CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5101-5113.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250364
• Catalysis, kinetics and reactors • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yun SHEN1,2( ), Dai ZHANG2, Xiaofeng XU1, Yueqiang CAO1,2(
), Dai ZHANG2, Xiaofeng XU1, Yueqiang CAO1,2( ), Jinghong ZHOU1,2(
), Jinghong ZHOU1,2( ), Wei LI2, Xinggui ZHOU1,2
), Wei LI2, Xinggui ZHOU1,2
Received:2025-04-09
Revised:2025-05-14
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-10-25
Contact:
Yueqiang CAO, Jinghong ZHOU
沈赟1,2( ), 张岱2, 徐晓峰1, 曹约强1,2(
), 张岱2, 徐晓峰1, 曹约强1,2( ), 周静红1,2(
), 周静红1,2( ), 李伟2, 周兴贵1,2
), 李伟2, 周兴贵1,2
通讯作者:
曹约强,周静红
作者简介:沈赟(2000—),男,硕士研究生,shenyun0902@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yun SHEN, Dai ZHANG, Xiaofeng XU, Yueqiang CAO, Jinghong ZHOU, Wei LI, Xinggui ZHOU. Mechanistic insights into the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate over Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalyst[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5101-5113.
沈赟, 张岱, 徐晓峰, 曹约强, 周静红, 李伟, 周兴贵. Ni-Ag/SiO2催化草酸二甲酯加氢制乙醇酸甲酯反应机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5101-5113.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 样品 | 负载量①/% | SBET② / (m2/g) | Vpore③/ (cm3/g) | DBJH③/ nm | QCO④/ (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Ag | |||||||
| SiO2 | — | — | 212 | 0.30 | 4.4 | — | — | — |
| 5Ni-1Ag | 4.6 | 0.98 | 247 | 0.61 | 8.24 | 0.0027 | 0.1241 | 0.1214 |
| 10Ni-1Ag | 9.8 | 0.98 | 267 | 0.58 | 7.00 | 0.0064 | 0.1289 | 0.1225 |
| 15Ni-1Ag | 14.7 | 0.97 | 285 | 0.54 | 5.90 | 0.0102 | 0.1344 | 0.1242 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag | 9.8 | 1.5 | 261 | 0.58 | 6.88 | 0.0104 | 0.1913 | 0.1809 |
| 10Ni-2Ag | 9.8 | 2 | 257 | 0.57 | 6.81 | 0.0121 | 0.2975 | 0.2854 |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts
| 样品 | 负载量①/% | SBET② / (m2/g) | Vpore③/ (cm3/g) | DBJH③/ nm | QCO④/ (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Ag | |||||||
| SiO2 | — | — | 212 | 0.30 | 4.4 | — | — | — |
| 5Ni-1Ag | 4.6 | 0.98 | 247 | 0.61 | 8.24 | 0.0027 | 0.1241 | 0.1214 |
| 10Ni-1Ag | 9.8 | 0.98 | 267 | 0.58 | 7.00 | 0.0064 | 0.1289 | 0.1225 |
| 15Ni-1Ag | 14.7 | 0.97 | 285 | 0.54 | 5.90 | 0.0102 | 0.1344 | 0.1242 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag | 9.8 | 1.5 | 261 | 0.58 | 6.88 | 0.0104 | 0.1913 | 0.1809 |
| 10Ni-2Ag | 9.8 | 2 | 257 | 0.57 | 6.81 | 0.0121 | 0.2975 | 0.2854 |
| 样品 | 低温区还原峰耗氢量/(10-3 mmol/g) | 中温区还原峰耗氢量/(10-2 mmol/g) | 高温区还原峰耗氢量/(mmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5Ni-1Ag | 4.380 | 3.375 | 0.465 |
| 10Ni-1Ag | 4.311 | 4.915 | 0.831 |
| 15Ni-1Ag | 4.368 | 8.149 | 1.166 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag | 5.948 | 5.893 | 0.818 |
| 10Ni-2Ag | 6.534 | 5.825 | 0.815 |
Table 2 Amount of hydrogen consumption corresponding to the H2-TPR peaks of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts
