化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (1): 257-275.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220955
收稿日期:2022-07-08
修回日期:2022-09-20
出版日期:2023-01-05
发布日期:2023-03-20
通讯作者:
任钟旗
作者简介:宇国佳(1995—),女,博士研究生,gjyubuct@163.com基金资助:
Guojia YU( ), Dongyu JIN(
), Dongyu JIN( ), Zhiyong ZHOU, Fan ZHANG, Zhongqi REN(
), Zhiyong ZHOU, Fan ZHANG, Zhongqi REN( )
)
Received:2022-07-08
Revised:2022-09-20
Online:2023-01-05
Published:2023-03-20
Contact:
Zhongqi REN
摘要:
多孔液体是结合了固-液两相优势的具有稳定永久空腔结构及流动性的新型材料,具有优异的物理化学特性和广阔的应用前景。本文回顾了多孔液体的研究和发展历程,重点总结了各种不同类型多孔液体的设计合成、物性表征和机理模拟计算方面的研究进展,详细分析了多孔液体的形成和作用机理,介绍了多孔液体在气体分离、手性诱导、萃取分离及催化等方面的应用及进展。最后,对多孔液体的未来发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
宇国佳, 靳冬玉, 周智勇, 张帆, 任钟旗. 多孔液体的设计合成与应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 257-275.
Guojia YU, Dongyu JIN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Fan ZHANG, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of porous liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 257-275.
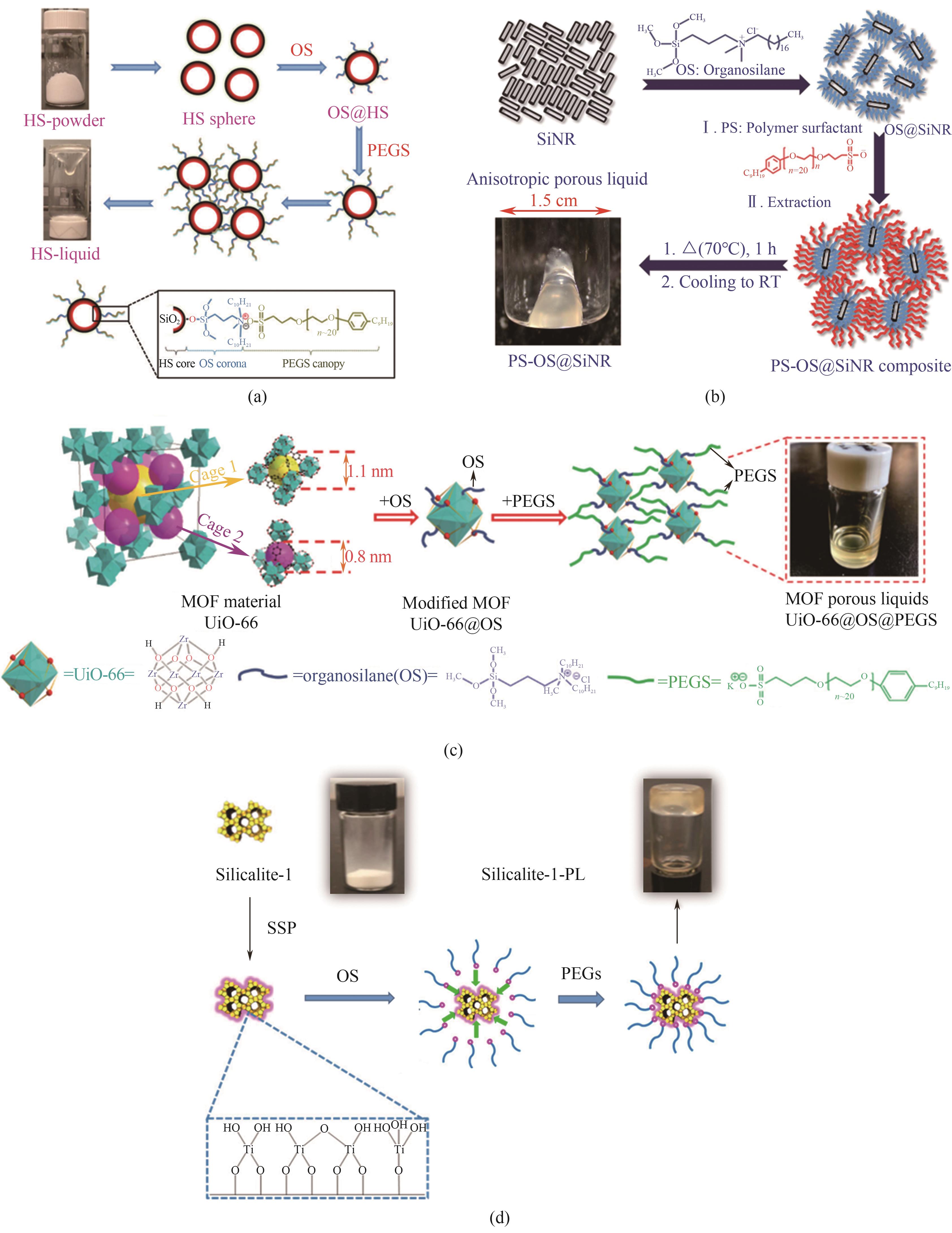
图4 合成示意图:(a)HS基多孔液体表面工程法[11];(b)基于不同长径比的空心二氧化硅纳米棒基多孔液体[16];(c)UiO-66@OS@PEGS多孔液体[17];(d)基于溶胶-凝胶法的silicalite-1基多孔液体[18]
Fig.4 Synthesis schematic diagrams: (a) HS-based PLs by surface engineering method[11]; (b) hollow silica nanorod-based PLs based on different aspect ratio[16]; (c) UiO-66@OS@PEGS PLs[17]; (d) silicalite-1-based PLs based on sol-gel method[18]
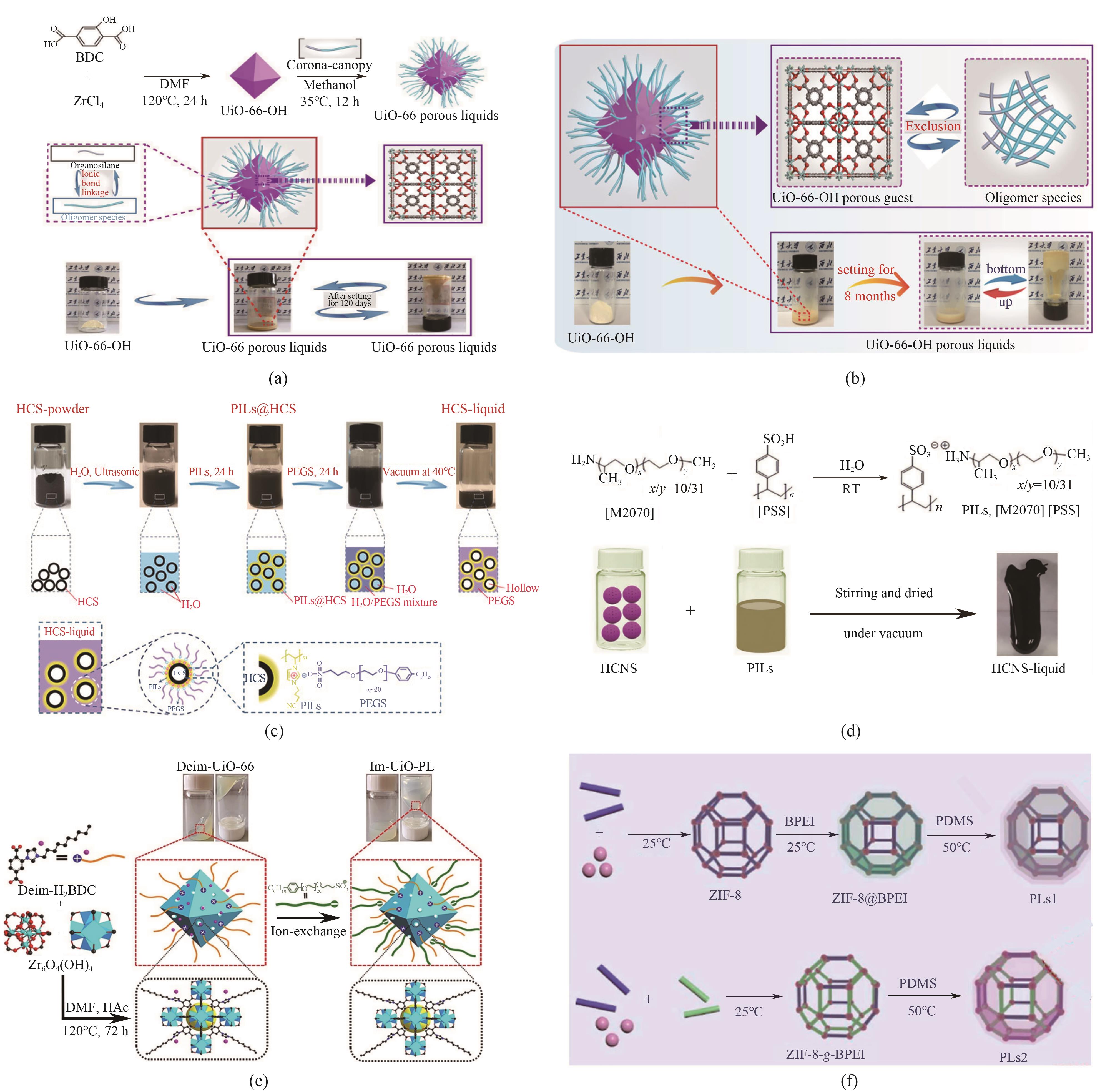
图5 合成示意图:(a)UiO-66 porous liquids[19];(b)UiO-66-OH porous liquids[20];(c)HCS-liquid[21];(d)[M2070][PSS]以及HCNS-liquid[22];(e)Im-UiO-PL[23];(f)基于ZIF-8@BPEI和ZIF-8-g-BPEI的多孔液体[24]
Fig.5 Synthesis schematic diagrams: (a) UiO-66 PLs[19]; (b) UiO-66-OH PLs [20]; (c) HCS-liquid [21]; (d) [M2070][PSS] and HCNS-liquid [22]; (e) Im-UiO-PL [23]; (f) PLs based on ZIF-8@BPEI and ZIF-8-g-BPEI[24]

图6 (a)n-C12的合成[31];(b)n-C12的八面体空心笼结构图[32];(c)以冠醚为位阻溶剂的多孔液体合成示意图[12];(d)多孔液体18-C-6-PL/15-C-5-PL的合成示意图[33];(e)液体配位笼的合成示意图[34];(f)孔隙度筛选结果[36];(g)加扰笼CC33:133-R和CC15-R的结构,以及对几种气体的吸收效果[37];(h)MOP基多孔液体的合成示意图[38]
Fig.6 (a) Synthesis of n-C12[31]; (b) Structure of octahedral hollow cage of n-C12[32]; (c) Synthesis schematic diagram of PL with crown ether[12]; (d) Synthesis schematic diagram of 18-C-6-PL/15-C-5-PL [33]; (e) Synthesis schematic diagram of liquid coordination cages[34]; (f) Plot summarising the results from the porosity screen[36]; (g) Structures of scrambled cages CC33:133-R and CC15-R, and the absorption effect on several gases[37]; (h) Synthesis schematic diagram of MOP-based PLs[38]

图7 (a)[Bpy][NTf2]的分子结构和ZIF-8的晶体结构以及合成的ZIF-8-[Bpy][NTf2]胶体的丁达尔效应[42];(b)ZIF-8/HKUST-1/Mg-MOF-74与[P6,6,6,14][NTf2]基多孔液体的合成示意图[43];(c)ZIF-8基多孔液体的合成示意图[44];(d)基于UiO-66-liquid/[M2070][IPA]的合成以及对气体分子吸附示意图[45];(e)MOF基多孔液体的合成示意图[14];(f)多孔液体对乙烷/乙烯的选择性分离效果[46];(g)H-ZSM-5-liquid/[P66614][Br]的合成示意图[51]
Fig.7 (a) Molecular structure of [Bpy][NTf2], crystal structure of ZIF-8 and the Tindal effect of the synthesized ZIF-8-[Bpy][NTf2] colloids[42]; (b) Synthesis schematic diagram of ZIF-8/HKUST-1/Mg-MOF-74 with [P6,6,6,14][NTf2]-based PLs[43]; (c) Synthesis schematic diagram of ZIF-8-based PLs[44]; (d) Synthesis schematic diagram of UiO-66-liquid/[M2070][IPA]-based and the adsorption of gas molecules[45]; (e) Synthesis schematic diagram of MOF-based PLs[14]; (f) Selective separation effect of porous liquid on ethane/ethylene[46]; (g) Synthesis schematic diagram of H-ZSM-5-liquid/[P66614][Br] [51]
