CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6680-6695.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250672
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tian YANG1,2( ), Huixia GUO1,2(
), Huixia GUO1,2( ), Mengci SUN1,2
), Mengci SUN1,2
Received:2025-06-23
Revised:2025-08-27
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2025-12-31
Contact:
Huixia GUO
通讯作者:
郭惠霞
作者简介:杨田(1999—),男,硕士研究生,2466684520@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Tian YANG, Huixia GUO, Mengci SUN. The CoFe2O4/CeO2 composite material activates PMS to degrade tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6680-6695.
杨田, 郭惠霞, 孙梦慈. CoFe2O4/CeO2复合材料活化PMS降解盐酸四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6680-6695.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
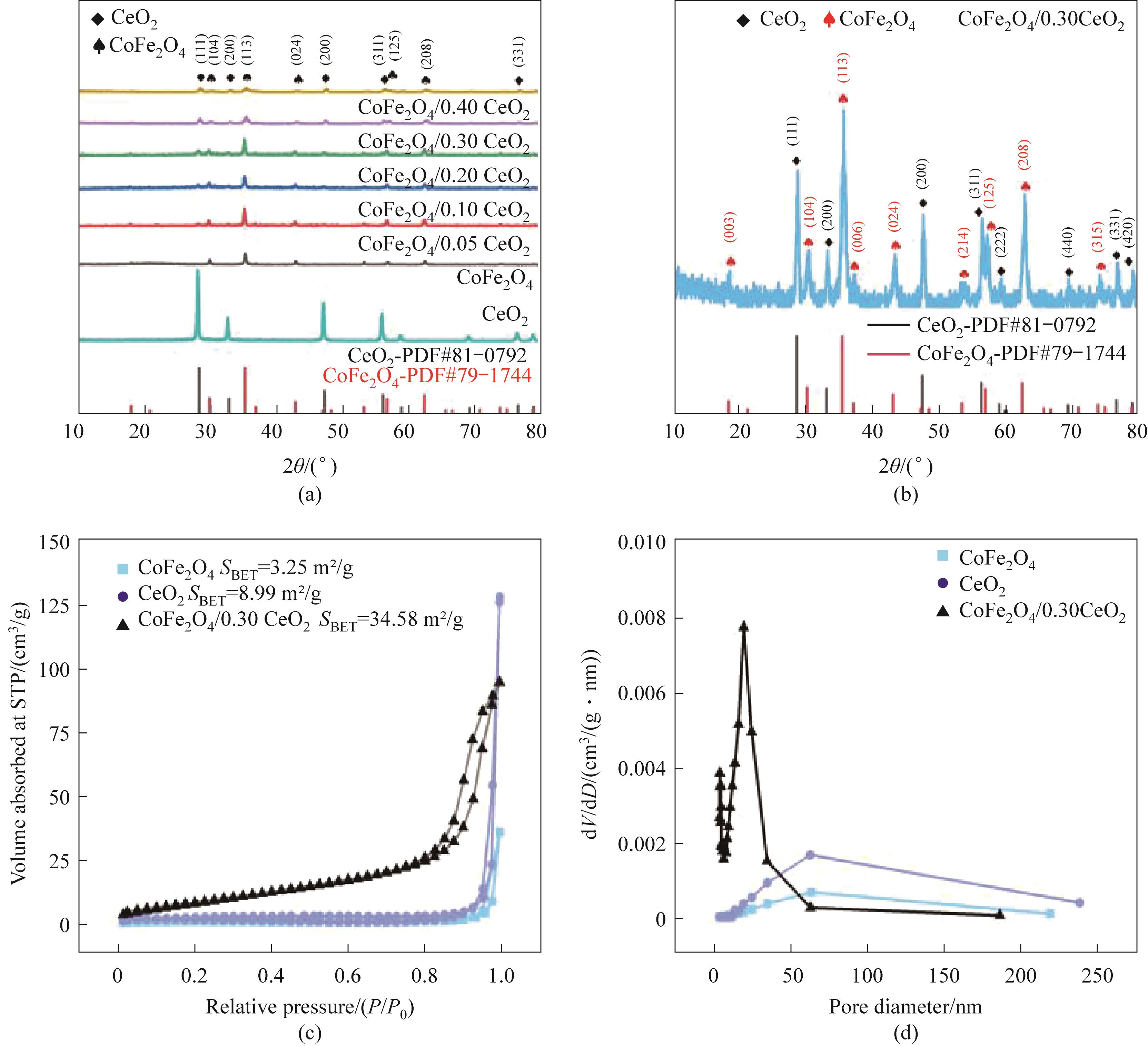
Fig.2 XRD patterns of the prepared samples (a,b); N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm (c) and aperture distribution map(d) of CoFe2O4, CeO2 and CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 3.25±0.02 | 0.06 | 62.78 |
| CeO2 | 8.99±0.02 | 0.20 | 61.23 |
| CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2 | 34.58±0.02 | 0.15 | 18.86 |
Table 1 Specific surface area, pore volume and average pore diameter of CoFe2O4, CeO2 and CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 3.25±0.02 | 0.06 | 62.78 |
| CeO2 | 8.99±0.02 | 0.20 | 61.23 |
| CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2 | 34.58±0.02 | 0.15 | 18.86 |
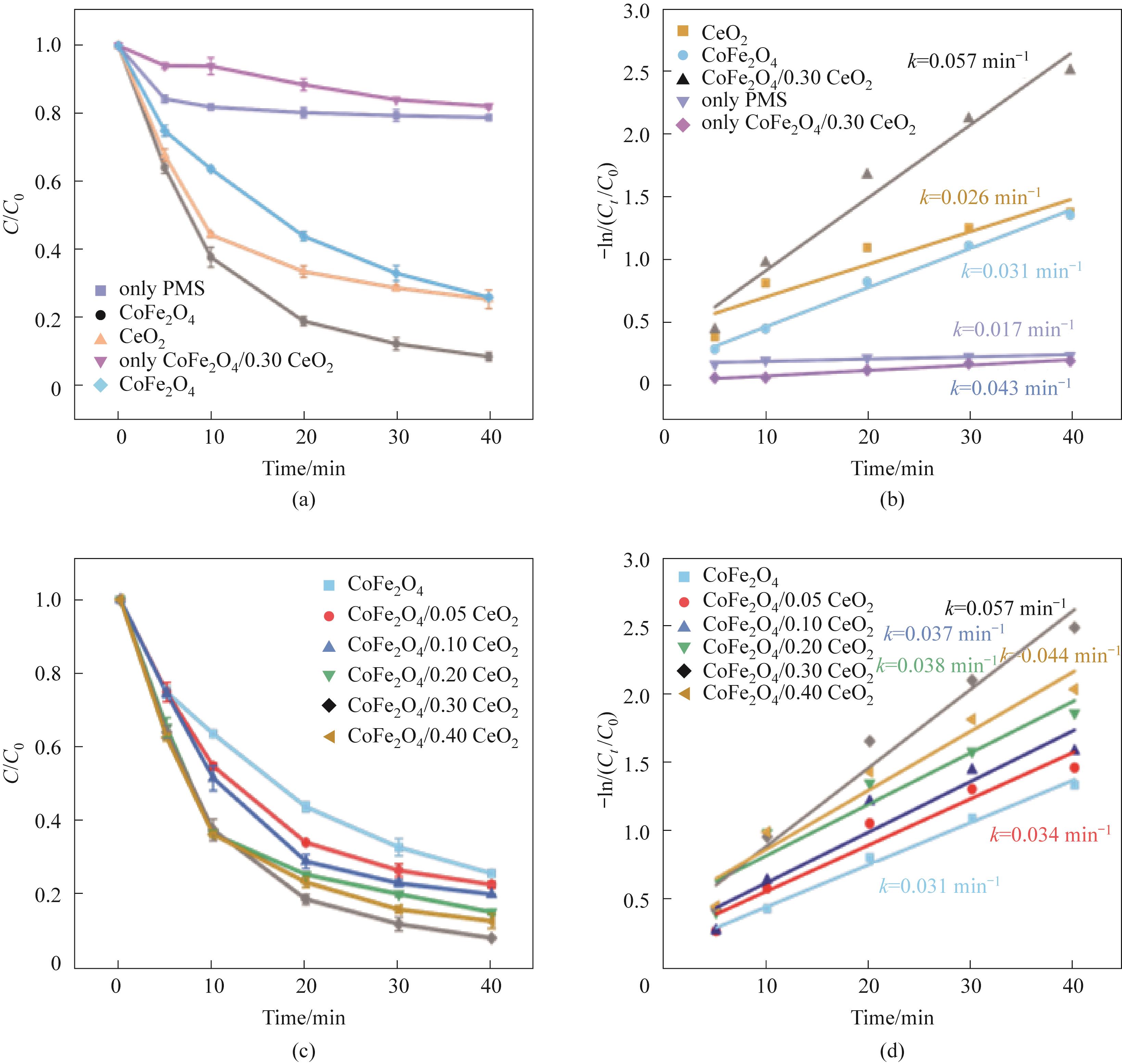
Fig.4 Influence of different systems on TC-HCl (a); The effect of different CeO2 complex amount on TC-HCl degradation efficiency (c); (a), (c) Corresponding pseudo-first-order kinetic model [(b),(d)] (experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
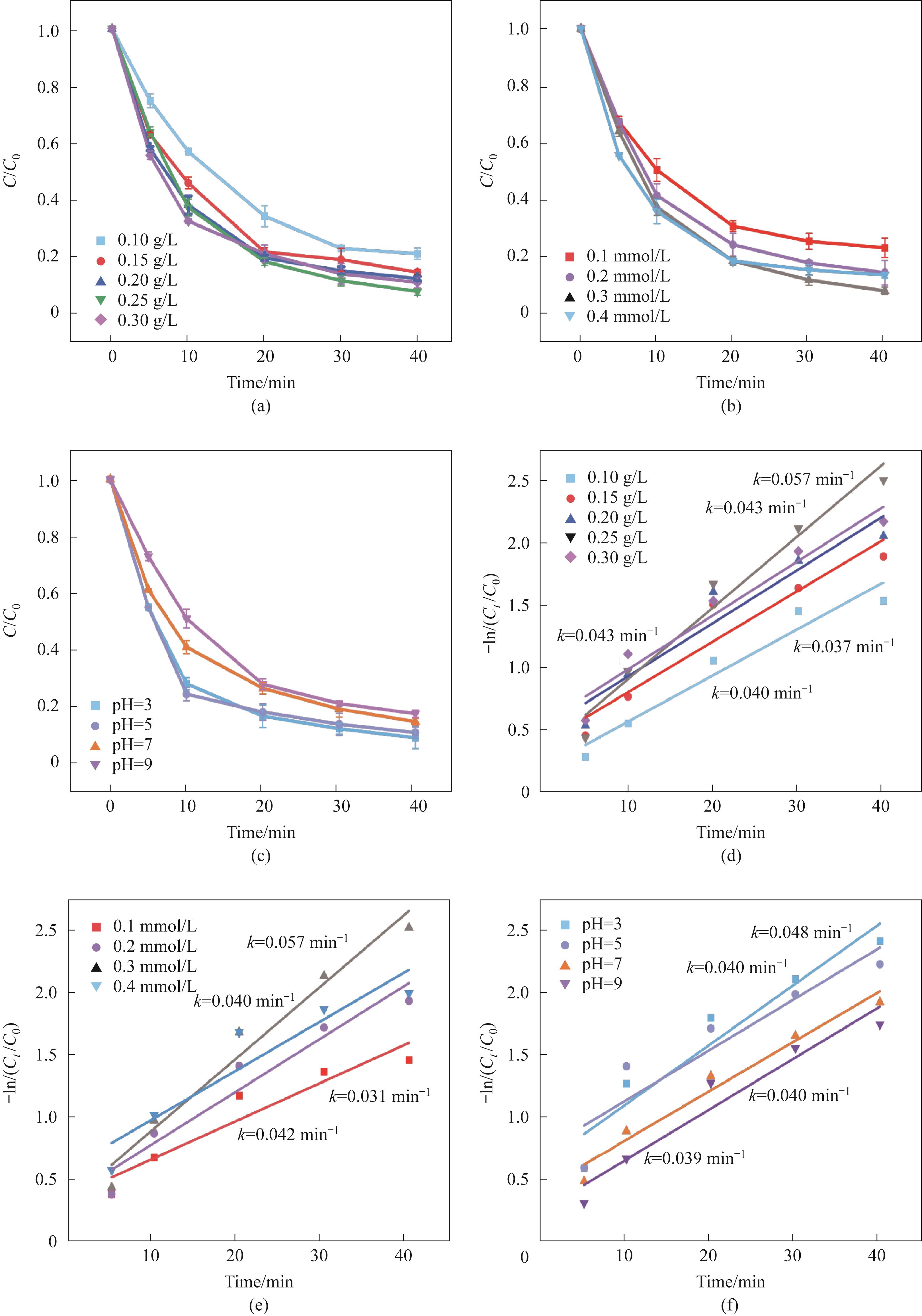
Fig.5 The influence of catalyst addition amount (a), PMS addition amount (b), and initial pH (c) on catalytic performance; (d)—(f) The pseudo-first-order kinetic model of the catalyst corresponding to (a—c)(experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
