CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 4988-5002.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250535
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Luxuan GUO1( ), Lingzhi HUANG1(
), Lingzhi HUANG1( ), Wenchao JIA1, Lu WU1, Hongwei ZHU2, Meihong NIU1, Haiqiang SHI1(
), Wenchao JIA1, Lu WU1, Hongwei ZHU2, Meihong NIU1, Haiqiang SHI1( )
)
Received:2025-05-13
Revised:2025-07-12
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-10-25
Contact:
Lingzhi HUANG, Haiqiang SHI
郭璐轩1( ), 黄灵芝1(
), 黄灵芝1( ), 贾文超1, 吴鲁1, 朱宏伟2, 牛梅红1, 石海强1(
), 贾文超1, 吴鲁1, 朱宏伟2, 牛梅红1, 石海强1( )
)
通讯作者:
黄灵芝,石海强
作者简介:郭璐轩(2000—),女,硕士研究生,762247528@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Luxuan GUO, Lingzhi HUANG, Wenchao JIA, Lu WU, Hongwei ZHU, Meihong NIU, Haiqiang SHI. Research progress on cationic modification of plant fibers based on DES solvent systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 4988-5002.
郭璐轩, 黄灵芝, 贾文超, 吴鲁, 朱宏伟, 牛梅红, 石海强. 基于DES溶剂体系的植物纤维阳离子改性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 4988-5002.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
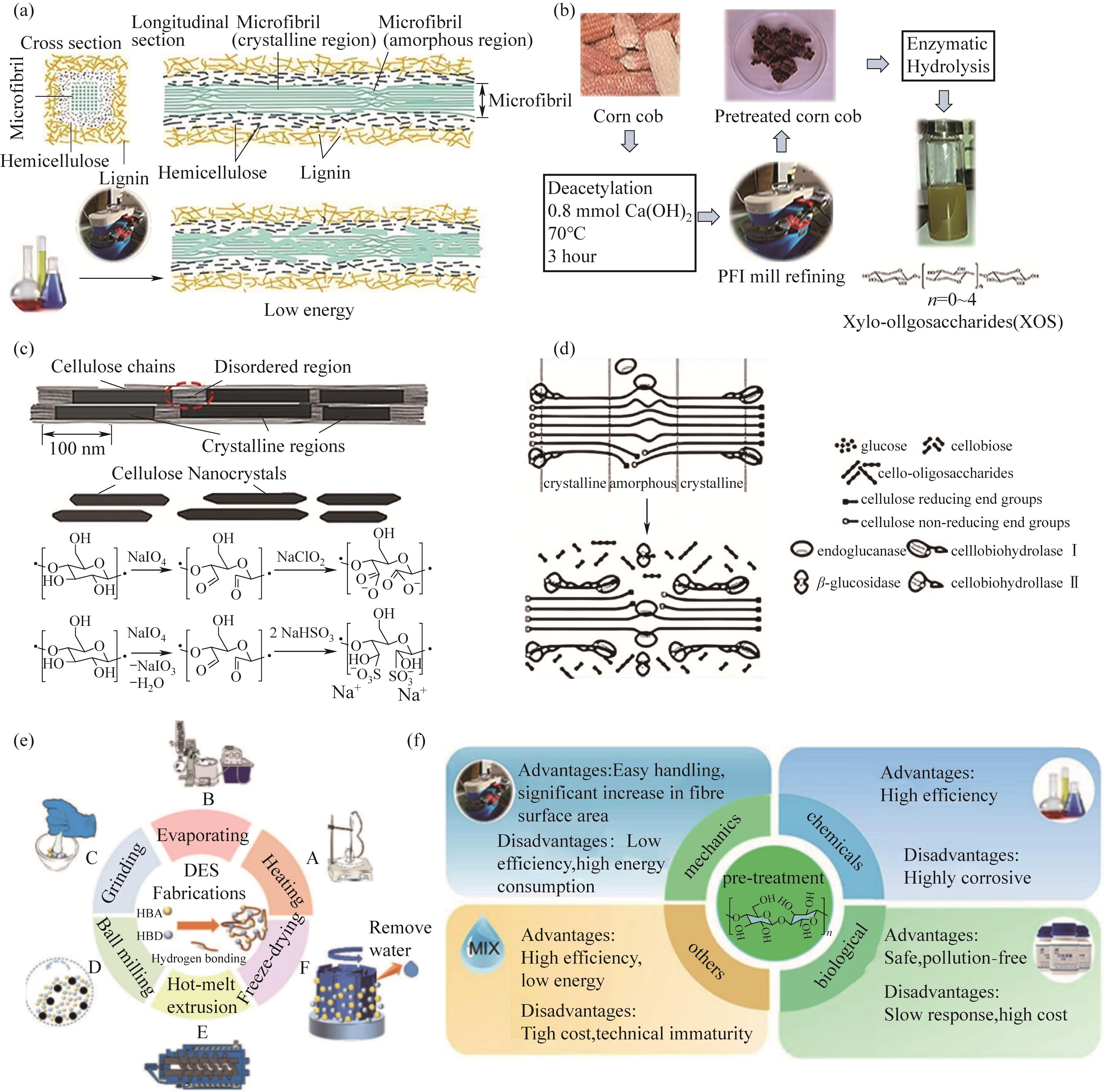
Fig.2 Plant fiber pretreatment method: (a) Pretreatment effect of plant fiber[5]; (b) PFI refining pretreatment [32]; (c) Pretreatment of acids and bases[33]; (d) Biological enzyme pretreatment[34]; (e) New pretreatment technology assists DES technology[14]; (f) Advantages and disadvantages of pretreatment technology
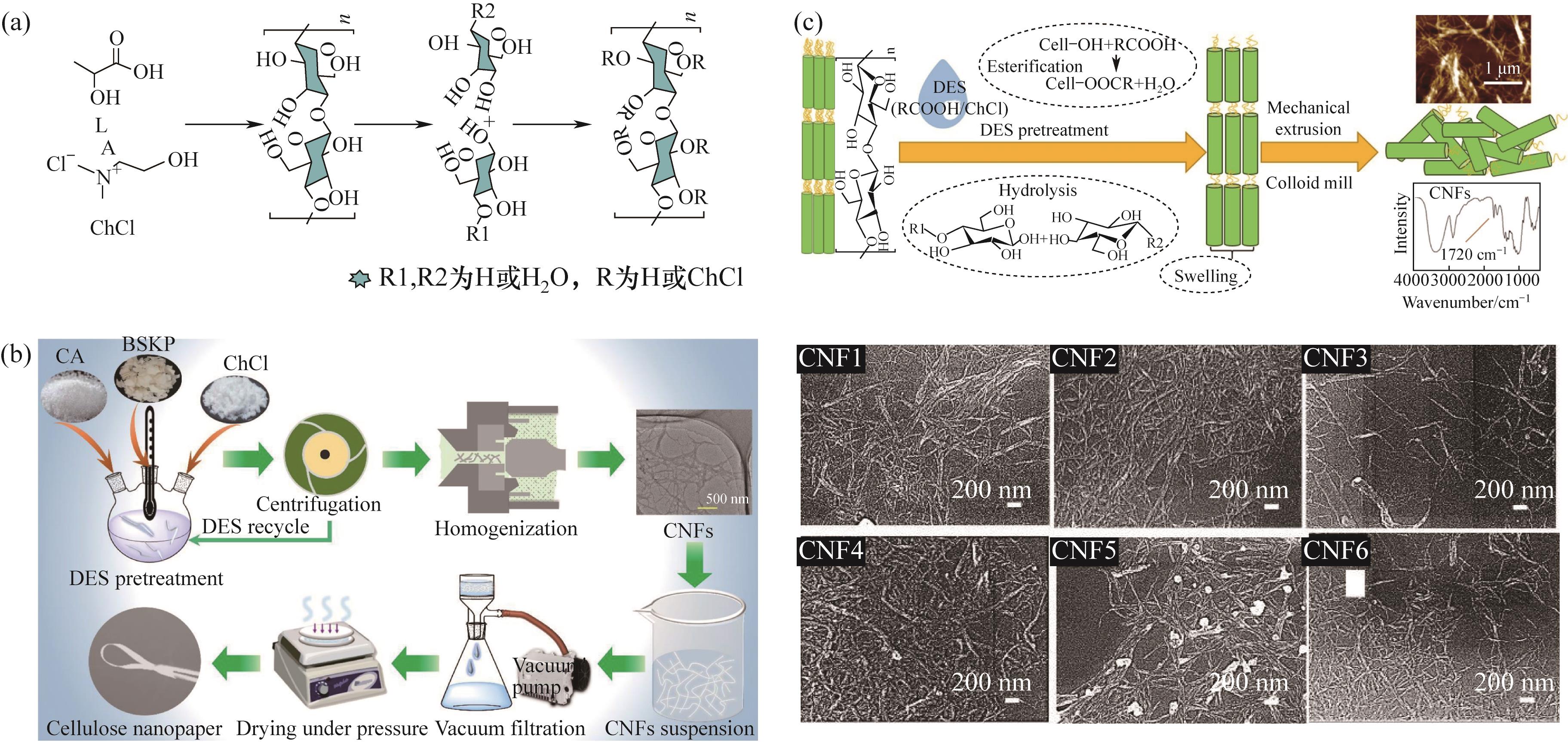
Fig.3 (a) Reaction mechanism of cationic cellulose with LA/ChCl DES; (b) Production of CNF by CA/ChCl DES combined microwave processing technology[51]; (c) Experimental process and SEM image of cellulose pretreatment with RCOOH/ChCl DES[52]
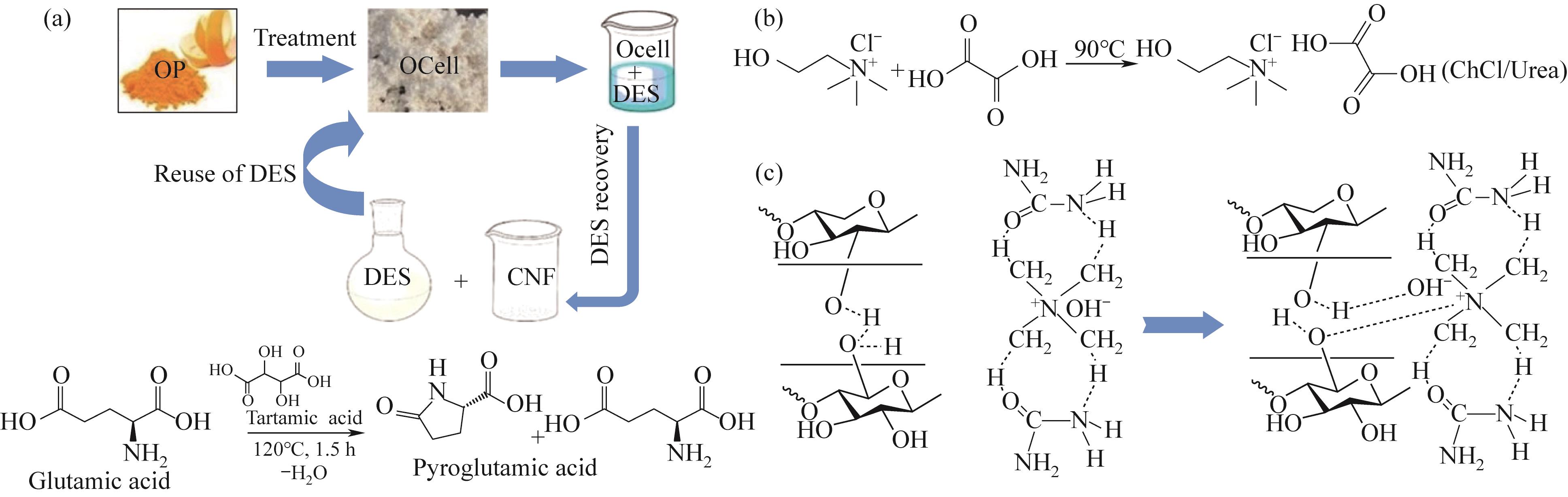
Fig.4 (a) Glu/TA DES cationized cellulose process and mechanism[56]; (b) Mechanism of action of ChCl/Urea DES cationized cellulose [60]; (c) Mechanism of action of TMAH·5H2O/Urea DES cationized cellulose[49]
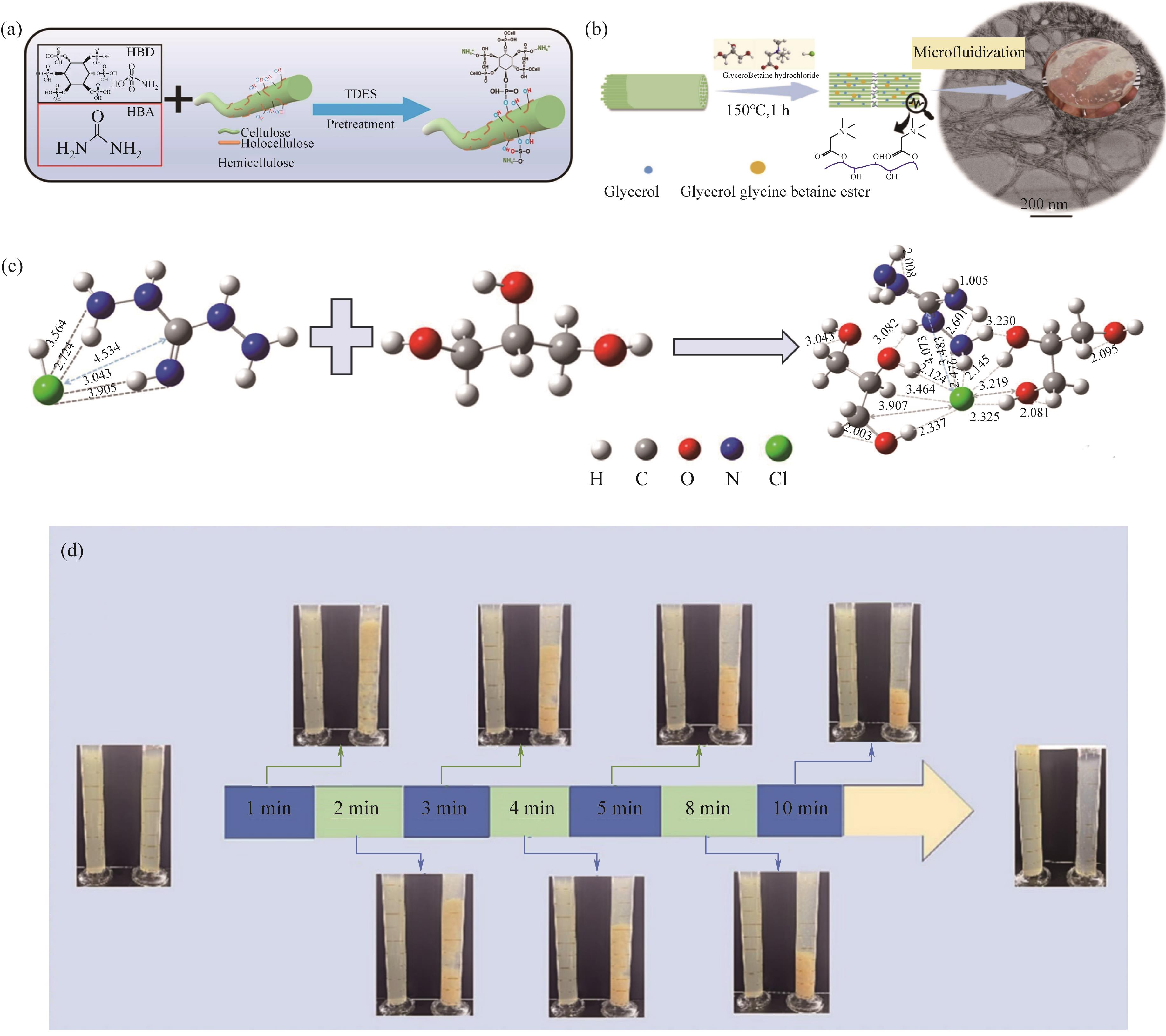
Fig.5 (a) Mechanism of TDES-modified cellulose introduced by P/N/S[61];(b) Mechanism of Bh/Gl DES cationization of cellulose[27]; (c) AhG/Gl DES interatomic distance reaction theory[62,64]; (d) C-CNC flocculation diagram at different times[64]
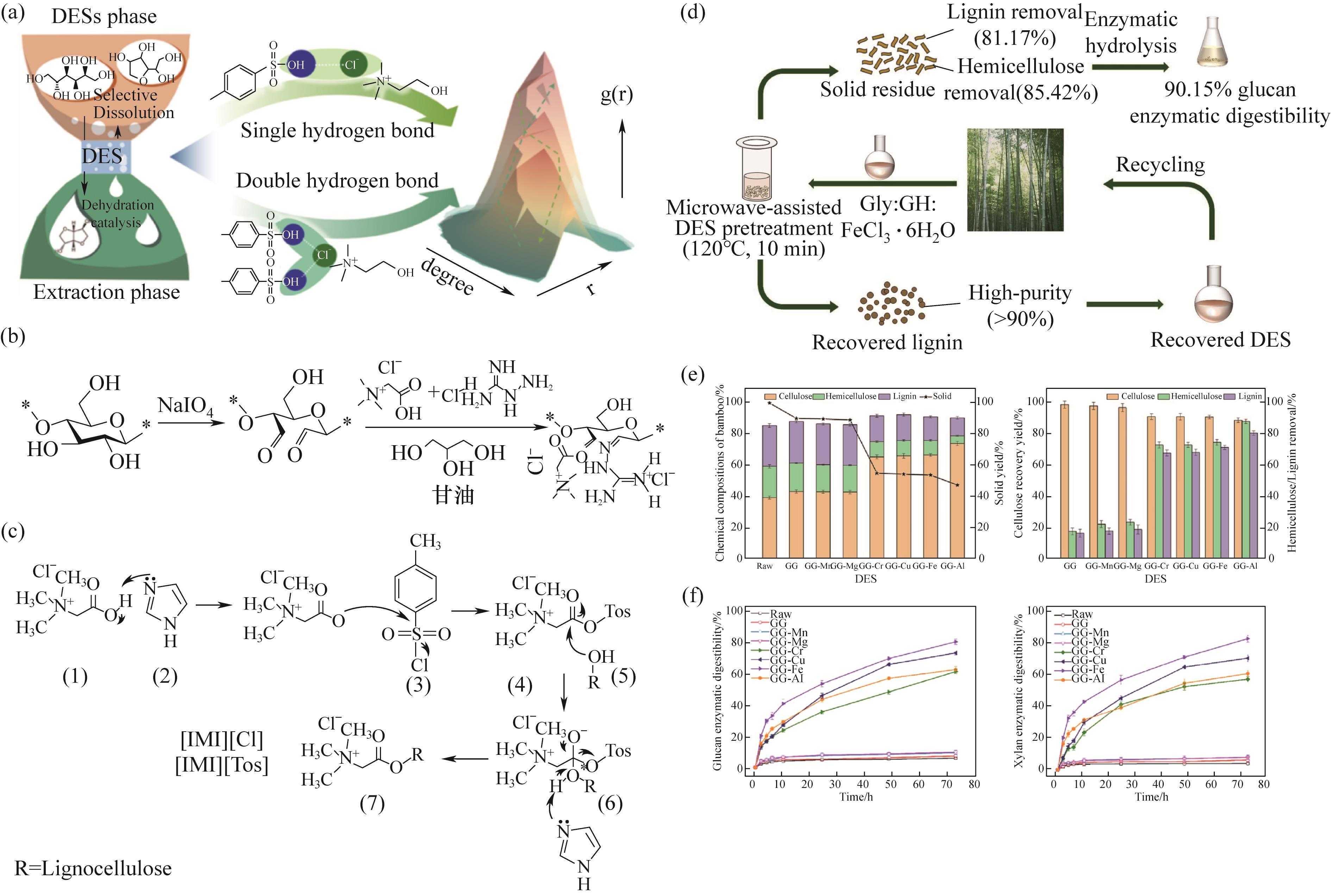
Fig.6 (a) Reaction mechanism of p-TSA/ChCl DES to sorbitol[67]; (b) NaIO4 two-step cationized cellulose[68]; (c) Mechanism of cationization of cellulose by Bh/p-TSA/TEMA DES[23]; (d) Reaction mechanism diagram of bamboo fiber treated with FeCl3/Gly/GH DES[69]; (e),(f) lignin removal rate, xylan yield and enzymatic digestibility of bamboo fiber samples[69]
| 分类 | 羧基酸-季铵盐 DES | 尿素-季铵盐 DES | 甘油-季铵盐 DES |
|---|---|---|---|
| 反应性 | 中等反应性,羧基与季铵盐的静电作用较强 | 较高反应性,尿素易与纤维羟基形成氢键 | 较低反应性,甘油需催化剂促进反应 |
| 反应机理 | 羧基与季铵盐的离子键结合,可能伴随酯化反应 | 尿素与纤维羟基缩合形成氨基甲酸酯或氢键网络 | 甘油羟基与纤维羟基醚化或形成交联结构 |
| 特点 | 耐水性较好,柔软性中等,稳定性高 | 吸湿性强,易生物降解成本低 | 亲水性佳,环保性好,反应条件温和 |
| 经济性 | 原料成本中等,需控制pH和温度 | 原料廉价,工艺简单,适合大规模生产 | 甘油来源广泛,但可能需要额外催化剂增加成本 |
Table 1 Summary of the reaction mechanism of binary DES cationic fibers
| 分类 | 羧基酸-季铵盐 DES | 尿素-季铵盐 DES | 甘油-季铵盐 DES |
|---|---|---|---|
| 反应性 | 中等反应性,羧基与季铵盐的静电作用较强 | 较高反应性,尿素易与纤维羟基形成氢键 | 较低反应性,甘油需催化剂促进反应 |
| 反应机理 | 羧基与季铵盐的离子键结合,可能伴随酯化反应 | 尿素与纤维羟基缩合形成氨基甲酸酯或氢键网络 | 甘油羟基与纤维羟基醚化或形成交联结构 |
| 特点 | 耐水性较好,柔软性中等,稳定性高 | 吸湿性强,易生物降解成本低 | 亲水性佳,环保性好,反应条件温和 |
| 经济性 | 原料成本中等,需控制pH和温度 | 原料廉价,工艺简单,适合大规模生产 | 甘油来源广泛,但可能需要额外催化剂增加成本 |
| 序号 | 原料 | DES | 辅助工艺 | 成品 | 产率/% | 应用 | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBD | HBA | 比例 | |||||||
| 1 | 漂白针叶木牛皮纸浆 | CA | ChCl | 1∶1 | 高压均质 | CNF | 84.19 | 纳米纸( CNP ) | [ |