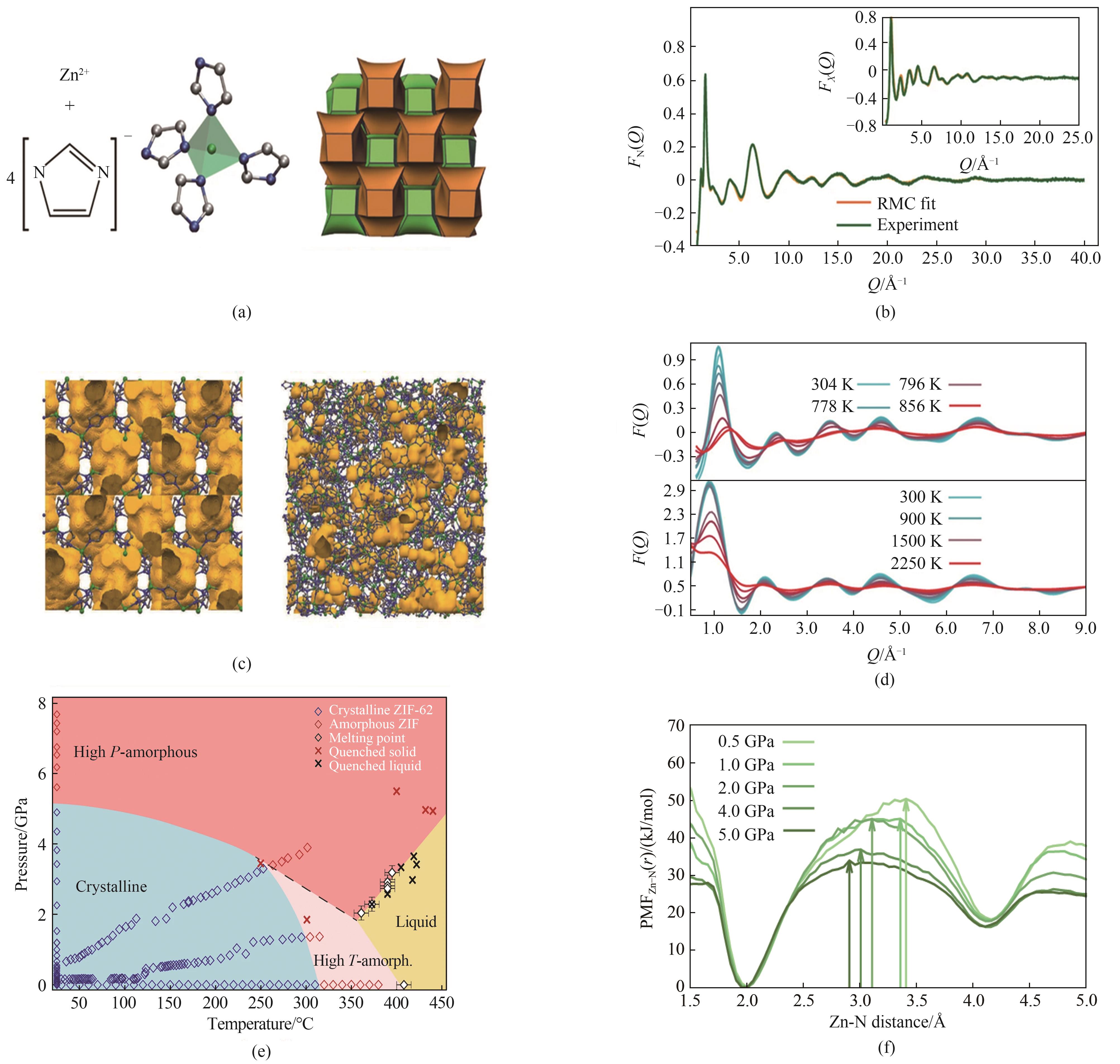
图8 (a)ZIF-4的基本构成单元和结构[13];(b)实验中子结构因子F(Q)数据[13];(c)ZIF-4的晶体结构以及熔融淬火玻璃的原子构型[13];(d)ZIF-4加热后的实验和计算的结构因子数据[13];(e)实验得出的ZIF-62的P-T相图[52];(f)1200 K时,在0.1~5.0 GPa压力间Zn-N距离的平均力势(PMF)[52]
Fig.8 (a) The basic building block of ZIF-4[13]; (b) Experimental neutron structure factor F(Q) data[13]; (c) Crystalline structure of ZIF-4 and atomic configuration of the melt-quenched glass[13]; (d) Experimental and calculated structure factors of ZIF-4 after heating[13]; (e) P-T phase diagram of ZIF-62[52]; (f) Potential of mean force (PMF) for the Zn-N distance of ZIF-62 at pressures between 0.1 GPa and 5.0 GPa, at a temperature of 1200 K[52]

图9 (a)不同直径二氧化硅纳米颗粒和8600个水分子的模型体系中纳米颗粒的距离[57];(b)[P66614][Br]与H-ZSM-5[100]面上的酸位点间的氢键作用分子动力学模拟图[51];(c)UiO-66/PDMS4k(蓝色)复合体系的平衡构型,以及PDMS4k(红线和蓝线)和UiO-66原子(绿线)的密度与复合体系平衡构型在Z坐标的关系[14];(d)ABS-1CO2的梯度等值面[59];(e)硅基多孔离子液体(HSL1)对CO2的吸附位点[60];(f)累积的气体分子数量与笼子中心的径向距离的函数以及笼内和附近的气体分子的PMF图[61];(g)含CO2的POCs的最优结构[62];(h)298.15 K和60 bar(1 bar=105 Pa)条件下,笼和溶剂的比例为1∶12的多孔液体中CO2和N2(CH4)的空间分布函数[63]
Fig.9 (a) Distances of nanoparticles in a model system with different diameters of silica nanoparticles and 8600 water molecules[57]; (b) Molecular dynamics simulation of the hydrogen bond between [P66614][Br] and acid sites on the H-ZSM-5[100] surface[51]; (c) Equilibrium configuration of the UiO-66/PDMS4k (blue) complex system and the density of PDMS4k (red and blue lines) and UiO-66 atoms (green line) versus the equilibrium configuration of the complex system in Z-coordinate[14]; (d) Gradient equivalence surface of ABS-1CO2[59]; (e) CO2 adsorption sites of silica-based porous ionic liquid (HSL1)[60]; (f) PMF diagram of the accumulated number of gas molecules as a function of the radial distance from the center of the cage, and the gas molecules in and near the cage[61]; (g) Optimal structures of CO2-containing POCs[62]; (h) Spatial distribution functions of CO2 and N2 (CH4) in PLs with a 1∶12 ratio of cage to solvent at 298.15 K and 60 bar (1 bar=105 Pa)[63]
| 名称 | CO2吸收量 | 测试条件 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| hollow silica PLs | 0.9 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| HCS-liquid | 0.57 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| HCNS-liquid | 4.66%(质量) | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| 15-C-5-PL | 0.375 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| 18-C-6-PL | 0.429 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
| COF-300-PLs | 0.78 mol/g | 273 K,0.03 bar | [ |
| POCs/[BPy][NTf2] | 104.30 µmol/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| POCs/hexachloropropene | 55 μmmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| PoLi-Bc | 5.5 cm3/g | 273 K,1 bar | [ |
| Im-UiO-PL | 5.93 mmol/g | 298 K,9 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-liquid/[M2070][IPA] | 1.66 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-liquid-M2070 | 0.86 mmol/g | 298 K,30 bar | [ |
| UiO-66@OS@PEGS | 28 mg/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-PL | 30.8 cm3/g | 273 K,10 bar | [ |
| PL1M2070 | 2.393 mmol/g | 298 K,2 MPa | [ |
| PLs-5% | 6.9 mg/g | 313 K | [ |
