CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (1): 189-198.DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20180813
• Biochemical engineering and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen CHEN1,2( ),Ying WANG1,2,Hong LIU1,2,Yan CHEN1,2,Mingdong YAO1,2(
),Ying WANG1,2,Hong LIU1,2,Yan CHEN1,2,Mingdong YAO1,2( ),Wenhai XIAO1,2
),Wenhai XIAO1,2
Received:2018-07-18
Revised:2018-10-26
Online:2019-01-05
Published:2019-01-05
Contact:
Mingdong YAO
陈琛1,2( ),王颖1,2,刘宏1,2,陈艳1,2,姚明东1,2(
),王颖1,2,刘宏1,2,陈艳1,2,姚明东1,2( ),肖文海1,2
),肖文海1,2
通讯作者:
姚明东
作者简介:陈琛(1992—),男,硕士研究生,<email>993203668@qq.com</email>|姚明东(1981—),男,副研究员,<email>mingdong.yao@tju.edu.cn</email>
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chen CHEN, Ying WANG, Hong LIU, Yan CHEN, Mingdong YAO, Wenhai XIAO. Exploring the key structural properties affecting the function of multi-step phytoene dehydrogenase CrtI[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(1): 189-198.
陈琛, 王颖, 刘宏, 陈艳, 姚明东, 肖文海. 影响多步脱氢酶CrtI功能的关键结构特征探索[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(1): 189-198.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://hgxb.cip.com.cn/EN/10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20180813
| Plasmids/strains | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
plasmids pJET1.2/blunt | blunt-end PCR fragments cloning vector | purchased |
| PCY01 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY02 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY03 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY04 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY05 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY06 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY07 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY08 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY09 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY36-54 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-BtCrtI(S311mutants)-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| S. cerevisiaestrains | ||
| SyBE_Sc14C10 | CEN.PK2-1C(MATα,his3Δ1,leu2-3_112,trp1-289,ura3-52,MAL2-8C,SUC2),Δgal1 Δgal7 Δgal10::HIS3, Δypl062w::KanMX | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C53 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C22 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C23 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C56 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C25 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C26 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C59 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C28 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C29 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C62 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C31 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C32 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C65 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C34 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C35 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C130 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C131 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C132 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C133 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C134 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C109-127 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI(S311mutants)-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
Table 1 Plasmid and strains involved in this study
| Plasmids/strains | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
plasmids pJET1.2/blunt | blunt-end PCR fragments cloning vector | purchased |
| PCY01 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY02 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY03 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY04 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| PCY05 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY06 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY07 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY08 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY09 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing LEU2 homologous arm with LEU2 marker, TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| PCY36-54 | pJET1.2/blunt possessing TRP1 homologous arm,TCYC1-BtCrtI(S311mutants)-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1 | our lab |