| 样品 | 低温区还原峰耗氢量/(10-3 mmol/g) | 中温区还原峰耗氢量/(10-2 mmol/g) | 高温区还原峰耗氢量/(mmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5Ni-1Ag | 4.380 | 3.375 | 0.465 |
| 10Ni-1Ag | 4.311 | 4.915 | 0.831 |
| 15Ni-1Ag | 4.368 | 8.149 | 1.166 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag | 5.948 | 5.893 | 0.818 |
| 10Ni-2Ag | 6.534 | 5.825 | 0.815 |
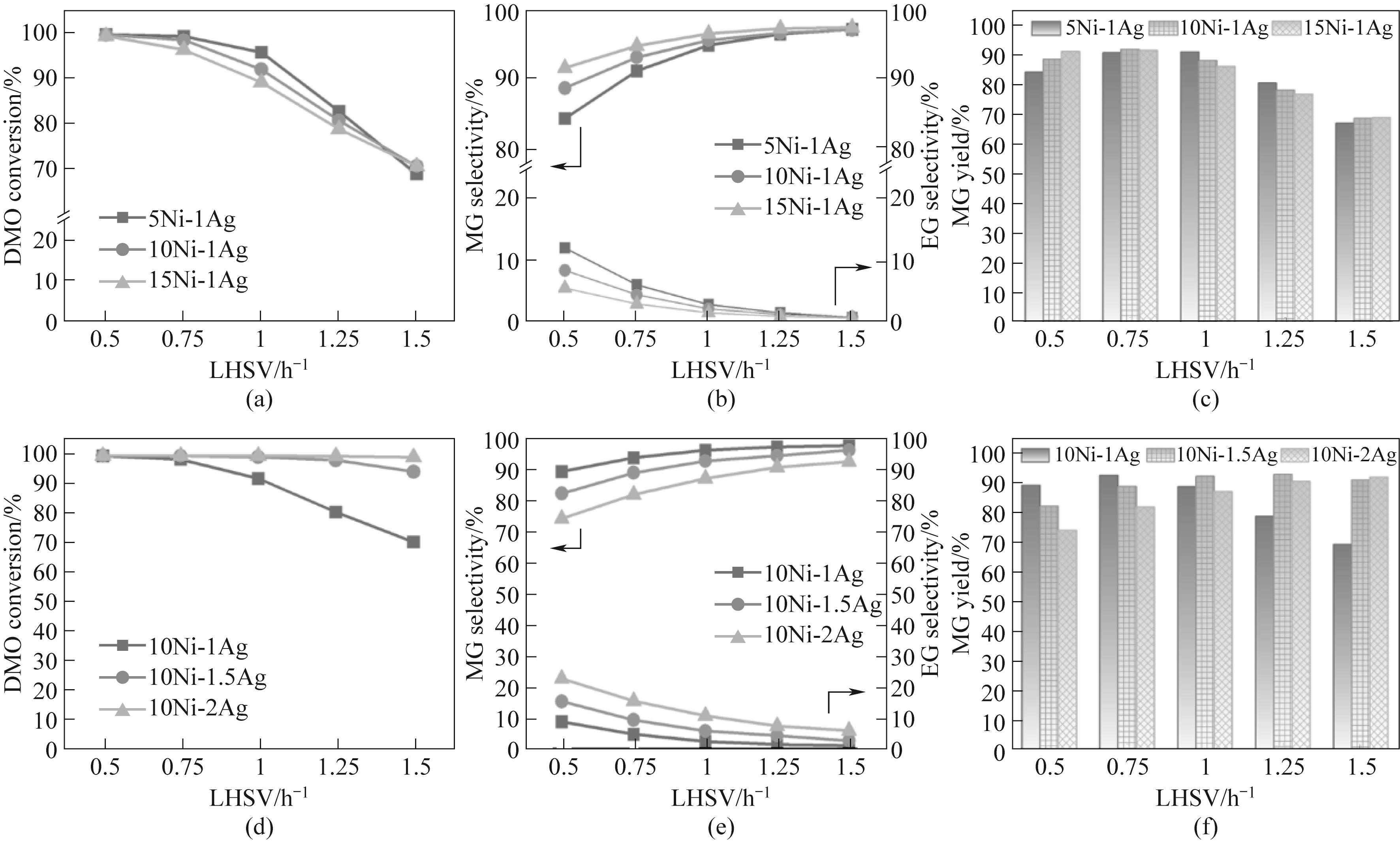
Fig.5 Performance of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts with (a)—(c) different Ni loadings and (d)—(f) different Ag loadings as a function of LHSV (reaction conditions: 220℃, 2.0 MPa, H2/DMO = 50)
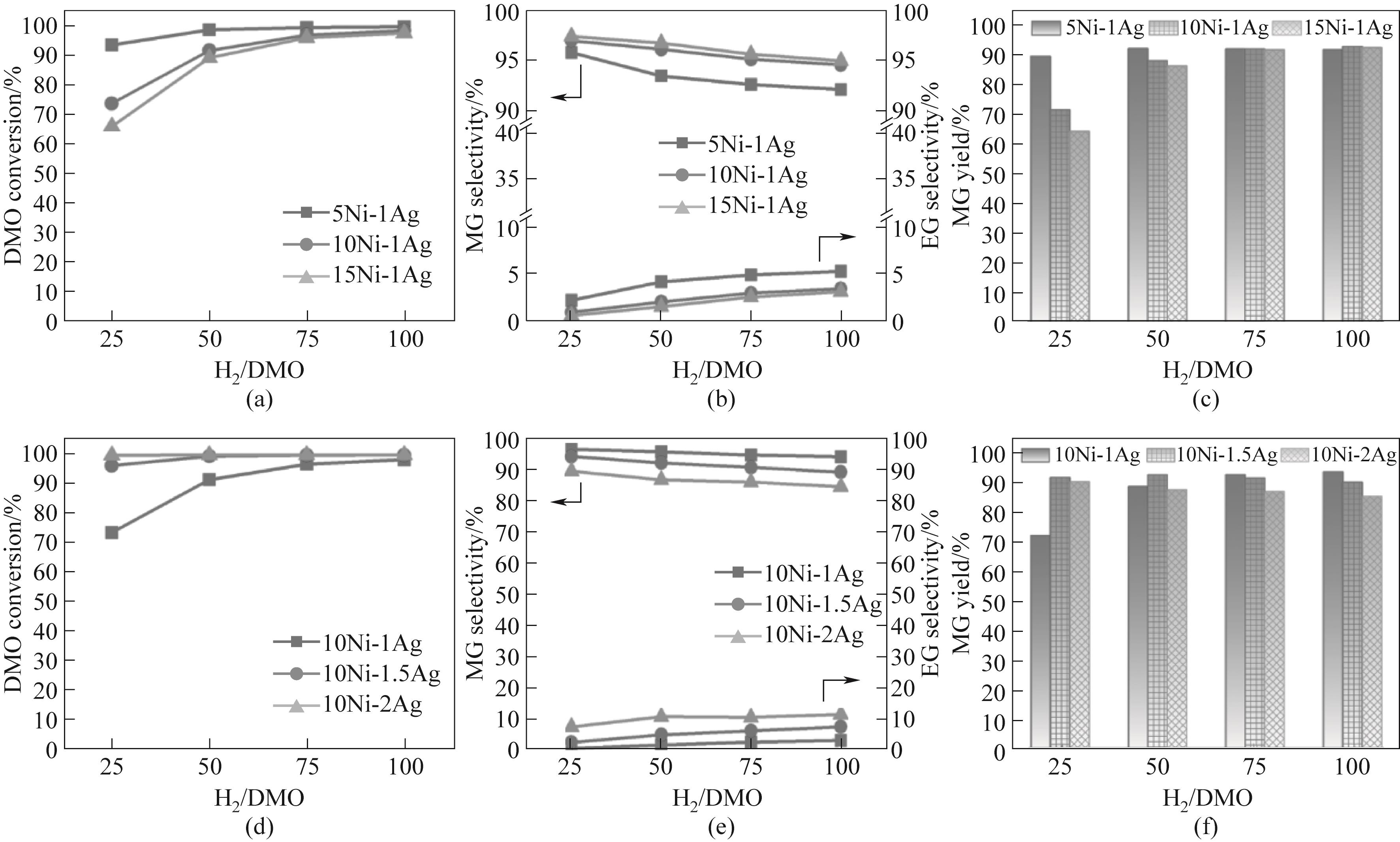
Fig.6 Performance of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts with (a)—(c) different Ni loadings and (d)—(f) different Ag loadings as a function of H2/DMO (reaction conditions: 220℃, 2.0 MPa, LHSV = 1 h-1)
| 催化剂 | LHSV/h-1 | H/D | DMO 转化率/% | 选择性/% | MG 收率% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MG | EG | 其他 | |||||
| 10Ni/SiO2 | 0.5 | 50 | 12.6 | 83.1 | 0.5 | 16.4 | 10.5 |
| 1 | 50 | 10.4 | 93.3 | 0.1 | 6.6 | 9.7 | |
| 10Ni-0.5Ag/SiO2 | 0.5 | 50 | 87.7 | 96.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 84.8 |
| 0.75 | 50 | 70.6 | 97.5 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 68.9 | |
| 1 | 50 | 58.0 | 97.5 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 56.5 | |
| 1.25 | 50 | 47.9 | 97.4 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 46.6 | |
| 1.5 | 50 | 39.9 | 97.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 38.8 | |
| 1 | 100 | 73.5 | 97.9 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 71.9 | |
| 1 | 75 | 64.5 | 97.9 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 63.2 | |
| 1 | 50 | 55.0 | 97.5 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 53.6 | |
| 1 | 25 | 40.2 | 96.6 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 38.8 | |
Table 3 Performance evaluation results of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts with different Ni and Ag loadings
| 催化剂 | LHSV/h-1 | H/D | DMO 转化率/% | 选择性/% | MG 收率% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MG | EG | 其他 | |||||
| 10Ni/SiO2 | 0.5 | 50 | 12.6 | 83.1 | 0.5 | 16.4 | 10.5 |
| 1 | 50 | 10.4 | 93.3 | 0.1 | 6.6 | 9.7 | |
| 10Ni-0.5Ag/SiO2 | 0.5 | 50 | 87.7 | 96.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 84.8 |
| 0.75 | 50 | 70.6 | 97.5 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 68.9 | |
| 1 | 50 | 58.0 | 97.5 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 56.5 | |
| 1.25 | 50 | 47.9 | 97.4 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 46.6 | |
| 1.5 | 50 | 39.9 | 97.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 38.8 | |
| 1 | 100 | 73.5 | 97.9 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 71.9 | |
| 1 | 75 | 64.5 | 97.9 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 63.2 | |