| 2 | 小麦秸秆 | AA | ChCl | 1,2,3∶1 | NaIO4 | LCNC | — | 水凝胶 | [ |
| 3 | 橙皮 | TA | Glu | 2∶1 | 机械、 超声 | CNF | 95.8 | 抗菌 | [ |
| 4 | 玉米秸秆 | GA、EG | TMBAC | 1∶1∶2 | 热解炉 | 固体残渣 | 66.9~71.9 | 生物油 | [ |
| 5 | 木薯渣 | CA、LA | ChCl | 1∶10∶1 | 球磨 | 木质纤维素 | 82.52 | 回收利用 | [ |
| 6 | 纤维素整体柱 | Urea | ChCl | 2∶1 | 热致相分离法 | 阳离子化纤维 | — | 阴离子吸附 | [ |
| 7 | 竹纤维 | CAA、Urea | ChCl | 1∶2∶1 | 研磨 | CMCNF | 70~85 | CMCNF | [ |
| 8 | 漂白硫酸盐桦木浆 | Gly | Bh | 2∶1 | 微射流仪 | CNF | 72.5 | 纤维素薄膜 | [ |
| 9 | 相思阔叶木浆 | Gly | AGH、ChCl | 4∶1∶1 | NaIO4 | CCNF | — | CCNF | [ |
| 10 | 毛竹 | Gly | AGH、FeCl3 | 2∶1∶1 | 微波加热耦合 | 残余纤维素 | 81.17 | 组分分离 | [ |
Table 2 Summary of DES treatment of plant fibers
| 序号 | 原料 | DES | 辅助工艺 | 成品 | 产率/% | 应用 | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBD | HBA | 比例 | |||||||
| 1 | 漂白针叶木牛皮纸浆 | CA | ChCl | 1∶1 | 高压均质 | CNF | 84.19 | 纳米纸( CNP ) | [ |
| 2 | 小麦秸秆 | AA | ChCl | 1,2,3∶1 | NaIO4 | LCNC | — | 水凝胶 | [ |
| 3 | 橙皮 | TA | Glu | 2∶1 | 机械、 超声 | CNF | 95.8 | 抗菌 | [ |
| 4 | 玉米秸秆 | GA、EG | TMBAC | 1∶1∶2 | 热解炉 | 固体残渣 | 66.9~71.9 | 生物油 | [ |
| 5 | 木薯渣 | CA、LA | ChCl | 1∶10∶1 | 球磨 | 木质纤维素 | 82.52 | 回收利用 | [ |
| 6 | 纤维素整体柱 | Urea | ChCl | 2∶1 | 热致相分离法 | 阳离子化纤维 | — | 阴离子吸附 | [ |
| 7 | 竹纤维 | CAA、Urea | ChCl | 1∶2∶1 | 研磨 | CMCNF | 70~85 | CMCNF | [ |
| 8 | 漂白硫酸盐桦木浆 | Gly | Bh | 2∶1 | 微射流仪 | CNF | 72.5 | 纤维素薄膜 | [ |
| 9 | 相思阔叶木浆 | Gly | AGH、ChCl | 4∶1∶1 | NaIO4 | CCNF | — | CCNF | [ |
| 10 | 毛竹 | Gly | AGH、FeCl3 | 2∶1∶1 | 微波加热耦合 | 残余纤维素 | 81.17 | 组分分离 | [ |
| [1] | Cheng J Y, Huang C, Zhan Y N, et al. A novel mineral-acid free biphasic deep eutectic solvent/γ-valerolactone system for furfural production and boosting the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129653. |
| [2] | 张世超, 刘佳璇, 李群. 植物纤维的阳离子化改性及其对纤维结构的影响[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2020, 35(5): 15-19. |
| Zhang S C, Liu J X, Li Q. Cationic modification of plant fibers and its effect on fiber structure[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2020, 35(5): 15-19. | |
| [3] | 张贺, 黄旭乐, 孙衍宁, 等. 纸浆纤维阳离子化改性的预处理及改性方法研究进展[J]. 中国造纸学报, 2023, 38(4): 96-106. |
| Zhang H, Huang X L, Sun Y N, et al. Research progress on pretreatment and modification methods of pulp fiber cationic modification[J]. Transactions of China Pulp and Paper, 2023, 38(4): 96-106. | |
| [4] | 黄旭乐, 靳汇奇, 盛雪茹, 等. 纤维素纤维基阴离子吸附剂制备研究进展:预处理及阳离子化改性[J]. 中国造纸学报, 2021, 36(4): 91-99. |
| Huang X L, Jin H Q, Sheng X R, et al. Research progress in the preparation of cellulose fiber-based anionic adsorbents: pretreatment and cationic modification[J]. Transactions of China Pulp and Paper, 2021, 36(4): 91-99. | |
| [5] | Chen C J, Kuang Y D, Zhu S Z, et al. Structure-property-function relationships of natural and engineered wood[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020, 5(9): 642-666. |
| [6] | Tang Z W, Lin X X, Yu M Q, et al. Recent advances in TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers: oxidation mechanism, characterization, properties and applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 259: 129081. |
| [7] | Liu A, Li X H, Xu W B, et al. Synthesis of novel deep eutectic solvent-modified nano cellulosic gel formulation-based strain sensor for human motion monitoring[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 284: 138188. |
| [8] | 朱旭海. 阳离子改性微纤化纤维素的制备及其吸附胆酸盐能力的研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2015. |
| Zhu X H. Preparation of cationic modified microfibrillated cellulose and its adsorption capacity for cholate[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2015. | |
