化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (10): 3979-3994.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230739
• 综述与专论 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-07-17
修回日期:2023-09-08
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-12-22
通讯作者:
吴志强
作者简介:张榕江(1994—),男,博士研究生,zhangrj@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Rongjiang ZHANG( ), Bo ZHANG, Gen LIU, Bolun YANG, Zhiqiang WU(
), Bo ZHANG, Gen LIU, Bolun YANG, Zhiqiang WU( )
)
Received:2023-07-17
Revised:2023-09-08
Online:2023-10-25
Published:2023-12-22
Contact:
Zhiqiang WU
摘要:
化学链技术在化学品生产过程强化方面表现出极大潜力,相较于传统工艺可提高㶲效率并降低碳排放。综述了目前常见的化学链制化学品工艺,主要包括化学链重整/部分氧化制合成气和氢气、低碳烷烃化学链氧化脱氢/选择性氢燃烧制烯烃、甲烷化学链氧化偶联制乙烯、甲烷化学链脱氢芳构化制苯、化学链选择性氧化制含氧有机化合物(如甲醇、环氧乙烷和甲酸等)。深入理解载氧体理化性质与化学链反应性能间的构效关系有助于实现载氧体理性设计。目前在载氧体设计方面已具备坚实的理论基础,从利用氧化物的热力学平衡氧分压筛选载氧体活性组分,到基于表面工程策略调控晶格氧释放动力学,再到通过合理构建结构和电子描述符,深入剖析载氧体性能强化策略。实验和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算数据驱动的可解释机器学习可实现载氧体的高通量筛选,极大拓宽了载氧体筛选范围,并降低试错成本。随着化学链技术的发展,载氧体这一概念可被进一步拓展至循环材料,如载氮体和载氯体等。光/电驱动的化学链过程为在低温或室温下实现高附加值产物的合成提供了新思路,拓宽了化学链技术的应用范围。此外,化学链技术还可用于共沸有机物分离过程强化,对低成本、低污染和低排放分离过程的开发具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
张榕江, 张博, 刘根, 杨伯伦, 吴志强. 化学链制化学品工艺及循环材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 3979-3994.
Rongjiang ZHANG, Bo ZHANG, Gen LIU, Bolun YANG, Zhiqiang WU. Progress in chemical looping process for chemical production and looping materials research[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 3979-3994.
| 载氧体 | 原料组成 | 再生气氛 | 温度/℃ | 空速或流速/(ml/min) | 转化率/% | 合成气产量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-(α-MoC)/Al2O3 | 5% CH4/Ar | 5% CO2/Ar | 500 | 100 | 62 | 4.2 | [ |
| Rh-LaCeO4-x | 10% CH4/Ar | 2% CO2/Ar | 650 | 50 | 88 | 0.5 | [ |
| La0.8Ce0.1Ni0.4Ti0.6O3 | 5% CH4/He | 5% O2/He | 650 | 50 | 45 | 3.5 | [ |
| Fe2O3@SBA-16 | 20% CH4/N2 | 10% O2/N2 | 800 | 200 | 28 | 3.3 | [ |
| Ni0.5WO x /Al2O3 | 16.7% CH4/Ar | 10% O2/He | 800 | 30 | 58 | 3.8 | [ |
| 10% CeO2/LaFeO3 | 5% CH4/Ar | H2O/N2 | 800 | 200 | 67 | 9.9 | [ |