| S. cerevisiaestrains | ||
| SyBE_Sc14C10 | CEN.PK2-1C(MATα,his3Δ1,leu2-3_112,trp1-289,ura3-52,MAL2-8C,SUC2),Δgal1 Δgal7 Δgal10::HIS3, Δypl062w::KanMX | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C53 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C22 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C23 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C56 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C25 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C26 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C59 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C28 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C29 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C62 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C31 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C32 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C65 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-AaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C34 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-PaCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C35 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C130 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C131 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-SaCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C132 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-AfCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C133 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-BtCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C134 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-XdCrtI-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
| SyBE_Sc14C109-127 | SyBE_Sc14C10, trp1::TRP1_TCYC1-BtCrtI(S311mutants)-PGAL10-PGAL1-PaCrtB-TPGK1,leu2::LEU2_TACT1-tHMG1-PGAL10-PGAL1-TmCrtE-TGPM1 | our lab |
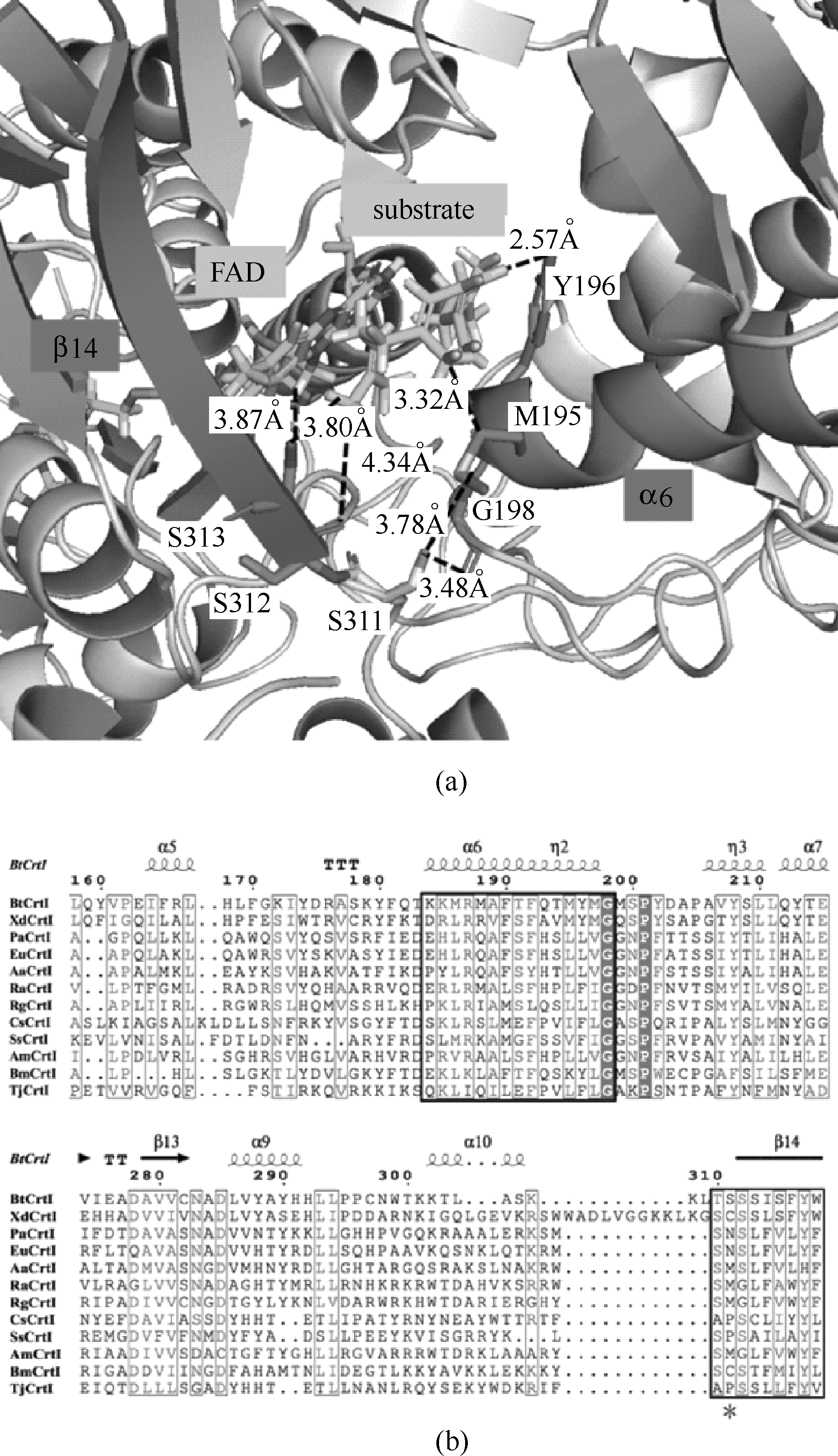
Fig.3 Active center structural model of FAD-BtCrtI and substrate (phytoene) complex(a)[cofactor FAD, substrate (phytoene), the key secondary structures β14 and α6 involved in the active center, S311 are labeled respectively; also the key residues and the corresponding interactions are labled by black font]; partial multi-sequence alignment of active center domain of CrtI from different species(b) [the secondary structures β14 and α6 are labled by black squares, and the corresponding site of S311 (BtCrtI) is labled by asterisk]

Fig.4 Yield difference of dehydrogenation products derived from site-saturation mutagenesis of S311(a); active center structural models of various complex of FAD-mutations of S311 and substrate [(b)-(f)]
| 1 | NamH, LewisN E, LermanJ A, et al. Network context and selection in the evolution to enzyme specificity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6098): 1101-1104. |
| 2 | RaisigA, SandmannG. 4, 4'-diapophytoene desaturase: catalytic properties of an enzyme from the C-30 carotenoid pathway of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1999, 181(19): 6184-6187. |
| 3 | ChenF F, DiH X, WangY X, et al. Small-molecule targeting of a diapophytoene desaturase inhibits S. aureus virulence[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(3): 174-179. |
| 4 | ChoiS K, NishidaY, MatsudaS, et al. Characterization of β-carotene ketolases, CrtW, from Marine Bacteria by complementation analysis in Escherichia coli[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2005, 7(5): 515-522. |
| 5 | ChoiS K, MatsudaS, HoshinoT, et al. Characterization of bacterial β-carotene 3, 3′-hydroxylases, CrtZ, and P450 in astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway and adonirubin production by gene combination in Escherichia coli[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(6): 1238-1246. |
| 6 | YoonS H, KimJ E, LeeS H, et al. Engineering the lycopene synthetic pathway in E.coli by comparison of the carotenoid genes of Pantoea agglomerans and Pantoea ananatis[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 74(1): 131-139. |
