CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3446-3458.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241297
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jin LI1( ), Shuiqing HU1, Yibin WENG2, Juntao JIANG1, Qinghong WANG1(
), Shuiqing HU1, Yibin WENG2, Juntao JIANG1, Qinghong WANG1( ), Chunmao CHEN1
), Chunmao CHEN1
Received:2024-11-13
Revised:2024-12-23
Online:2025-08-13
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Qinghong WANG
李晋1( ), 胡水清1, 翁艺斌2, 姜峻韬1, 王庆宏1(
), 胡水清1, 翁艺斌2, 姜峻韬1, 王庆宏1( ), 陈春茂1
), 陈春茂1
通讯作者:
王庆宏
作者简介:李晋(1993—),男,博士,讲师,lijincup@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jin LI, Shuiqing HU, Yibin WENG, Juntao JIANG, Qinghong WANG, Chunmao CHEN. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of refinery waste activated sludge based on pretreatment strategy by spend caustic[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3446-3458.
李晋, 胡水清, 翁艺斌, 姜峻韬, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 基于碱渣预处理策略强化炼厂污泥厌氧消化效能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3446-3458.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
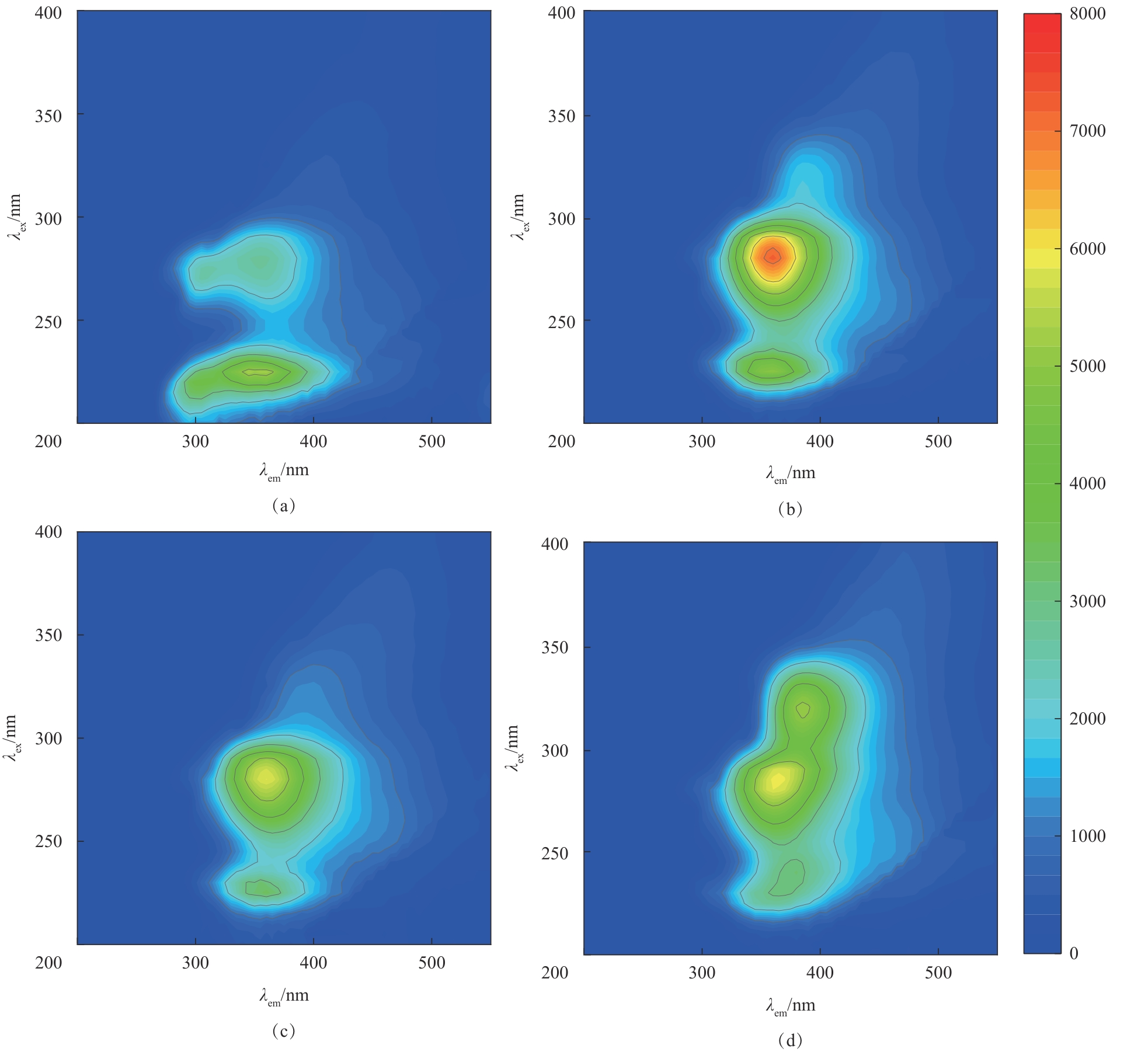
Fig.2 Three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matters after RSC pretreatments (a), thermal-RSC (b), electrolysis-RSC (c) and alkaline fermentation (d)
| 项目 | 空白组 | 碱渣组 | 热-碱渣组 | 电解-碱渣组 | 碱性发酵组 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 进料TS含量/(g·L-1) | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 |
| 预处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | 0 | 59.21 | 19.67 | 14.38 |
| 中和费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | 5.86 | 2.43 | 4.24 | 2.98 |
| 厌氧消化费用/(CNY·t-1) | 14.38 | 14.38 | 0 | 14.38 | 0 |
| TS去除率/% | 13.52 | 18.75 | 25.48 | 26.23 | 24.78 |
| 委外处置费用/(CNY·t-1) | 294.03 | 276.25 | 253.37 | 250.82 | 255.75 |
| 氢气产率/(dm3·t-1) | 48.00 | 251.32 | 142.04 | 407.80 | 313.32 |
| 甲烷产率/(dm3·t-1) | 233.54 | 719.63 | 1176.34 | 1295.15 | 1423.46 |
| 能源收益/ CNY | -1.81 | -5.84 | -8.85 | -10.39 | -11.07 |
| 碱渣投加量/(L·t-1) | 0 | 30 | 10 | 27.5 | 20 |
| 减少的碱渣处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | -6 | -2 | -5.5 | -4 |
| 总处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 306.60 | 284.65 | 304.36 | 273.22 | 258.04 |
Table 1 Economic evaluation of WAS anaerobic digestion by different pretreatment methods
| 项目 | 空白组 | 碱渣组 | 热-碱渣组 | 电解-碱渣组 | 碱性发酵组 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 进料TS含量/(g·L-1) | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 | 19.24 |
| 预处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | 0 | 59.21 | 19.67 | 14.38 |
| 中和费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | 5.86 | 2.43 | 4.24 | 2.98 |
| 厌氧消化费用/(CNY·t-1) | 14.38 | 14.38 | 0 | 14.38 | 0 |
| TS去除率/% | 13.52 | 18.75 | 25.48 | 26.23 | 24.78 |
| 委外处置费用/(CNY·t-1) | 294.03 | 276.25 | 253.37 | 250.82 | 255.75 |
| 氢气产率/(dm3·t-1) | 48.00 | 251.32 | 142.04 | 407.80 | 313.32 |
| 甲烷产率/(dm3·t-1) | 233.54 | 719.63 | 1176.34 | 1295.15 | 1423.46 |
| 能源收益/ CNY | -1.81 | -5.84 | -8.85 | -10.39 | -11.07 |
| 碱渣投加量/(L·t-1) | 0 | 30 | 10 | 27.5 | 20 |
| 减少的碱渣处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 0 | -6 | -2 | -5.5 | -4 |
| 总处理费用/(CNY·t-1) | 306.60 | 284.65 | 304.36 | 273.22 | 258.04 |
| [1] | 李晋, 谢萍, 陈平, 等. 废白土热解残渣强化炼化剩余污泥水热液厌氧产能[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(12): 65-71, 77. |