| [9] | Jia Z W, Li X L, Xu S B, et al. Novel ternary deep eutectic solvents pretreatment of corn stalk to realize high-value utilization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500: 156567. |
| [10] | Jiang J G, Carrillo-Enríquez N C, Oguzlu H, et al. High production yield and more thermally stable lignin-containing cellulose nanocrystals isolated using a ternary acidic deep eutectic solvent[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(18): 7182-7191. |
| [11] | Mariño M A, Paredes M G, Martinez N, et al. A ternary eutectic solvent for cellulose nanocrystal production: exploring the recyclability and pre-pilot scale-up[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2023, 11: 1233889. |
| [12] | Zhuo H, Dong X Y, Liu Q Y, et al. Bamboo-inspired ultra-strong nanofiber-reinforced composite hydrogels[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 980. |
| [13] | Zhang F L, Pang Z Q, Dong C H, et al. Preparing cationic cotton linter cellulose with high substitution degree by ultrasonic treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 132: 214-220. |
| [14] | Fu M T, Zhang H M, Bai J I, et al. Application of deep eutectic solvents with modern extraction techniques for the recovery of natural products: a review[J]. ACS Food Science & Technology, 2025, 5(2): 444-461. |
| [15] | 汪昭奇, 黄金田. 超声协同TEMPO氧化纳米纤维素膜的制备及表征[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(4): 68-75. |
| Wang Z Q, Huang J T. Preparation and characterization of ultrasonic and TEMPO oxidized nanocellulose films[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 43(4): 68-75. | |
| [16] | 万春容, 董泽宏, 王凯, 等. 阳离子化纤维素的制备及应用进展[J]. 纸和造纸, 2022, 41(2): 10-15. |
| Wan C R, Dong Z H, Wang K,et al. Progress in preparation and application of cationic cellulose[J]. Paper and Paper Making, 2022, 41(2): 10-15. | |
| [17] | Zhang H, Zhou M F, Jin H Q, et al. Enzyme activity test paper with high wet strength and anion adsorption properties fabricated from whole cationized softwood chemical fiber[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 273: 132769. |
| [18] | Signori-Iamin G, Aguado R J, Tarrés Q, et al. Exploring the synergistic effect of anionic and cationic fibrillated cellulose as sustainable additives in papermaking[J]. Cellulose, 2024, 31(15): 9349-9368. |
| [19] | Sehaqui H, Mautner A, Perez de Larraya U, et al. Cationic cellulose nanofibers from waste pulp residues and their nitrate, fluoride, sulphate and phosphate adsorption properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 135: 334-340. |
| [20] | Wu C W, Li J, et al. Preparation of cationic softwood kraft pulp fibres as retention additive to produce reconstituted tobacco sheet via paper-making[J]. Cellulose Chemistry and Technology, 2020, 54(5/6): 505-513. |
| [21] | Vuoti S, Narasimha K, Reinikainen K. Green wastewater treatment flocculants and fixatives prepared from cellulose using high-consistency processing and deep eutectic solvents[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2018, 26: 83-91. |
| [22] | Zaman M, Xiao H N, Chibante F, et al. Synthesis and characterization of cationically modified nanocrystalline cellulose[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 89(1): 163-170. |
| [23] | Sirviö J A. Cationization of lignocellulosic fibers with betaine in deep eutectic solvent: facile route to charge stabilized cellulose and wood nanofibers[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 198: 34-40. |
| [24] | Sirviö J A, Ukkola J, Liimatainen H. Direct sulfation of cellulose fibers using a reactive deep eutectic solvent to produce highly charged cellulose nanofibers[J]. Cellulose, 2019, 26(4): 2303-2316. |
