CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (1): 459-468.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221096
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jing ZHANG1( ), Tao LIU1, Wei ZHANG1,2, Zhenyu CHU1, Wanqin JIN1(
), Tao LIU1, Wei ZHANG1,2, Zhenyu CHU1, Wanqin JIN1( )
)
Received:2022-08-02
Revised:2022-10-26
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
Wanqin JIN
张静1( ), 刘涛1, 张伟1,2, 储震宇1, 金万勤1(
), 刘涛1, 张伟1,2, 储震宇1, 金万勤1( )
)
通讯作者:
金万勤
作者简介:张静(1997—),女,博士研究生,202061104133@njtech.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jing ZHANG, Tao LIU, Wei ZHANG, Zhenyu CHU, Wanqin JIN. Preparation of a novel separation-sensing membrane and its dynamic monitoring of blood glucose[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 459-468.
张静, 刘涛, 张伟, 储震宇, 金万勤. 一种新型分离传感膜的制备及其血糖的动态监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 459-468.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
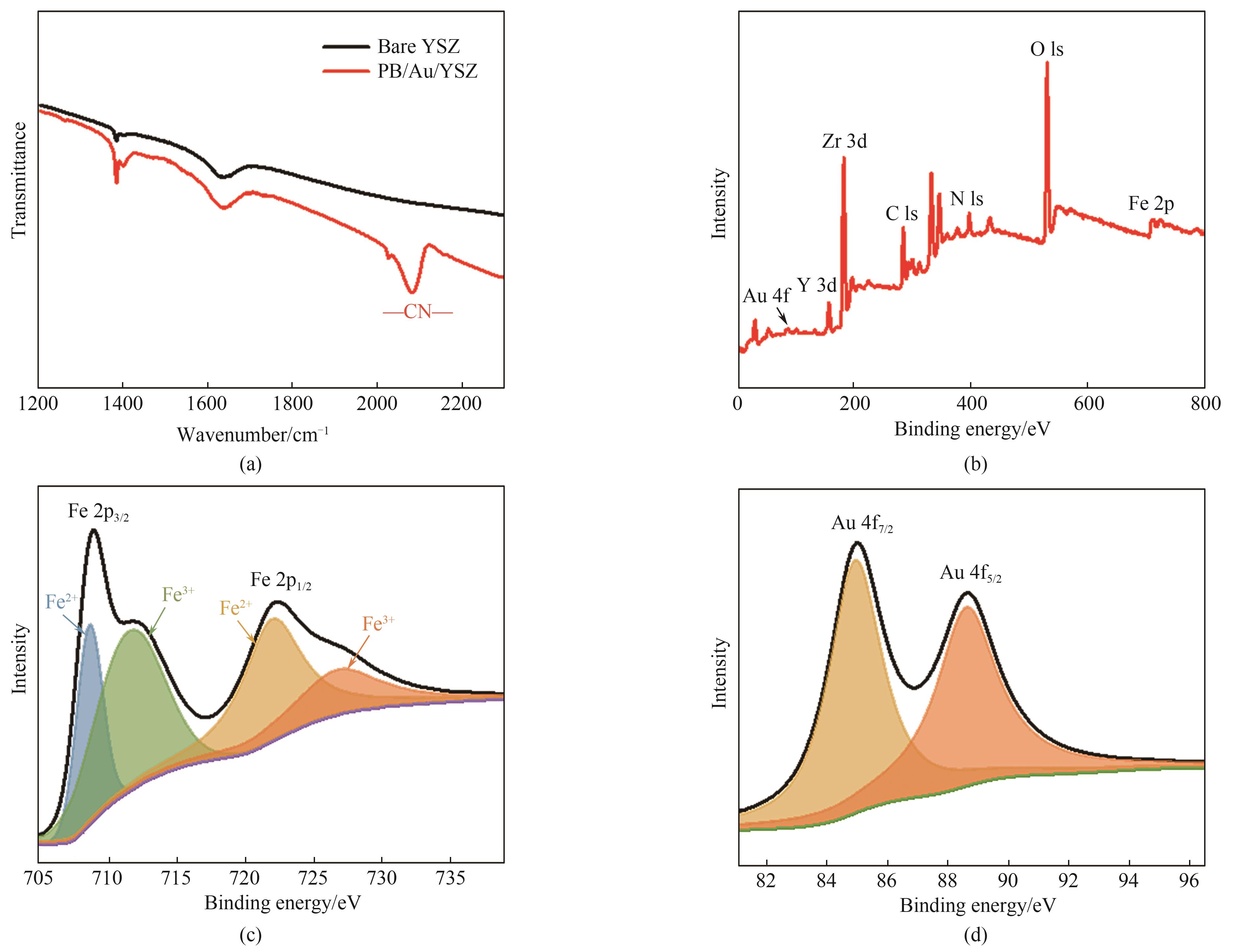
Fig.5 (a) FT-IR spectra of YSZ support and PB/Au/YSZ separation-sensing membrane; (b) XPS full spectra of PB/Au/YSZ separation-sensing membrane; (c), (d) XPS spectra of Fe 2p and Au 4f
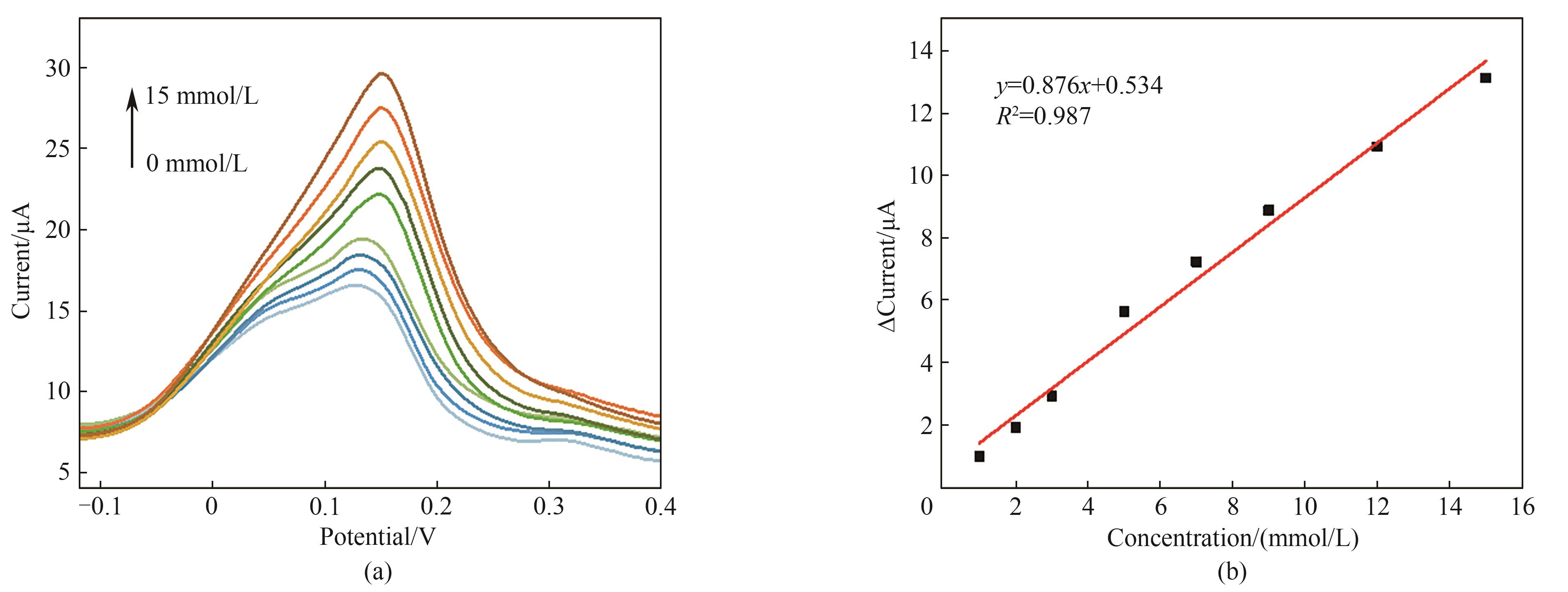
Fig.11 (a) DPV curves of PB/Au/YSZ separation-sensing membrane toward various glucose concentrations; (b) the calibration curve of DPV peak current change and glucose concentration
| 项目 | 序号 | 红细胞 | 白细胞 | 血小板 | 血红蛋白 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YSZ | 1 | 1×109/L | 0 | 28×109/L | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 12×109/L | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 8×109/L | 0 | |
| PB/Au/YSZ | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 1 Separation effect test of YSZ blank membrane and PB/Au/YSZ membrane
| 项目 | 序号 | 红细胞 | 白细胞 | 血小板 | 血红蛋白 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YSZ | 1 | 1×109/L | 0 | 28×109/L | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 12×109/L | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 8×109/L | 0 | |
| PB/Au/YSZ | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | Lee H, Hong Y J, Baik S, et al. Enzyme-based glucose sensor: from invasive to wearable device[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2018, 7(8): e1701150. |
| 2 | Yoo E H, Lee S Y. Glucose biosensors: an overview of use in clinical practice[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(5): 4558-4576. |
| 3 | Gordon C. Blood glucose monitoring in diabetes: rationale and procedure[J]. British Journal of Nursing, 2019, 28(7): 434-439. |
