化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (9): 3640-3653.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230534
程业品1( ), 胡达清2, 徐奕莎1, 刘华彦1, 卢晗锋1, 崔国凯1(
), 胡达清2, 徐奕莎1, 刘华彦1, 卢晗锋1, 崔国凯1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-01
修回日期:2023-07-31
出版日期:2023-09-25
发布日期:2023-11-20
通讯作者:
崔国凯
作者简介:程业品(1998—),男,硕士研究生,2112101154@zjut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yepin CHENG1( ), Daqing HU2, Yisha XU1, Huayan LIU1, Hanfeng LU1, Guokai CUI1(
), Daqing HU2, Yisha XU1, Huayan LIU1, Hanfeng LU1, Guokai CUI1( )
)
Received:2023-06-01
Revised:2023-07-31
Online:2023-09-25
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Guokai CUI
摘要:
CO2作为一种温室气体,是一种宝贵的C1资源,为实现“碳达峰、碳中和”战略目标,大力发展二氧化碳利用与封存技术是当务之急。离子液体是由有机阳离子和有机或无机阴离子组成的绿色溶剂,而低共熔溶剂是由氢键受体和氢键供体通过氢键形成的一种新型的溶剂。离子液体基低共熔溶剂不仅拥有离子液体相似的性质,如低饱和蒸气压、宽液温范围、高热化学稳定性、结构性能可调控等,还具备了低共熔溶剂的氢键特性。本文综述了离子液体基低共熔溶剂在CO2热催化、电催化、生物催化领域的应用,并分析了各种催化方式中的CO2转化机理和影响因素,展望了低共熔溶剂应用于转化CO2的前景,对目前该领域的发展所面临的主要问题和进一步的研究工作提出了建议。
中图分类号:
程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653.
Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653.
| DES | 底物 | 温度/℃ | 时间/h | 产率①/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ch][Cl]/Urea (1∶2) | PO | — | 110 | 10 | 99 | [ |
| [Emim][I]/m-DHB (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | RT | 6 | 90(79) | [ |
| [P4442NH2][Br]/DEG (1∶3) | PO | 0.8 | 60 | 4 | 96(94) | [ |
| [AcCh][Br]/LMA (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | 80 | 2 | 98(96) | [ |
| [Ch][I]/Citric acid (2∶1) | PO | 0.5 | 70 | 3 | 98 | [ |
| [DBUH][Br]/DEA (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | RT | 48 | 97 | [ |
| [Ch][Cl]/PEG200 (1∶2) | PO | 0.8 | 150 | 5 | 99.1 | [ |
| [Ch][I]/NHS (1∶2) | PO | 1.0 | 30 | 10 | 96 | [ |
| [Bmim][Cl]/GA/BA(7∶1∶1) | PO | 0.8 | 70 | 7 | 98.3(82.1) | [ |
| [Ch][Br]/Im (2∶1) | PO | 1.0 | 100 | 4 | 97(97) | [ |
| [P4444][Br]/3-AP(1∶2) | PO | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 96(90) | [ |
| 环氧氯丙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 99 | ||
| 丁基环氧丙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 89 | ||
| 环氧苯乙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 87 | ||
| 环氧环己烯 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 19 | ||
| [N4444][I]/2-HMP(1∶1) | PO | 0.1 | 25 | 20 | 97 | [ |
表1 离子液体基低共熔溶剂转化CO2
Tabel 1 CO2 conversion by ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents
| DES | 底物 | 温度/℃ | 时间/h | 产率①/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ch][Cl]/Urea (1∶2) | PO | — | 110 | 10 | 99 | [ |
| [Emim][I]/m-DHB (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | RT | 6 | 90(79) | [ |
| [P4442NH2][Br]/DEG (1∶3) | PO | 0.8 | 60 | 4 | 96(94) | [ |
| [AcCh][Br]/LMA (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | 80 | 2 | 98(96) | [ |
| [Ch][I]/Citric acid (2∶1) | PO | 0.5 | 70 | 3 | 98 | [ |
| [DBUH][Br]/DEA (2∶1) | PO | 0.1 | RT | 48 | 97 | [ |
| [Ch][Cl]/PEG200 (1∶2) | PO | 0.8 | 150 | 5 | 99.1 | [ |
| [Ch][I]/NHS (1∶2) | PO | 1.0 | 30 | 10 | 96 | [ |
| [Bmim][Cl]/GA/BA(7∶1∶1) | PO | 0.8 | 70 | 7 | 98.3(82.1) | [ |
| [Ch][Br]/Im (2∶1) | PO | 1.0 | 100 | 4 | 97(97) | [ |
