CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (5): 1951-1965.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240075
• Process system engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhihong HUANG( ), Li ZHOU(
), Li ZHOU( ), Shiyang CHAI, Xu JI
), Shiyang CHAI, Xu JI
Received:2024-01-16
Revised:2024-02-19
Online:2024-06-25
Published:2024-05-25
Contact:
Li ZHOU
通讯作者:
周利
作者简介:黄志鸿(1999—),男,硕士研究生,rick_zhihong@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zhihong HUANG, Li ZHOU, Shiyang CHAI, Xu JI. Integrating optimization of hydrogenation units in multi-period hydrogen network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1951-1965.
黄志鸿, 周利, 柴士阳, 吉旭. 耦合加氢装置优化的多周期氢网络集成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1951-1965.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 周期 | 入口进料流量/(t·h-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 150.00 | 373.81 | 216.67 | 50.00 |
| 3月 | 134.25 | 392.84 | 243.92 | 38.91 |
| 5月 | 178.34 | 328.95 | 202.29 | 44.58 |
| 7月 | 163.93 | 319.92 | 189.47 | 46.32 |
| 9月 | 126.39 | 448.39 | 239.32 | 48.25 |
| 11月 | 159.28 | 402.58 | 227.34 | 43.29 |
Table 1 Feed flow data at the inlet of hydrotreating units
| 周期 | 入口进料流量/(t·h-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 150.00 | 373.81 | 216.67 | 50.00 |
| 3月 | 134.25 | 392.84 | 243.92 | 38.91 |
| 5月 | 178.34 | 328.95 | 202.29 | 44.58 |
| 7月 | 163.93 | 319.92 | 189.47 | 46.32 |
| 9月 | 126.39 | 448.39 | 239.32 | 48.25 |
| 11月 | 159.28 | 402.58 | 227.34 | 43.29 |
| 周期 | 硫含量/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 4800 | 3011 | 390 | 600 |
| 3月 | 6243 | 3854 | 491 | 792 |
| 5月 | 4176 | 2620 | 339 | 522 |
| 7月 | 5616 | 3704 | 476 | 717 |
| 9月 | 3792 | 2379 | 308 | 474 |
| 11月 | 5997 | 3764 | 488 | 752 |
Table 2 The inlet feed sulfur content data of the hydrotreating units
| 周期 | 硫含量/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 4800 | 3011 | 390 | 600 |
| 3月 | 6243 | 3854 | 491 | 792 |
| 5月 | 4176 | 2620 | 339 | 522 |
| 7月 | 5616 | 3704 | 476 | 717 |
| 9月 | 3792 | 2379 | 308 | 474 |
| 11月 | 5997 | 3764 | 488 | 752 |
| 周期 | 空速/h-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 1.920 | 2.000 | 3.000 | 2.250 |
| 3月 | 1.718 | 2.102 | 3.377 | 1.751 |
| 5月 | 2.283 | 1.760 | 2.801 | 2.006 |
| 7月 | 2.098 | 1.712 | 2.623 | 2.084 |
| 9月 | 1.618 | 2.399 | 3.314 | 2.171 |
| 11月 | 2.039 | 2.154 | 3.148 | 1.948 |
Table 3 LHSV of hydrotreating units
| 周期 | 空速/h-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT | |
| 1月 | 1.920 | 2.000 | 3.000 | 2.250 |
| 3月 | 1.718 | 2.102 | 3.377 | 1.751 |
| 5月 | 2.283 | 1.760 | 2.801 | 2.006 |
| 7月 | 2.098 | 1.712 | 2.623 | 2.084 |
| 9月 | 1.618 | 2.399 | 3.314 | 2.171 |
| 11月 | 2.039 | 2.154 | 3.148 | 1.948 |
| 操作条件和约束 | DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应温度/K | 633.0 | 648.0 | 513.0 | 553.0 |
| 反应压力/bar | 67.2 | 70.0 | 27.0 | 38.3 |
| 反应空速/h-1 | 1.920 | 2.000 | 3.000 | 2.250 |
| 气体硫含量限制/% | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 最低氢气纯度/% | 90 | 90 | 86 | 88 |
产品硫含量 (不大于)/(mg/kg) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 400 |
Table 4 Operating conditions and inlet stream concentration constrains for the hydrotreating units
| 操作条件和约束 | DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | KHT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应温度/K | 633.0 | 648.0 | 513.0 | 553.0 |
| 反应压力/bar | 67.2 | 70.0 | 27.0 | 38.3 |