| 1 | 50 | 55.0 | 97.5 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 53.6 | |
| 1 | 25 | 40.2 | 96.6 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 38.8 | |
| 催化剂 | H2-TPD | DMO-TPD | A(H2)/A(DMO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.70 | 0.35 | 1.98 |
| 10Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 1.31 |
| 15Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 1.23 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag/SiO2 | 1.07 | 0.68 | 1.59 |
| 10Ni-2Ag/SiO2 | 1.27 | 0.69 | 1.85 |
Table 4 TPD area of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalysts with different Ni and Ag loadings
| 催化剂 | H2-TPD | DMO-TPD | A(H2)/A(DMO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.70 | 0.35 | 1.98 |
| 10Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 1.31 |
| 15Ni-1Ag/SiO2 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 1.23 |
| 10Ni-1.5Ag/SiO2 | 1.07 | 0.68 | 1.59 |
| 10Ni-2Ag/SiO2 | 1.27 | 0.69 | 1.85 |
| [1] | Yang Q C, Fan Y J, Liu C L, et al. A promising alternative potential solution for sustainable and economical development of coal to ethylene glycol industry: dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate process[J]. Energy, 2023, 277: 127668. |
| [2] | Zhou R J, Yan W Q, Cao Y Q, et al. Probing the structure sensitivity of dimethyl oxalate partial hydrogenation over Ag nanoparticles: a combined experimental and microkinetic study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 259: 117830. |
| [3] | Xie T H, Ai S, Huang Y C, et al. Synthesis and purification of glycolic acid from the mixture of methyl levulinate and methyl glycolate via acid-mediated hydrolysis reactions and extraction[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 268: 118718. |
| [4] | An J W, Wang X H, Zhao J X, et al. Density-functional theory study on hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate over copper catalyst: effect of copper valence state[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2020, 482: 110667. |
| [5] | Huang H J, Wang B, Wang Y, et al. Partial hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate on Cu/SiO2 catalyst modified by sodium silicate[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 358: 68-73. |
| [6] | Sun Y, Wang H, Shen J H, et al. Highly effective synthesis of methyl glycolate with heteropolyacids as catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2009, 10(5): 678-681. |
| [7] | Luo Z W, Xu X F, Dong G L, et al. Regulating mesopore structures of support toward enhanced selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate on Ag catalysts[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138397. |
| [8] | Dong G L, Luo Z W, Cao Y Q, et al. Understanding size-dependent hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate over Ag catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 401: 252-261. |