| 7 | XieW P, LvX M, YeL D, et al. Construction of lycopene overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae by combining directed evolution and metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 30: 69-78. |
| 8 | VerwaalR, WangJ, MeijnenJ P, et al. High-level production of beta-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by successive transformation with carotenogenic genes from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(13): 4342-4350. |
| 9 | RohmerM, KnaniM, SimoninP, et al. Isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria: a novel pathway for the early steps leading to isopentenyl diphosphate[J]. Biochemical Journal, 1993, 295: 517-524. |
| 10 | BlockK, ChaylinS, PhillipsH. Mevalonic acid pyrophosphate and isopentenylpyrophosphate [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1959, 234: 2595-2604. |
| 11 | FrengovaG I, BeshkovaD M. Carotenoids from Rhodotorula and Phaffia: yeasts of biotechnological importance[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 36(2): 163-180. |
| 12 | SteigerS, JackischY, SandmannG. Carotenoid biosynthesis in Gloeobacter violaceus PCC4721 involves a single CrtI-type phytoene desaturase instead of typical cyanobacterial enzymes[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2005, 184(4): 207-214. |
| 13 | DomonkosI, KisM, GombosZ, et al. Carotenoids, versatile components of oxygenic photosynthesis[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2013, 52(4): 539-561. |
| 14 | CunninghamF X, SunZ R, ChamovitzD, et al. Molecular structure and enzymatic function oi lycopene cyclase from the Cyanobacteriumsynechococcus sp strain PCC7942[J]. Plant Cell, 1994, 6(8): 1107-1121. |
| 15 | RaisigA, BartleyG, ScolnikP, et al. Purification in an active state and properties of the 3-step phytoene desaturase from Rhodobacter capsulatus overexpressed in Escherichia coil[J]. The Journal of Biochemistry, 1996, 119(3): 559-564. |
| 16 | SchmidtC, UmenoD, ArnoldF H. Molecular breeding of carotenoid biosynthetic pathways[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2000, 18: 750-753. |
| 17 | HausmannA, SandmannG. A single five-step desaturase is involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis pathway to beta-carotene and torulene in Neurospora crassa[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2000, 30(2): 147-153. |
| 18 | ZhangJ, LuL, YinL, et al. Carotenogenesis gene cluster and phytoene desaturase catalyzing both three- and four-step desaturations from Rhodobacter azotoformans[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2012, 333(2): 138-145. |
| 19 | LiC, ZhangN, SongJ, et al. A single desaturase gene from red yeast Sporidiobolus pararoseus is responsible for both four- and five-step dehydrogenation of phytoene[J]. Gene, 2016, 590(1): 169-176. |
| 20 | HaradaJ, NagashimaK V, TakaichiS, et al. Phytoene desaturase, CrtI, of the purple photosynthetic bacterium, Rubrivivax gelatinosus, produces both neurosporene and lycopene[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2001, 42(10): 1112-1118. |
| 21 | WangC, LiaoJ. Alteration of product specificity of Rhodobacter sphaeroides phytoene desaturase by directed evolution[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276: 41161-41164 |
| 22 | StickforthP, SandmannG. Structural and kinetics properties of a mutated phytoene desaturase from Rubrivivax gelatinosus with modified product specificity[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2011, 505(1): 118-122. |
| 23 | SchaubP, YuQ, GemmeckerS, et al. On the Structure and function of the phytoene desaturase CrtI from Pantoea ananatis, a membrane-peripheral and FAD-dependent oxidase/isomerase[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(6): e39550. |
| 24 | DaileyT A, DaileyH A. Identification of an FAD superfamily containing protoporphyrinogen oxidases, monoamine oxidases, and phytoene desaturase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(22): 13658-13662. |
| 25 | LopezA B, YangY, ThannhauserT W, et al. Phytoene desaturase is present in a large protein complex in the plastid membrane[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2008, 133(2): 190-198. |