| ZIF-8 PLs | 3.43 cm3/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| H-ZSM-5 PLs | 0.46 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| ZIF-67-PLs-10 | 9.542 mmol/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| ZIF-8 PLs | 1.2 mmol/g | 303 K,5 bar | [ |
| ZIF-8/[DBU-PEG][NTf2] | 1.54 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| PAF-1/Genosorb PLs | 0.72 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
| Al(fum)(OH)/PDMS PLs | 0.95 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
表1 不同类型多孔液体对CO2的吸收效果
Table 1 Effect of different types of porous liquids on CO2 absorption
| 名称 | CO2吸收量 | 测试条件 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| hollow silica PLs | 0.9 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| HCS-liquid | 0.57 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| HCNS-liquid | 4.66%(质量) | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| 15-C-5-PL | 0.375 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| 18-C-6-PL | 0.429 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
| COF-300-PLs | 0.78 mol/g | 273 K,0.03 bar | [ |
| POCs/[BPy][NTf2] | 104.30 µmol/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| POCs/hexachloropropene | 55 μmmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| PoLi-Bc | 5.5 cm3/g | 273 K,1 bar | [ |
| Im-UiO-PL | 5.93 mmol/g | 298 K,9 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-liquid/[M2070][IPA] | 1.66 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-liquid-M2070 | 0.86 mmol/g | 298 K,30 bar | [ |
| UiO-66@OS@PEGS | 28 mg/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| UiO-66-PL | 30.8 cm3/g | 273 K,10 bar | [ |
| PL1M2070 | 2.393 mmol/g | 298 K,2 MPa | [ |
| PLs-5% | 6.9 mg/g | 313 K | [ |
| ZIF-8 PLs | 3.43 cm3/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| H-ZSM-5 PLs | 0.46 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| ZIF-67-PLs-10 | 9.542 mmol/g | 298 K,1 bar | [ |
| ZIF-8 PLs | 1.2 mmol/g | 303 K,5 bar | [ |
| ZIF-8/[DBU-PEG][NTf2] | 1.54 mmol/g | 298 K,10 bar | [ |
| PAF-1/Genosorb PLs | 0.72 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
| Al(fum)(OH)/PDMS PLs | 0.95 mmol/g | 298 K,5 bar | [ |
| 1 | O’Reilly N, Giri N, James S L. Porous liquids[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2007, 13(11): 3020-3025. |
| 2 | Bennett T D, Coudert F X, James S L, et al. The changing state of porous materials[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20(9): 1179-1187. |
| 3 | Liu H, Liu B, Lin L C, et al. A hybrid absorption-adsorption method to efficiently capture carbon[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 1-7. |
| 4 | Knebel A, Bavykina A, Datta S J, et al. Solution processable metal-organic frameworks for mixed matrix membranes using porous liquids[J]. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(12): 1346-1353. |
| 5 | Wang D C, Xin Y Y, Yao D D, et al. Shining light on porous liquids: from fundamentals to syntheses, applications and future challenges[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(1): 2104162. |
| 6 | 王德超, 辛洋洋, 李晓倩, 等. 多孔液体在气体捕集与分离领域的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(10): 1874-1886. |
| Wang D C, Xin Y Y, Li X Q, et al. Porous liquids and their applications in gas capture and separation[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(10): 1874-1886. | |