| [9] | Qu R Y, Junge K, Beller M. Hydrogenation of carboxylic acids, esters, and related compounds over heterogeneous catalysts: a step toward sustainable and carbon-neutral processes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(3): 1103-1165. |
| [10] | Chen H M, Tan J J, Zhu Y L, et al. An effective and stable Ni2P/TiO2 catalyst for the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 73: 46-49. |
| [11] | Zhu J, Cao L Q, Li C Y, et al. Nanoporous Ni3P evolutionarily structured onto a Ni foam for highly selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(41): 37635-37643. |
| [12] | Ouyang M Y, Wang J, Peng B, et al. Effect of Ti on Ag catalyst supported on spherical fibrous silica for partial hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 466: 592-600. |
| [13] | Dong G L, Cao Y Q, Zheng S N, et al. Catalyst consisting of Ag nanoparticles anchored on amine-derivatized mesoporous silica nanospheres for the selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 391: 155-162. |
| [14] | Luo Z W, Ge X H, Fang D, et al. In situ exsolution to fabricate interfacial Ni0/Ni δ + sites for regulating reaction pathways in hydrogenation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2024, 434: 115528. |
| [15] | 方笛, 罗祖伟, 曹约强, 等. 催化剂制备方法对Ni-Ag/SiO2 催化草酸二甲酯加氢制乙醇酸甲酯性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2024, 52(10): 1495-1507. |
| Fang D, Luo Z W, Cao Y Q, et al. Influence of Ni-Ag/SiO2 catalyst preparation method on its performance in hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2024, 52(10): 1495-1507. | |
| [16] | Luo Z W, Shen Y, Fang D, et al. Insights into support effects of Ag/SiO2 catalysts for dimethyl glycolate semi-hydrogenation to methyl glycolate[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2024, 559: 114109. |
| [17] | Yan W Q, Zhang J B, Xiao L, et al. Toward rational catalyst design for partial hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate: a descriptor-based microkinetic analysis[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(20): 5763-5773. |
| [18] | Cao Y Q, Chen B, Guerrero-Sánchez J, et al. Controlling selectivity in unsaturated aldehyde hydrogenation using single-site alloy catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(10): 9150-9157. |
| [19] | Giannakakis G, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M, Charles H Sykes E. Single-atom alloys as a reductionist approach to the rational design of heterogeneous catalysts[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(1): 237-247. |
| [20] | Wang S, Zhao Z J, Chang X, et al. Activation and spillover of hydrogen on sub-1 nm palladium nanoclusters confined within sodalite zeolite for the semi-hydrogenation of alkynes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(23): 7668-7672. |
| [21] | Jiang L Z, Liu K L, Hung S F, et al. Facet engineering accelerates spillover hydrogenation on highly diluted metal nanocatalysts[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(10): 848-853. |
