CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6729-6738.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250366
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu CAO1,2( ), Xinyu DU1,2, Ang GAO1,2, Kang LIANG1,2, Yongmao CAI3(
), Xinyu DU1,2, Ang GAO1,2, Kang LIANG1,2, Yongmao CAI3( ), Jinbo PANG4, Jing ZHOU1,5(
), Jinbo PANG4, Jing ZHOU1,5( )
)
Received:2025-04-09
Revised:2025-05-04
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2025-12-31
Contact:
Yongmao CAI, Jing ZHOU
曹宇1,2( ), 杜心宇1,2, 高昂1,2, 梁康1,2, 蔡永茂3(
), 杜心宇1,2, 高昂1,2, 梁康1,2, 蔡永茂3( ), 逄金波4, 周静1,5(
), 逄金波4, 周静1,5( )
)
通讯作者:
蔡永茂,周静
作者简介:曹宇(1986—),男,博士,教授,ycao@neepu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yu CAO, Xinyu DU, Ang GAO, Kang LIANG, Yongmao CAI, Jinbo PANG, Jing ZHOU. Enhanced sodium-ion multilayer adsorption performance of sulfur-functionalized M2N-type Mxene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6729-6738.
曹宇, 杜心宇, 高昂, 梁康, 蔡永茂, 逄金波, 周静. 硫功能化M2N型MXene的钠离子多层吸附性能增强机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6729-6738.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 晶体 | 晶格常数/Å | 键长/Å | 厚度/Å | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M—N | M—S | |||
| Sc2N | 3.15 | 2.20 | — | 2.47 |
| Sc2NS2 | 3.30 | 2.28 | 2.52 | 5.87 |
| Ti2N | 2.96 | 2.06 | — | 2.31 |
| Ti2NS2 | 3.16 | 2.16 | 2.39 | 5.43 |
| V2N | 2.89 | 1.96 | — | 2.09 |
| V2NS2 | 3.05 | 2.04 | 2.36 | 5.25 |
| Zr2N | 3.22 | 2.24 | — | 2.51 |
| Zr2NS2 | 3.42 | 2.36 | 2.53 | 5.73 |
| Nb2N | 3.12 | 2.12 | — | 2.26 |
| Nb2NS2 | 3.28 | 2.21 | 2.48 | 5.50 |
Table 1 Specific parameters of the crystal structures of M2N and M2NS2
| 晶体 | 晶格常数/Å | 键长/Å | 厚度/Å | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M—N | M—S | |||
| Sc2N | 3.15 | 2.20 | — | 2.47 |
| Sc2NS2 | 3.30 | 2.28 | 2.52 | 5.87 |
| Ti2N | 2.96 | 2.06 | — | 2.31 |
| Ti2NS2 | 3.16 | 2.16 | 2.39 | 5.43 |
| V2N | 2.89 | 1.96 | — | 2.09 |
| V2NS2 | 3.05 | 2.04 | 2.36 | 5.25 |
| Zr2N | 3.22 | 2.24 | — | 2.51 |
| Zr2NS2 | 3.42 | 2.36 | 2.53 | 5.73 |
| Nb2N | 3.12 | 2.12 | — | 2.26 |
| Nb2NS2 | 3.28 | 2.21 | 2.48 | 5.50 |
| 项目 | 未功能化MXene | 硫功能化MXene | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sc2N | Ti2N | V2N | Zr2N | Nb2N | Sc2NS2 | Ti2NS2 | V2NS2 | Zr2NS2 | Nb2NS2 | |
| 第一层平均吸附能/eV | -0.38 | -0.41 | -0.35 | -0.51 | -0.49 | -1.26 | -0.60 | -0.08 | -0.78 | -0.20 |
| 第二层平均吸附能/eV | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.07 | -0.07 | -0.01 | 0.14 | -0.12 | 0.001 |
| 第三层平均吸附能/eV | — | — | — | — | — | -0.02 | 0.14 | — | -0.05 | — |
| 迁移路径 | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | M1-M1 | N-N | M1-M1 |
| 迁移能垒/eV | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.044 | 0.168 | 0.142 | 0.114 | 0.165 | 0.099 |
Table 2 Average adsorption energy and migration paths of MXene, as well as the corresponding migration energy barriers
| 项目 | 未功能化MXene | 硫功能化MXene | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sc2N | Ti2N | V2N | Zr2N | Nb2N | Sc2NS2 | Ti2NS2 | V2NS2 | Zr2NS2 | Nb2NS2 | |
| 第一层平均吸附能/eV | -0.38 | -0.41 | -0.35 | -0.51 | -0.49 | -1.26 | -0.60 | -0.08 | -0.78 | -0.20 |
| 第二层平均吸附能/eV | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.07 | -0.07 | -0.01 | 0.14 | -0.12 | 0.001 |
| 第三层平均吸附能/eV | — | — | — | — | — | -0.02 | 0.14 | — | -0.05 | — |
| 迁移路径 | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | N-N | M1-M1 | N-N | M1-M1 |
| 迁移能垒/eV | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.044 | 0.168 | 0.142 | 0.114 | 0.165 | 0.099 |
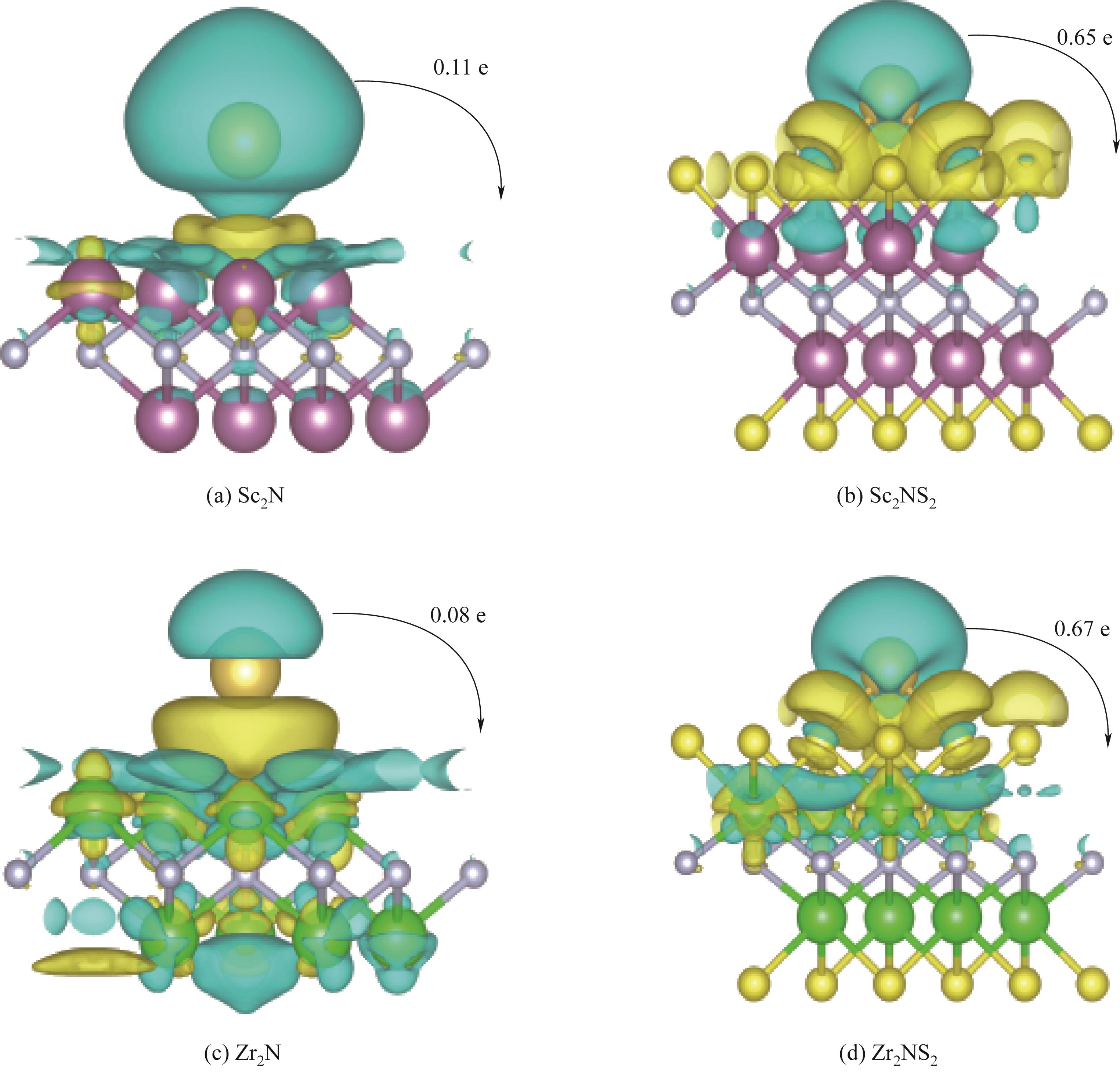