| [25] | Sirviö J A, Visanko M, Liimatainen H. Deep eutectic solvent system based on choline chloride-urea as a pre-treatment for nanofibrillation of wood cellulose[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(6): 3401-3406. |
| [26] | Karimian D, Anzuoni V, Smania Z, et al. Enhanced nanocellulose production from cotton and textile waste using binary and ternary natural deep eutectic solvents[J]. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2025, 9(1): 2400525. |
| [27] | Hong S, Yuan Y, Li P P, et al. Enhancement of the nanofibrillation of birch cellulose pretreated with natural deep eutectic solvent[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 154: 112677. |
| [28] | Lu Y Z, Yu J, Ma J X, et al. High-yield preparation of cellulose nanofiber by small quantity acid assisted milling in glycerol[J]. Cellulose, 2019, 26(6): 3735-3745. |
| [29] | Zhang Q, Zhu E Q, Li T Q, et al. High-value utilization of cellulose: intriguing and important effects of hydrogen bonding interactions─a mini-review[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2024, 25(10): 6296-6318. |
| [30] | Li L H, Sun M Z, Hao B J, et al. Dilemma of low-cost filter paper as separator: toughen its wet strength for robust aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2024, 15(2): 380-390. |
| [31] | Xia S Q, Baker G A, Li H, et al. Aqueous ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents for cellulosic biomass pretreatment and saccharification[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(21): 10586-10596. |
| [32] | Jaekel E E, Torres G R, Antonietti M, et al. Cotton-quality fibers from complexation between anionic and cationic cellulose nanoparticles[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 18406. |
| [33] | Ong V Z, Wu T Y, Chu K K L, et al. A combined pretreatment with ultrasound-assisted alkaline solution and aqueous deep eutectic solvent for enhancing delignification and enzymatic hydrolysis from oil palm fronds[J] Industrial Crops and Products, 2021, 160: 112974. |
| [34] | Wang S D, Gao W H, Chen K F, et al. Deconstruction of cellulosic fibers to fibrils based on enzymatic pretreatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 267: 426-430. |
| [35] | Liu Y Z, Chen W S, Xia Q Q, et al. Efficient cleavage of lignin-carbohydrate complexes and ultrafast extraction of lignin oligomers from wood biomass by microwave-assisted treatment with deep eutectic solvent[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(8): 1692-1700. |
| [36] | Wang S, Han H, Lei X Q, et al. Cellulose nanofibers produced from spaghetti squash peel by deep eutectic solvents and ultrasonication[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 261: 129777. |
| [37] | Xiong Y J, Li W, Qin Z Z, et al. A green extraction technology of lignocellulose from cassava residue by mechanical activation-assisted ternary deep eutectic solvent[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 281: 136339. |
| [38] | Xiao Z, Zhao Q, Li Q, et al. Mechanochemistry-assisted fabrication of (carboxymethyl)cellulose mediated by minute surface-confined water[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(41): 14999-15011. |
| [39] | Meraj A, Jawaid M, Singh S P, et al. Isolation and characterisation of lignin using natural deep eutectic solvents pretreated kenaf fibre biomass[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 8672. |
| [40] | Mousa S A, Abdallah H, Khairy S A. The use of green synthesized TiO2/MnO2 nanoparticles in solar power membranes for pulp and paper industry wastewater treatment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 2102. |