| [22] | Qi H M, Wang X L, Lei M, et al. Highly efficient catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene on cobalt- immobilized nitrogen-doped carbon: a dual-sites synergistic effect between cobalt single atoms and cobalt nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500: 157057. |
| [23] | Kyriakou G, Boucher M B, Jewell A D, et al. Isolated metal atom geometries as a strategy for selective heterogeneous hydrogenations[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6073): 1209-1212. |
| [24] | Yang D, Tao S, Zhu H Y, et al. Construction of Rh-N4 single atoms and Rh clusters dual-active sites for synergistic heterogeneous hydroformylation of olefins with ultra-high turnover frequency[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147505. |
| [25] | Müslehiddinoğlu J, Vannice M A. CO adsorption on supported and promoted Ag epoxidation catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 213(2): 305-320. |
| [26] | Li J, Xiong H C, Liu X Z, et al. Weak CO binding sites induced by Cu-Ag interfaces promote CO electroreduction to multi-carbon liquid products[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 698. |
| [27] | 董桂霖, 罗祖伟, 曹约强, 等. 液相还原温度对草酸酯加氢制乙醇酸甲酯银硅催化剂性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 232-240. |
| Dong G L, Luo Z W, Cao Y Q, et al. Effect of liquid-phase reduction temperature on performance of silver-silica catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 232-240. | |
| [28] | Kuhaudomlap S, Mekasuwandumrong O, Praserthdam P, et al. Influence of highly stable Ni2+ species in Ni phyllosilicate catalysts on selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 8(1): 249-261. |
| [29] | Yang F F, Wang H, Han J Y, et al. Enhanced selective deoxygenation of m-cresol to toluene on Ni/SiO2 catalysts derived from nickel phyllosilicate[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 330: 149-156. |
| [30] | Kong X, Zhu Y F, Zheng H Y, et al. Ni nanoparticles inlaid nickel phyllosilicate as a metal-acid bifunctional catalyst for low-temperature hydrogenolysis reactions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(10): 5914-5920. |
| [31] | Zheng J W, Lin H Q, Zheng X L, et al. Highly efficient mesostructured Ag/SBA-15 catalysts for the chemoselective synthesis of methyl glycolate by dimethyl oxalate hydrogenation[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2013, 40: 129-133. |
| [32] | Qu Z P, Huang W X, Cheng M J, et al. Restructuring and redispersion of silver on SiO2 under oxidizing/reducing atmospheres and its activity toward CO oxidation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2005, 109(33): 15842-15848. |
| [33] | Zhou J F, Duan X P, Ye L M, et al. Enhanced chemoselective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate over bimetallic Ag-Ni/SBA-15 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 505: 344-353. |