| 反应空速/h-1 | 1.920 | 2.000 | 3.000 | 2.250 |
| 气体硫含量限制/% | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 最低氢气纯度/% | 90 | 90 | 86 | 88 |
产品硫含量 (不大于)/(mg/kg) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 400 |
| 周期 | 模型计算耗氢/ (kmol/h) | 实际耗氢/ (kmol/h) | 计算偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1月 | 855 | 913 | -6 |
| 3月 | 978 | 1026 | -5 |
| 5月 | 623 | 672 | -7 |
| 7月 | 749 | 762 | -2 |
| 9月 | 1024 | 1097 | -7 |
| 11月 | 787 | 831 | -5 |
Table 5 Calculation and actual hydrogen consumption of DHT-1
| 周期 | 模型计算耗氢/ (kmol/h) | 实际耗氢/ (kmol/h) | 计算偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1月 | 855 | 913 | -6 |
| 3月 | 978 | 1026 | -5 |
| 5月 | 623 | 672 | -7 |
| 7月 | 749 | 762 | -2 |
| 9月 | 1024 | 1097 | -7 |
| 11月 | 787 | 831 | -5 |
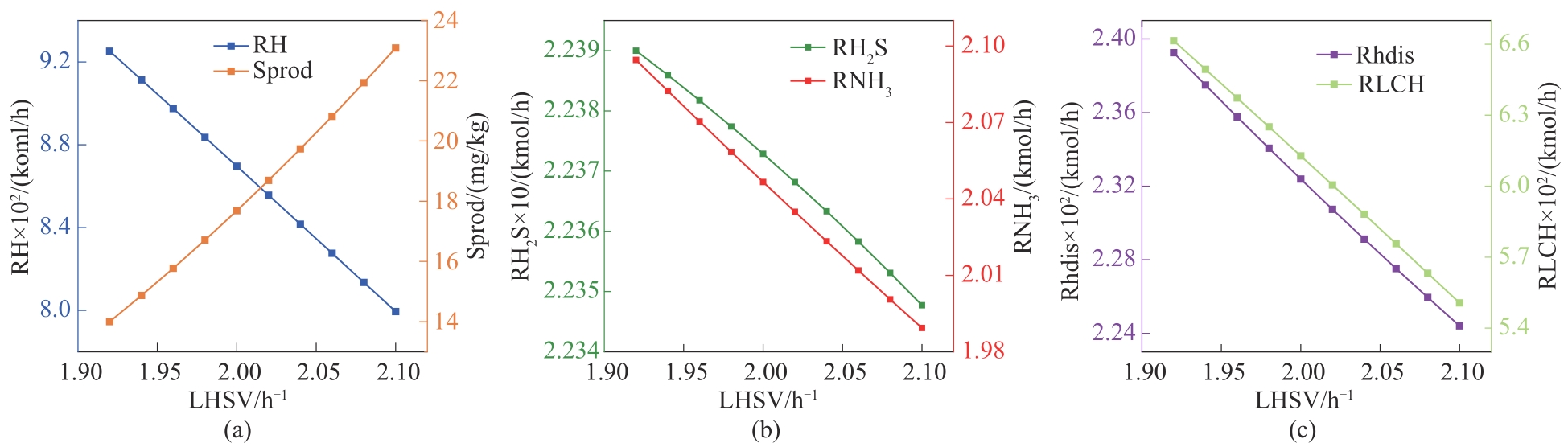
Fig.5 The impact trend of LHSV changes on hydrogen consumption in hydrotreating units(RH, Sprod, RH2S, RNH3, Rhdis and RLCH represent total hydrogen consumption, sulfur content of product, hydrogen consumption for desulfurization, hydrogen consumption for denitrification, consumption for dissolved hydrogen and hydrogen consumption for light hydrocarbon generation, respectively)
| 周期 | T/K | P/bar | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | |
| 1月 | 644.6 | 656.8 | 520.7 | 65.0 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 3月 | 641.7 | 665.0 | 530.0 | 65.0 | 70.8 | 27.6 |
| 5月 | 660.0 | 636.5 | 511.3 | 65.5 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 7月 | 660.0 | 644.1 | 516.8 | 66.0 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 9月 | 616.0 | 665.0 | 519.0 | 65.0 | 71.2 | 25.9 |
| 11月 | 660.0 | 665.0 | 530.8 | 65.6 | 71.8 | 25.2 |
Table 6 Optimal operation conditions of hydrotreating units
| 周期 | T/K | P/bar | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT | |
| 1月 | 644.6 | 656.8 | 520.7 | 65.0 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 3月 | 641.7 | 665.0 | 530.0 | 65.0 | 70.8 | 27.6 |
| 5月 | 660.0 | 636.5 | 511.3 | 65.5 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 7月 | 660.0 | 644.1 | 516.8 | 66.0 | 68.0 | 25.0 |
| 9月 | 616.0 | 665.0 | 519.0 | 65.0 | 71.2 | 25.9 |
| 11月 | 660.0 | 665.0 | 530.8 | 65.6 | 71.8 | 25.2 |
| 周期 | 加氢精制装置氢耗/(kmol/h) | 总变化/ (kmol/h) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT-1 | ||||||||
| 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | ||
| 1月 | 855 | 818 | -4.28 | 1063 | 1047 | -1.54 | 385 | 235 | -39.00 | -203 |
| 3月 | 978 | 949 | -3.04 | 1022 | 1071 | 4.80 | 194 | 167 | -14.03 | -8 |
| 5月 | 623 | 591 | -5.17 | 1173 | 1124 | -4.14 | 488 | 370 | -24.06 | -198 |
| 7月 | 749 | 737 | -1.52 | 1204 | 1171 | -2.75 | 578 | 457 | -20.89 | -165 |
| 9月 | 1024 | 981 | -4.25 | 845 | 901 | 6.74 | 224 | 131 | -41.37 | -79 |
| 11月 | 787 | 770 | -2.20 | 994 | 1060 | 6.73 | 297 | 122 | -58.83 | -125 |
Table 7 Hydrogen consumption before and after optimizing operating conditions of hydrotreating units
| 周期 | 加氢精制装置氢耗/(kmol/h) | 总变化/ (kmol/h) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHT-1 | DHT-2 | GHT-1 | ||||||||
| 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | ||
| 1月 | 855 | 818 | -4.28 | 1063 | 1047 | -1.54 | 385 | 235 | -39.00 | -203 |
| 3月 | 978 | 949 | -3.04 | 1022 | 1071 | 4.80 | 194 | 167 | -14.03 | -8 |
| 5月 | 623 | 591 | -5.17 | 1173 | 1124 | -4.14 | 488 | 370 | -24.06 | -198 |