Fig.2 Differential charge density diagrams (The isosurface energy level is set to 0.0010 e/Bohr3, yellow and light blue respectively represent the accumulation and consumption of charges)
| [1] | Tian Y, An Y L, Feng J K, et al. MXenes and their derivatives for advanced aqueous rechargeable batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 52: 225-249. |
| [2] | Bommier C, Ji X L, Greaney P A. Electrochemical properties and theoretical capacity for sodium storage in hard carbon: insights from first principles calculations[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(3): 658-677. |
| [3] | Dunn B, Kamath H, Tarascon J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| [4] | Rojo T, Hu Y S, Forsyth M, et al. Sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(17): 1800880. |
| [5] | An Y L, Tian Y, Wei C L, et al. Dealloying: an effective method for scalable fabrication of 0D, 1D, 2D, 3D materials and its application in energy storage[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 37: 101094. |
| [6] | Zhang X Q, Dong M F, Xiong Y L, et al. Aqueous rechargeable Li+/Na+ hybrid ion battery with high energy density and long cycle life[J]. Small, 2020, 16(41): 2003585. |
| [7] | Kim H, Kim J C, Bianchini M, et al. Recent progress and perspective in electrode materials for K-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(9): 1702384. |
| [8] | Sunkari D, Deshmukh K, Panda S, et al. Recent progress in MXene-based materials for lithium-ion and lithium-sulphur batteries: a comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 92: 112017. |
| [9] | Huang Z F, Farahmandjou M, Marlton F, et al. Surface and structure engineering of MXenes for rechargeable batteries beyond lithium[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2024, 10(1): 253-268. |
| [10] | Siriwardane E M D, Demiroglu I, Sevik C, et al. Assessment of sulfur-functionalized MXenes for Li-ion battery applications[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(39): 21293-21304. |
| [11] | Huang Y, Lu Q Q, Wu D L, et al. Flexible MXene films for batteries and beyond[J]. Carbon Energy, 2022, 4(4): 598-620. |
| [12] | Zhang Y S, Lu Q B, Zhang L S, et al. Adjustable MXene-based materials in metal-ion batteries: progress, prospects, and challenges[J]. Small Structures, 2024, 5(1): 2300255. |
| [13] | 曹宇, 张国辉, 高昂, 等. 二维MXene材料在太阳能电池和金属离子电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 412-428. |
| Cao Y, Zhang G H, Gao A, et al. Research progress of two-dimensional MXene materials in solar cells and metal-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 412-428. | |
| [14] | 曹宇, 张国辉, 王长刚, 等. 二维六方Mo2B2作为金属离子电池负极材料的第一性原理研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2024, 52(7): 2232-2242. |
| Cao Y, Zhang G H, Wang C G, et al. First principles study of two-dimensional h-Mo2B2 as a negative electrode for metal-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2024, 52(7): 2232-2242. | |
| [15] | Shahzad U, Marwani P H M, Saeed M, et al. Two-dimensional MXenes as emerging materials: a comprehensive review[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2023, 8(25): e202300737. |
| [16] | Yang K, Liu Y X, Zhao F, et al. Multifunction of MXene in lithium-sulfur batteries: a review[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2024, 38(15): 13837-13857. |
| [17] | Shi J K, Du M, Chen Y H, et al. MXene functionalized cathodes, anodes, and separators for batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 507: 160809. |
| [18] | Li M, Lu J, Luo K, et al. Element replacement approach by reaction with lewis acidic molten salts to synthesize nanolaminated MAX phases and MXenes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(11): 4730-4737. |
