化工学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (7): 2775-2785.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190027
收稿日期:2019-01-09
修回日期:2019-04-16
出版日期:2019-07-05
发布日期:2019-07-05
通讯作者:
杨伟
作者简介:朱计划(1992—),男,硕士研究生,<email>497691268@qq.com</email>
基金资助:
Jihua ZHU( ),Yao CHEN,Xiulian QIU,Yuming HUANG,Cheng ZHENG,Wei YANG(
),Yao CHEN,Xiulian QIU,Yuming HUANG,Cheng ZHENG,Wei YANG( )
)
Received:2019-01-09
Revised:2019-04-16
Online:2019-07-05
Published:2019-07-05
Contact:
Wei YANG
摘要:
采用微波辅助溶剂热法的合成途径,成功制备出镁掺杂的磷酸锰镁锂(LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C)电极材料。采用X-射线衍射、扫描电镜、恒电流充放电等测试方法对晶体结构,微观形态和电化学性能进行表征。结果表明微波辅助溶剂热样品LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C为具备较大比表面积和介孔结构的片层状形貌材料。该片层状纳米结构有利于锂离子脱嵌/镶嵌反应,Mg2+掺杂在片层状纳米晶体合成过程中发挥着重要作用,可以提高材料的电化学活性和电化学表现。其中LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料在0.1 C和5 C倍率下最高可逆放电容量分别为141.2和95.3 (mA·h)/g,具备较高的放电容量和倍率性能表现。与传统溶剂热法相比,微波辅助溶剂热法的反应时间显著降低且制备得到的材料具备优异的电化学性能表现,对于制备其他锂离子电池材料具有指导意义。
中图分类号:
朱计划, 陈姚, 丘秀莲, 黄宇明, 郑成, 杨伟. 微波辅助溶剂热法制备LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C正极材料[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2775-2785.
Jihua ZHU, Yao CHEN, Xiulian QIU, Yuming HUANG, Cheng ZHENG, Wei YANG. Preparation of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C cathode materials by microwave-assisted solvothermal method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2775-2785.
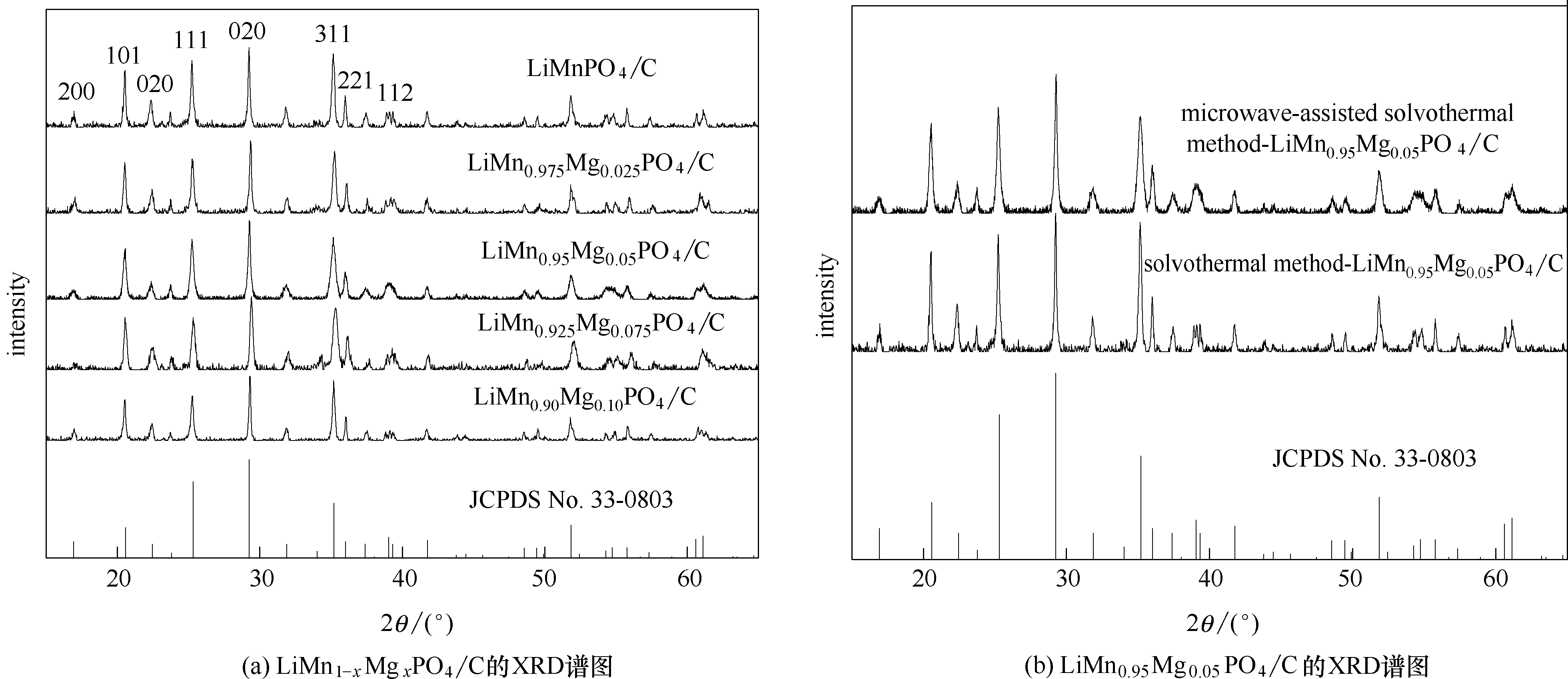
图1 微波辅助溶剂热LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C样品和采用不同合成方法制备LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料的XRD谱图
Fig.1 XRD patterns of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075 and 0.1) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes
| 样品 | a/? | b/? | c/? | v/?3 | I020/I311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 10.445 | 6.107 | 4.751 | 302.36 | 1.08 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 10.438 | 6.102 | 4.758 | 301.85 | 1.16 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 10.429 | 6.094 | 4.744 | 301.22 | 1.25 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 10.421 | 6.085 | 4.742 | 300.71 | 1.18 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.10PO4/C | 10.417 | 6.077 | 4.738 | 299.93 | 1.07 |
表1 微波辅助溶剂热LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075和0.1)样品的单元晶胞参数