| 7 | 李晓倩, 张靖, 苏芳芳, 等. 多孔离子液体的构筑及应用[J]. 化学进展, 2022, 80: 848-860. |
| Li X Q, Zhang J, Su F F, et al. Construction and application of porous ionic liquids[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2022, 80: 848-860. | |
| 8 | Robbins T A, Knobler C B, Bellew D R, et al. A highly adaptive and strongly binding hemicarcerand[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1994, 116(1): 111-122. |
| 9 | Hsu S C N, Ramesh M, Espenson J H, et al. Membership rules for a molecular box: the admission process and protection provided to guest molecules[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2003, 115(23): 2767-2770. |
| 10 | Bourlinos A B, Chowdhury S R, Jiang D D, et al. Weakly solvated PEG-functionalized silica nanoparticles with liquid-like behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40(18): 5095-5097. |
| 11 | Zhang J S, Chai S H, Qiao Z A, et al. Porous liquids: a promising class of media for gas separation[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(3): 946-950. |
| 12 | Giri N, Del Popolo M G, Melaugh G, et al. Liquids with permanent porosity[J]. Nature, 2015, 527(7577): 216-220. |
| 13 | Gaillac R, Pullumbi P, Beyer K A, et al. Liquid Metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(11): 1149-1154. |
| 14 | He S F, Chen L H, Cui J, et al. General way to construct micro-and mesoporous metal-organic framework-based porous liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(50): 19708-19714. |
| 15 | Erdosy D P, Wenny M B, Cho J, et al. Microporous water with high gas solubilities[J]. Nature, 2022, 608(7924): 712-718. |
| 16 | Kumar R, Dhasaiyan P, Naveenkumar P M, et al. A solvent-free porous liquid comprising hollow nanorod-polymer surfactant conjugates[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2019, 1(10): 4067-4075. |
| 17 | Zhao X R, An S H, Dai J L, et al. Transforming surface-modified metal organic framework powder into room temperature porous liquids via an electrical balance strategy[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(29): 12715-12722. |
| 18 | Liu Y T, Bai Y, Tian T. Preparation of porous liquid based on silicalite-1[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(23): 3984. |
| 19 | Wang D C, Xin Y Y, Li X Q, et al. Transforming metal-organic frameworks into porous liquids via a covalent linkage strategy for CO2 capture[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(2): 2600-2609. |
| 20 | Wang D C, Xin Y Y, Li X Q, et al. A universal approach to turn UiO-66 into type 1 porous liquids via post-synthetic modification with corona-canopy species for CO2 capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 416: 127625. |
| 21 | Li P P, Schott J A, Zhang J S, et al. Electrostatic-assisted liquefaction of porous carbons[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2017, 56(47): 14958-14962. |
| 22 | Li P P, Wang D C, Zhang L, et al. An in situ coupling strategy toward porous carbon liquid with permanent porosity[J]. Small, 2021, 17(10): 2006687. |
| 23 | Zou Y H, Huang Y B, Si D H, et al. Porous metal-organic framework liquids for enhanced CO2 adsorption and catalytic conversion[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2021, 60(38): 20915-20920. |