| [P4444][Br]/3-AP(1∶2) | PO | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 96(90) | [ |
| 环氧氯丙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 99 | ||
| 丁基环氧丙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 89 | ||
| 环氧苯乙烷 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 87 | ||
| 环氧环己烯 | 1.0 | 80 | 1 | 19 | ||
| [N4444][I]/2-HMP(1∶1) | PO | 0.1 | 25 | 20 | 97 | [ |
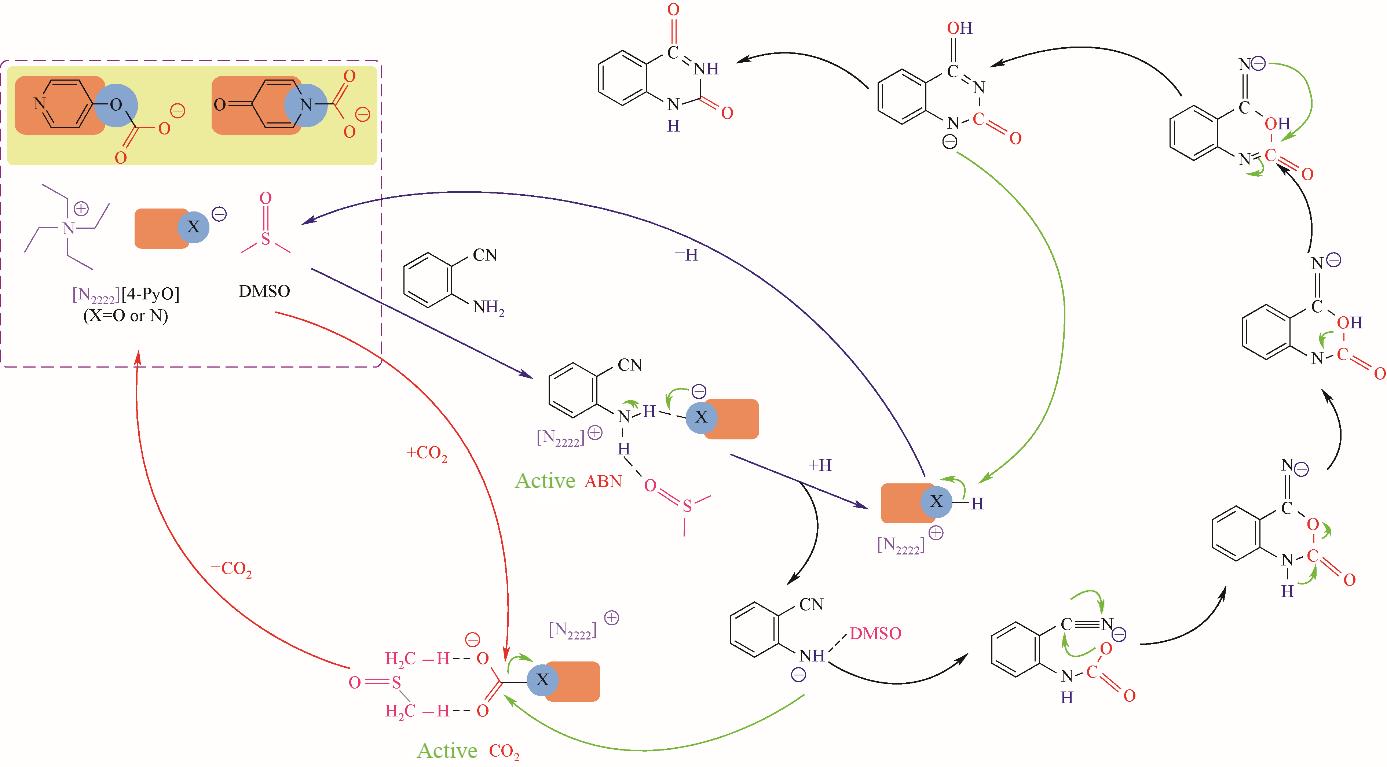
图7 [N2222][4-PyO]/DMSO (1∶4) 催化CO2与2-氨基苯甲腈反应的可能机理[58]
Fig.7 Possible reaction mechanism of CO2 with 2-aminobenzonitrile using [N2222][4-PyO]/DMSO (1∶4) as the catalyst[58]
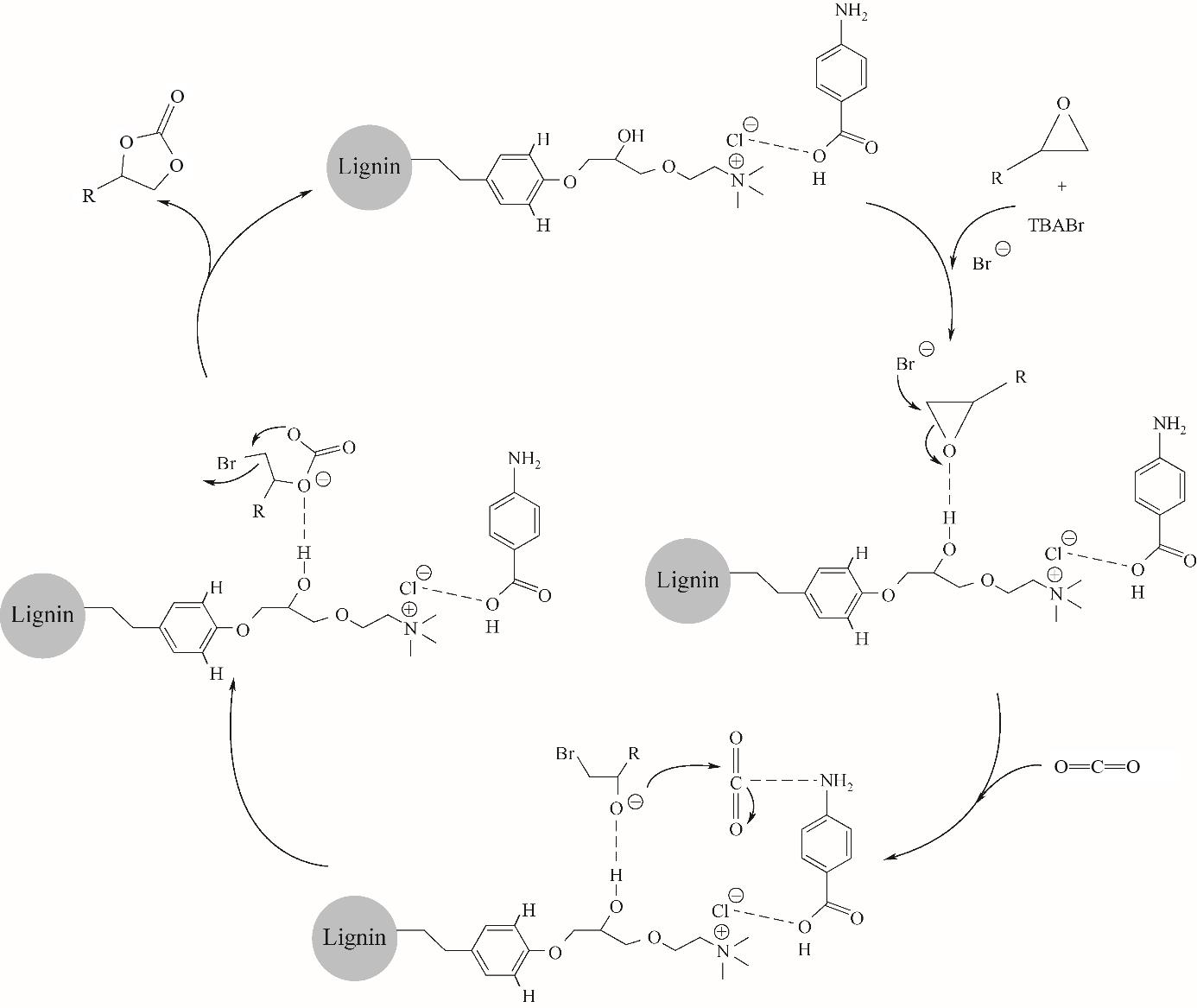
图10 木质素-[Ch][Cl]-PABA和四丁基溴化铵(TBABr)协同催化CO2化学固定的反应机理[62]
Fig.10 A plausible reaction mechanism for CO2 chemical fixation with epoxide co-catalyzed by lignin-[Ch][Cl]-PABA and TBABr[62]

图11 不同条件下的电酶法生产甲醇反应及含盐溶液中CO2浓度[64]
Fig.11 Electro-enzymatic reaction for methanol production under different conditions and the CO2 concentration in the SerGly-contained solution[64]
| 1 | Rochelle G T. Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5948): 1652-1654. |
| 2 | Tlili A, Frogneux X, Blondiaux E, et al. Creating added value with a waste: methylation of amines with CO2 and H2 [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(10): 2543-2545. |
| 3 | Zhang Z J, Yao Z Z, Xiang S C, et al. Perspective of microporous metal-organic frameworks for CO2 capture and separation[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(9): 2868-2899. |
| 4 | Kirchner B, Intemann B. Catch the carbon dioxide[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2016, 8(5): 401-402. |
| 5 | Sanz-Pérez E S, Murdock C R, Didas S A, et al. Direct capture of CO2 from ambient air[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 11840-11876. |
| 6 | Markewitz P, Kuckshinrichs W, Leitner W, et al. Worldwide innovations in the development of carbon capture technologies and the utilization of CO2 [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(6): 7281-7305. |
| 7 | Kenarsari S D, Yang D L, Jiang G D, et al. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(45): 22739-22773. |
| 8 | Xiong D Z, Cui G K, Wang J J, et al. Reversible hydrophobic-hydrophilic transition of ionic liquids driven by carbon dioxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(25): 7265-7269. |
| 9 | Wang C M, Guo Y, Zhu X, et al. Highly efficient CO2 capture by tunable alkanolamine-based ionic liquids with multidentate cation coordination[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(52): 6526-6528. |
| 10 | Luo X Y, Guo Y, Ding F, et al. Significant improvements in CO2 capture by pyridine-containing anion-functionalized ionic liquids through multiple-site cooperative interactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(27): 7053-7057. |
| 11 | Cui G K, Wang J J, Zhang S J. Active chemisorption sites in functionalized ionic liquids for carbon capture[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(15): 4307-4339. |
| 12 | Chen K H, Lin W J, Yu X N, et al. Designing of anion-functionalized ionic liquids for efficient capture of SO2 from flue gas[J]. AIChE Journal, 2015, 61(6): 2028-2034. |