| 7月 | 749 | 737 | -1.52 | 1204 | 1171 | -2.75 | 578 | 457 | -20.89 | -165 |
| 9月 | 1024 | 981 | -4.25 | 845 | 901 | 6.74 | 224 | 131 | -41.37 | -79 |
| 11月 | 787 | 770 | -2.20 | 994 | 1060 | 6.73 | 297 | 122 | -58.83 | -125 |
| 周期 | 氢气消耗/(kmol/h) | 成本/CNY | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氢气成本 | 脱硫成本 | 电力成本 | 燃烧收益 | 运营成本 | ||
| 1月 | 2329 | 4.14×107 | 6.17×106 | 3.54×106 | 1.01×106 | 5.02×107 |
| 3月 | 2812 | 5.86×107 | 8.47×106 | 4.27×106 | 1.42×106 | 7.01×107 |
| 5月 | 2474 | 4.66×107 | 6.39×106 | 4.30×106 | 8.81×105 | 5.66×107 |
| 7月 | 2768 | 5.70×107 | 8.23×106 | 4.18×106 | 1.45×106 | 6.82×107 |
| 9月 | 2289 | 4.00×107 | 6.17×106 | 4.58×106 | 7.69×105 | 5.02×107 |
| 11月 | 2399 | 4.39×107 | 9.05×106 | 4.44×106 | 1.11×106 | 5.65×107 |
| 总计 | — | 2.88×108 | 4.45×107 | 2.52×107 | 6.64×106 | 3.52×108 |
Table 8 Hydrogen consumption and costs for each time period
| 周期 | 氢气消耗/(kmol/h) | 成本/CNY | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氢气成本 | 脱硫成本 | 电力成本 | 燃烧收益 | 运营成本 | ||
| 1月 | 2329 | 4.14×107 | 6.17×106 | 3.54×106 | 1.01×106 | 5.02×107 |
| 3月 | 2812 | 5.86×107 | 8.47×106 | 4.27×106 | 1.42×106 | 7.01×107 |
| 5月 | 2474 | 4.66×107 | 6.39×106 | 4.30×106 | 8.81×105 | 5.66×107 |
| 7月 | 2768 | 5.70×107 | 8.23×106 | 4.18×106 | 1.45×106 | 6.82×107 |
| 9月 | 2289 | 4.00×107 | 6.17×106 | 4.58×106 | 7.69×105 | 5.02×107 |
| 11月 | 2399 | 4.39×107 | 9.05×106 | 4.44×106 | 1.11×106 | 5.65×107 |
| 总计 | — | 2.88×108 | 4.45×107 | 2.52×107 | 6.64×106 | 3.52×108 |
| 周期 | 新鲜氢气消耗/(kmol/h) | 运营成本/CNY | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | |
| 1月 | 2531 | 2329 | -7.98 | 5.71×107 | 5.02×107 | -12.14 |
| 3月 | 2825 | 2812 | -0.46 | 7.06×107 | 7.01×107 | -0.80 |
| 5月 | 2670 | 2474 | -7.34 | 6.32×107 | 5.66×107 | -10.54 |
| 7月 | 2868 | 2768 | -3.49 | 7.14×107 | 6.82×107 | -4.55 |
| 9月 | 2370 | 2289 | -3.42 | 5.29×107 | 5.02×107 | -5.17 |
| 11月 | 2526 | 2399 | -5.03 | 6.10×107 | 5.65×107 | -7.40 |
| 总计 | — | — | — | 3.76×108 | 3.52×108 | -6.55 |
Table 9 Comparison of hydrogen consumption and total cost before and after optimization
| 周期 | 新鲜氢气消耗/(kmol/h) | 运营成本/CNY | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | 优化前 | 优化后 | 变动/% | |
| 1月 | 2531 | 2329 | -7.98 | 5.71×107 | 5.02×107 | -12.14 |
| 3月 | 2825 | 2812 | -0.46 | 7.06×107 | 7.01×107 | -0.80 |
| 5月 | 2670 | 2474 | -7.34 | 6.32×107 | 5.66×107 | -10.54 |
| 7月 | 2868 | 2768 | -3.49 | 7.14×107 | 6.82×107 | -4.55 |
| 9月 | 2370 | 2289 | -3.42 | 5.29×107 | 5.02×107 | -5.17 |
| 11月 | 2526 | 2399 | -5.03 | 6.10×107 | 5.65×107 | -7.40 |
| 总计 | — | — | — | 3.76×108 | 3.52×108 | -6.55 |
| 模型 | 成本/CNY | 与原氢气网络 成本对比/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氢气成本 | 脱硫成本 | 电力成本 | 燃烧收益 | 总成本 | ||
| 原氢气网络模型 | 4.81×108 | — | 2.38×107 | 3.81×107 | 4.68×108 | — |
| 集成氢气网络模型 | 3.13×108 | 4.47×107 | 2.57×107 | 6.02×106 | 3.76×108 | -19.53 |
| 优化加氢精制装置操作参数 | 2.88×108 | 4.45×107 | 2.52×107 | 6.64×106 | 3.52×108 | -24.82 |
Table 10 Comparison of annual operational costs for each model
| 模型 | 成本/CNY | 与原氢气网络 成本对比/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氢气成本 | 脱硫成本 | 电力成本 | 燃烧收益 | 总成本 | ||
| 原氢气网络模型 | 4.81×108 | — | 2.38×107 | 3.81×107 | 4.68×108 | — |
| 集成氢气网络模型 | 3.13×108 | 4.47×107 | 2.57×107 | 6.02×106 | 3.76×108 | -19.53 |
| 优化加氢精制装置操作参数 | 2.88×108 | 4.45×107 | 2.52×107 | 6.64×106 | 3.52×108 | -24.82 |