| [19] | Huang P F, Han W Q. Recent advances and perspectives of lewis acidic etching route: an emerging preparation strategy for MXenes[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 68. |
| [20] | Er D Q, Li J W, Naguib M, et al. Ti₃C₂ MXene as a high capacity electrode material for metal (Li, Na, K, Ca) ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(14): 11173-11179. |
| [21] | ÇakIr D, Sevik C, Gülseren O, et al. Mo2C as a high capacity anode material: a first-principles study[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(16): 6029-6035. |
| [22] | Zhang L L, Chen Y G, Yu L H, et al. Efficient sulfur atom-doped three-dimensional porous MXene-assisted sodium ion batteries[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2024, 53(15): 6583-6591. |
| [23] | Luo H X, Long P, Xiao J R, et al. Mo2CS2 MXene as a promising anode material for metal ion batteries: a first-principles study[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2024, 38: 108285. |
| [24] | Meng Q Q, Ma J L, Zhang Y H, et al. The S-functionalized Ti3C2 Mxene as a high capacity electrode material for Na-ion batteries: a DFT study[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(7): 3385-3392. |
| [25] | Yan T X, Xiao M X, Song H Y, et al. S- and Cl-functionalized Nb2C MXenes as novel anode materials for sodium-ion batteries: a first-principles study[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 47(13): 6412-6419. |
| [26] | Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186. |
| [27] | Blöchl P E. Projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(24): 17953-17979. |
| [28] | Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868. |
| [29] | Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15): 154104. |
| [30] | Grimme S, Ehrlich S, Goerigk L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32(7): 1456-1465. |
| [31] | Togo A, Tanaka I. First principles phonon calculations in materials science[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 108: 1-5. |
| [32] | Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jónsson H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2006, 36(3): 354-360. |
| [33] | Henkelman G, Uberuaga B P, Jónsson H. A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2000, 113(22): 9901-9904. |
| [34] | Mohammadi M, Noori B. Simulation of Ti2N and S/Se-functionalized Ti2N electrode in ion-batteries[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2023, 668: 415239. |
| [35] | Liu H L, Cai Y M, Guo Z D, et al. Two-dimensional V2N MXene monolayer as a high-capacity anode material for lithium-ion batteries and beyond: first-principles calculations[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(21): 17756-17764. |
| [36] | Lu X F, Qi J P, Ren J Q, et al. First-principles study of the effect of O and S functional groups on the lithium storage properties of Zr2N materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(6): 2227-2240. |
| [37] | Yin X P, Lu Z X, Wang J, et al. Enabling fast Na+ transfer kinetics in the whole-voltage-region of hard-carbon anodes for ultrahigh-rate sodium storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(13): 2109282. |
| [38] | Massaro A, Muñoz-García A B, Maddalena P, et al. First-principles study of Na insertion at TiO2 anatase surfaces: new hints for Na-ion battery design[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2020, 2(7): 2745-2751. |
| [39] | Masood M K, Liu K, Wang J, et al. Theoretical prediction of stable WB4 monolayer as a high-capacity anode material for alkali-metal ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2024, 186: 111814. |