| [41] | Sonyeam J, Chaipanya R, Suksomboon S, et al. Process design for acidic and alcohol based deep eutectic solvent pretreatment and high pressure homogenization of palm bunches for nanocellulose production[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 7550. |
| [42] | Dai M R, Dong Y Y, Ma S, et al. Efficient enzymatic hydrolysis of active oxygen and solid alkali/dilute sulfuric acid-pretreated corn cob[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024, 220: 119202. |
| [43] | Kassaye S, Pant K K, Jain S. Synergistic effect of ionic liquid and dilute sulphuric acid in the hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2016, 148: 289-294. |
| [44] | Li S L, Jiang W K, Wang H M, et al. Integrated preparation of functional lignin nanoparticles and levulinic acid directly from the pre-hydrolysis liquor of poplar wood[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 265: 130906. |
| [45] | Xu X J, Gai J M, Li Y R, et al. Integrated acetic acid and deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on poplar for co-production of xylo-oligosaccharides, fermentable sugars and lignin antioxidants/adsorbents[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 259(Pt 2): 129138. |
| [46] | Wang L, Zhu X Y, Chen X, et al. Isolation and characteristics of nanocellulose from hardwood pulp via phytic acid pretreatment[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 182: 114921. |
| [47] | Zhang Y D, Deng W F, Wang Z B, et al. A green cellulose dissolution system for producing tunable regenerated nanocellulose formate[J]. ACS Nano, 2025, 19(23): 21243-21259. |
| [48] | Swatloski R P, Spear S K, Holbrey J D, et al. Dissolution of cellose with lonic liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(18): 4974-4975. |
| [49] | Li L, Zhang M Z, Feng Y, et al. Deep eutectic solvent (TMAH·5H2O/Urea) with low viscosity for cellulose dissolution at room temperature[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 339: 122260. |
| [50] | Sirviö J A, Visanko M, Liimatainen H. Acidic deep eutectic solvents as hydrolytic media for cellulose nanocrystal production[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2016, 17(9): 3025-3032. |
| [51] | Liu W, Du H S, Liu K, et al. Sustainable preparation of cellulose nanofibrils via choline chloride-citric acid deep eutectic solvent pretreatment combined with high-pressure homogenization[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 267: 118220. |
| [52] | Liu S L, Zhang Q, Gou S H, et al. Esterification of cellulose using carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents to produce high-yield cellulose nanofibers[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 251: 117018. |
| [53] | Lozano M V C, Sciutto G, Prati S, et al. Deep eutectic solvents: green solvents for the removal of degraded gelatin on cellulose nitrate cinematographic films[J]. Heritage Science, 2022, 10(1): 114. |
| [54] | Xiao Q, Dai M Q, Zhou H, et al. Formation and structure evolution of starch nanoplatelets by deep eutectic solvent of choline chloride/oxalic acid dihydrate treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 282: 119105. |
| [55] | Gundupalli M P, Cheenkachorn K, Chuetor S, et al. Assessment of pure, mixed and diluted deep eutectic solvents on Napier grass (Cenchrus purpureus): compositional and characterization studies of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2023, 306: 120599. |
| [56] | Baheg N M, Abdel-Hakim A, El-Wakil A E A, et al. Development of novel natural deep eutectic solvent for cellulose nanofibrillation of orange peel via new surface functionalization[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(40): 14793-14806. |
