化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (11): 5443-5454.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210761
收稿日期:2021-06-07
修回日期:2021-08-20
出版日期:2021-11-05
发布日期:2021-11-12
通讯作者:
李锦锦,罗正鸿
作者简介:李锦锦(1987—),女,博士,助理研究员,基金资助:
Jinjin LI1( ),You WU2,Yinning ZHOU1,Zhenghong LUO1(
),You WU2,Yinning ZHOU1,Zhenghong LUO1( )
)
Received:2021-06-07
Revised:2021-08-20
Online:2021-11-05
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Jinjin LI,Zhenghong LUO
摘要:
多孔聚合物材料具有孔隙率高、加工性能好、质量轻的特点,在化学工程、生物医学工程及环境工程等领域具有广阔的应用前景。高内相乳液模板法为多孔聚合物材料提供了一种简单高效的制备途径,且以此方法制备的多孔材料形状及结构可控,因而引起了人们的广泛关注。本文聚焦于两亲嵌段共聚物稳定的高内相乳液及其所制备多孔聚合物的最新研究进展。同时,介绍了该类型多孔聚合物材料在吸附分离、生物医学、能量存储及催化材料等领域的应用。最后,对该领域的未来发展进行了展望。
中图分类号:
李锦锦, 吴优, 周寅宁, 罗正鸿. 两亲嵌段共聚物基高内相乳液模板的制备与应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5443-5454.
Jinjin LI, You WU, Yinning ZHOU, Zhenghong LUO. Progress in preparation and application of amphiphilic block copolymer stabilized high internal phase emulsion templates[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5443-5454.
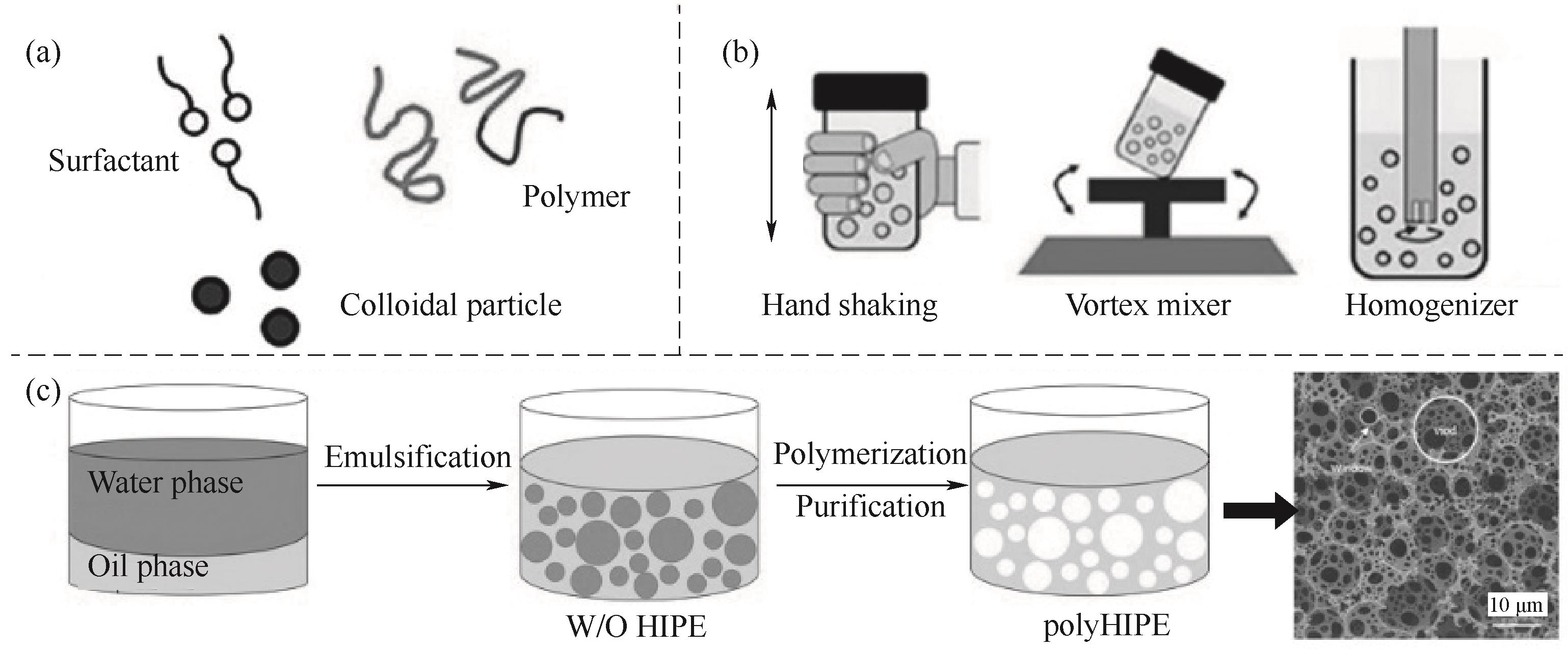
图1 基于稳定的高内相乳液模板合成多孔聚合物polyHIPE[12]:用于形成HIPE的稳定剂(a); HIPE的乳化方式(b); polyHIPE制备过程示意及其连通多孔结构(c)
Fig.1 Synthesis of polyHIPE from stable HIPE templating[12]: HIPE stabilizers (a); emulsification method of HIPE (b); schematic representation for the preparation of polyHIPE and its interconnected porous structure (c)

图2 Pluronic三嵌段共聚物:左侧为聚合物的分子结构,右侧为Pluronic 网格(不同颜色代表共聚物在环境条件下的物理状态: 绿色代表液态,红色代表膏状,橘色代表片状)[25-26]
Fig.2 Pluronic triblock copolymer: molecular structure of the copolymer (left) and the pluronic grid (right; colour code: physical state of copolymers under ambient conditions, green — liquid, red — paste, orange — flake) [25-26]

图3 BCP基polyHIPE的制备及其对亲/疏水溶剂的吸收性能[35]: 反应型BCP在O/W乳液中合成polyHIPE的路线(a);所制备材料的典型多孔结构(SEM图)(b);溶剂溶胀前后样品的对比(c)
Fig.3 Preparation of BCP-based polyHIPEs and their amphiphilic uptakes[35]: a scheme illustrating the synthesis of polyHIPE through the polymerization of a reactive BCP in an O/W emulsion (a); typical porous structure (SEM) (b); comparison of dry polyHIPE sample with samples that underwent equilibrium swelling in a liquid (c)

图4 BCP基polyHIPE的表面功能化机理[41]:由BCP稳定的HIPE的光学显微镜照片(a);聚合后形成的polyHIPE的SEM图(b);相比于低分子量表面活性剂,基于两嵌段共聚物制备的polyHIPE可通过物理或化学缠结实现表面功能化(c)
Fig.4 Mechanism of di-block copolymer based polyHIPE surface functionalization[41]: optical micrograph of HIPE (a); SEM image of polyHIPE (b); HIPEs stabilized by di-block copolymers as surfactants can be surface functionalized through physical or chemical entanglement compared to low molecular weight surfactants (c)
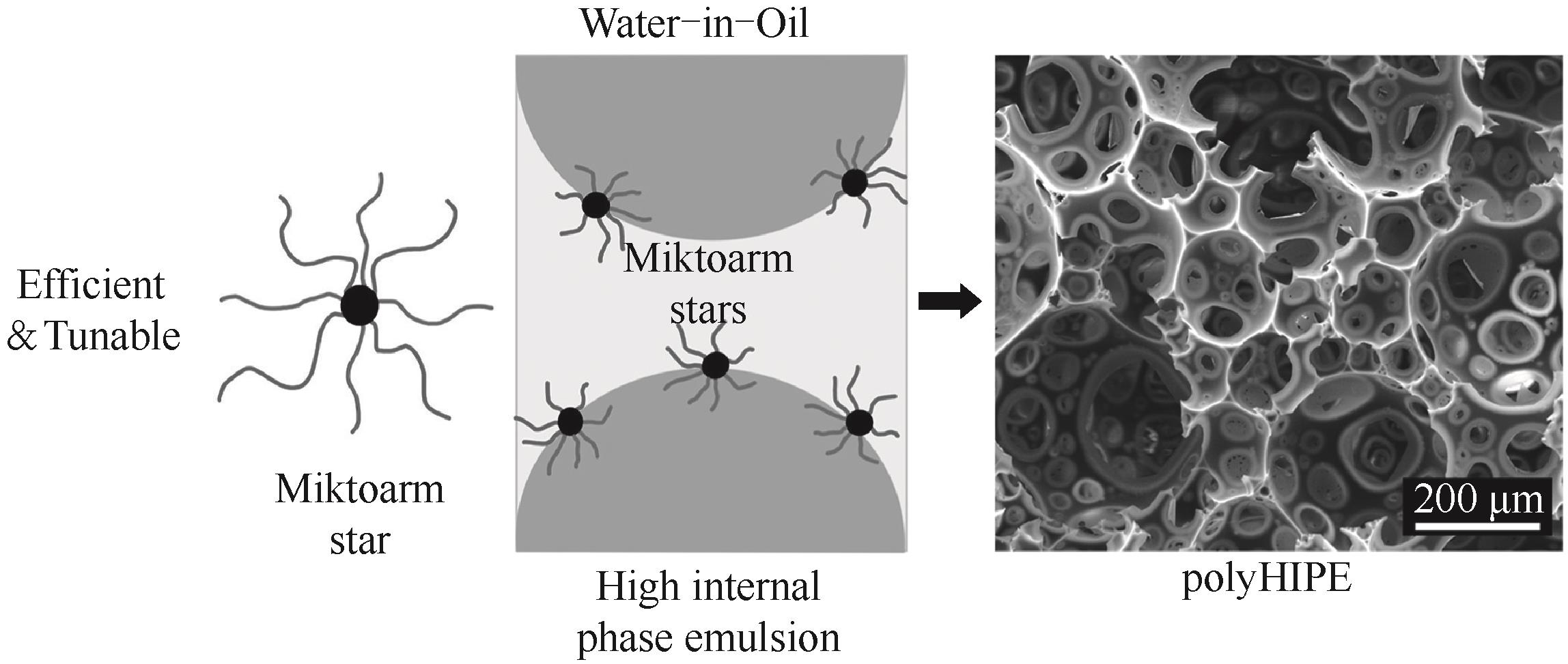
图5 星形稳定剂在油水界面的构象及所制备polyHIPE的SEM图[50]