| 4 | Tang L, Chang S J, Chen C J, et al. Non-invasive blood glucose monitoring technology: a review[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(23): 6925. |
| 5 | Alhaddad A Y, Aly H, Gad H, et al. Sense and learn: recent advances in wearable sensing and machine learning for blood glucose monitoring and trend-detection[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 876672. |
| 6 | Bruen D, Delaney C, Florea L, et al. Glucose sensing for diabetes monitoring: recent developments[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): E1866. |
| 7 | Kesavadev J, Misra A, Saboo B, et al. Blood glucose levels should be considered as a new vital sign indicative of prognosis during hospitalization[J]. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome, 2021, 15(1): 221-227. |
| 8 | Park C S. Predictive roles of intraoperative blood glucose for post-transplant outcomes in liver transplantation[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2015, 21(22): 6835-6841. |
| 9 | Chen J, Wu C H, Wang X H, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on blood glucose: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2020, 11: 574541. |
| 10 | Xiao F, Zhou Y C, Zhang M B, et al. Hyperglycemia and blood glucose deterioration are risk factors for severe COVID-19 with diabetes: a two-center cohort study[J]. Journal of Medical Virology, 2022, 94(5): 1967-1975. |
| 11 | Chu Z Y, Zhang W, You Q N, et al. A separation-sensing membrane performing precise real-time serum analysis during blood drawing[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(42): 18701-18708. |
| 12 | 徐南平. 面向应用过程的陶瓷膜材料设计、制备与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. |
| Xu N P. Process-Oriented Design, Preparation and Application of Ceramic Membranes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. | |
| 13 | 邢卫红, 金万勤, 陈日志, 等. 陶瓷膜连续反应器的设计与工程应用[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(7): 1666-1673. |
| Xing W H, Jin W Q, Chen R Z, et al. Design and application of continuous ceramic membrane reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 61(7): 1666-1673. | |
| 14 | 金万勤, 徐南平. 限域传质分离膜[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 50-56. |
| Jin W Q, Xu N P. Membrane separation based on mechanism of confined mass transfer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 50-56. | |
| 15 | 武军伟, 邢卫红, 张峰, 等. 一体式流化床膜反应器合成二甲基二氯硅烷[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2776-2784. |