Table 1 Refined unit-cell parameters for LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1)
| 样品 | a/? | b/? | c/? | v/?3 | I020/I311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 10.445 | 6.107 | 4.751 | 302.36 | 1.08 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 10.438 | 6.102 | 4.758 | 301.85 | 1.16 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 10.429 | 6.094 | 4.744 | 301.22 | 1.25 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 10.421 | 6.085 | 4.742 | 300.71 | 1.18 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.10PO4/C | 10.417 | 6.077 | 4.738 | 299.93 | 1.07 |

图2 微波辅助水热法和传统水热法制备的LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C材料SEM图
Fig.2 SEM images of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C synthesized by microwave-assisted solvothermal and traditional solvothermal route
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 电导率/(S/cm) | 离子扩散系数/(cm2/s) | 碳含量/%(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 64.2 | 4.5×10-4 | 9.72×10-14 | 7.13 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 79.9 | 6.3×10-4 | 1.56×10-13 | 7.21 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 88.2 | 7.6×10-4 | 4.32×10-13 | 7.16 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 82.8 | 5.4×10-4 | 1.95×10-13 | 7.08 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.1PO4/C | 68.6 | 3.8×10-4 | 8.71×10-14 | 7.11 |
表2 LiMn1-xMgxPO4/材料的比表面积、电子电导率、锂离子扩散系数和碳含量
Table 2 Specific surface area, electronic conductivity,lithium-ion diffusion coefficients and carbon content of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 电导率/(S/cm) | 离子扩散系数/(cm2/s) | 碳含量/%(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 64.2 | 4.5×10-4 | 9.72×10-14 | 7.13 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 79.9 | 6.3×10-4 | 1.56×10-13 | 7.21 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 88.2 | 7.6×10-4 | 4.32×10-13 | 7.16 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 82.8 | 5.4×10-4 | 1.95×10-13 | 7.08 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.1PO4/C | 68.6 | 3.8×10-4 | 8.71×10-14 | 7.11 |

图5 微波辅助溶剂热LiMnPO4/C样品(a)和LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C样品(b)的氮气吸脱附曲线和孔径分布(插图)
Fig.5 Nitrogen ad/desorption isotherms and pore size distributions(inset) of LiMnPO4/C (a) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C (b)
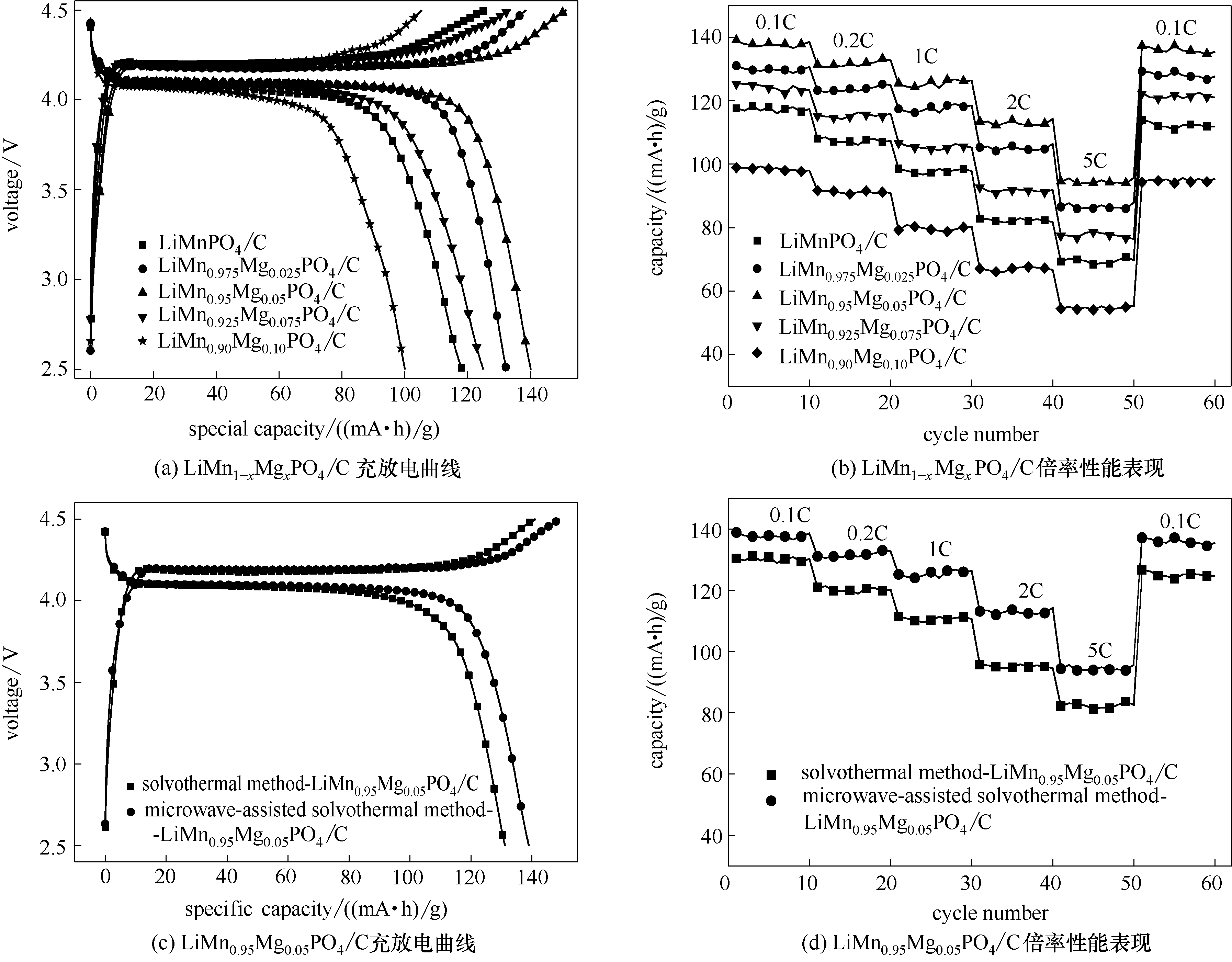