Fig.5 Structure of star polymer, its stabilizing mechanism at oil-water interface and the as-prepared polyHIPE[50]
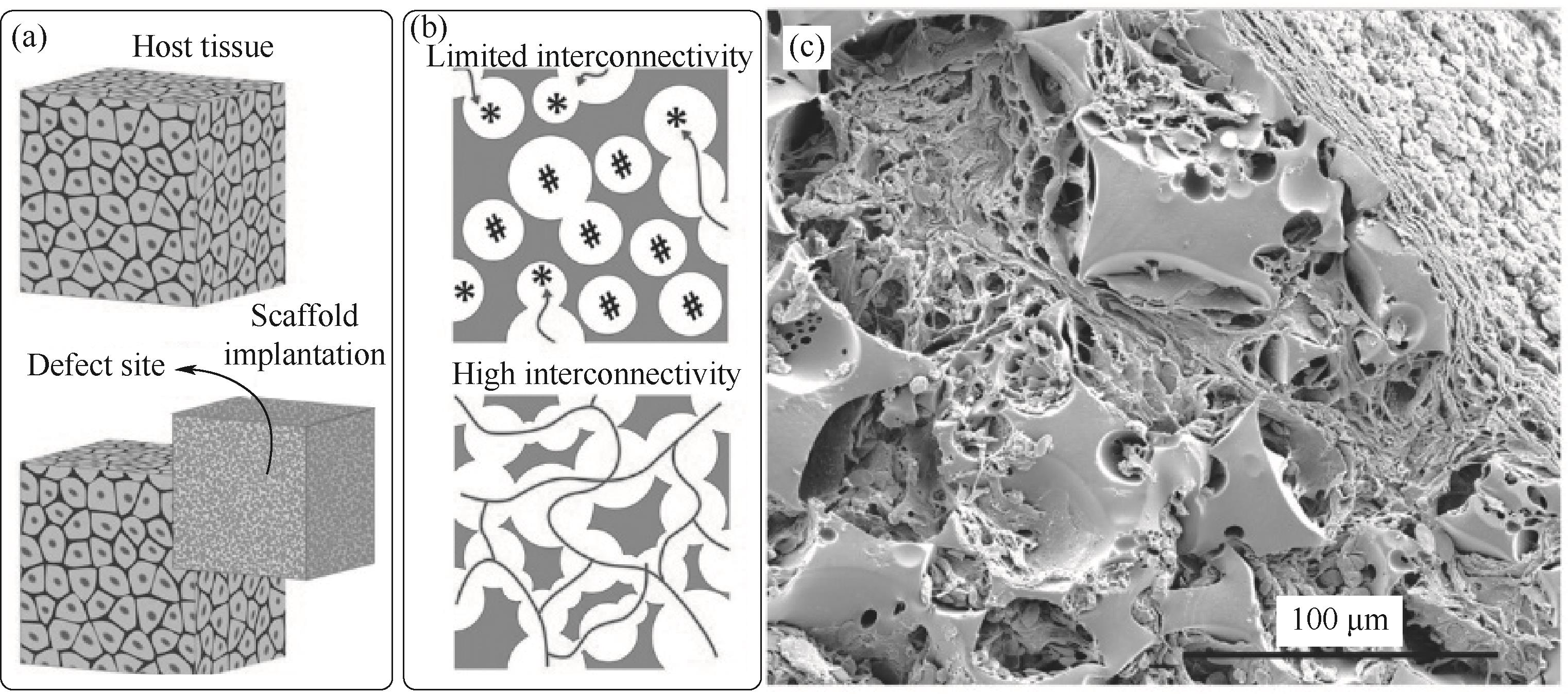
图7 孔连通性(开孔结构)对支架材料设计的重要性[54]:支架材料植入缺损位置示意图(a);不同连通孔道结构的支架材料对于组织/细胞生长的影响(b);组织生长渗透的PCL-polyHIPE支架材料扫描电镜图(c)
Fig.7 Significance of the interconnectivity on scaffold design[54]: scaffolds that are implanted to the defect site (a); difference of cell penetration in the scaffold with low and interconnectivity (b); SEM image of the PCL-polyHIPE that shows tissue infiltration through the interconnected pores of the scaffold (c)
| 1 | Tan L, Tan B. Hypercrosslinked porous polymer materials: design, synthesis, and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(11): 3322-3356. |
| 2 | de France K J, Xu F, Hoare T. Structured macroporous hydrogels: progress, challenges, and opportunities[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2018, 7(1): 1700927. |
| 3 | Wu J L, Xu F, Li S M, et al. Porous polymers as multifunctional material platforms toward task-specific applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(4): 1802922. |
| 4 | Zhang A, Bai H, Li L. Breath figure: a nature-inspired preparation method for ordered porous films[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(18): 9801-9868. |
| 5 | Li C, Li Q, Kaneti Y V, et al. Self-assembly of block copolymers towards mesoporous materials for energy storage and conversion systems[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(14): 4681-4736. |
| 6 | Silverstein M S. PolyHIPEs: recent advances in emulsion-templated porous polymers[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2014, 39(1): 199-234. |
| 7 | Zhang H F, Cooper A I. Synthesis and applications of emulsion-templated porous materials[J]. Soft Matter, 2005, 1(2): 107. |
| 8 | Zhang T, Sanguramath R A, Israel S, et al. Emulsion templating: porous polymers and beyond[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(15): 5445-5479. |
| 9 | Cameron N R, Sherrington D C. High internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) — structure, properties and use in polymer preparation[M]//Biopolymers Liquid Crystalline Polymers Phase Emulsion. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1996: 163-214. |
| 10 | Silverstein M S. Emulsion-templated porous polymers: a retrospective perspective[J]. Polymer, 2014, 55(1): 304-320. |
| 11 | Silverstein M S. Emulsion-templated polymers: contemporary contemplations[J]. Polymer, 2017, 126: 261-282. |
| 12 | Moon S, Kim J Q, Kim B Q, et al. Processable composites with extreme material capacities: toward designer high internal phase emulsions and foams[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(11): 4838-4854. |