| 24 | Li X Q, Yao D D, Wang D C, et al. Amino-functionalized ZIFs-based porous liquids with low viscosity for efficient low-pressure CO2 capture and CO2/N2 separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132296. |
| 25 | Liu J, Thallapally P K, McGrail B P, et al. Progress in adsorption-based CO2 capture by metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(6): 2308-2322. |
| 26 | Masoomi M Y, Morsali A, Dhakshinamoorthy A, et al. Mixed‐metal MOFs: unique opportunities in metal-organic framework (MOF) functionality and design[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2019, 58(43): 15188-15205. |
| 27 | Tozawa T, Jones J T A, Swamy S I, et al. Porous organic cages[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(12): 973-978. |
| 28 | Hasell T, Cooper A I. Porous organic cages: soluble, modular and molecular pores[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1(9): 1-14. |
| 29 | Geng K Y, He T, Liu R Y, et al. Covalent organic frameworks: design, synthesis, and functions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(16): 8814-8933. |
| 30 | Feng X, Ding X S, Jiang D L. Covalent organic frameworks[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(18): 6010-6022. |
| 31 | Giri N, Davidson C E, Melaugh G, et al. Alkylated organic cages: from porous crystals to neat liquids[J]. Chemical Science, 2012, 3(6): 2153-2157. |
| 32 | Melaugh G, Giri N, Davidson C E, et al. Designing and understanding permanent microporosity in liquids[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(20): 9422-9431. |
| 33 | Jie K C, Onishi N, Schott J A, et al. Transforming porous organic cages into porous ionic liquids via a supramolecular complexation strategy[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2020, 59(6): 2268-2272. |
| 34 | Ma L, Haynes C J E, Grommet A B, et al. Coordination cages as permanently porous ionic liquids[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2020, 12(3): 270-275. |
| 35 | Greenaway R L, Holden D, Eden E G B, et al. Understanding gas capacity, guest selectivity, and diffusion in porous liquids[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(4): 2640-2651. |
| 36 | Kearsey R J, Alston B, Briggs M E, et al. Accelerated robotic discovery of type Ⅱ porous liquids[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(41): 9454-9465. |
| 37 | Egleston B D, Luzyanin K V, Brand M C, et al. Controlling gas selectivity in molecular porous liquids by tuning the cage window size[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(19): 7362-7366. |
| 38 | Deng Z, Ying W, Gong K, et al. Facilitate gas transport through metal-organic polyhedra constructed porous liquid membrane[J]. Small, 2020, 16(11): 1907016. |
| 39 | Kaur G, Kumar H, Singla M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: a comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022,351: 118556. |
| 40 | Ibrahim M H, Hayyan M, Hashim M A, et al. The role of ionic liquids in desulfurization of fuels: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 76: 1534-1549. |
| 41 | Yan Q, Zang H J, Wu C C, et al. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of novel ionic liquids based on thiazolium cation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2015, 204: 156-161. |
| 42 | Liu S J, Liu J D, Hou X D, et al. Porous liquid: a stable ZIF-8 colloid in ionic liquid with permanent porosity[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34(12): 3654-3660. |