| 13 | Cui G K, Zheng J J, Luo X Y, et al. Tuning anion-functionalized ionic liquids for improved SO2 capture[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(40): 10620-10624. |
| 14 | Wang C M, Zheng J J, Cui G K, et al. Highly efficient SO2 capture through tuning the interaction between anion-functionalized ionic liquids and SO2 [J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(12): 1166-1168. |
| 15 | Huang K, Chen Y L, Zhang X M, et al. SO2 absorption in acid salt ionic liquids/sulfolane binary mixtures: experimental study and thermodynamic analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 237: 478-486. |
| 16 | Cui G K, Zhang F T, Zhou X Y, et al. Acylamido-based anion-functionalized ionic liquids for efficient SO2 capture through multiple-site interactions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(9): 2264-2270. |
| 17 | Huang K, Cai D N, Chen Y L, et al. Thermodynamic validation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium carboxylates as task-specific ionic liquids for H2S absorption [J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(6): 2227-2235. |
| 18 | Huang K, Cai D N, Chen Y L, et al. Dual lewis base functionalization of ionic liquids for highly efficient and selective capture of H2S[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2014, 79(2): 241-249. |
| 19 | Zheng W T, Wu D S, Feng X, et al. Low viscous protic ionic liquids functionalized with multiple Lewis base for highly efficient capture of H2S[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 263: 209-217. |
| 20 | Huang K, Zhang J Y, Hu X B, et al. Absorption of H2S and CO2 in aqueous solutions of tertiary-amine functionalized protic ionic liquids[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(12): 14060-14069. |
| 21 | Guo B, Duan E H, Zhong Y F, et al. Absorption and oxidation of H2S in caprolactam tetrabutyl ammonium bromide ionic liquid[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(1): 159-161. |
| 22 | Huang K, Zhang X M, Hu X B, et al. Hydrophobic protic ionic liquids tethered with tertiary amine group for highly efficient and selective absorption of H2S from CO2 [J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(12): 4480-4490. |
| 23 | Cao N N, Gan L, Xiao Q X, et al. Highly efficient and reversible nitric oxide capture by functionalized ionic liquids through multiple-site absorption[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(7): 2990-2995. |
| 24 | Duan E H, Guo B, Zhang D D, et al. Absorption of NO and NO2 in caprolactam tetrabutyl ammonium halide ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2011, 61(12): 1393-1397. |
| 25 | Revelli A L, Mutelet F, Jaubert J N. Reducing of nitrous oxide emissions using ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2010, 114(24): 8199-8206. |
| 26 | Tao D J, Chen F F, Tian Z Q, et al. Highly efficient carbon monoxide capture by carbanion-functionalized ionic liquids through C-site interactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(24): 6843-6847. |
| 27 | Huang H Y, Padin J, Yang R T. Comparison of π-complexations of ethylene and carbon monoxide with Cu+ and Ag+ [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(7): 2720-2725. |