| Wu J W, Xing W H, Zhang F, et al. Synthesis of dimethyldichlorosilane by fluidized bed membrane reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2776-2784. | |
| 16 | Viganò S M, di Filippo S, Manzoni C, et al. Membrane characteristics[M]//Hemodialysis—from Basic Research to Clinical Trials. Basel: KARGER, 2008: 162-167. |
| 17 | Makdisi G, Wang I W. Extra corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) review of a lifesaving technology[J]. Journal of Thoracic Disease, 2015, 7(7): E166-E176. |
| 18 | Clark Jr L C, Lyons C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1962, 102(1): 29-45. |
| 19 | Asal M, Özen Ö, Şahinler M, et al. Recent developments in enzyme, DNA and immuno-based biosensors[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(6): E1924. |
| 20 | Gao J, Jeffries L, Mach K E, et al. A multiplex electrochemical biosensor for bloodstream infection diagnosis[J]. SLAS Technology, 2017, 22(4): 466-474. |
| 21 | Razumiene J, Gureviciene V, Sakinyte I, et al. The synergy of thermally reduced graphene oxide in amperometric urea biosensor: application for medical technologies[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(16): 4496. |
| 22 | Xie Y, Chu Z Y, Jin W Q. Beyond separation: membranes towards medicine[J]. Journal of Membrane Science Letters, 2022, 2(1): 100020. |
| 23 | Yao X Y, Liu Y, Chu Z Y, et al. Membranes for the life sciences and their future roles in medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 49: 1-20. |
| 24 | Chu Z Y, Li L L, Liu G P, et al. A novel membrane with heterogeneously functionalized nanocrystal layers performing blood separation and sensing synchronously[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(86): 12706-12709. |
| 25 | Shi Y F, Han X Y, Pan S, et al. Gold nanomaterials and bone/cartilage tissue engineering: biomedical applications and molecular mechanisms[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 724188. |
| 26 | Siddique S, Chow J C L. Gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and cancer therapy[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(11): 3824. |
| 27 | Tian Y Y, Qiang S, Wang L H. Gold nanomaterials for imaging-guided near-infrared in vivo cancer therapy[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2019, 7: 398. |
| 28 | Jiang D F, Chu Z Y, Peng J M, et al. Screen-printed biosensor chips with Prussian blue nanocubes for the detection of physiological analytes[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 228: 679-687. |
