CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (10): 4277-4285.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230574
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenhua TONG( ), Yilong LI, Yongkui ZHANG, Yabo WANG(
), Yilong LI, Yongkui ZHANG, Yabo WANG( )
)
Received:2023-06-14
Revised:2023-08-10
Online:2023-12-22
Published:2023-10-25
Contact:
Yabo WANG
通讯作者:
王雅博
作者简介:童文华(1994—),女,博士研究生,twh8123@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Wenhua TONG, Yilong LI, Yongkui ZHANG, Yabo WANG. Study on alkali-assisted degradation of tributyl phosphate by manganese tetroxide and phosphorus recovery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4277-4285.
童文华, 李义隆, 张永奎, 王雅博. 碱辅助四氧化三锰降解磷酸三丁酯及磷元素回收研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4277-4285.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 序号 | 化合物名称 | 分子量 | 分子结构 | 检测情况 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甲基-次磷酸单丁酯 | 136 | 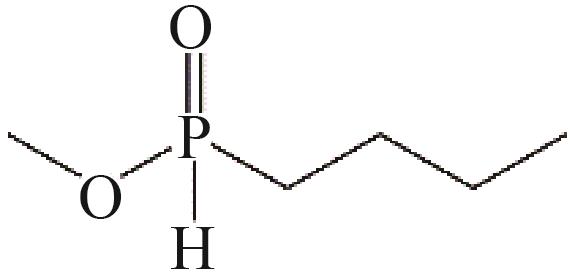 | √ | — |
| 2 | 次磷酸单丁酯 | 122 |  | √ | — |
| 3 | 磷酸 | 98 |  | √ | [ |
| 4 | 4-戊烯-2-酮 | 84 |  | √ | — |
| 5 | 亚磷酸 | 82 |  | √ | — |
| 6 | 1-丁醇 | 74 |  | √ | [ |
| 7 | 丁酮 | 72 | 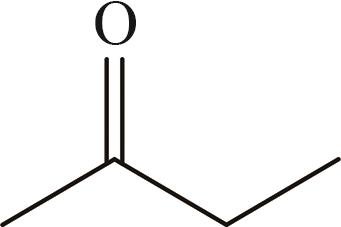 | √ | — |
| 8 | 3-甲基-1-丁烯 | 69 | 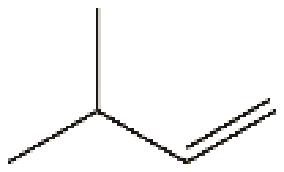 | √ | — |
| 9 | 乙酸 | 60 | 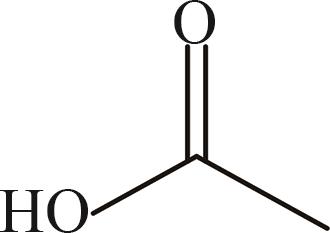 | √ | [ |
| 10 | 丁烷 | 58 | 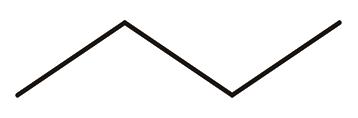 | √ | — |
| 11 | 丁烯 | 56 | 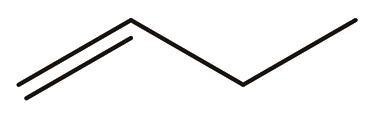 | √ | [ |
| 12 | 丙烷 | 44 |  | √ | — |
| 13 | 一氧化碳 | 28 | C≡O | √ | — |
Table 1 Possible end products of alkali-assisted TBP degradation by Mn3O4
| 序号 | 化合物名称 | 分子量 | 分子结构 | 检测情况 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甲基-次磷酸单丁酯 | 136 |  | √ | — |
| 2 | 次磷酸单丁酯 | 122 |  | √ | — |
| 3 | 磷酸 | 98 |  | √ | [ |
| 4 | 4-戊烯-2-酮 | 84 |  | √ | — |
| 5 | 亚磷酸 | 82 |  | √ | — |
| 6 | 1-丁醇 | 74 |  | √ | [ |
| 7 | 丁酮 | 72 |  | √ | — |
| 8 | 3-甲基-1-丁烯 | 69 |  | √ | — |
| 9 | 乙酸 | 60 |  | √ | [ |
| 10 | 丁烷 | 58 |  | √ | — |
| 11 | 丁烯 | 56 |  | √ | [ |
| 12 | 丙烷 | 44 |  | √ | — |
| 13 | 一氧化碳 | 28 | C≡O | √ | — |
| 1 | Ennis W B, Thompson H E, Smith H H. Tributyl phosphate as a solvent for preparing concentrated and oil-miscible solutions of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and similar substances[J]. Science, 1946, 103(2677): 476. |
| 2 | Tatsumi T, Yamamoto K, Tajima H, et al. Shape selective epoxidation of alkenes catalyzed by polyoxometalate-intercalated hydrotalcite[J]. Chemistry Letters, 1992, 21(5): 815-818. |
| 3 | Cierpiszewski R, Miesia̧c I, Regel-Rosocka M, et al. Removal of zinc(Ⅱ) from spent hydrochloric acid solutions from zinc hot galvanizing plants[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(3): 598-603. |
| 4 | 宋永会, 魏健, 马印臣, 等. 络合萃取法处理金刚烷胺制药废水[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(12): 1513-1518. |
| Song Y H, Wei J, Ma Y C, et al. Treatment of amantadine pharmaceutical wastewater by complexation extraction[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(12): 1513-1518. | |
| 5 | Homsirikamol C, Sunsandee N, Pancharoen U, et al. Synergistic extraction of amoxicillin from aqueous solution by using binary mixtures of Aliquat 336, D2EHPA and TBP[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 162: 30-36. |
| 6 | Sood D D, Patil S K. Chemistry of nuclear fuel reprocessing: current status[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 1996, 203(2): 547-573. |
| 7 | Liao C Y, Kim U J, Kannan K. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in sediment from northern Chinese coastal waters[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135328. |