| 43 | Gomes M C, Pison L, Cervinka C, et al. Porous ionic liquids or liquid metal-organic frameworks? [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2018, 57(37): 11909-11912. |
| 44 | Shan W, Fulvio P F, Kong L Y, et al. New class of type Ⅲ porous liquids: a promising platform for rational adjustment of gas sorption behavior[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(1): 32-36. |
| 45 | Zhao X M, Yuan Y H, Li P P, et al. A polyether amine modified metal organic framework enhanced the CO2 adsorption capacity of room temperature porous liquids[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(87): 13179-13182. |
| 46 | Lai B B, Cahir J, Tsang M Y, et al. Type 3 porous liquids for the separation of ethane and ethene[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 13(1): 932-936. |
| 47 | Hasell T, Schmidtmann M, Cooper A I. Molecular doping of porous organic cages[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(38): 14920-14923. |
| 48 | Briggs M E, Cooper A I. A perspective on the synthesis, purification, and characterization of porous organic cages[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(1): 149-157. |
| 49 | Olsbye U, Svelle S, Bjørgen M, et al. Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons: how zeolite cavity and pore size controls product selectivity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(24): 5810-5831. |
| 50 | Carta M, Malpass-Evans R, Croad M, et al. An efficient polymer molecular sieve for membrane gas separations[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6117): 303-307. |
| 51 | Li P P, Chen H, Schott J A, et al. Porous liquid zeolites: hydrogen bonding-stabilized H-ZSM-5 in branched ionic liquids[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(4): 1515-1519. |
| 52 | Widmer R N, Lampronti G I, Anzellini S, et al. Pressure promoted low-temperature melting of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(4): 370-376. |
| 53 | Li X Q, Wang D C, He Z J, et al. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-based porous liquids with low viscosity for CO2 and toluene uptakes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 129239. |
| 54 | Jagiello J, Sterling M, Eliasova P, et al. Structural analysis of IPC zeolites and related materials using positron annihilation spectroscopy and high-resolution argon adsorption[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(22): 15269-15277. |
| 55 | Mow R E, Lipton A S, Shulda S, et al. Colloidal three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks and their application as porous liquids[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(44): 23455-23462. |
| 56 | Xin Y Y, Wang D C, Yao D D, et al. Post-synthetic modification of UiO-66-OH toward porous liquids for CO2 capture[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 46(5): 2189-2197. |
| 57 | Sheng L S, Chen Z Q, Wang Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of stability and fluidity of porous liquids[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 536: 147951. |
| 58 | Sheng L S, Chen Z Q. Molecular dynamics study of dispersion and fluidity of porous liquids with different pore sizes[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 333: 115890. |