图6 微波辅助溶剂热LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1)样品充放电容量(a)与倍率性能(b),采用不同合成方法制备LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料充放电容量(c)与倍率性能(d)
Fig.6 Charge/discharge diagrams (a) and rate capability(b) of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) and charge/discharge diagrams (c) and rate capability (d) of LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes
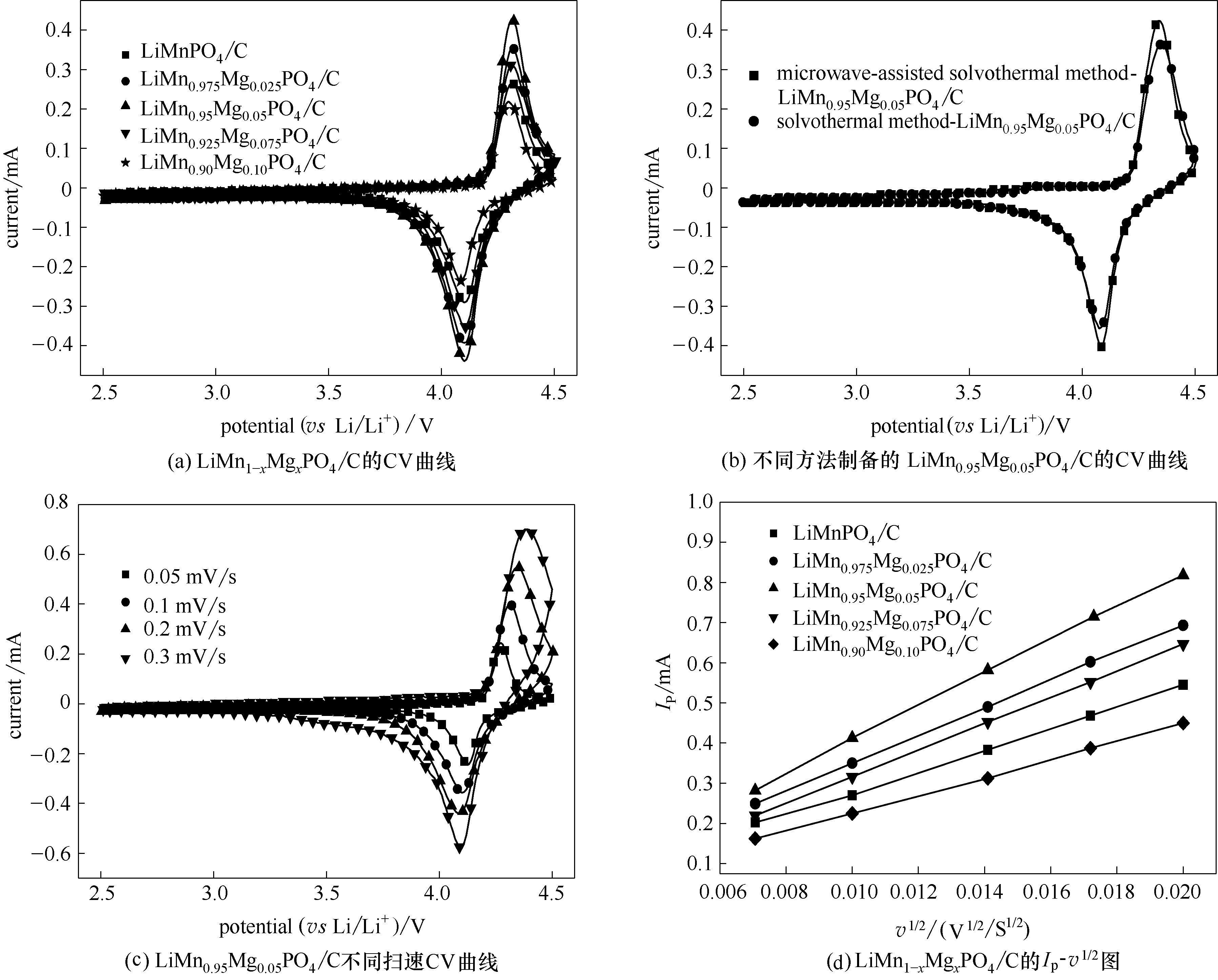
图7 0.1 mV/s扫速下微波辅助溶剂热法合成LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C材料(a)和采用不同合成方法制备LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料(b)的CV曲线,不同扫描速率下微波辅助溶剂热法合成LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料的CV曲线(c)和正极峰值电流与扫描速率平方根之间的线性拟合图(d)
Fig.7 CV curves of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) (a) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes(b) at a scan rate of 0.1 mV/s; LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through microwave-assisted solvothermal route at different scan rates (c), plots of cathodic peak current (Ip) as function of square root of scan rate (v1/2) (d)

图8 微波辅助溶剂热LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C样品(a)和采用不同合成方法制备LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C材料(b)的EIS图
Fig.8 EIS plots of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) (a) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes (b)
| 1 | ArmandM, TarasconJ M. Building better batteries [J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | DunnB, KamathH, TarasconJ M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices [J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058):928-935. |
| 3 | NittaN, WuF, LeeJ T, et al. Li-ion battery materials: present and future [J]. Materials Today, 2015, 18(5):252-264. |
| 4 | PadhiA K, NajundaswamyK S, GoodenoughJ B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194. |
| 5 | MasquelierC, CroguennecL. Polyanionic (phosphates, silicates, sulfates) frameworks as electrode materials for rechargeable Li (or Na) batteries [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(8):6552-6591. |
| 6 | AravindanV, GnanarajJ, LeeY S, et al. LiMnPO4—a next generation cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(11): 3518-3539. |
| 7 | DengY F, YangC X, ZouK X, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1-yMnyPO4 (0.5 ≤ y < 1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(13): 1614-6840. |