| 13 | Kramer S, Cameron N R, Krajnc P. Porous polymers from high internal phase emulsions as scaffolds for biological applications[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(11): 1786. |
| 14 | Pulko I, Krajnc P. High internal phase emulsion templating - a path to hierarchically porous functional polymers[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2012, 33(20): 1731-1746. |
| 15 | Kimmins S D, Cameron N R. Functional porous polymers by emulsion templating: recent advances[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(2): 211-225. |
| 16 | Cameron N R, Sherrington D C, Albiston L, et al. Study of the formation of the open-cellular morphology of poly(styrene/divinylbenzene) polyHIPE materials by cryo-SEM[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 1996, 274(6): 592-595. |
| 17 | Menner A, Bismarck A. New evidence for the mechanism of the pore formation in polymerising high internal phase emulsions or why polyHIPEs have an interconnected pore network structure[J]. Macromolecular Symposia, 2006, 242(1): 19-24. |
| 18 | Luo Y W, Wang A N, Gao X. Pushing the mechanical strength of polyHIPEs up to the theoretical limit through living radical polymerization[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(6): 1824-1830. |
| 19 | Luo Y W, Wang A N, Gao X. Miniemulsion template polymerization to prepare a sub-micrometer porous polymeric monolith with an inter-connected structure and very high mechanical strength[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(29): 7547. |
| 20 | Ikem V, Menner A, Bismarck A. High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by functionalized silica particles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(4): 632. |
| 21 | Yang L, Liu Y, Filipe C D M, et al. Development of a highly sensitive, broad-range hierarchically structured reduced graphene oxide/polyHIPE foam for pressure sensing[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(4): 4318-4327. |
| 22 | Jiao B, Shi A M, Wang Q, et al. High-internal-phase Pickering emulsions stabilized solely by peanut-protein-isolate microgel particles with multiple potential applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2018, 130(30): 9418-9422. |
| 23 | Zhu H, Lei L, Li B G, et al. Development of novel materials from polymerization of Pickering emulsion templates[M]//Pauer W. Polymer Reaction Engineering of Dispersed Systems. Advances in Polymer Science. Cham: Springer, 2017, 280: 101-119. |
| 24 | Ikem V O, Menner A, Horozov T S, et al. Highly permeable macroporous polymers synthesized from Pickering medium and high internal phase emulsion templates[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(32): 3588-3592. |