| 催化剂 | 工作内容 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 / MnFe2O4 | ZrO2/ MnFe2O4 -10 = 0.20 g/L,PDS = 6.0 mmol/L,pH = 7.1,TC=20 mg/L,120 min后TC降解效率达到85.2% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/高岭石 | CFO/K-40%= 0.50 g/L,H2O2 = 1.0 ml,pH = 4,TC=30 mg/L,30 min内降解效率可达84.82% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/氮化碳 | CFO/CN = 0.5 g/L,PMS = 1.0 mmol/L,TC=44.4 mg/L,10 min后TC降解效率达到86% | [ |
| CoFe2O4@MoS2 | CoFe2O4/MoS2 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.5 mmol/L,pH = 7,TC=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到93% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/二氧化硅 | CFO/MCM-41 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.15 mmol/L,pH = 7,SMX=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到90.39% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/CeO2 | CoFe2O4/CeO2 = 0.25 g/L,PMS =0.15 mmol/L,TC-HCl=10 mg/L,40 min后TC-HCl降解效率达到91.94% | 本文 |
Table 2 Summarized the results of similar work
| 催化剂 | 工作内容 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 / MnFe2O4 | ZrO2/ MnFe2O4 -10 = 0.20 g/L,PDS = 6.0 mmol/L,pH = 7.1,TC=20 mg/L,120 min后TC降解效率达到85.2% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/高岭石 | CFO/K-40%= 0.50 g/L,H2O2 = 1.0 ml,pH = 4,TC=30 mg/L,30 min内降解效率可达84.82% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/氮化碳 | CFO/CN = 0.5 g/L,PMS = 1.0 mmol/L,TC=44.4 mg/L,10 min后TC降解效率达到86% | [ |
| CoFe2O4@MoS2 | CoFe2O4/MoS2 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.5 mmol/L,pH = 7,TC=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到93% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/二氧化硅 | CFO/MCM-41 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.15 mmol/L,pH = 7,SMX=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到90.39% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/CeO2 | CoFe2O4/CeO2 = 0.25 g/L,PMS =0.15 mmol/L,TC-HCl=10 mg/L,40 min后TC-HCl降解效率达到91.94% | 本文 |
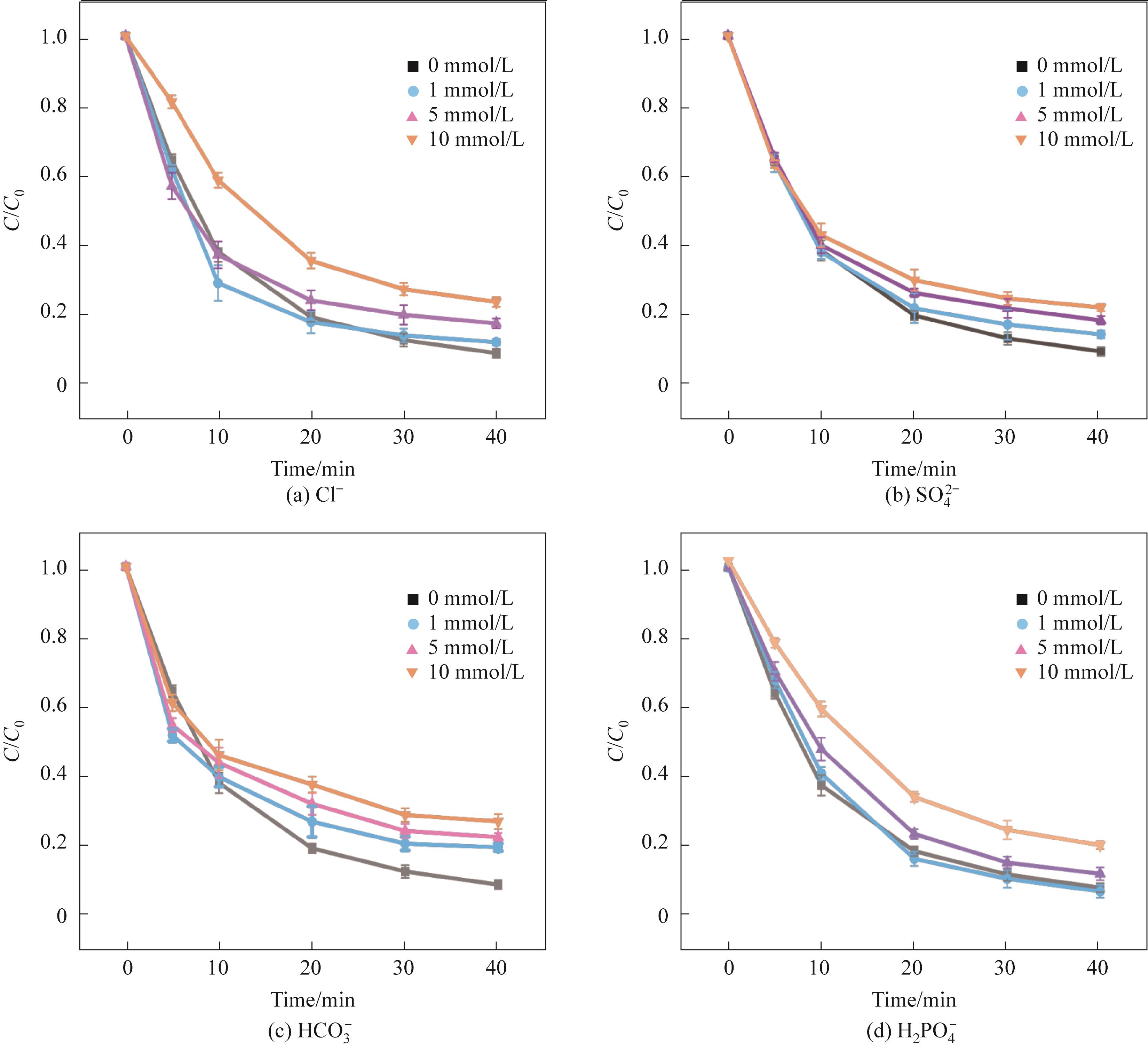
Fig.6 Effects of different concentrations of inorganic anions on TC-HCl degradation(Experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