| [40] | Muhammad I, Wang S, Liu J Y, et al. Boron-graphdiyne as an anode material for Li, Na, and K ion batteries with high capacities and low diffusion barriers[J].Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2019, 11(1): 014106. |
| [1] | Xin WU, Jianying GONG, Xiangyu LI, Yutao WANG, Xiaolong YANG, Zhen JIANG. Experimental study on the droplet motion on the hydrophobic surface under ultrasonic excitation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [2] | Ziqing ZANG, Xiuzhen LI, Yingying TAN, Xiaoqing LIU. Investigation on effect of fractionation on performance of two-stage separation-based auto-cascade refrigeration cycle [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [3] | Zixiang ZHAO, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Hongxiang XUE. Numerical modelling of water hammer induced by two phase flow with large temperature difference [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [4] | Hao HUANG, Wen WANG, Longkun HE. Simulation and analysis on precooling process of membrane LNG carriers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [5] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [6] | Qingtai CAO, Songyuan GUO, Jianqiang LI, Zan JIANG, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Jingyi WU, Guang YANG. Numerical study on influence of perforated plate on retention performance of liquid oxygen tank under negative gravity [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [7] | Jiuchun SUN, Yunlong SANG, Haitao WANG, Hao JIA, Yan ZHU. Study on influence of jet flow on slurry transport characteristics in slurry chamber of shield tunneling machines [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [8] | Yifan SHI, Gang KE, Hao CHEN, Xiaosheng HUANG, Fang YE, Chengjiao LI, Hang GUO. Simulation of temperature control in large-scale high and low temperature environmental laboratory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [9] | Ting HE, Shuyang HUANG, Kun HUANG, Liqiong CHEN. Research on the coupled process of natural gas chemical absorption decarbonization and high temperature heat pump based on waste heat utilization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [10] | Aihua MA, Shuai ZHAO, Lin WANG, Minghui CHANG. Research on dynamic simulation methods for solar-powered absorption refrigeration cycles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [11] | Chengyun WU, Haoran SUN. Performance simulation and fuel penalty investigation of civil aircraft air conditioning systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [12] | Wei LI, Hao CHEN, Gang KE, Xiaosheng HUANG, Chengjiao LI, Hang GUO, Fang YE. Simulation of the fresh air system in the simulation platform of the high-altitude environmental adaptability laboratory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| [13] | Senqing ZHUO, Hua CHEN, Wei CHEN, Bin SHANG, Hengheng LIU, Tangtang GU, Wei BAI, Longyan WANG, Haomin CAO, Guoliang DING. Model development and software implementation for predicting APF of multi-split air conditioning system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 370-376. |
| [14] | Xin XIAO, Geng YANG, Yunfeng WANG. Simulation of solar heat pump system integration of cascade latent heat thermal energy storage based on TRNSYS [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 393-400. |
| [15] | Xiaoguang MI, Guogang SUN, Hao CHENG, Xiaohui ZHANG. Performance simulation model and validation of printed circuit natural gas cooler [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||