| 25 | Alexandridis P, Alan Hatton T. Poly(ethylene oxide)–poly(propylene oxide)–poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1995, 96(1/2): 1-46. |
| 26 | Pitto-Barry A, Barry N P E. Pluronic® block-copolymers in medicine: from chemical and biological versatility to rationalisation and clinical advances[J]. Polym. Chem., 2014, 5(10): 3291-3297. |
| 27 | Utroša P, Onder O C, Žagar E, et al. Shape memory behavior of emulsion-templated poly(ε-caprolactone) synthesized by organocatalyzed ring-opening polymerization[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(23): 9291-9298. |
| 28 | Parın F N, Mert E H. Hydrophilic closed-cell macroporous foam preparation by emulsion templating[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 277: 128287. |
| 29 | Jurjevec S, Debuigne A, Žagar E, et al. An environmentally benign post-polymerization functionalization strategy towards unprecedented poly(vinylamine) polyHIPEs[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2021, 12(8): 1155-1164. |
| 30 | Zhang T, Gui H G, Xu Z G, et al. Hydrophobic polyurethane polyHIPEs templated from mannitol within nonaqueous high internal phase emulsions for oil spill recovery[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2019, 57(12): 1315-1321. |
| 31 | Makrygianni M, Christofili A, Deimede V. Emulsion-templated macroporous ammonium based polymers: synthesis and dye adsorption study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 610: 125634. |
| 32 | Jurjevec S, Žagar E, Kovačič S. Functional macroporous amphoteric polyelectrolyte monoliths with tunable structures and properties through emulsion-templated synthesis[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 575: 480-488. |
| 33 | Zhang T, Li X M, Wang W J, et al. Interface-initiated polymerization enables one-pot synthesis of hydrophilic and oleophobic foams through emulsion templating[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2019, 40(21): 1900288. |
| 34 | Jiang B, Zhang T, Xu Z G, et al. Wet-spun porous fibers from high internal phase emulsions: continuous preparation and high stretchability[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2021, 59(11): 1055-1064. |
| 35 | Zhang T, Silverstein M S. Microphase-separated macroporous polymers from an emulsion-templated reactive triblock copolymer[J]. Macromolecules, 2018, 51(10): 3828-3835. |
| 36 | Zhang T, Silverstein M S. Robust, highly porous hydrogels templated within emulsions stabilized using a reactive, crosslinking triblock copolymer[J]. Polymer, 2019, 168: 146-154. |
| 37 | Wang Y K, Wan X Z, He J X, et al. A one-step fabrication and modification of HIPE-templated fluoro-porous polymer using PEG-b-PHFBMA macrosurfactant[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(12): 4970-4986. |