| [57] | Ma W, Yan S M, Meng M, et al. Preparation of betaine-modified cationic cellulose and its application in the treatment of reactive dye wastewater[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(15): 40522. |
| [58] | Li P P, Sirviö J A, Haapala A, et al. Cellulose nanofibrils from nonderivatizing urea-based deep eutectic solvent pretreatments[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(3): 2846-2855. |
| [59] | Yang Z H, Asoh T A, Uyama H. Cationic functionalization of cellulose monoliths using a urea-choline based deep eutectic solvent and their applications[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2019, 160: 126-135. |
| [60] | Tang L, Wang B, Bai S R, et al. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals with high stability from okara by green solvent pretreatment assisted TEMPO oxidation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 324: 121485. |
| [61] | Ye J R, Gao Y B, Xu Q T, et al. P/N/S synergistic flame retardant holocellulose nanofibrils efficiently pretreated from ternary deep eutectic solvents[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 477: 147142. |
| [62] | Zhang Y T, Liu Y, Dong C H, et al. Transparent, thermal stable, water resistant and high gas barrier films from cellulose nanocrystals prepared by reactive deep eutectic solvents[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 276: 134107. |
| [63] | Li P P, Sirviö J A, Asante B, et al. Recyclable deep eutectic solvent for the production of cationic nanocelluloses[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 199: 219-227. |
| [64] | Zhang X P, Huo D, Wei J X, et al. Synthesis of amino-functionalized nanocellulose by guanidine based deep eutectic solvent and its application in fine fibers retention[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 260: 129473. |
| [65] | Sun S L, Cao X F, Li H L, et al. Simultaneous and efficient production of furfural and subsequent glucose in MTHF/H2O biphasic system via parameter regulation[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(3): 557. |
| [66] | Xie J X, Xu J, Zhang Z H, et al. New ternary deep eutectic solvents with cycle performance for efficient pretreated radiata pine forming to lignin containing cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138591. |
| [67] | Feng X D, Jin D, Zhu Y C, et al. Insights into the role of deep eutectic solvents in sorbitol dehydration: a combined experimental and molecular dynamics study[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(46): 17035-17043. |
| [68] | 胡亚茹, 杨正棒, 王莹, 等. 基于三元低共熔溶剂体系制备阳离子化改性纤维素纳米纤丝及其性能研究[J]. 中国造纸, 2023, 42(10): 12-18. |
| Hu Y R, Yang Z B, Wang Y, et al. Preparation and performance of cationic modified cellulose nanofibril based on ternary deep eutectic solvent system[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2023, 42(10): 12-18. | |
| [69] | Feng Y Y, Eberhardt T L, Meng F Y, et al. Efficient extraction of lignin from moso bamboo by microwave-assisted ternary deep eutectic solvent pretreatment for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 400: 130666. |
| [70] | Ma G R, Yin W Q, Shi Z J, et al. Direct carboxymethylation of cellulose fibers by ternary reactive deep eutectic solvents for the preparation of high-yield cellulose nanofibrils[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(15): 5871-5883. |
| [71] | Li B Y, Feng S Y, Huang J L, et al. Facile fractionation of poplar by a novel ternary deep eutectic solvent (DES) for cellulosic ethanol production under mild pretreatment conditions [J]. Industrial Crops & Products, 2025, 223: 120132. |
