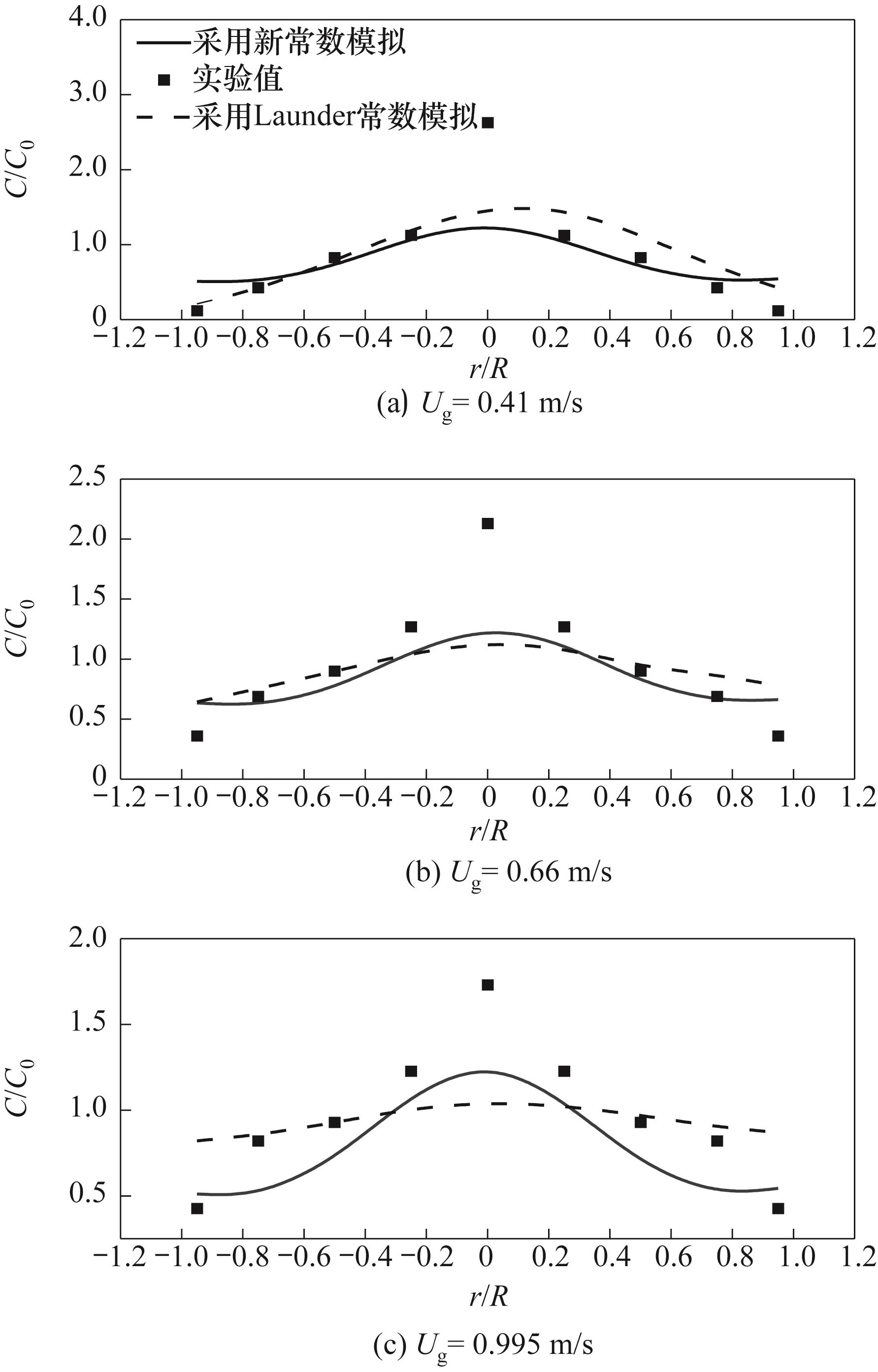
Fig.8 Comparison of tracer gas concentration calculated by different model constants with experimental data at various gas velocities(XJ= 37.5%, H= 0.15 m)
| [1] | 郭慕孙, 李洪钟. 流态化手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| Guo M S, Li H Z. Handbook of Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. | |
| [2] | 李洪钟, 朱庆山, 谢朝晖, 等. 流化床结构传递理论与工业应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. |
| Li H Z, Zhu Q S, Xie Z H, et al. Structure Transfer Theory and Industrial Application of Fluidized Bed[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. | |
| [3] | 刘明言, 马永丽, 白丁荣, 等. 多相流态化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022. |
| Liu M Y, Ma Y L, Bai D R, et al. Heterogeneous Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022. | |
| [4] | Koenigsdorff R, Werther J. Gas-solids mixing and flow structure modeling of the upper dilute zone of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 1995, 82(3): 317-329. |
| [5] | Pan S Y, Ma J L, Chen X P, et al. Diffusion combustion of NH3 in a single bubble of fluidized bed[J]. Fuel, 2023, 352: 129080. |
| [6] | Yang F L, Hlavacek V. Carbochlorination kinetics of titanium dioxide with carbon and carbon monoxide as reductant[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1998, 29(6): 1297-1307. |
| [7] | 杨建华, 杨海瑞, 岳光溪. 循环流化床提升段径向气体混合的试验研究[J]. 热能动力工程, 2008, 23(5): 494-499, 555. |
| Yang J H, Yang H R, Yue G X. Experimental study of radial gas mixing at the riser section of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2008, 23(5): 494-499, 555. | |
| [8] | Ji J Q, Cheng L M, Wei Y J, et al. Predictions of NO x /N2O emissions from an ultra-supercritical CFB boiler using a 2-D comprehensive CFD combustion model[J]. Particuology, 2020, 49: 77-87. |
| [9] | Dang T Y N, Gallucci F, van Sint Annaland M. Gas mixing study in freely bubbling and turbulent gas-solid fluidized beds with a novel infrared technique coupled with digital image analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 116: 38-48. |
| [10] | Chen H Z, Mu C A, Ding Y X. Investigating hydrodynamics and gas diffusion coefficient in CFB of binary particles with significant differences in particle properties[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2024, 203: 109903. |
| [11] | Zhou C G, Rosén C, Engvall K. Biomass oxygen/steam gasification in a pressurized bubbling fluidized bed: agglomeration behavior[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 172: 230-250. |
| [12] | Yang C G, Li S G, Song W L, et al. Pyrolysis behavior of large coal particles in a lab-scale bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(1): 126-132. |
| [13] | Hemati M, Spieker K, Laguérie C, et al. Experimental study of sawdust and coal particle mixing in sand or catalyst fluidized beds[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1990, 68(5): 768-772. |
| [14] | Joseph G G, Leboreiro J, Hrenya C M, et al. Experimental segregation profiles in bubbling gas-fluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 2007, 53(11): 2804-2813. |
| [15] | Das M, Meikap B C, Saha R K. Characteristics of axial and radial segregation of single and mixed particle system based on terminal settling velocity in the riser of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 145(1): 32-43. |
| [16] | Chen H Z, Tian X X, Gu S M, et al. Effect of mixing state of binary particles on bubble behavior in 2D fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2018, 205(8): 1119-1128. |
| [17] | de Munck M J A, Marrevee D P F, Peters E A J F, et al. Experimental study on binary solids drying in a vibro-fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 435: 119437. |