| [34] | Hengne A M, Malawadkar A V, Biradar N S, et al. Surface synergism of an Ag-Ni/ZrO2 nanocomposite for the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of bio-derived platform molecules[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(19): 9730-9736. |
| [35] | Lazar M, Mihet M, Dan M, et al. Preparation and characterization of nickel based multicomponent catalysts[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2009, 182: 012049. |
| [36] | Burattin P, Che M, Louis C. Ni/SiO2 materials prepared by deposition-precipitation: influence of the reduction conditions and mechanism of formation of metal particles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(45): 10482-10489. |
| [37] | Wang J Y, Fu Y, Kong W B, et al. Design of a carbon-resistant Ni@S-2 reforming catalyst: controllable Ni nanoparticles sandwiched in a peasecod-like structure[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 282: 119546. |
| [38] | Yang H, Li J, Chang Q, et al. Ni nanoparticles inlaid in amorphous silicon nitride-derived nickel phyllosilicate: a highly stable and active catalyst for ammonia decomposition[J]. Fuel, 2025,394:135119. |
| [39] | Pei G X, Liu X Y, Wang A Q, et al. Selective hydrogenation of acetylene in an ethylene-rich stream over silica supported Ag-Ni bimetallic catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2017, 545: 90-96. |
| [40] | Cheng S, Meng T, Mao D S, et al. Ni-modified Ag/SiO2 catalysts for selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(3): 407. |
| [41] | Yin A Y, Guo X Y, Prof K F, et al. Ion-exchange temperature effect on Cu/HMS catalysts for the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol[J]. ChemCatChem, 2010, 2(2): 206-213. |
| [42] | Ghiat I, Boudjemaa A, Saadi A, et al. Efficient hydrogen generation over a novel Ni phyllosilicate photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2019, 382: 111952. |
| [43] | Waterhouse G I N, Bowmaker G A, Metson J B. Oxidation of a polycrystalline silver foil by reaction with ozone[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2001, 183(3/4): 191-204. |
| [44] | Chen H M, Tan J J, Cui J L, et al. Promoting effect of boron oxide on Ag/SiO2 catalyst for the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2017, 433: 346-353. |
| [45] | Cui G Q, Zhang X, Wang H, et al. ZrO2- x modified Cu nanocatalysts with synergistic catalysis towards carbon-oxygen bond hydrogenation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 280: 119406. |
| [46] | Cui G Q, Meng X Y, Zhang X, et al. Low-temperature hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol via ternary synergistic catalysis of Cu and acid-base sites[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 248: 394-404. |
| [47] | Wang C Z, Chen P J, Li Y K, et al. In situ DRIFTS study of CO coupling to dimethyl oxalate over structured Al-fiber@ns-AlOOH@Pd catalyst[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 344: 173-183. |