| [72] | Wang L Y, Yi J, Cheng F, et al. A novel efficient liquefaction process for corn starch through ternary deep eutectic solvent: products characterization and liquefaction mechanism[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 289: 138929. |
| [73] | Pan J K, Carter-Fenk K A, Hung S T, et al. Dynamics of deep eutectic mixtures of tetraethylammonium halides/ethylene glycol investigated with ultrafast infrared spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2025, 129(10): 2718-2729. |
| [74] | Wang Z W, Liu Y Z, Barta K, et al. The effect of acidic ternary deep eutectic solvent treatment on native lignin[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(38): 12569-12579. |
| [75] | Liu Y Z, Deak N, Wang Z W, et al. Tunable and functional deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulose valorization[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5424. |
| [76] | Wang Y X, Ryu J, Kim K H, et al. Investigation of the effects of ternary deep eutectic solvent composition on pretreatment of sorghum stover[J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(12): e18227. |
| [77] | Ji Q H, Yu X J, Yagoub A E A, et al. Efficient cleavage of strong hydrogen bonds in sugarcane bagasse by ternary acidic deep eutectic solvent and ultrasonication to facile fabrication of cellulose nanofibers[J]. Cellulose, 2021, 28(10): 6159-6182. |
| [78] | Zhao X R, Lyu G J, Meng X, et al. Novel ternary deep eutectic solvent fractionation for effective utilization of willow[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 407: 131148. |
| [79] | Pradhan D, Jaiswal S, Tiwari B K, et al. Choline chloride-oxalic acid dihydrate deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of Barley straw for production of cellulose nanofibers[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 281: 136213. |
| [80] | Yan Z Y, Wang Z R, Chen Y H, et al. Preparation of lignin nanoparticles via ultra-fast microwave-assisted fractionation of lignocellulose using ternary deep eutectic solvents[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(6): 1557-1568. |
| [81] | Zhu J Y, Zhu P H, Zhu Y L, et al. Surface charge manipulation for improved humidity sensing of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 335: 122059. |
| [82] | Putra S S S, Basirun W J, Hayyan A, et al. Ternary metal-organic framework composite with nanocellulose and deep eutectic solvent for the adsorptive removal of 3-MCPD esters[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 2025, 19(2): 1202-1219. |
| [83] | Gomez F J V, Espino M, Fernández M A, et al. A greener approach to prepare natural deep eutectic solvents[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3(22): 6122-6125. |
| [84] | Wu H H, Zhang K L, Jiang H Y, et al. Eutectic strategy for the solvent-free synthesis of hydrophobic cellulosic cross-linked networks with broad multifunctional applications[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2024, 13(11): 1558-1564. |
| [85] | Kim Y, Bang J, Kim J, et al. Cationic surface-modified regenerated nanocellulose hydrogel for efficient Cr(Ⅵ) remediation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 278: 118930. |
| [86] | Aguado R J, Mazega A, Tarrés Q, et al. The role of electrostatic interactions of anionic and cationic cellulose derivatives for industrial applications: a critical review[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2023, 201: 116898. |