| Li J, Xie P, Chen P, et al. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of refinery excess sludge hydrothermal liquid by pyrolytic residue of spent bleaching earth[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2022, 42(12): 65-71, 77. | |
| [2] | 罗进财, 王欣芸, 孙鸿, 等. 改善剩余污泥厌氧消化产甲烷性能的新策略:导电材料介导微生物种间直接电子传递[J]. 应用化工, 2024, 53(4): 918-924. |
| Luo J C, Wang X Y, Sun H, et al. A new strategy to improve methanogenesis from anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: conductive materials mediate direct interspecies electron transfer of microorganisms[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(4): 918-924. | |
| [3] | 杨丽丽, 张勇, 胡定成, 等. 利用物理法-热水解预处理剩余污泥技术的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2024, 53(8): 1975-1979, 1988. |
| Yang L L, Zhang Y, Hu D C, et al. Research progress of pretreatment of residual sludge by physical thermal hydrolysis[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(8): 1975-1979, 1988. | |
| [4] | Dasgupta A, Chandel M K. Enhancement of biogas production from organic fraction of municipal solid waste using hydrothermal pretreatment[J]. Bioresource Technology Reports, 2019, 7: 100281. |
| [5] | Lizama A C, Figueiras C C, Herrera R R, et al. Effects of ultrasonic pretreatment on the solubilization and kinetic study of biogas production from anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 123: 1-9. |
| [6] | 王海东, 张文存, 王丽莉, 等. 污泥厌氧消化预处理技术综述[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(7): 1973-1977. |
| Wang H D, Zhang W C, Wang L L, et al. Review of pretreatment process of sludge anaerobic digestion[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(7): 1973-1977. | |
| [7] | 侯银萍, 蔡斌斌, 张安龙, 等. 不同预处理方法促进剩余污泥破胞及厌氧消化产气效率的研究[J]. 陕西科技大学学报, 2022, 40(2): 13-19, 27. |
| Hou Y P, Cai B B, Zhang A L, et al. Research on promoting sludge cracking and the biogas production efficiency of anaerobic digestion by different pretreatment methods[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2022, 40(2): 13-19, 27. | |
| [8] | 沈嘉辉, 王侃宏, 梁玉帅, 等. 游离氨预处理污泥促进有机物释放过程研究[J]. 现代化工, 2023, 43(7): 104-112. |
| [29] | Yao B, Liu M, Yu L Q, et al. Mechanism of biochar in alleviating the inhibition of anaerobic digestion under ciprofloxacin press[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 480: 135949. |
| [30] | Zhu D M, Wang Z X, Liu K Q, et al. Multi-cycle anaerobic digestion of hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous phase: role of carbon and iron based conductive materials in inhibitory compounds degradation, microbial structure shaping, and interspecies electron transfer regulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140019. |
| [31] | Ma X Z, Li S L, Pan R K, et al. Effect of biochar on the mitigation of organic volatile fatty acid emission during aerobic biostabilization of biosolids and the underlying mechanism[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 390: 136213. |
| [32] | 陈烨, 孙治雷, 吴能友, 等. 海洋沉积物中甲烷代谢微生物的研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(6): 82-92. |
| Chen Y, Sun Z L, Wu N Y, et al. Advances in the study of methane-metabolizing microbial communities in marine sediments[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(6): 82-92. | |
| [33] | 于亚梅, 沈雁文, 朱南文, 等. 生物炭和石墨的电化学性质对剩余污泥厌氧消化产甲烷的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 807-820. |
| Yu Y M, Shen Y W, Zhu N W, et al. Effect of electrochemical properties of biochar and graphite on methane production in anaerobic digestion of excess activated sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(3): 807-820. | |