| 38 | Azhar U, Zong C Y, Wan X Z, et al. Methyl methacrylate HIPE solely stabilized by fluorinated di-block copolymer for fabrication of highly porous and interconnected polymer monoliths[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2018, 24(45): 11619-11626. |
| 39 | Azhar U, Yaqub R, Li H T, et al. Di-block copolymer stabilized methyl methacrylate based polyHIPEs: influence of hydrophilic and hydrophobic co-monomers on morphology, wettability and thermal properties[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(2): 3801-3816. |
| 40 | Wu Y, Zhou Y N, Xu Q J, et al. Porous PS- and PMMA-based polymeric monoliths prepared by PEO-PS block copolymers stabilized high internal phase emulsion templates[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 26: 101962. |
| 41 | Viswanathan P, Johnson D W, Hurley C, et al. 3D surface functionalization of emulsion-templated polymeric foams[J]. Macromolecules, 2014, 47(20): 7091-7098. |
| 42 | Mathieu K, Jérôme C, Debuigne A. Influence of the macromolecular surfactant features and reactivity on morphology and surface properties of emulsion-templated porous polymers[J]. Macromolecules, 2015, 48(18): 6489-6498. |
| 43 | Azhar U, Huyan C X, Wan X Z, et al. A cationic fluorosurfactant for fabrication of high-performance fluoropolymer foams with controllable morphology[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 124: 194-202. |
| 44 | Cameron N R. High internal phase emulsion templating as a route to well-defined porous polymers[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(5): 1439-1449. |
| 45 | Li Z C, Liu H R, Zeng L, et al. The facile synthesis of PMMA polyHIPEs with highly interconnected porous microstructures[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2016, 51(19): 9005-9018. |
| 46 | Lei M, Peng Z H, Dong Q, et al. A novel capsular tension ring as local sustained-release carrier for preventing posterior capsule opacification[J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 89: 148-156. |
| 47 | Khodabandeh A, Arrua R D, Mansour F R, et al. PEO-based brush-type amphiphilic macro-RAFT agents and their assembled polyHIPE monolithic structures for applications in separation science[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 7847. |
| 48 | Gui H G, Guan G W, Zhang T, et al. Microphase-separated, hierarchical macroporous polyurethane from a nonaqueous emulsion-templated reactive block copolymer[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 365: 369-377. |
| 49 | Li W W, Yu Y, Lamson M, et al. PEO-based star copolymers as stabilizers for water-in-oil or oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Macromolecules, 2012, 45(23): 9419-9426. |