| 8 | DevarajuM K, HonmaI. Hydrothermal and solvothermal process towards development of LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn) nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012, 2(3):284-297. |
| 9 | MorganD, van der VenA, CederG. Li conductivity in LixMPO4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) olivine materials [J]. Electrochemical and Solid State Letters, 2004, 7(2): A30-A32. |
| 10 | YamadaA, HosoyaM, ChungS C, et al. Olivine-type cathodes: achievements and problems[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 119-121(6): 232-238. |
| 11 | ZhaoM, FuY, XuN, et al. High performance LiMnPO4/C prepared by a crystallite size control method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(36):15070-15077. |
| 12 | DinhH C, MhoS I, YeoI H, et al. Superior high rate capability of size-controlled LiMnPO4/C nanosheets with preferential orientation[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(122):100709-100714. |
| 13 | LeiZ H, NaveedA, LeiJ Y, et al. High performance nano-sized LiMn1-xFexPO4 cathode materials for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7 (69):43708-43715. |
| 14 | YanS Y, WangC Y, GuR M, et al. Enhanced kinetic behaviors of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C cathode material by Fe substitution and carbon coating[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2015, 19(10): 2943-2950. |
| 15 | OhS M, OhS W, YoonC S, et al. High-performance carbon-LiMnPO4 nanocomposite cathode for lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(19): 3260-3265. |
| 16 | WangF X, WangXW, ChangZ, et al. Electrode materials with tailored facets for electrochemical energy storage [J]. Nanoscale Horizons, 2016, 1(4): 272-289. |
| 17 | JungY H, ParkW B, PyoM, et al. A multi-element doping design for a high-performance LiMnPO4 cathode via metaheuristics computation [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(19): 8939-8945 |
| 18 | LuQ, HutchingsG S, ZhouY, et al. Nanostructured flexible Mg-modified LiMnPO4 matrix as high-rate cathode materials for Li-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(18): 6368-6373. |
| 19 | WangY, YangH, WuC Y, et al. Facile and controllable one-pot synthesis of nickel-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 nanosheets as high performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(35):18674-18683. |