| 8 | 张金凤, 逯南南, 侯书国, 等. 磷酸三丁酯的生物毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(3): 366-384. |
| Zhang J F, Lu N N, Hou S G, et al. Research progress on biotoxicity of tributyl phosphate[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(3): 366-384. | |
| 9 | 董竞武, 叶于薇, 仲伟鉴, 等. 生物标志物用于有机磷农药的迟发性神经毒性研究[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2006, 23(1): 41-44, 47. |
| Dong J W, Ye Y W, Zhong W J, et al. Acute delayed neurotoxicity study of organophosphorous pesticides by biomarker methods[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 2006, 23(1): 41-44, 47. | |
| 10 | Castleman B I, Ziem G E. American conference of governmental industrial hygienists: low threshold of credibility[J]. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1994, 26(1): 133-143. |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 国家危险废物名录(2021年版) [N]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2020-11-27. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. National hazardous waste list (2021 edition)[N]. Gazette of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, 2020-11-27. | |
| 12 | 杨丽莉. 放射性废TBP处理技术[J]. 辐射防护通讯, 2016, 36(1): 40-44. |
| Yang L L. Radioactive spent TBP treatment technologies[J]. Radiation Protection Bulletin, 2016, 36(1): 40-44. | |
| 13 | Wang C, Yu G C, Wang J L. Fenton oxidative degradation of spent organic solvents from nuclear fuel reprocessing plant[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2020, 130: 103563. |
| 14 | 丁欢, 李军, 金央, 等. 磷酸三丁酯在碱中的降解研究[J]. 化学工程师, 2015, 29(11): 51-53, 60. |
| Ding H, Li J, Jin Y, et al. Study on the degradation of tri-n-butyl phosphate in alkali[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2015, 29(11): 51-53, 60. | |
| 15 | 刘学军, 苑国琪, 成琼, 等. 含氚泵油处理技术研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2010, 44(S1): 124-127. |
| Liu X J, Yuan G Q, Cheng Q, et al. Treatment technology for pump oil with tritium[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2010, 44(S1): 124-127. | |
| 16 | 王泽斌. 高放射性核废料玻璃固化及成分设计[J]. 玻璃搪瓷与眼镜, 2022, 50(10): 37-43, 36. |
| Wang Z B. Glass curing and composition design of high-level radioactive nuclear waste[J]. Glass Enamel & Ophthalmic Optics, 2022, 50(10): 37-43, 36. | |
| 17 | Liu J, Lin H, Dong Y B, et al. Elucidating the biodegradation mechanism of tributyl phosphate (TBP) by Sphingomonas sp. isolated from TBP-contaminated mine tailings[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 250: 284-291. |
| 18 | Idziak K, Czakiert T, Krzywanski J, et al. Safety and environmental reasons for the use of Ni-, Co-, Cu-, Mn- and Fe-based oxygen carriers in CLC/CLOU applications: an overview[J]. Fuel, 2020, 268: 117245. |
| 19 | Bi W Z, Chen T J, Zhao R D, et al. Characteristics of a CaSO4 oxygen carrier for chemical-looping combustion: reaction with polyvinylchloride pyrolysis gases in a two-stage reactor[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(44): 34913-34920. |
| 20 | Chen P, Sun X Q, Gao M G, et al. Transformation and migration of cadmium during chemical-looping combustion/gasification of municipal solid waste[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 365: 389-399. |
| 21 | Niu X, Shen L H, Gu H M, et al. Characteristics of hematite and fly ash during chemical looping combustion of sewage sludge[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 268: 236-244. |
| 22 | Niu X, Shen L H, Gu H M, et al. Sewage sludge combustion in a CLC process using nickel-based oxygen carrier[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 260: 631-641. |