| 28 | Liu Y M, Tian Z Q, Qu F, et al. Tuning ion-pair interaction in cuprous-based protic ionic liquids for significantly improved CO capture[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(13): 11894-11900. |
| 29 | Li Z J, Zhang X P, Dong H F, et al. Efficient absorption of ammonia with hydroxyl-functionalized ionic liquids[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(99): 81362-81370. |
| 30 | Shang D W, Bai L, Zeng S J, et al. Enhanced NH3 capture by imidazolium-based protic ionic liquids with different anions and cation substituents[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2018, 93(5): 1228-1236. |
| 31 | Shang D W, Zhang X P, Zeng S J, et al. Protic ionic liquid [Bim][NTf2] with strong hydrogen bond donating ability for highly efficient ammonia absorption[J]. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(4): 937-945. |
| 32 | Li P F, Shang D, Tu W H, et al. NH3 absorption performance and reversible absorption mechanisms of protic ionic liquids with six-membered N-heterocyclic cations[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 248: 117087. |
| 33 | Vekariya R L. A review of ionic liquids: applications towards catalytic organic transformations[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 227: 44-60. |
| 34 | Huddleston J G, Willauer H D, Swatloski R P, et al. Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for 'clean' liquid— liquid extraction[J]. Chemical Communications, 1998(16): 1765-1766. |
| 35 | Egorova K S, Gordeev E G, Ananikov V P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 7132-7189. |
| 36 | Sun W Z, Wang M C, Zhang Y Q, et al. Protic vs aprotic ionic liquid for CO2 fixation: a simulation study[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2020, 5(2): 183-194. |
| 37 | Bi K L, Xu B H, Ding W L, et al. Mechanism of CO2 reduction in carbonylation reaction promoted by ionic liquid additives: a computational and experimental study[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2023, 8(1): 296-307. |
| 38 | Xu Y S, Zhang R N, Zhou Y, et al. Tuning ionic liquid-based functional deep eutectic solvents and other functional mixtures for CO2 capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 463: 142298. |
| 39 | 阮佳纬, 叶香珠, 陈立芳, 等. 离子液体和低共熔溶剂催化二氧化碳合成有机碳酸酯的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1176-1186. |
| Ruan J W, Ye X Z, Chen L F, et al. Recent progress in synthesis of organic carbonates from carbon dioxide catalyzed by ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1176-1186. | |
| 40 | 徐奕莎, 崔国凯, 葛春亮, 等. 低共熔溶剂在CO2捕集分离中的应用[J]. 能源环境保护, 2021, 35(6): 10-17. |
| Xu Y S, Cui G K, Ge C L, et al. Deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture and separation[J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2021, 35(6): 10-17. | |
| 41 | Wang Y, Hou Y C, Wu W Z, et al. Roles of a hydrogen bond donor and a hydrogen bond acceptor in the extraction of toluene from n-heptane using deep eutectic solvents[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(10): 3089-3097. |