| [34] | 尹若愚, 李乃玉, 全向春, 等. 负载纳米零价铁及Fe3O4颗粒对厌氧颗粒污泥长期运行性能及微生物群落结构影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(11): 24-32. |
| Yin R Y, Li N Y, Quan X C, et al. Effects of zero valent iron and ferriferrous oxide loading on methanogenesis performance of anaerobic granular sludge and microbial community under a long-term operation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2023, 43(11): 24-32. | |
| [35] | 尚欣宇, 孙晓娇, 徐艳, 等. 纳米铁氧化物对Pelotomaculum schinkii培养系丙酸厌氧降解产甲烷的影响[J]. 微生物学杂志, 2024, 44(1): 32-39. |
| Shang X Y, Sun X J, Xu Y, et al. Influence of iron oxides nanoparticles on anaerobic degradation of propionic acid in Pelotomaculum schinkii cultivation system to produce mathane[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2024, 44(1): 32-39. | |
| [36] | 许晓晴, 陈烨, 甄毓, 等. 渤海沉积物中产甲烷途径及产甲烷菌群落特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(3): 50-61. |
| [8] | Shen J H, Wang K H, Liang Y S, et al. Study on promotion of organic matters release through pretreatment of sludge by free ammonia[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 43(7): 104-112. |
| [9] | 王晨路, 刘吉宝, 解立平, 等. 铁(Ⅱ)-炭活化过硫酸盐对剩余污泥中溶解性有机物释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(12): 4009-4017. |
| Wang C L, Liu J B, Xie L P, et al. Influence on DOM release from sewage sludge by Fe(Ⅱ)-AC activating persulfate[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(12): 4009-4017. | |
| [10] | Li H, Li C C, Liu W J, et al. Optimized alkaline pretreatment of sludge before anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 123: 189-194. |
| [11] | Ye J, Hu A D, Ren G P, et al. Red mud enhances methanogenesis with the simultaneous improvement of hydrolysis-acidification and electrical conductivity[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 131-137. |
| [12] | Li J, Wang Q H, Liang J H, et al. An enhanced disintegration using refinery spent caustic for anaerobic digestion of refinery waste activated sludge[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 284: 112022. |
| [13] | 蔡美辰, 戚丹丹, 刘林林, 等. 碱预处理提高剩余污泥厌氧产甲烷性能研究[J]. 中国沼气, 2020, 38(4): 3-8. |
| Cai M C, Qi D D, Liu L L, et al. Enhancing anaerobic methane production of sewage sludge by alkaline pretreatment[J]. China Biogas, 2020, 38(4): 3-8. | |
| [14] | Pratap V, Kumar S, Yadav B R. Effect of low-temperature thermal-alkali pre-treatment on waste activated sludge solubilisation[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 189: 530-540. |
| [15] | Zhen G Y, Lu X Q, Li Y Y, et al. Combined electrical-alkali pretreatment to increase the anaerobic hydrolysis rate of waste activated sludge during anaerobic digestion[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 128: 93-102. |
| [16] | Ramos-Suarez M, Zhang Y, Heaven S. Acidogenic fermentation of organic residual solids: effect of different alkaline sources on pH, alkalinity, and fermentation performance[J]. Fermentation, 2024, 10(11): 571. |
| [17] | 李晋, 梁家豪, 马文峰, 等. 热-碱渣预处理强化炼厂剩余活性污泥厌氧消化性能[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(12): 6609-6619. |
| Li J, Liang J H, Ma W F, et al. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of refinery waste activated sludge using thermal-refinery spend caustic pretreatment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(12): 6609-6619. | |