| La1.6Sr0.4FeCoO6 | 40% CH4/N2 | H2O/N2 | 850 | 50 | 45 | 7.0 | [ |
| La0.5Ce0.5FeO3 | 10% CH4/N2 | 10% CO2/N2 | 850 | 80 | 80 | 4.2 | [ |
| BaFe3Al9O19 | 5% CH4/He | 5% O2/He | 850 | 15 | 86 | 4.2 | [ |
| La0.85Sr0.15Fe0.95Al0.05O3 | 5% CH4/N2 | 5% CO2/N2 | 900 | 700 | 79 | 10.6 | [ |
| NiFe2O4@SBA-15 | 10% CH4/Ar | 10% O2/Ar | 900 | 100 | 47 | 5.2 | [ |
| Y3Fe2Al3O12 | 5% CH4/He | — | 900 | 30 | 94 | 4.7 | [ |
| FeWO3/SiO2 | 10% CH4/N2 | 21% O2/N2 | 900 | 60 | 62 | 4.1 | [ |
表1 甲烷化学链重整载氧体反应性能对比
Table 1 Comparison of reaction performance of oxygen carriers for methane chemical looping reforming
| 载氧体 | 原料组成 | 再生气氛 | 温度/℃ | 空速或流速/(ml/min) | 转化率/% | 合成气产量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-(α-MoC)/Al2O3 | 5% CH4/Ar | 5% CO2/Ar | 500 | 100 | 62 | 4.2 | [ |
| Rh-LaCeO4-x | 10% CH4/Ar | 2% CO2/Ar | 650 | 50 | 88 | 0.5 | [ |
| La0.8Ce0.1Ni0.4Ti0.6O3 | 5% CH4/He | 5% O2/He | 650 | 50 | 45 | 3.5 | [ |
| Fe2O3@SBA-16 | 20% CH4/N2 | 10% O2/N2 | 800 | 200 | 28 | 3.3 | [ |
| Ni0.5WO x /Al2O3 | 16.7% CH4/Ar | 10% O2/He | 800 | 30 | 58 | 3.8 | [ |
| 10% CeO2/LaFeO3 | 5% CH4/Ar | H2O/N2 | 800 | 200 | 67 | 9.9 | [ |
| La1.6Sr0.4FeCoO6 | 40% CH4/N2 | H2O/N2 | 850 | 50 | 45 | 7.0 | [ |
| La0.5Ce0.5FeO3 | 10% CH4/N2 | 10% CO2/N2 | 850 | 80 | 80 | 4.2 | [ |
| BaFe3Al9O19 | 5% CH4/He | 5% O2/He | 850 | 15 | 86 | 4.2 | [ |
| La0.85Sr0.15Fe0.95Al0.05O3 | 5% CH4/N2 | 5% CO2/N2 | 900 | 700 | 79 | 10.6 | [ |
| NiFe2O4@SBA-15 | 10% CH4/Ar | 10% O2/Ar | 900 | 100 | 47 | 5.2 | [ |
| Y3Fe2Al3O12 | 5% CH4/He | — | 900 | 30 | 94 | 4.7 | [ |
| FeWO3/SiO2 | 10% CH4/N2 | 21% O2/N2 | 900 | 60 | 62 | 4.1 | [ |
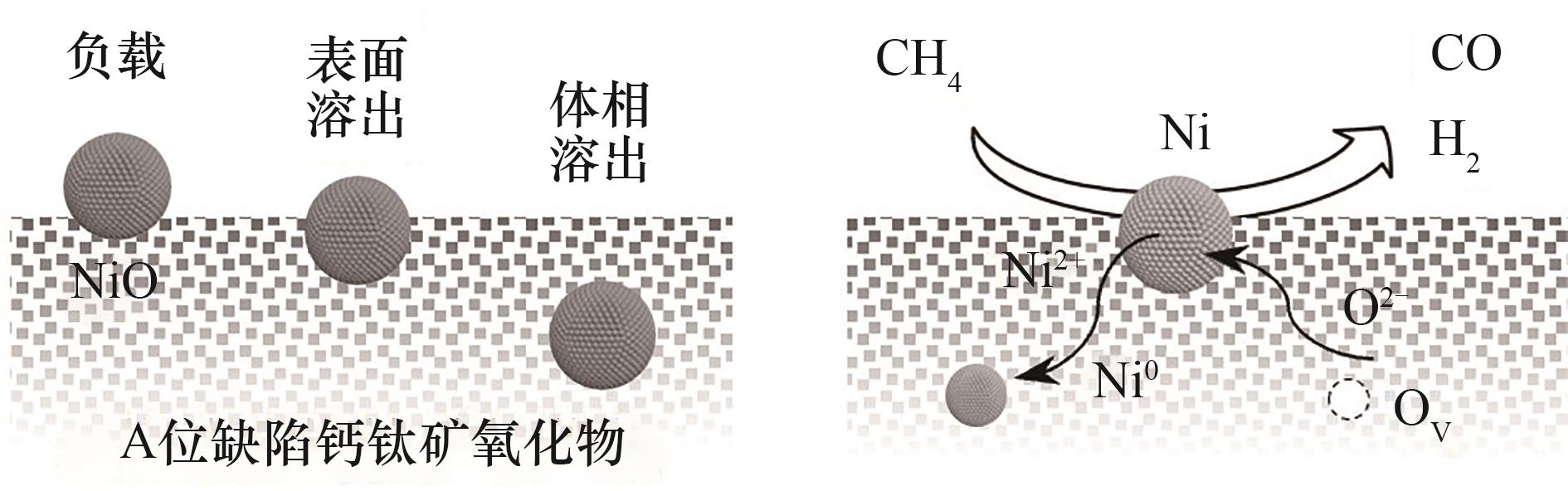
图2 负载与溶出颗粒的对比以及溶出颗粒促进晶格氧迁移[21]
Fig.2 Comparison of supported and exsolved particles and the promotion of lattice oxygen migration by exsolved particles[21]
| 反应类型 | 载氧体 | 原料组成 | 再生气氛 | 温度/℃ | GHSV/h-1 | 转化率/% | 选择性/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-ODH | 0.2Ce/SrFeO3 | 25% C2H6/Ar | 25% CO2/Ar | 700~750 | 6000 | 29 | 82 | [ |
| FeCeTiO x | 20% C2H6/N2 | 20% CO2/Ar | 600 | — | 13 | 84 | [ | |