| 1 | De La Paz-Zavala C, Burgos-Vázquez E, Rodríguez-Rodríguez J E, et al. Ultra low sulfur diesel simulation. Application to commercial units[J]. Fuel, 2013, 110: 227-234. |
| 2 | Wu L, Liu Y Z, Zhang Q D. Operational optimization of a hydrotreating system based on removal of sulfur compounds in hydrotreaters coupled with a fluid catalytic cracker[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(9): 9850-9862. |
| 3 | 石宝明, 廖健, 白雪松. 炼厂氢气的管理[J]. 化工技术经济, 2003, 21(1): 55-59. |
| Shi B M, Liao J, Bai X S. Hydrogen management in refinery[J]. Chemical Techno Economics, 2003, 21(1): 55-59. | |
| 4 | Towler G P, Mann R, Serriere A J L, et al. Refinery hydrogen management: cost analysis of chemically-integrated facilities[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1996, 35(7): 2378-2388. |
| 5 | Alves J J, Towler G P. Analysis of refinery hydrogen distribution systems[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(23): 5759-5769. |
| 6 | Zhang Q, Feng X, Liu G L, et al. A novel graphical method for the integration of hydrogen distribution systems with purification reuse[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(4): 797-809. |
| 7 | Hallale N, Liu F. Refinery hydrogen management for clean fuels production[J]. Advances in Environmental Research, 2001, 6(1): 81-98. |
| 8 | Liu F, Zhang N. Strategy of purifier selection and integration in hydrogen networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2004, 82(10): 1315-1330. |
| 9 | Peramanu S. Economics of hydrogen recovery processes for the purification of hydroprocessor purge and off-gases[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1999, 24(5): 405-424. |
| 10 | 梁肖强, 刘永忠, 张亮. 集中式提纯器的设置与具有中间等级氢气网络的优化[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(3): 577-582. |
| Liang X Q, Liu Y Z, Zhang L. Installation of a centralized purifier and optimization of hydrogen network with intermediate levels[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(3): 577-582. | |
| 11 | Liao Z W, Wang J D, Yang Y R, et al. Integrating purifiers in refinery hydrogen networks: a retrofit case study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2010, 18(3): 233-241. |
| 12 | Zhang Q, Liu G L, Feng X, et al. Hydrogen networks synthesis considering separation performance of purifiers[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(16): 8357-8373. |
| 13 | 杨敏博, 冯霄. 提纯回用氢网络的夹点变化规律[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(12): 4544-4549. |
| Yang M B, Feng X. Change rules of pinch point for hydrogen distribution systems with purification reuse[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(12): 4544-4549. | |
| 14 | Lou J Y, Liao Z W, Jiang B B, et al. Pinch sliding approach for targeting hydrogen and water networks with different types of purifier[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(25): 8538-8549. |
| 15 | Liao Z W, Tu G N, Lou J Y, et al. The influence of purifier models on hydrogen network optimization: insights from a case study[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(10): 5243-5249. |
| 16 | Liao Z W, Rong G, Wang J D, et al. Rigorous algorithmic targeting methods for hydrogen networks(part Ⅱ): Systems with one hydrogen purification unit[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(5): 821-833. |
| 17 | 李开宇, 刘桂莲. 储氢提纯和氢网络的耦合优化[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1143-1153. |