| 59 | Yin J, Zhang J R, Wang C, et al. Theoretical insights into CO2/N2 selectivity of the porous ionic liquids constructed by ion-dipole interactions[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 344: 117676. |
| 60 | Zhang J R, Lv N X, Chao Y H, et al. The interaction nature between hollow silica-based porous ionic liquids and CO2: a DFT study[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 2020, 100: 107694. |
| 61 | Zhang F, Yang F C, Huang J S, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of gas storage in porous liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2016, 120(29): 7195-7200. |
| 62 | Yin J, Fu W D, Zhang J R, et al. Unraveling the mechanism of CO2 capture and separation by porous liquids[J]. RSC advances, 2020, 10(70): 42706-42717. |
| 63 | Yin Z J, Chen H Y, Yang L, et al. Investigations of CO2 capture from gas mixtures using porous liquids[J]. Langmuir, 2021, 37(3): 1255-1266. |
| 64 | Bhattacharjee A, Kumar R, Sharma K P. Composite porous liquid for recyclable sequestration, storage and in situ catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide at room temperature[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(16): 3303-3314. |
| 65 | Zhou Y J, Avila J, Berthet N, et al. Integrated, one-pot carbon capture and utilisation using porous ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(64): 7922-7925. |
| 66 | Li X Q, Wang D C, He Z J, et al. Dual stimuli-responsive porous ionic liquids with reversible phase transition behavior based on ionic liquid crystals for CO2 and C2H4 adsorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(25): 13333-13344. |
| 67 | Shi T, Zheng Y P, Wang T Y, et al. Effect of pore size on the carbon dioxide adsorption behavior of porous liquids based on hollow silica[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2018, 19(1): 130-137. |
| 68 | Kai A T, Egleston B D, Tarzia A, et al. Modular type Ⅲ porous liquids based on porous organic cage microparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(51): 2106116. |
| 69 | Sheng L S, Chen Z Q, Wang X, et al. Transforming porous silica nanoparticles into porous liquids with different canopy structures for CO2 capture[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(7): 5687-5697. |
| 70 | Avila J, Lepre L F, Santini C C, et al. High-performance porous ionic liquids for low-pressure CO2 capture[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2021, 60(23): 12876-12882. |
| 71 | Cahir J, Tsang M Y, Lai B B, et al. Type 3 porous liquids based on non-ionic liquid phases—a broad and tailorable platform of selective, fluid gas sorbents[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(8): 2077-2084. |
| 72 | Wang Y, Sun Y W, Bian H, et al. Cyclodextrin porous liquid materials for efficient chiral recognition and separation of nucleosides[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(41): 45916-45928. |
| 73 | Wang Y, Feng Z, Sun Y W, et al. Chiral induction in a novel self-assembled supramolecular system composed of α-cyclodextrin porous liquids, chiral silver nanoparticles and planar conjugated molecules[J]. Soft Matter, 2022, 18(5): 975-982. |
| 74 | Chen L, Reiss P S, Chong S Y, et al. Separation of rare gases and chiral molecules by selective binding in porous organic cages[J]. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(10): 954-960. |