| 42 | Krishnan A, Gopinath K P, Vo D V N, et al. Ionic liquids, deep eutectic solvents and liquid polymers as green solvents in carbon capture technologies: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2020, 18(6): 2031-2054. |
| 43 | Aissaoui T, Alnashef I, Qureshi U, et al. Potential applications of deep eutectic solvents in natural gas sweetening for CO2 capture[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2017, 33: 523-550. |
| 44 | Zhu A L, Jiang T, Han B X, et al. Supported choline chloride/urea as a heterogeneous catalyst for chemical fixation of carbon dioxide to cyclic carbonates[J]. Green Chemistry, 2007, 9(2): 169-172. |
| 45 | Liu Y, Cao Z, Zhou Z, et al. Imidazolium-based deep eutectic solvents as multifunctional catalysts for multisite synergistic activation of epoxides and ambient synthesis of cyclic carbonates[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2021, 53: 101717. |
| 46 | Cui Y Y, Wang X K, Dong L, et al. Tunable and functional phosphonium-based deep eutectic solvents for synthesizing of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides under mild conditions[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2023, 70: 102442. |
| 47 | Yang X Q, Liu Z M, Chen P, et al. Effective synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides catalyzed by acetylcholine bromide-based deep eutectic solvents[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2022, 58: 101936. |
| 48 | He L A, Zhang W W, Yang Y F, et al. Novel biomass-derived deep eutectic solvents promoted cycloaddition of CO2 with epoxides under mild and additive-free conditions[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2021, 54: 101750. |
| 49 | Yang X Q, Zou Q Z, Zhao T X, et al. Deep eutectic solvents as efficient catalysts for fixation of CO2 to cyclic carbonates at ambient temperature and pressure through synergetic catalysis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(31): 10437-10443. |
| 50 | Wu K, Su T, Hao D M, et al. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents for efficient cycloaddition of CO2 with propylene oxide[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(69): 9579-9582. |
| 51 | Liu F S, Gu Y Q, Zhao P H, et al. N-hydroxysuccinimide based deep eutectic catalysts as a promising platform for conversion of CO2 into cyclic carbonates at ambient temperature[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2019, 33: 419-426. |
| 52 | Wang S, Zhu Z G, Hao D M, et al. Synthesis cyclic carbonates with BmimCl-based ternary deep eutectic solvents system[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2020, 40: 101250. |
| 53 | Sheng T, Ou J L, Zhao T X, et al. Efficient fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonate catalyzed by choline bromide/imidazole derivatives-based deep eutectic solvents[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2023, 536: 112907. |
| 54 | Liu F S, Gu Y Q, Xin H, et al. Multifunctional phosphonium-based deep eutectic ionic liquids: insights into simultaneous activation of CO2 and epoxide and their subsequent cycloaddition[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(19): 16674-16681. |