| Li K Y, Liu G L. Coupling optimization of hydrogen-storage based purification and hydrogen network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1143-1153. | |
| 18 | Zhang Q, Yang M B, Liu G L, et al. Relative concentration based pinch analysis for targeting and design of hydrogen and water networks with single contaminant[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112: 4799-4814. |
| 19 | Kumar A, Gautami G, Khanam S. Hydrogen distribution in the refinery using mathematical modeling[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(9): 3763-3772. |
| 20 | Fonseca A, Sá V, Bento H, et al. Hydrogen distribution network optimization: a refinery case study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2008, 16(16): 1755-1763. |
| 21 | Lou Y Q, Liao Z W, Sun J Y, et al. A novel two-step method to design inter-plant hydrogen network[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(12): 5686-5695. |
| 22 | Singh B B, Zhang N. Impact of gas phase impurities on refinery hydrogen network management[R]. New York: American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2005. |
| 23 | Jia N, Zhang N. Multi-component optimisation for refinery hydrogen networks[J]. Energy, 2011, 36(8): 4663-4670. |
| 24 | Zhou L, Liao Z W, Wang J D, et al. Hydrogen sulfide removal process embedded optimization of hydrogen network[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(23): 18163-18174. |
| 25 | Wu L, Liang X Q, Kang L X, et al. Integration strategies of hydrogen network in a refinery based on operational optimization of hydrotreating units[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 25(8): 1061-1068. |
| 26 | Mao J B, Liu G L, Wang Y J, et al. Integration of a hydrogen network with the vacuum gas oil hydrocracking reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2015, 45: 85-90. |
| 27 | Umana B, Shoaib A, Zhang N, et al. Integrating hydroprocessors in refinery hydrogen network optimisation[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 133: 169-182. |
| 28 | Umana B, Zhang N, Smith R. Development of vacuum residue hydrodesulphurization-hydrocracking models and their integration with refinery hydrogen networks[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(8): 2391-2406. |
| 29 | Rodriguez P A A. Modeling of hydrogen consumption and process optimization for hydrotreating of light gas oils[D]. Saskatchewan: University of Saskatchewan, 2017. |
| 30 | Choudhary T V, Parrott S, Johnson B. Unraveling heavy oil desulfurization chemistry: targeting clean fuels[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(6): 1944-1947. |
| 31 | 李大东, 聂红, 孙丽丽. 加氢处理工艺与工程[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2016. |
| Li D D, Nie H, Sun L L. Hydrogenation Process and Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2016. | |
| 32 | Cotta R M, Wolf-Maciel M R, Filho R M. A cape of HDT industrial reactor for middle distillates[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2000, 24(2/3/4/5/6/7): 1731-1735. |
| 33 | Hasenberg D M, Campagnolo Jr J F. Modeling and simulation of a reaction for hydrotreating hydrocarbon oil: US5841678[P]. 1998-11-24. |
| 34 | McCarl B A, Meeraus A, Eijk P V D, et al. McCarl GAMS user guide[Z]. GAMS Development Corporation, 2014. |
| [1] | Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Laiming LUO, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Design and performance of 5 kW reforming methanol high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1697-1704. |