| [48] | Castonguay M, Roy J R, Rochefort A, et al. Orientation and conformation of methyl pyruvate on Ni(111)[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2000, 122(3): 518-524. |
| [49] | Castonguay M, Roy J R, Lavoie S, et al. Selective C—C bond activation of methyl pyruvate on Ni(111) to yield surface methoxycarbonyl[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(26): 6429-6430. |
| [50] | Rachmady W, Vannice M A. Acetic acid reduction by H2 over supported Pt catalysts: a DRIFTS and TPD/TPR study[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 207(2): 317-330. |
| [51] | Gao X P, Zhou Y N, Jing F L, et al. Layered double hydroxides derived ZnO-Al2O3 supported Pd-Ag catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 35(6): 1009-1015. |
| [52] | Zou J L, Duan X P, Liu X, et al. Identifying the activity origin of silver catalysts induced by interfacial electron localization for regioselective CO bond hydrogenation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140110. |
| [53] | Velu S, Gangwal S K. Synthesis of alumina supported nickel nanoparticle catalysts and evaluation of nickel metal dispersions by temperature programmed desorption[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2006, 177(7/8): 803-811. |
| [54] | Chen S, Pan X Y, Miao C X, et al. Study of catalytic hydrodeoxygenation performance for the Ni/KIT-6 catalysts[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2018, 22(5): 614-627. |
| [55] | Liu K R, Yan P F, Jiang H, et al. Silver initiated hydrogen spillover on anatase TiO2 creates active sites for selective hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 369: 396-404. |
| [56] | Dong C, Mu R T, Li R T, et al. Disentangling local interfacial confinement and remote spillover effects in oxide-oxide interactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(31): 17056-17065. |
| [57] | Shin E J, Keane M A. Gas-phase hydrogenation/hydrogenolysis of phenol over supported nickel catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2000, 39(4): 883-892. |
| [1] | Yuntao ZHOU, Lifeng CUI, Jie ZHANG, Fuhong YU, Xingang LI, Ye TIAN. Ga2O3 modified CuCeO catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [2] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [3] | Han LIU, Jiaxin CUI, Mengfan YIN, Tao ZHENG, Rui ZHANG, Xianghai MENG, Zhichang LIU, Haiyan LIU, Chunming XU. Crystal structure of xylene·CuAlCl4 and measurement of solid-liquid equilibrium of binary system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2241-2250. |
| [4] | Chuanchao HE, Jinghong ZHOU, Yueqiang CAO, Yao SHI, Xinggui ZHOU. Bed-particle dual scale coupled simulation on Ag/SiO2 catalyzed hydrogenation of oxalate to methyl glycolate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 654-666. |