| 55 | Wang L, Zhang G Y, Kodama K, et al. An efficient metal- and solvent-free organocatalytic system for chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates under mild conditions[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(5): 1229-1233. |
| 56 | Inaloo I D, Majnooni S. Carbon dioxide utilization in the efficient synthesis of carbamates by deep eutectic solvents (DES) as green and attractive solvent/catalyst systems[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(28): 11275-11281. |
| 57 | Karimi M, Jodaei A, Khajvandi A, et al. In-situ capture and conversion of atmospheric CO2 into nano-CaCO3 using a novel pathway based on deep eutectic choline chloride-calcium chloride[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 206: 516-522. |
| 58 | Cui G K, Xu Y S, Hu D Q, et al. Tuning functional ionic deep eutectic solvents as green sorbents and catalysts for highly efficient capture and transformation of CO2 to quinazoline-2, 4(1H, 3H)-dione and its derivatives[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 469: 143991. |
| 59 | Imteyaz S, Suresh C M, Kausar T, et al. Carbon dioxide capture and its electrochemical reduction study in deep eutectic solvent (DES) via experimental and molecular simulation approaches[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2023, 68: 102349. |
| 60 | Bohlen B, Wastl D, Radomski J, et al. Electrochemical CO2 reduction to formate on indium catalysts prepared by electrodeposition in deep eutectic solvents[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2020, 110: 106597. |
| 61 | Zhang Z B, Li F F, Nie Y, et al. Zinc-based deep eutectic solvent—an efficient carbonic anhydrase mimic for CO2 hydration and conversion[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 276: 119446. |
| 62 | Xiong X Q, Zhang H, Lai S L, et al. Lignin modified by deep eutectic solvents as green, reusable, and bio-based catalysts for efficient chemical fixation of CO2 [J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2020, 149: 104502. |
| 63 | Boroujeni M B, Laeini M S, Nazeri M T, et al. A novel and green in situ strategy for the synthesis of metallophthalocyanines on chitosan and investigation their catalytic activity in the CO2 fixation[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2019, 149(8): 2089-2097. |
| 64 | Zhang Z B, Wang H, Nie Y, et al. Natural deep eutectic solvents enhanced electro-enzymatic conversion of CO2 to methanol[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 894106. |
| 65 | Cui G K, Zhao N, Wang J J, et al. Computer-assisted design of imidazolate-based ionic liquids for improving sulfur dioxide capture, carbon dioxide capture, and sulfur dioxide/carbon dioxide selectivity[J]. Chemistry-an Asian Journal, 2017, 12(21): 2863-2872. |
| 66 | Wang L Y, Xu Y L, Li Z D, et al. CO2/CH4 and H2S/CO2 selectivity by ionic liquids in natural gas sweetening[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(1): 10-23. |
| 67 | Yang D Z, Han Y L, Qi H B, et al. Efficient absorption of SO2 by EmimCl-EG deep eutectic solvents[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(8): 6382-6386. |