| 23 | González C, Gutierrez J I, González-Velasco J, et al. Application of differential scanning calorimetry to the reduction of several manganese oxides[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 1998, 52: 985-989. |
| 24 | Luo J, Hu W R, Suo Z L, et al. Co-pyrolysis of spent radioactive ion exchange resin and manganese dioxide: decrease the decomposition temperatures of functional groups[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126275. |
| 25 | Tong W H, Wang J P, Du X H, et al. Tributyl phosphate degradation and phosphorus immobilization by MnO2: reaction condition optimization and mechanism exploration[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 432: 128725. |
| 26 | Zhou Z, Li X Z, Li J J, et al. Promoting CO2 methanation performance of Ru/TiO2 through Co-activity of exposing (001) facets and oxygen vacancies of TiO2 [J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2022, 146: 106677. |
| 27 | Chen Y, Dai Y T, Li Y W, et al. Oxygen vacancies-mediated CuO@N-doped carbon nanocomposites for non-radical-dominated photothermal catalytic degradation of contaminants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 389: 136054. |
| 28 | Drinks E, Lepeytre C, Lorentz C, et al. UV—a photocatalytic degradation of the radionuclide complexants tributylphosphate and dibutylphosphate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 352: 143-150. |
| 29 | D’halluin T, Lepeytre C, Leydier A, et al. Degradation mechanism of tributyl phosphate by UV/H2O2 treatment and parameters optimization towards the design of a pilot reactor[J]. Environmental Technology, 2021, 42(27): 4247-4259. |
| 30 | Tashiro Y, Kodama R, Sugai H, et al. Nonphosphate degradation products of tributyl phosphate and their reactivities in purex media under extreme conditions[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2000, 129(1): 93-100. |
| [1] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [2] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [4] | Jintong LI, Shun QIU, Wenshou SUN. Oxalic acid and UV enhanced arsenic leaching from coal in flue gas desulfurization by coal slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [5] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [6] | Manzheng ZHANG, Meng XIAO, Peiwei YAN, Zheng MIAO, Jinliang XU, Xianbing JI. Working fluid screening and thermodynamic optimization of hazardous waste incineration coupled organic Rankine cycle system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [7] | Chen HAN, Youmin SITU, Bin ZHU, Jianliang XU, Xiaolei GUO, Haifeng LIU. Study of reaction and flow characteristics in multi-nozzle pulverized coal gasifier with co-processing of wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [8] | Xiaokun HE, Rui LIU, Yuan XUE, Ran ZUO. Review of gas phase and surface reactions in AlN MOCVD [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2800-2813. |
| [9] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [10] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [11] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [12] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [13] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [14] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [15] | Lanhe ZHANG, Qingyi LAI, Tiezheng WANG, Xiaozhuo GUAN, Mingshuang ZHANG, Xin CHENG, Xiaohui XU, Yanping JIA. Effect of H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge properties in SBR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||