| 50 | Horowitz R, Lamson M, Cohen O, et al. Highly efficient and tunable miktoarm stars for HIPE stabilization and polyHIPE synthesis[J]. Polymer, 2021, 217: 123444. |
| 51 | Li C H, Weng S Q, Jin M, et al. Dendritic macrosurfactant assembly for physical functionalization of HIPE-templated polymers[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(4): 779. |
| 52 | Feng Y Y, Wan Y J, Jin M, et al. Large-scale preparation of a 3D patchy surface with dissimilar dendritic amphiphiles[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14(6): 1043-1049. |
| 53 | Li C H, Jin M, Wan D C. Evolution of a radical-triggered polymerizing high internal phase emulsion into an open-cellular monolith[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 220(16): 1900216. |
| 54 | Aldemir D B, Claeyssens F. Basic principles of emulsion templating and its use as an emerging manufacturing method of tissue engineering scaffolds[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 875. |
| 55 | Zhu Y F, Wang W B, Yu H, et al. Preparation of porous adsorbent via Pickering emulsion template for water treatment: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 88: 217-236. |
| 56 | Taylor-Pashow K M L, Pribyl J G. PolyHIPEs for separations and chemical transformations: a review[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2019, 37(1): 1-26. |
| 57 | Zhang T, Silverstein M S. Highly porous, emulsion-templated, zwitterionic hydrogels: amplified and accelerated uptakes with enhanced environmental sensitivity[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2018, 9(25): 3479-3487. |
| 58 | Gui H G, Zhang T, Guo Q P. Nanofibrous, emulsion-templated syndiotactic polystyrenes with superhydrophobicity for oil spill cleanup[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(39): 36063-36072. |
| 59 | Li X M, Zhang T, Xu Z G, et al. Amphiphobic polyHIPEs with pH-triggered transition to hydrophilicity–oleophobicity for the controlled removal of water from oil–water mixtures[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2020, 11(43): 6935-6943. |
| 60 | Yang X C, Yin Z Q, Zhang X Y, et al. Fabrication of emulsion-templated macroporous poly(ε-caprolactone) towards highly effective and sustainable oil/water separation[J]. Polymer, 2020, 204: 122852. |
| 61 | Golub D, Krajnc P. Emulsion templated hydrophilic polymethacrylates. Morphological features, water and dye absorption[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2020, 149: 104515. |
| 62 | Zhu J J, Wu L B, Bu Z Y, et al. Synthesis and CO2 capture behavior of porous cross-linked polymers containing pendant triazole groups[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(36): 10155-10163. |