| [5] | Shunnian XU, Xiao FENG, Dejun SHI, Zhiguo SUN, Chenwei ZHANG, Gang WANG, Jinsen GAO, Chunming XU. Research on direct hydro-upgrading of crude oils and the dissociation of asphaltene supramolecules [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 812-824. |
| [6] | Yifei LI, Yanfei SU, Tian YIN, Haoqiang JIANG, Zhiming XU, Linzhou ZHANG, Quan SHI, Chunming XU. Molecular composition and structure characterization of coal liquefaction product oil based on GC×GC-TOF MS [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 543-553. |
| [7] | Yuxin JIN, Wenli WU, Hua TONG, Daiqi YE, Limin CHEN. Study on synergistic catalysis by highly dispersed dual-site Co species for CO2-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane to ethylene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5128-5140. |
| [8] | Jingyu WANG, Jia LIU, Jixiang XU, Lei WANG. Synthesis of lamellar PtZn@Silicalite-1 zeolite and its catalytic properties for propane dehydrogenation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3188-3197. |
| [9] | Dezheng HU, Rong WANG, Shidong WANG, Wenfei YANG, Hongwei ZHANG, Pei YUAN. Construction of amorphous NiP@γ-Al2O3 catalyst rich in Ni δ+ for petroleum resin hydrogenation with enhanced hydrogenation and desulfurization activity [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3152-3162. |
| [10] | Lu YANG, Congcong LIU, Tongtong MENG, Boyuan ZHANG, Tengfei YANG, Wen’an DENG, Xiaobin WANG. Hydrogenation and coke-suppression performance of dispersed catalyst in coal/heavy oil co-processing reactions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2556-2564. |
| [11] | Yu HAN, Le ZHOU, Xin ZHANG, Yong LUO, Baochang SUN, Haikui ZOU, Jianfeng CHEN. Preparation of high adhesion Pd/SiO2/NF monolithic catalyst and its hydrogenation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1533-1542. |
| [12] | Yiwei FAN, Wei LIU, Yingying LI, Peixia WANG, Jisong ZHANG. Research progress on catalytic dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole as liquid organic hydrogen carrier [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1198-1208. |
| [13] | Lin ZHOU, Bin YE, Xinyi SUN, Lingxin KONG, Yan XU, Yujun ZHAO. Study on the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic anhydride by mesoporous carbon-supported Ni catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4264-4273. |
| [14] | Hongyu LI, Xiangkun LIU, Yao SHI, Yueqiang CAO, Gang QIAN, Xuezhi DUAN. Numerical simulation of particle-resolved fixed-bed reactor for selective acetylene hydrogenation process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3610-3622. |
| [15] | Shiyu YAN, Jiaojiao GAO, Taishun YANG, Shangzhi XIE, Yanjuan YANG, Jing XU. Effect of coordination environment of ruthenium-based catalysts on their performance for polyethylene hydrogenolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3588-3599. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||