| 20 | DuanJ G, HuG R, CaoY B, et al. Synthesis of high-performance Fe-Mg-co-doped LiMnPO4/C via a mechano-chemical liquid-phase activation technique[J]. Ionics, 2016, 22(5): 609-619 |
| 21 | ZhangJ, LuoS, WangQ, et al. Yttrium substituting in Mn site to improve electrochemical kinetics activity of sol-gel synthesized LiMnPO4/C as cathode for lithium ion battery [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2017, 21(11): 3189-3194. |
| 22 | WangC, LiS, HanY, et al. Assembly of LiMnPO4 nanoplates into microclusters as a high-performance cathode in lithium-ion batteries [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(33): 27618-27624 |
| 23 | PanX, GaoZ. Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of dispersed LiMnPO4 wedges[J]. Crystengcomm, 2013, 15(38): 7808-7814. |
| 24 | GuoH, WuC, XieJ, et al. Controllable synthesis of high-performance LiMnPO4 nanocrystals by a facile one-spot solvothermal process[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(27): 10581-10588. |
| 25 | AssatG, ManthiramA. Rapid microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of non-olivine cecum polymorphs of LiMPO4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) at low temperature and pressure[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(20): 10015-10022. |
| 26 | ZhuJ N, LiW C, ChengF, et al. Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C with superior performance as Li-ion battery cathodes by a two-stage microwave solvothermal process[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(26): 13920-13925. |
| 27 | ÖAhmet. Positive effects of a particular type of microwave-assisted methodology on the electrochemical properties of olivine LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Co and Ni) cathode materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 331: 501-509. |
| 28 | CuiY T, XuN, KouL Q, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of different morphological LiMnPO4/C nanoparticles from hollow-sphere Li3PO4 precursor via a delicate polyol-assisted hydrothermal method [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 249(3): 42-47. |
| 29 | GuoH, WuC, LiaoL, et al. Performance improvement of lithium manganese phosphate by controllable morphology tailoring with acid-engaged nano engineering[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(2): 667-674. |