| [18] | 李静海, 欧阳洁, 高士秋, 等. 颗粒流体复杂系统的多尺度模拟[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. |
| Li J H, Ouyang J, Gao S Q, et al. Multi-scale Simulation of Particle-fluid Complex Systems[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005 | |
| [19] | 王维, 洪坤, 鲁波娜, 等. 流态化模拟: 基于介尺度结构的多尺度CFD[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 95-106. |
| Wang W, Hong K, Lu B N, et al. Fluidized bed simulation: structure-dependent multiscale CFD[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 95-106. | |
| [20] | Wang J W. A review of eulerian simulation of geldart A particles in gas-fluidized beds[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(12): 5567-5577. |
| [21] | Hou B L, Li H Z, Zhu Q S. Relationship between flow structure and mass transfer in fast fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 163(1/2): 108-118. |
| [22] | Chen H Z, Gu S M, Li H Z. Simulation gas-solid flow in the downer with new structure-based drag model[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 323: 163-175. |
| [23] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 等. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| Zhu H, Zhang Y, Qi N N, et al. Effect of particle viscosity in two-fluid model on homogeneous liquid-solid fluidization under Euler-Euler framework[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. | |
| [24] | 刘岑凡, 张楠, 王维. 鼓泡床中基于气泡结构的多相反应模型[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(5): 2057-2062. |
| Liu C F, Zhang N, Wang W. Multiphase reaction model based on bubble structures in bubbling bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(5): 2057-2062. | |
| [25] | Spalart P R, Moser R D, Rogers M M. Spectral methods for the Navier-Stokes equations with one infinite and two periodic directions[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1991, 96(2): 297-324. |
| [26] | He P. A high order finite difference solver for massively parallel simulations of stably stratified turbulent channel flows[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2016, 127: 161-173. |
| [27] | Hu J J, Lu Z, Yang Y. Improving prediction of preferential concentration in particle-laden turbulence using the neural-network interpolation[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2024, 9(3): 034606. |
| [28] | Tsuji Y, Morikawa Y, Shiomi H. LDV measurements of an air-solid two-phase flow in a vertical pipe[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1984, 139: 417-434. |
| [29] | Tanaka T, Eaton J K. Classification of turbulence modification by dispersed spheres using a novel dimensionless number[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 101(11): 114502. |
| [30] | 王兵, 刘毅, 王希麟. 颗粒粒径和气载比改变时湍流调制的变化[J]. 航空动力学报, 2009, 24(8): 1818-1823. |
| Wang B, Liu Y, Wang X L. Turbulence modulations caused by change of particle size and particle mass loading ratio[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2009, 24(8): 1818-1823. | |
| [31] | Panarese A, Bruno D, Colonna G, et al. A Monte Carlo model for determination of binary diffusion coefficients in gases[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2011, 230(14): 5716-5721. |
| [32] | Launder B E, Spalding D B. Lectures in Mathematical Models of Turbulence[M]. London: Academic Press, 1972. |
| [33] | Launder B E. Second-moment closure: present and future[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 1989, 10(4): 282-300. |
| [34] | Zou Z, Li H Z, Zhu Q S. The bubbling behavior of cohesive particles in the 2D fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 212(1): 258-266. |
| [35] | Cano-Pleite E, Shimizu Y, Acosta-Iborra A, et al. Effect of vertical vibration and particle size on the solids hold-up and mean bubble behavior in a pseudo-2D fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 304: 384-398. |