| [87] | Sanchez-Salvador J L, Xu H Y, Balea A, et al. Enhancement of the production of TEMPO-mediated oxidation cellulose nanofibrils by kneading[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 261: 129612. |
| [88] | Chen S H, Yue N, Cui M, et al. Integrating direct reuse and extraction recovery of TEMPO for production of cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 294: 119803. |
| [89] | Guo X H, Yang R D, Wang Y, et al. Cationic cellulose nanofibers/chitosan auxiliary-dominated win-win strategy for paper yarn with superior color and physical performances[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 330: 121833. |
| [1] | Ziteng YAN, Feilong ZHAN, Guoliang DING. Structural design and effect verification of casing-type distributor used in air-conditioners [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [2] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [3] | Fanchen KONG, Shuo ZHANG, Mingsheng TANG, Huiming ZOU, Zhouhang HU, Changqing TIAN. Simulation of gas bearings in carbon dioxide linear compressors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [4] | Guorui HUANG, Yao ZHAO, Mingxi XIE, Erjian CHEN, Yanjun DAI. Experimental study on a novel waste heat recovery system based on desiccant coated exchanger in data center [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [5] | Xiaofeng CAO, Huahai ZHANG, Jiangyun WANG, Limin WANG. Structural design and flow characteristics of conical gas laminar flow element [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4440-4448. |
| [6] | Zequan LI, Tianyu CAI, Jiajun LIU, Qizhi CHEN, Peiwen XIAO, Xiaofei XU, Shuangliang ZHAO. Synthesis and application of lignin-based flocculants [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4709-4722. |
| [7] | Yu WANG, Yingnan FENG, Tao WANG, Zhiping ZHAO. Constructing nano-composite nanofiltration membranes by in-situ growth: membrane preparation and application [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4723-4736. |
| [8] | Jing ZHAO, Shuchen DONG, Gaoyang LI, Youke HUANG, Haosen SHI, Shuwen MIAO, Chenyan TAN, Tangqi ZHU, Yongshuai LI, Hui PAN, Hao LING. Simulation and optimization of battery performance based on the electrochemical model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4922-4932. |
| [9] | Peng TIAN, Zhonglin ZHANG, Chao REN, Guochao MENG, Xiaogang HAO, Yegang LIU, Qiwang HOU, Abuliti ABUDULA, Guoqing GUAN. Modeling and optimization of rectisol process based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [10] | Jie WANG, Qucheng LIN, Xianming ZHANG. Global optimization of mixed gas multistage membrane separation system based on decomposition algorithm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [11] | Luming CHEN, Yingli LIU, Haifeng LU, Qiaoyu GAN, Ying CHANG. Study on stress evolution and hopper design of ultrafine powder under aeration conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3853-3863. |
| [12] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [13] | Aqiang WU, Xiangqun ZHUGE, Tong LIU, Mingxing WANG, Kun LUO. Impact of nanoscale Prussian blue suspension electrolyte on the performance of lithium-oxygen batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4310-4317. |
| [14] | Shichang LIU, Yibai LI, Jing WANG, Yongzhong LIU. Modular design and optimization of hydrogen-driven electrochemical CO2 capture systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4108-4118. |
| [15] | Ke LI, Haolin XIE, Jian WEN. Multi-objective genetic algorithm optimization for thermal insulation performance of liquid hydrogen tank with multiple vapor-cooled shields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4217-4227. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||