| 63 | Zhu J J, Wu L B, Bu Z Y, et al. Polyethylenimine-grafted HKUST-type MOF/PolyHIPE porous composites (PEI@PGD-H) as highly efficient CO2 adsorbents[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(10): 4257-4266. |
| 64 | Ingavle G, Vaidya A, Kale V. Constructing three-dimensional microenvironments using engineered biomaterials for hematopoietic stem cell expansion[J]. Tissue Engineering Part B, Reviews, 2019, 25(4): 312-329. |
| 65 | Busby W, Cameron N R, Jahoda C A B. Emulsion-derived foams (polyHIPEs) containing poly(ε-caprolactone) as matrixes for tissue engineering[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2001, 2(1): 154-164. |
| 66 | Yadav A, Pal J, Nandan B, et al. Macroporous scaffolds of cross-linked poly(ɛ-caprolactone) via high internal phase emulsion templating[J]. Polymer, 2019, 176: 66-73. |
| 67 | Busby W, Cameron N R, Jahoda C A. Tissue engineering matrixes by emulsion templating[J]. Polymer International, 2002, 51(10): 871-881. |
| 68 | Pérez-García M G, Gutiérrez M C, Mota-Morales J D, et al. Synthesis of biodegradable macroporous poly(l-lactide)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blend using oil-in-eutectic-mixture high-internal-phase emulsions as template[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(26): 16939-16949. |
| 69 | Wang L W, Liu Y J, Bao L, et al. Preparation of acrylamide-based poly-HIPEs with enhanced mechanical strength using PVDBM-b-PEG-emulsified CO2 -in-water emulsions[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(23): 46346. |
| 70 | Corti M, Calleri E, Perteghella S, et al. Polyacrylate/polyacrylate-PEG biomaterials obtained by high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) with tailorable drug release and effective mechanical and biological properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2019, 105: 110060. |
| 71 | Gui H G, Zhang T, Guo Q P. Closed-cell, emulsion-templated hydrogels for latent heat storage applications[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2018, 9(29): 3970-3973. |
| 72 | Zhang T, Xu Z G, Chi H J, et al. Closed-cell, phase change material-encapsulated monoliths from a reactive surfactant-stabilized high internal phase emulsion for thermal energy storage[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2020, 2(7): 2578-2585. |
| 73 | Zhang T, Xu Z G, Li X M, et al. Closed-cell, phase change material-encapsulated, emulsion-templated monoliths for latent heat storage: flexibility and rapid preparation[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 21: 100831. |
| 74 | Danninger D, Hartmann F, Paschinger W, et al. Stretchable polymerized high internal phase emulsion separators for high performance soft batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(19): 2000467. |