| 30 | WangL, ZhangH, LiuQ, et al. Modifying high-voltage olivine-type LiMnPO4 cathode via Mg substitution in high-orientation crystal [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(11): 5928-5935. |
| 31 | HuC, YiH, FangH, et al. Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4via Mn-site co-substitution with Fe and Mg [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(12): 1784-1787. |
| 32 | KumarP R, VenkateswarluM, MisraM, et al. Enhanced conductivity and electrical relaxation studies of carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanorods[J]. Ionics, 2012, 19(3): 461-469. |
| 33 | ZhaoY, PengL L, LiuB R, et al. Single-crystalline LiFePO4 nanosheets for high-rate Li-ion batteries [J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(5): 2849-2853. |
| 34 | BakenovZ, TaniguchiI. LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C cathodes for lithium batteries prepared by a combination of spray pyrolysis with wet ball milling [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(4): A430-A436. |
| [1] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | 刘远超, 关斌, 钟建斌, 徐一帆, 蒋旭浩, 李耑. 单层XSe2(X=Zr/Hf)的热电输运特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [3] | 康飞, 吕伟光, 巨锋, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池放电路径与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [4] | 陈佳起, 赵万玉, 姚睿充, 侯道林, 董社英. 开心果壳基碳点的合成及其对Q235碳钢的缓蚀行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [5] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [7] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [8] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [9] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [10] | 邢美波, 张中天, 景栋梁, 张洪发. 磁调控水基碳纳米管协同多孔材料强化相变储/释能特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [11] | 余娅洁, 李静茹, 周树锋, 李清彪, 詹国武. 基于天然生物模板构建纳米材料及集成催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| [12] | 王志龙, 杨烨, 赵真真, 田涛, 赵桐, 崔亚辉. 搅拌时间和混合顺序对锂离子电池正极浆料分散特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| [13] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [14] | 董茂林, 陈李栋, 黄六莲, 吴伟兵, 戴红旗, 卞辉洋. 酸性助水溶剂制备木质纳米纤维素及功能应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2281-2295. |
| [15] | 李靖, 沈聪浩, 郭大亮, 李静, 沙力争, 童欣. 木质素基碳纤维复合材料在储能元件中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2322-2334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号