| 68 | Zhao T X, Liang J, Zhang Y T, et al. Unexpectedly efficient SO2 capture and conversion to sulfur in novel imidazole-based deep eutectic solvents[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(65): 8964-8967. |
| 69 | Long G C, Yang C L, Yang X Q, et al. Bisazole-based deep eutectic solvents for efficient SO2 absorption and conversion without any additives[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(7): 2608-2613. |
| 70 | Wu H Y, Shen M Y, Chen X C, et al. New absorbents for hydrogen sulfide: deep eutectic solvents of tetrabutylammonium bromide/carboxylic acids and choline chloride/carboxylic acids[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 224: 281-289. |
| 71 | Zhong F Y, Zhou L S, Shen J A, et al. Rational design of azole-based deep eutectic solvents for highly efficient and reversible capture of ammonia[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(16): 14170-14179. |
| 72 | Cao Y K, Zhang X P, Zeng S J, et al. Protic ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents with multiple hydrogen bonding sites for efficient absorption of NH3 [J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(8): 16253-16261. |
| 73 | Jiang W J, Zhong F Y, Zhou L S, et al. Chemical dual-site capture of NH3 by unprecedentedly low-viscosity deep eutectic solvents[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(16): 2399-2402. |
| 74 | Patiño J, Gutiérrez M C, Carriazo D, et al. Deep eutectic assisted synthesis of carbon adsorbents highly suitable for low-pressure separation of CO2-CH4 gas mixtures[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(9): 8699-8707. |
| 75 | Liu F J, Chen W, Mi J X, et al. Thermodynamic and molecular insights into the absorption of H2S, CO2, and CH4 in choline chloride plus urea mixtures[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(5): e16574. |
| 76 | Shi M Z, Xiong W J, Tu Z H, et al. Task-specific deep eutectic solvents for the highly efficient and selective separation of H2S[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 276: 119357. |
| 77 | Hu J Y, Liu H Z, Han B X. Basic ionic liquids promoted chemical transformation of CO2 to organic carbonates[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2018, 61(12): 1486-1493. |
| 78 | Chen K H, Shi G L, Zhang W D, et al. Computer-assisted design of ionic liquids for efficient synthesis of 3(2H)-furanones: a domino reaction triggered by CO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(43): 14198-14201. |
| 79 | Hu J Y, Ma J, Zhu Q G, et al. Transformation of atmospheric CO2 catalyzed by protic ionic liquids: efficient synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(18): 5399-5403. |
| 80 | Hu J Y, Ma J, Zhang Z F, et al. A route to convert CO2: synthesis of 3, 4, 5-trisubstituted oxazolones[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(2): 1219-1225. |
| 81 | Shi G L, Chen K H, Wang Y T, et al. Highly efficient synthesis of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones from CO2 by hydroxyl functionalized aprotic ionic liquids[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(5): 5760-5765. |