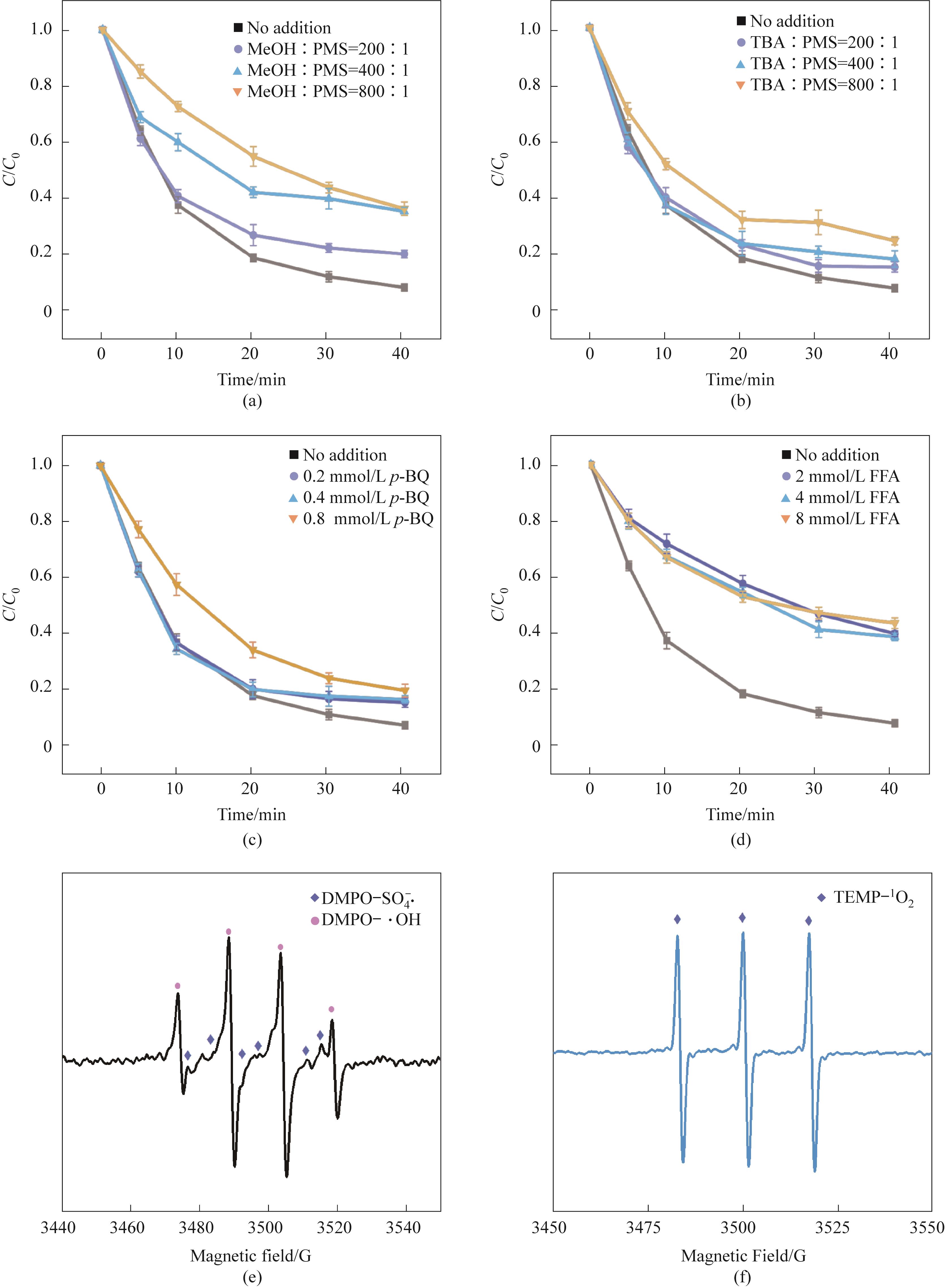
Fig.7 Effects of different concentrations of scavengers on the removal of TC-HCl in CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS system(a)—(d); EPR spectra captured by DMPO showed SO4-·, ·OH(e); (f) TEMP captures EPR spectrum (Experimental conditions:Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
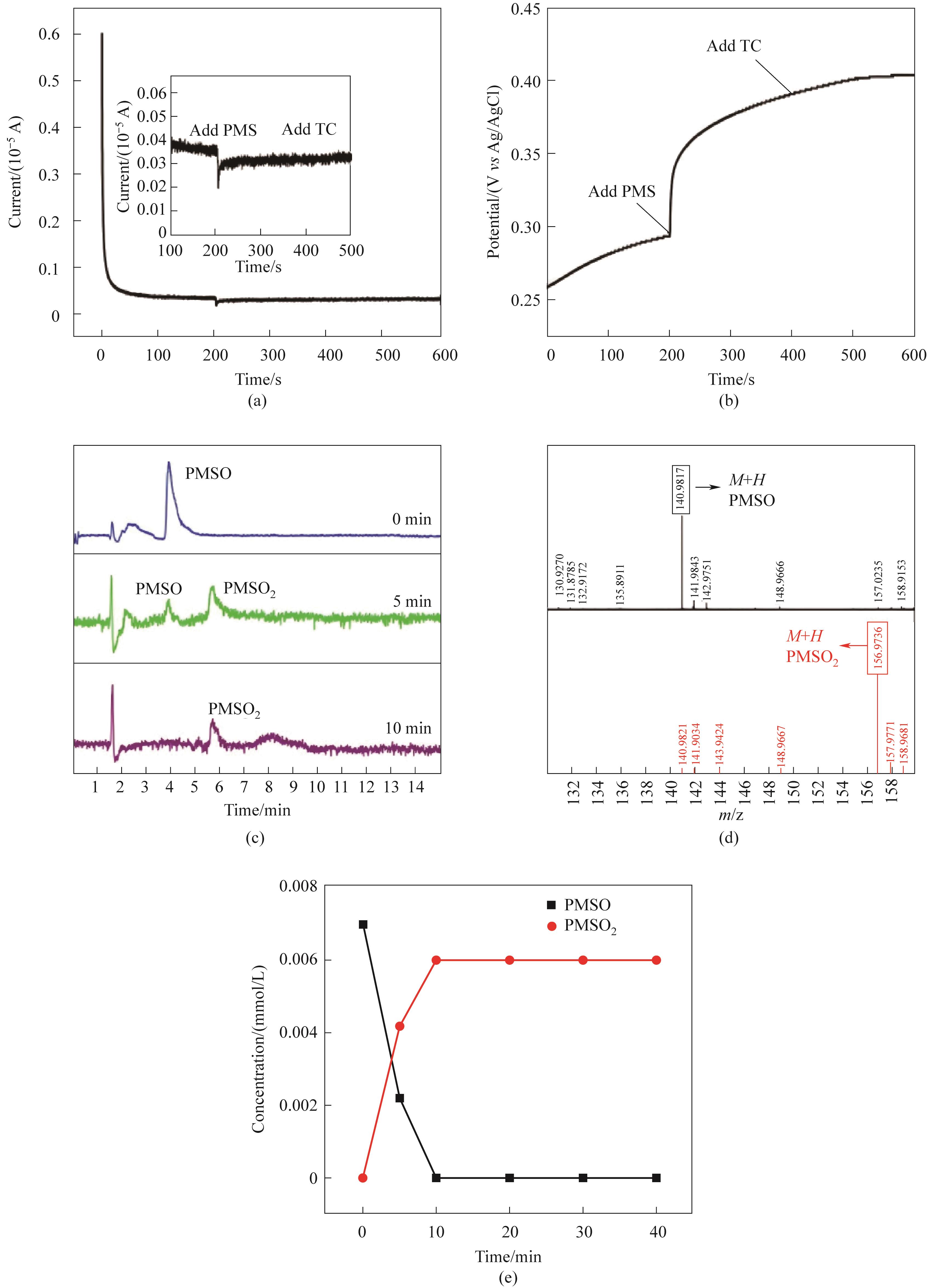
Fig.9 The i-t curve(a); OCP curve(b) of CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS system LC-MS chromatogram of the degradation of PMSO to generate PMSO2(c); The secondary mass spectra of PMSO and PMSO2 (d); The curves of the degradation of PMSO and the generation of PMSO2 (e)(Experimental conditions:Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
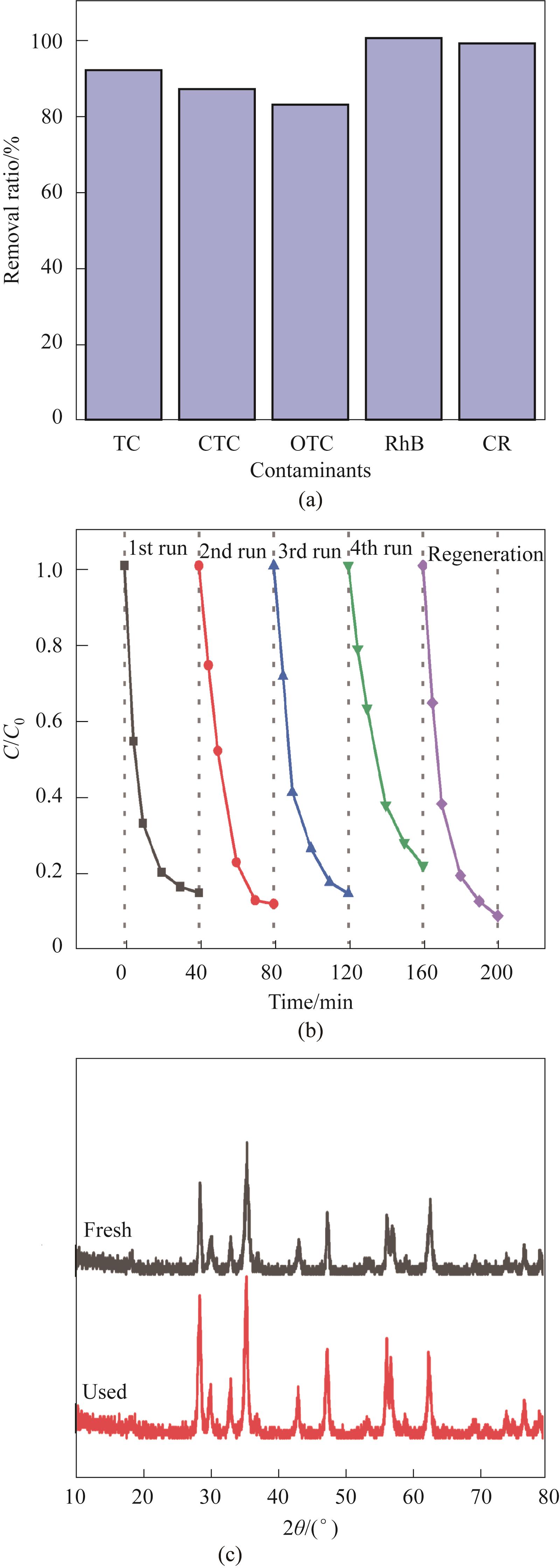
Fig.13 Degradability of other pollutants(a); Cyclic experiment (b); Before and after the use of XRD (c) (Experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
| [1] | Zhou M Y, Liu K, Peng Q, et al. Long-acting CoAl2O4 spinel catalyst developed on activated alumina pellets by facile synthesis to activate peroxymonosulfate: controllable cobalt leaching and environmental adaptability[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 310: 114702. |
| [2] | Peng Y T, Tang H M, Yao B, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by spinel ferrite and their composites in degradation of organic pollutants: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 414: 128800. |
| [3] | Wang Y H, Sun Y L, Wang R Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt embedded in layered δ-MnO2 for degradation of dimethyl phthalate: mechanisms, degradation pathway, and DFT calculation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 451: 130901. |
| [4] | Zhu K X, Jin C Z, Zhao C X, et al. Modulation synthesis of multi-shelled cobalt-iron oxides as efficient catalysts for peroxymonosulfate-mediated organics degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 1537-1549. |