| [18] | Li J, Xin W Z, Liang J H, et al. Alkaline fermentation of refinery waste activated sludge mediated by refinery spent caustic for volatile fatty acids production[J]. Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 324: 116317. |
| [19] | Wang D B, Huang Y X, Xu Q X, et al. Free ammonia aids ultrasound pretreatment to enhance short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 275: 163-171. |
| [20] | Zeng Q, Zan F X, Hao T W, et al. Electrochemical pretreatment for stabilization of waste activated sludge: simultaneously enhancing dewaterability, inactivating pathogens and mitigating hydrogen sulfide[J]. Water Research, 2019, 166: 115035. |
| [21] | Yukesh Kannah R, Kavitha S, Rajesh Banu J, et al. Synergetic effect of combined pretreatment for energy efficient biogas generation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 232: 235-246. |
| [22] | 郭送军, 韦进毅, 王晨路, 等. 基于FT-ICR MS的蒸汽爆破预处理强化污泥厌氧消化的有机物分子解析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(4): 1337-1345. |
| Guo S J, Wei J Y, Wang C L, et al. Molecular analysis of organic compounds in anaerobic digestion of sludge enhanced by steam explosion pretreatment based on FT-ICR MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2023, 17(4): 1337-1345. | |
| [23] | 郝晓地, 唐兴, 李季, 等. 腐殖酸影响剩余污泥厌氧消化过程实验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8): 3061-3068. |
| Hao X D, Tang X, Li J, et al. Experimental study on the effect of humic acid on the process of anaerobic digestion of excess sludge[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(8): 3061-3068. | |
| [24] | Muenmee S, Theepharaksapan S, Boonnorat J. Effect of food to microbe (F/M) ratio on anaerobic digestion of refinery waste sludge under mesophilic conditions: biogas potential and phytotoxicity[J]. Current Applied Science and Technology, 2022, 1: 1-11. |
| [25] | Wang J S, Zhang Z J, Ye X, et al. Enhanced solubilization and biochemical methane potential of waste activated sludge by combined free nitrous acid and potassium ferrate pretreatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 297: 122376. |
| [26] | He H Y, Liu Y L, Wang X S, et al. Effects of newly prepared alkaline ferrate on sludge disintegration and methane production: reaction mechanism and model simulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 343: 520-529. |
| [36] | Xu X Q, Chen Y, Zhen Y, et al. Methanogenic pathways and methanogen communities in the sediments from Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(3): 50-61. |
| [37] | 阮敏, 孙宇桐, 黄忠良, 等. 污泥预处理-厌氧消化体系的能源经济性评价[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1503-1516. |
| Ruan M, Sun Y T, Huang Z L, et al. Energy economy evaluation of sludge pretreatment-anaerobic digestion system[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1503-1516. | |
| [27] | Yuan Z W, He C, Shi Q, et al. Molecular insights into the transformation of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate concentrate during biodegradation and coagulation processes using ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(14): 8110-8118. |
| [28] | Harirchi S, Wainaina S, Sar T, et al. Microbiological insights into anaerobic digestion for biogas, hydrogen or volatile fatty acids (VFAs): a review[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(3): 6521-6557. |