| 26 | 李博, 梁楠, 刘夺, 等. 合成8-二甲基异戊烯基柚皮素的人工酿酒酵母菌株构建[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2017, 37(9): 71-81. |
| LiB, LiangN, LiuD, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of 8-dimenthylally naringenin[J]. China Biotechnology, 2017, 37(9): 71-81. | |
| 27 | GietzR D. Yeast transformation by the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2014, 1205: 1-12. |
| 28 | NormiY M, HiraishiT, TaguchiS, et al. Site-directed saturation mutagenesis at residue F420 and recombination with another beneficial mutation of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2005, 27(10): 705-712 |
| 29 | XieW P, LiuM, LvX M, et al. Construction of a controllable beta-carotene biosynthetic pathway by decentralized assembly strategy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2014, 111(1): 125-133. |
| 30 | JeknićZ, JeknićS, JevremovićS, et al. Alteration of flower color in Iris germanica L. ‘Fire Bride through ectopic expression of phytoene synthase gene (CrtB) from Pantoea agglomerans[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(8): 1307-1321. |
| 31 | AhnJ W, KimK J. Crystal structure of 1′-OH-carotenoid 3, 4-desaturase from Nonlabens dokdonensis DSW-6[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2015, 77: 29-37. |
| 32 | CavasottoC N, PhatakS S. Homology modeling in drug discovery: current trends and applications[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2009, 14(13/14): 676-683. |
| 33 | TrottO, OlsonA J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2010, 31: 455-461. |
| 34 | IrwinJ J, SterlingT, MysingerM M, et al. ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology[J]. Journad of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2012, 52: 1757-1768. |
| 35 | DelanoW L. The PyMol molecular graphics system[J]. Proteins Structure Function and Bioinformatics, 2002, 30: 442-454. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [3] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [4] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [5] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [6] | Lanhe ZHANG, Qingyi LAI, Tiezheng WANG, Xiaozhuo GUAN, Mingshuang ZHANG, Xin CHENG, Xiaohui XU, Yanping JIA. Effect of H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge properties in SBR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [7] | Lufan JIA, Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG. Aqueous two-phase system based adherent droplet microfluidics for enhanced enzymatic reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [8] | Zhuotao TAN, Siyu QI, Mengjiao XU, Jie DAI, Chenjie ZHU, Hanjie YING. Application of the redox cascade systems with coenzyme self-cycling in biocatalytic processes: opportunities and challenges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 45-59. |
| [9] | Yang HU, Yan SUN. Self-propulsion of enzyme and enzyme-induced micro-/nanomotor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 116-132. |
| [10] | Xin LIU, Jun GE, Chun LI. Light-driven microbial hybrid systems improve level of biomanufacturing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 330-341. |
| [11] | Xue LIU, Lijuan ZHANG, Guangrong ZHAO. Commensalistic Escherichia coli coculture for biosynthesis of daidzein [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4015-4024. |
| [12] | Shaojie AN, Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI. Construction of pH sensitive artificial glutathione peroxidase based on the formation and dissociation of molecular machine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678. |
| [13] | Mai ZHANG, Yao TIAN, Zhiqi GUO, Ye WANG, Guangjin DOU, Hao SONG. Design and optimization of photocatalysis-biological hybrid system for green synthesis of fuels and chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2774-2789. |
| [14] | Xinzhe ZHANG, Wentao SUN, Bo LYU, Chun LI. Oxidative modification of plant natural products and microbial manufacturing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2790-2805. |
| [15] | Jiachen SUN, Wentao SUN, Hui SUN, Bo LYU, Chun LI. Licorice flavone synthase Ⅱ catalyzes liquiritigenin to specifically synthesize 7,4′-dihydroxyflavone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3202-3211. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||