| [5] | Luo J M, Bo S F, Qin Y N, et al. Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 395: 125063. |
| [6] | Pi Y Q, Gao H Q, Cao Y D, et al. Cobalt ferrite supported on carbon nitride matrix prepared using waste battery materials as a peroxymonosulfate activator for the degradation of levofloxacin hydrochloride[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122377. |
| [7] | Wang Y, Gao C Y, Zhang Y Z, et al. Bimetal-organic framework derived CoFe/NC porous hybrid nanorods as high-performance persulfate activators for bisphenol A degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127800. |
| [8] | Pan Y J, Meng F Y, Bai J X, et al. Highly efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by CoFe2O4@attapulgite-biochar composites: degradation properties and mechanism insights[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(3): 112579. |
| [9] | Guo Z Y, Jin H Y, Sun H Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by novel magnetically recyclable CoFe2O4/MXene quantum dots composites for rapid degradation of tetracycline: synergistic performance and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 370: 122398. |
| [10] | Zhu Z H, Yang X, He J, et al. Deciphering the structural origin for the remarkable CO oxidation activities of the CuO-based catalysts with diverse morphological CeO2 supports[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 114385. |
| [11] | Geng Y, Jin K, Mei J, et al. CeO2 grafted with different heteropoly acids for selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382: 121032. |
| [12] | Deng R Y, He Q, Yang D X, et al. Enhanced synergistic performance of nano-Fe0-CeO2 composites for the degradation of diclofenac in DBD plasma[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126884. |
| [13] | Zhang L J, Wang N, Wang F Y, et al. Robust high-entropy spinel oxides for peroxymonosulfate activation: stabilization effect and enhancement mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150826. |