| 82 | Zhao Y F, Yu B, Yang Z Z, et al. A protic ionic liquid catalyzes CO2 conversion at atmospheric pressure and room temperature: synthesis of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(23): 5922-5925. |
| 83 | Zhao Y F, Wu Y Y, Yuan G F, et al. Azole-anion-based aprotic ionic liquids: functional solvents for atmospheric CO2 transformation into various heterocyclic compounds[J]. Chemistry-an Asian Journal, 2016, 11(19): 2735-2740. |
| 84 | Xue C F, Feng L, Zhang Q, et al. High and fast carbon dioxide capture of hydroxypyridine-based ionogel depending on pore structure of mesoporous silica vesicle in the simulated flue gas[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2019, 84: 111-120. |
| 85 | Hiremath V, Jadhav A H, Lee H, et al. Highly reversible CO2 capture using amino acid functionalized ionic liquids immobilized on mesoporous silica[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 287: 602-617. |
| 86 | Cheng J, Li Y N, Hu L Q, et al. CO2 adsorption performance of ionic liquid [P66614][2-Op] loaded onto molecular sieve MCM-41 compared to pure ionic liquid in biohythane/pure CO2 atmospheres[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(4): 3251-3256. |
| 87 | Cheng J, Li Y N, Hu L Q, et al. CO2 absorption and diffusion in ionic liquid [P66614][Triz] modified molecular sieves SBA-15 with various pore lengths[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 172: 216-224. |
| 88 | Ding M, Jiang H L. Incorporation of imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid)s into a metal-organic framework for CO2 capture and conversion [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(4): 3194-3201. |
| 89 | Wu N H, Ji X Y, Xie W L, et al. Confinement phenomenon effect on the CO2 absorption working capacity in ionic liquids immobilized into porous solid supports[J]. Langmuir, 2017, 33(42): 11719-11726. |
| 90 | Li R A, Zhang K L, Chen G X, et al. Stiff, self-healable, transparent polymers with synergetic hydrogen bonding interactions[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2021, 33(13): 5189-5196. |
| [1] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [2] | 王琪, 张斌, 张晓昕, 武虎建, 战海涛, 王涛. 氯铝酸-三乙胺离子液体/P2O5催化合成伊索克酸和2-乙基蒽醌[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [3] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [4] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [5] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [6] | 王俐智, 杭钱程, 郑叶玲, 丁延, 陈家继, 叶青, 李进龙. 离子液体萃取剂萃取精馏分离丙酸甲酯+甲醇共沸物[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741. |
| [7] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [8] | 陆俊凤, 孙怀宇, 王艳磊, 何宏艳. 离子液体界面极化及其调控氢键性质的分子机理[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3665-3680. |
| [9] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [10] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [11] | 宋明昊, 赵霏, 刘淑晴, 李国选, 杨声, 雷志刚. 离子液体脱除模拟油中挥发酚的多尺度模拟与研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [12] | 杨绍旗, 赵淑蘅, 陈伦刚, 王晨光, 胡建军, 周清, 马隆龙. Raney镍-质子型离子液体体系催化木质素平台分子加氢脱氧制备烷烃[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [13] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [14] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [15] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号