| 29 | Long X X, Chen H Y, Huang T J, et al. Removal of Cd(Ⅱ) from micro-polluted water by magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@Prussian blue[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(9): 2497. |
| 30 | Liu T, Zhao Q, Xie Y, et al. In situ fabrication of aloe-like Au-ZnO micro/nanoarrays for ultrasensitive biosensing of catechol[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2020, 156: 112145. |
| 31 | Yang P Q, Pang J, Hu F H, et al. An ultrasensitive biosensing flexible chip using a novel silver@Prussian blue core-shell nanocube composite[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 276: 31-41. |
| 32 | Qu J Y, Kang S P, Du X P, et al. Synthesis, characterization and applications of a new Prussian blue type material[J]. Electroanalysis, 2013, 25(7): 1722-1726. |
| 33 | Holade Y, Servat K, Rousseau J, et al. Electrochemical and physicochemical characterizations of gold-based nanomaterials: correlation between surface composition and electrocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(14): H929-H937. |
| 34 | Elouarzaki K, le Goff A, Holzinger M, et al. From gold porphyrins to gold nanoparticles: catalytic nanomaterials for glucose oxidation[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(15): 8556-8560. |
| [1] | Yanpeng WU, Xiaoyu LI, Qiaoyang ZHONG. Experimental analysis on filtration performance of electrospun nanofibers with amphiphobic membrane of oily fine particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 259-264. |
| [2] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [3] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [4] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [5] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [6] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [7] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [8] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [9] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [10] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [11] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [12] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [13] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [14] | Yongyao SUN, Qiuying GAO, Wenguang ZENG, Jiaming WANG, Yifei CHEN, Yongzhe ZHOU, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Design and optimization of membrane-based integration process for advanced utilization of associated gases in N2-EOR oilfields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [15] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||