| [14] | Ren T F, Yang S Y, Wu S, et al. High-energy ball milling enhancing the reactivity of microscale zero-valent aluminum toward the activation of persulfate and the degradation of trichloroethylene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 100-111. |
| [15] | Huang W Q, Xiao S, Zhong H, et al. Activation of persulfates by carbonaceous materials: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418: 129297. |
| [16] | Li X, Qin Y, Jia Y, et al. Preparation and application of Fe/biochar (Fe-BC) catalysts in wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129766. |
| [17] | Wu Y W, Chen X T, Han Y, et al. Highly efficient utilization of nano-Fe(0) embedded in mesoporous carbon for activation of peroxydisulfate[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 9081-9090. |
| [18] | Niu L J, Zhang G M, Xian G, et al. Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic γ - F e 2 O 3 / C e O 2 catalyst: performance, activation mechanism and degradation pathway[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 259: 118156. |
| [19] | Liu Z M, Gao Z M, Wu Q. Activation of persulfate by magnetic zirconium-doped manganese ferrite for efficient degradation of tetracycline[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 423: 130283. |
| [20] | Li J M, Li S Y, Cao Z, et al. Heterostructure CoFe2O4/kaolinite composite for efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride through synergetic photo-Fenton reaction[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2023, 244: 107102. |
| [21] | Pan B, Chen W, Zhou L X, et al. CoFe2O4/carbon nitride Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalytic PMS activation for efficient tetracycline degradation: accelerated electron transfer[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 191: 2522-2532. |
| [22] | Peng X M, Yang Z H, Hu F P, et al. Mechanistic investigation of rapid catalytic degradation of tetracycline using CoFe2O4@MoS2 by activation of peroxymonosulfate[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 287: 120525. |