| 75 | Wu J M, Wu X M, Zhao P P, et al. Extraction desulphurization of fuels using ZIF-8-based porous liquid[J]. Fuel, 2021, 300: 121013. |
| 76 | 桂鑫. PL-MCM-41多孔液体材料制备及对模拟油品中硫,氮脱除性能研究[D]. 北京:中国石油大学, 2019. |
| Gui X. Synthesis of PL-MCM-41 porous liquid and study on the performance of desulfurization and denitrification in the simulated oil[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2019. | |
| 77 | Wang Z H, Zhao P P, Wu J M, et al. ZIF-8-porous ionic liquids for the extraction of 2, 2, 3, 3-tetrafluoro-1-propanol and water mixture[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(19): 8557-8562. |
| 78 | Horin I, Shalev O, Cohen Y. Aggregation mode, host-guest chemistry in water, and extraction capability of an uncharged, water-soluble, liquid pillar [5] arene derivative[J]. ChemistryOpen, 2021, 10(11): 1111-1115. |
| 79 | Hemming E B, Masters A F, Maschmeyer T. The encapsulation of metal nanoparticles within porous liquids[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(75): 11179-11182. |
| 80 | Hemming E B, Masters A F, Maschmeyer T. Exploring opportunities for platinum nanoparticles encapsulated in porous liquids as hydrogenation catalysts[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2020, 26(31): 7059-7064. |
| 81 | Yang N, Lu L J, Zhu L H, et al. Phosphomolybdic acid encapsulated in ZIF-8-based porous ionic liquids for reactive extraction desulfurization of fuels[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2022, 9(1): 165-178. |
| [1] | 金伟其, 吴月荣, 王霞, 李力, 裘溯, 袁盼, 王铭赫. 化工园区工业气体泄漏气云红外成像检测技术与国产化装备进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 32-44. |
| [2] | 董茂林, 陈李栋, 黄六莲, 吴伟兵, 戴红旗, 卞辉洋. 酸性助水溶剂制备木质纳米纤维素及功能应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2281-2295. |
| [3] | 董益秀, 王如竹. 高温热泵的循环、工质研究及应用展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 133-144. |
| [4] | 高端辉, 肖卫强, 高峰, 夏倩, 汪曼秋, 卢昕博, 詹晓力, 张庆华. 聚酰亚胺基气凝胶材料的制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2757-2773. |
| [5] | 王祺, 房阔, 贺聪慧, 王凯军. 流动电极电容去离子技术综述:研究进展与未来挑战[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 975-989. |
| [6] | 汪艳秋,仲兆祥,邢卫红. 三维金属氧化物纳米材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2339-2353. |
| [7] | 史玉婷, 皇甫林, 李长明, 王月, 高士秋, 伞晓广, 韩振南, 余剑. V2O5-MoO3/TiO2催化滤袋的制备及中试应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5598-5606. |
| [8] | 齐娜, 宋伟, 刘立明, 吴静. 生物催化C—C成键反应及其应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 216-228. |
| [9] | 王天宇, 蒋文明, 刘杨. 含油污泥阴燃处理技术研究与进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1411-1423. |
| [10] | 郭晓璐,喻健良,闫兴清,徐鹏,徐双庆. 超临界CO2管道泄漏特性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5430-5442. |
| [11] | 张霄玲,鲍佳宁,李运甲,皇甫林,李文松,高士秋,许光文,李长明,余剑. 工业MnOx颗粒催化剂的制备及其低温脱硝应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5169-5177. |
| [12] | 曾昭文, 郑成, 毛桃嫣, 魏渊, 肖润辉, 彭思玉. 微波在化工过程中的研究及应用进展[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S1): 1-14. |
| [13] | 生丽莎, 陈振乾. 静电辅助多孔液体的制备及特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1163-1170. |
| [14] | 常圣强, 李望良, 张晓宇, 马力强, 鲁长波, 安高军. 生物质气化发电技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(8): 3318-3330. |
| [15] | 林志峰, 胡日茗, 周晓龙. 镍基催化剂的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(S1): 26-36. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号