| [1] | Jiuchun SUN, Yunlong SANG, Haitao WANG, Hao JIA, Yan ZHU. Study on influence of jet flow on slurry transport characteristics in slurry chamber of shield tunneling machines [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [2] | Songyuan GUO, Xiaoqing ZHOU, Wubing MIAO, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Qingtai CAO, Chengcheng CHEN, Guang YANG, Jingyi WU. Numerical study on characteristics of pressurized discharge in liquid oxygen tank equipped with porous plate in the ascent period of rocket [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [3] | Juhui CHEN, Ke CHEN, Dan LI, Tianyi YANG, Michael ZHURAVKOV, Siarhel LAPATSIN, Wenrui JIANG. Fluidization research on the FCC-assisted nanoparticle hybrid system based on the multicomponent DQMOM model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2616-2625. |
| [4] | Dongliang XU, Binbin ZHAO, Yimei SUN, Tingting LIU, Xiaoran LIU, Minggong CHEN. Simulation and optimal design of RPB based on modified porous medium model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1569-1582. |
| [5] | Dongling XU, Yue MA, Lu GONG, Guili MA, Jinke WANG, Fengzhi GUO, Haolun WANG, Sijia LI, Shuyuan LI, Changtao YUE. Co-pyrolysis study of oil shale and bituminous coal in fixed fluidized bed reactor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1742-1753. |
| [6] | Heng ZHANG, Dianlu KUI, Hong CHANG, Zhigang ZHAN. Effect of mechanical stress on the interfacial transport properties of gas diffusion layers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 637-644. |
| [7] | Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Current status and prospects of research on fluidization characteristics of high-density particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 466-483. |
| [8] | Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Numerical simulation of hydrogen reduction of U3O8 in fluidized bed reactors using CPFD method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| [9] | He ZHU, Yi ZHANG, Nana QI, Kai ZHANG. Effect of particle viscosity in two-fluid model on homogeneous liquid-solid fluidization under Euler-Euler framework [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [10] | Aiming DENG, Yurong HE, Tianqi TANG, Yanwei HU. Simulation of effect of draft plate on particle growth process in spray fluidized beds [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2787-2799. |
| [11] | Zhenghang LUO, Jingyu LI, Weixiong CHEN, Daotong CHONG, Junjie YAN. Numerical simulation of heat transfer characteristic and bubble force analysis of low flow rate vapor condensation under rolling motion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2800-2811. |
| [12] | Jialei CAO, Liyan SUN, Dewang ZENG, Fan YIN, Zixiang GAO, Rui XIAO. Numerical simulation of chemical looping hydrogen generation with dual fluidized bed reactors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2865-2874. |
| [13] | Fangming LYU, Zhiming BAO, Bowen WANG, Kui JIAO. Investigation on impact of gas diffusion layer intrusion into channel on water management in fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2929-2938. |
| [14] | Lou ZHU, Yangfan SONG, Meng WANG, Ruipeng SHI, Yanmin LI, Hongwei CHEN, Zhuo LIU, Xiang WEI. Power generation characteristics of central pulse gas-liquid-solid circulating fluidized bed microbial fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2991-3001. |
| [15] | Fei LU, Bona LU, Guangwen XU. Analysis of criteria for ideal flow patterns in gas-solid micro fluidized bed reaction analyzer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2201-2213. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||