| [23] | Gao P, Fan X H, Su Y N, et al. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation for sulfamethoxazole degradation by CoFe2O4 decorated mesoporous silica through a simple one-step grinding-calcination method[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2025, 13(3): 116890. |
| [24] | Dong X B, Ren B X, Sun Z M, et al. Monodispersed CuFe2O4 nanoparticles anchored on natural kaolinite as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for bisphenol A degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 253: 206-217. |
| [25] | Wang S, Long J R, Jiang T, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4/CeO2/g-C3N4 composites with a visible-light response as a high efficiency Fenton photocatalyst to synergistically degrade tetracycline[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 278: 119609. |
| [26] | Zhao D S, Fan W L, Wang Z H, et al. Sustainable cycling and mechanism of C o ( Ⅱ ) / C o ( Ⅳ ) / C o ( Ⅲ ) with S(Ⅳ) highly triggered by C o ( Ⅳ ) in E / C o ( Ⅱ ) / S ( Ⅳ ) for enhanced removal of reactive brilliant red X-3B[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 343: 126997. |
| [27] | Wang Z, Jiang J, Pang S Y, et al. Is sulfate radical really generated from peroxydisulfate activated by iron ( Ⅱ ) for environmental decontamination?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(19): 11276-11284. |
| [28] | Wang Z, Qiu W, Pang S Y, et al. Further understanding the involvement of F e ( Ⅳ ) in peroxydisulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation by F e ( Ⅱ ) for oxidative water treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 842-847. |
| [29] | Zong Y, Zhang H, Zhang X M, et al. High-valent cobalt-oxo species triggers hydroxyl radical for collaborative environmental decontamination[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 300: 120722. |
| [30] | Zhang H, Luo M F, Zhou P, et al. Enhanced ferrate(Ⅵ) oxidation of sulfamethoxazole in water by CaO2: the role of Fe(Ⅳ) and Fe(Ⅴ)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 128045. |
| [31] | Si Q S, Guo W Q, Wang H Z, et al. Difunctional carbon quantum dots/g-C3N4 with in-plane electron buffer for intense tetracycline degradation under visible light: tight adsorption and smooth electron transfer[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 299: 120694. |