| [2] | Yansong CHEN, Da RUAN, Yuanbo LIU, Tong ZHENG, Shuaishuai ZHANG, Xuehu MA. Topology optimization and performance research of microchannel heat exchangers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 823-835. |
| [3] | Wenjun LI, Zhongyang ZHAO, Zhen NI, Can ZHOU, Chenghang ZHENG, Xiang GAO. CFD numerical simulation of wet flue gas desulfurization:performance improvement based on gas-liquid mass transfer enhancement [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 505-519. |
| [4] | Liuyang YU, Shubo LIU, Shengzhe JIA, Hang MA, Banglong WAN, Qiwen SU, Jingkang WANG, Weiwei TANG, Yujuan HE, Junbo GONG. Current status and research progress of purification technology of electronic grade phosphoric acid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 1-19. |
| [5] | Yang YU, Yiqing LUO, Ronghui WEI, Wenhui ZHANG, Xigang YUAN. A resilient supply chain design method considering node disruption risk [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 338-353. |
| [6] | Zhewen CHEN, Junjie WEI, Yuming ZHANG. System integration and energy conversion mechanism of the power technology with integrated supercritical water gasification of coal and SOFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [7] | Yue CAO, Chong YU, Zhi LI, Minglei YANG. Industrial data driven transition state detection with multi-mode switching of a hydrocracking unit [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3841-3854. |
| [8] | Cong QI, Zi DING, Jie YU, Maoqing TANG, Lin LIANG. Study on solar thermoelectric power generation characteristics based on selective absorption nanofilm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [9] | Yuyuan ZHENG, Zhiwei GE, Xiangyu HAN, Liang WANG, Haisheng CHEN. Progress and prospect of medium and high temperature thermochemical energy storage of calcium-based materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [10] | Zhaolun WEN, Peirui LI, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiao DU, Qiwang HOU, Yegang LIU, Xiaogang HAO, Guoqing GUAN. Design and optimization of cryogenic air separation process with dividing wall column based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [11] | Guixian LI, Abo CAO, Wenliang MENG, Dongliang WANG, Yong YANG, Huairong ZHOU. Process design and evaluation of CO2 to methanol coupled with SOEC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2999-3009. |
| [12] | Jinbo JIANG, Xin PENG, Wenxuan XU, Rixiu MEN, Chang LIU, Xudong PENG. Study on leakage characteristics and parameter influence of pump-out spiral groove oil-gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2538-2554. |
| [13] | Yuanzhe SHAO, Zhonggai ZHAO, Fei LIU. Quality-related non-stationary process fault detection method by common trends model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2522-2537. |
| [14] | Shanghao LIU, Shengkun JIA, Yiqing LUO, Xigang YUAN. Optimization of ternary-distillation sequence based on gradient boosting decision tree [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2075-2087. |
| [15] | Bimao ZHOU, Shisen XU, Xiaoxiao WANG, Gang LIU, Xiaoyu LI, Yongqiang REN, Houzhang TAN. Effect of burner bias angle on distribution characteristics of gasifier slag layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1939-1949. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||