| [1] | Ting HE, Kai ZHANG, Wensheng LIN, Liqiong CHEN, Jiafu CHEN. Research on integrated process of cryogenic CO2 removal under supercritical pressure and liquefaction for biogas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [2] | Xuerui LU, Guoyan ZHOU, Qi FANG, Mengzheng YU, Xiucheng ZHANG, Shandong TU. Numerical study on the carbon deposition effect in external reformer of solid oxide fuel cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| [3] | Chenru ZHOU, Chenwei LIU, Zhiyuan WANG, Minhui QI, Sanbao DONG, Xiangyu WANG, Mingzhong LI. Effect of methanol and ethylene glycol on adhesion strength of methane hydrates [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3596-3604. |
| [4] | Zhaoming MAI, Yingtao WU, Wei WANG, Haibao MU, Zuohua HUANG, Chenglong TANG. Study on nonlinear ignition characteristics and dilution gas effect of n-dodecane methane dual fuel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3115-3124. |
| [5] | Ruijie MA, Zixuan HUANG, Xueqian GUAN, Guangjin CHEN, Bei LIU. Efficient ethane and methane separation using ZIF-8/DMPU slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2262-2269. |
| [6] | Weijie ZHANG, Jiawen HE, Yiming ZHANG, Deli LI, Guangya HU, Xiao CAI, Jinhua WANG, Zuohua HUANG. Effects of fuel stratification on flow field and flame structure of multi-stage swirling methane combustion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1754-1764. |
| [7] | Meilin SHI, Lianda ZHAO, Xingjian DENG, Jingsong WANG, Haibin ZUO, Qingguo XUE. Research progress on catalytic methane reforming process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 25-39. |
| [8] | Huanjuan ZHAO, Yingxin BAO, Kang YU, Jing LIU, Xinming QIAN. Quantitative experimental study on detonation instability of multi-component [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 339-348. |
| [9] | Hongbiao XU, Liang YANG, Zidong LI, Daoping LIU. Kinetics of methane hydrate formation in saline droplets/copper foam composite system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3287-3296. |
| [10] | Yiqi ZHANG, Xuesong TAN, Wuhuan LI, Quan ZHANG, Changlin MIAO, Xinshu ZHUANG. Efficient fractionation of sugarcane bagasse with phenoxyethanol under mild condition [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2274-2282. |
| [11] | Lihao LIU, Ting HUANG, Yu YONG, Xinhao LUO, Zeming ZHAO, Shangfei SONG, Bohui SHI, Guangjin CHEN, Jing GONG. CH4-hydrate formation and solid-phase deposition in salt-sand coexisting flow systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1987-2000. |
| [12] | Pei WANG, Ruiming DUAN, Guangru ZHANG, Wanqin JIN. Modeling and simulation analysis of solar driven membrane separation biomethane hydrogen production process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 967-973. |
| [13] | Haotian MA, Tirui JING, Chengcheng LIU, Turap YUSAN, Zhe ZHANG, Yidi WANG, Qinghong WANG, Chunmao CHEN, Chunming XU. Study on reduction performance and kinetics of Sr-modified LaFeO3 for methane chemical looping reforming [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4532-4546. |
| [14] | Shuang LIANG, Xingxun LI, Longyan GAO, Xuqiang GUO, Guangjin CHEN, Changyu SUN. Research on kinetics of methane hydrate film growth on water droplet in oil phase [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4369-4377. |
| [15] | Xiaoyang LIU, Jianliang YU, Yujie HOU, Xingqing YAN, Zhenhua ZHANG, Xianshu LYU. Effect of spiral microchannel on detonation propagation of hydrogen-doped methane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3139-3148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||