| [32] | Zhao Z D, Zhou W J, Lin D H, et al. Construction of dual active sites on diatomic metal (FeCo-N/C-x) catalysts for enhanced Fenton-like catalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 309: 121256. |
| [1] | Wei ZHAO, Wenle XING, Zhaoxu HAN, Xingzhong YUAN, Longbo JIANG. Progress of g-C3N4-based metal-free heterojunction photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [2] | Hui LIU, Jia WANG, Jing ZHAO, Chuanchang LI, Youfu LYU. Research on heat generation behavior and capacity attenuation of large capacity energy storage battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4903-4912. |
| [3] | Xiaochen ZHANG, Zhongshan LU, Teng GUO, Heng GUI, Hongbing SONG, Meng XIAO. Isolation and study of the degradation mechanism of hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene-degrading strain [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4205-4216. |
| [4] | Bing LIAO, Xinyu ZHU, Qianqian HUANG, Wen XU, Mengyao KOU, Na GUO. Performance and mechanism of enhanced Fenton system by hydroxylamine hydrochloride for removal of 2, 4-DCP under near-neutral conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4273-4283. |
| [5] | Lei WU, Zixuan HU, Yuan GAO, Changbo LIU, Husheng CAO, Tiantian LIU, Ruiyu ZHU, Jun ZHOU. Oxidation remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil by microwave combined with biochar activated persulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3659-3670. |
| [6] | Qingping ZHAO, Min ZHANG, Hui ZHAO, Gang WANG, Yongfu QIU. Hydrogen bond effect and kinetic studies on hydroesterification of ethylene to methyl propionate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2701-2713. |
| [7] | Jun HE, Yong LI, Nan ZHAO, Xiaojun HE. Study on the properties of carbon with Se doping cobalt sulfide in lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| [8] | Zhongqing CHEN, Jiaxu LIU, Yanyu WANG, Hongquan JING, Cuihong HOU, Lingbo QU. Effect of K-B-Al ternary system on the melting characteristics and glass structure of tailings [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1323-1333. |