| 75 | Stiernet P, Aqil A, Zhu X M, et al. Multicomponent radziszewski emulsion polymerization toward macroporous poly(ionic liquid) catalysts[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2020, 9(1): 134-139. |
| 76 | Mravljak R, Bizjak O, Božič B, et al. Flow-through polyHIPE silver-based catalytic reactor[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(6): 880. |
| 77 | Foudazi R. HIPEs to polyHIPEs[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2021, 164: 104917. |
| 78 | Aldemir D B, Dikici S, Reilly G C, et al. A novel bilayer polycaprolactone membrane for guided bone regeneration: combining electrospinning and emulsion templating[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(16): 2643. |
| 79 | Li J J, Zhou Y N, Luo Z H, et al. Engineering bicontinuous polymeric monoliths through high internal phase emulsion templating[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2020, 22: 100813. |
| 80 | Wenger L, Radtke C P, Göpper J, et al. 3D-printable and enzymatically active composite materials based on hydrogel-filled high internal phase emulsions[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 713. |
| [1] | 林典, 江国梅, 徐秀彬, 赵波, 刘冬梅, 吴旭. 硅基类液防原油黏附涂层的研制及其减阻性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3438-3445. |
| [2] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [3] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [4] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [5] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [6] | 杨琴, 秦传鉴, 李明梓, 杨文晶, 赵卫杰, 刘虎. 用于柔性传感的双形状记忆MXene基水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [7] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [8] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [9] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 何勇, 梁德青. 离子液体与动力学抑制剂作用下混合气体水合物生成特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1703-1711. |
| [10] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [11] | 吕阳光, 左培培, 杨正金, 徐铜文. 三嗪框架聚合物膜用于有机纳滤甲醇/正己烷分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606. |
| [12] | 罗来明, 张劲, 郭志斌, 王海宁, 卢善富, 相艳. 1~5 kW高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆的理论模拟与组装测试[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [13] | 刘海芹, 李博文, 凌喆, 刘亮, 俞娟, 范一民, 勇强. 羟基-炔点击化学改性半乳甘露聚糖薄膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1370-1378. |
| [14] | 张雪婷, 胡激江, 赵晶, 李伯耿. 高分子量聚丙二醇在微通道反应器中的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1343-1351. |
| [15] | 吴心远, 刘奇磊, 曹博渊, 张磊, 都健. Group2vec:基于无监督机器学习的基团向量表示及其物性预测应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1187-1194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号