| [9] | Yue GAO, Ding LI, Yumiao GAO. Study on catalytic oxidation remediation technology of organic polluted site soil [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1297-1304. |
| [10] | Chenlong GUO, Zhengqi PENG, Bingxue JIANG, Zhengkai WU, Deliang WANG, Qingyue WANG, Jieyuan ZHENG, Lim Khak Ho, Shengbin SHI, Xuan YANG, Pingwei LIU, Wenjun WANG. Advances in upcycling of post-consumer PET [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 532-542. |
| [11] | Shengqiang YIN, Xiangyu ZHONG, Manyu GONG, Lu LI, Yuanzheng LIU, Shoubin ZHOU, Junbing XIAO, Changhui LIU, Chuankun JIA. Characterization of properties and thermal conductivity enhancement of activated carbonized peach gum-based composite phase change materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6614-6625. |
| [12] | Zhizhong PENG, Xuelei LANG, Qiang FANG, Huifang JING, dazhong ZHONG, Jinping LI, Qiang ZHAO. Ag-Sn interfacial electronic structure modulation for high-efficiency CO2 electroreduction at 1 A/cm2 under acidic conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6376-6386. |
| [13] | Yuchen WANG, Wanzong WANG, Xin ZHANG, Maoqiang GUO, Xiaoming ZHOU, Lizhi SHENG. Electrochemical performance of high-mass-loading porous carbons derived from catalpa pod shells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6748-6760. |
| [14] | Jiaqi QIU, Zhongqing YANG, Zhigang ZHANG, Hailong GAN, Chunxiu HUO, Zhishuai DOU, Jingyu RAN. Mechanistic study of Mn/Ce co-doping for enhanced oxygen species conversion and catalytic combustion of dilute methane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5604-5616. |
| [15] | Yongzhen CHEN, Wenji SONG, Erxiong CHEN, Kun QIN, Yujie ZHOU, Qun DU, Ziping FENG. Flow characteristics and pigging performance degradation of high-concentration ice slurry in pipelines [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5842-5852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||