| Co0.3Mo0.7/Fe2O3 | 10%~16.7% C2H6/Ar | 16.7% O2/Ar | 775~825 | 6000 | 56 | 87 | [ | |
| Mg-La1.6Sr0.4FeCoO6 | 40% C2H6/N2 | 20% O2/N2 | 650~750 | — | 53 | 89 | [ | |
| NaW-LaMnO3 | 40% C2H6/N2 | 20% O2/N2 | 750~800 | — | 71 | 85 | [ | |
| La0.8Sr0.2FeO3@Li2CO3 | 12.5%~80% C2H6/N2 | — | 700 | — | 50 | 91 | [ | |
| Mo-V-O氧化物 | 19% C3H8/N2 | 21% O2/N2 | 500 | 2500 | 36 | 89 | [ | |
| La0.8Sr0.2FeO3@LiBr | 19% C4H10/Ar | — | 500 | — | 75 | 56 | [ | |
| CL-SHC | Ni/HY | 10% C2H6/He | 5% O2/He | 600 | 5100 | 18 | 97 | [ |
| Na2WO4-CaMn0.9Fe0.1O3 | 80% C2H6/Ar | 20% O2/Ar | 650~750 | 600 | 41 | 90 | [ | |
| Mg6MnO8@Na2WO4 | 80% C2H6/Ar | 17% O2/Ar | 850 | 4500 | 81 | 76 | [ | |
| Mg6MnO8@Na3PO4 | 80% C2H6/He | 17% O2/He | 800~850 | 4500 | 78 | 57 | [ | |
| Ce0.92Pb0.08O2/PbO | C3H8∶C3H6∶H2=4∶1∶1 | 1% O2/Ar | 550 | 13200 | 50 | 85 | [ | |
| Ce0.9Bi0.1O2 | C3H8∶C3H6∶H2=4∶1∶1 | 1% O2/Ar | 550 | 13200 | 33 | 77 | [ |
表2 低碳烷烃化学链脱氢载氧体反应性能对比
Table 2 Comparison of reaction performance of oxygen carriers for light alkanes chemical looping dehydrogenation
| 反应类型 | 载氧体 | 原料组成 | 再生气氛 | 温度/℃ | GHSV/h-1 | 转化率/% | 选择性/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-ODH | 0.2Ce/SrFeO3 | 25% C2H6/Ar | 25% CO2/Ar | 700~750 | 6000 | 29 | 82 | [ |
| FeCeTiO x | 20% C2H6/N2 | 20% CO2/Ar | 600 | — | 13 | 84 | [ | |
| Co0.3Mo0.7/Fe2O3 | 10%~16.7% C2H6/Ar | 16.7% O2/Ar | 775~825 | 6000 | 56 | 87 | [ | |
| Mg-La1.6Sr0.4FeCoO6 | 40% C2H6/N2 | 20% O2/N2 | 650~750 | — | 53 | 89 | [ | |
| NaW-LaMnO3 | 40% C2H6/N2 | 20% O2/N2 | 750~800 | — | 71 | 85 | [ | |
| La0.8Sr0.2FeO3@Li2CO3 | 12.5%~80% C2H6/N2 | — | 700 | — | 50 | 91 | [ | |
| Mo-V-O氧化物 | 19% C3H8/N2 | 21% O2/N2 | 500 | 2500 | 36 | 89 | [ | |
| La0.8Sr0.2FeO3@LiBr | 19% C4H10/Ar | — | 500 | — | 75 | 56 | [ | |
| CL-SHC | Ni/HY | 10% C2H6/He | 5% O2/He | 600 | 5100 | 18 | 97 | [ |
| Na2WO4-CaMn0.9Fe0.1O3 | 80% C2H6/Ar | 20% O2/Ar | 650~750 | 600 | 41 | 90 | [ | |
| Mg6MnO8@Na2WO4 | 80% C2H6/Ar | 17% O2/Ar | 850 | 4500 | 81 | 76 | [ | |
| Mg6MnO8@Na3PO4 | 80% C2H6/He | 17% O2/He | 800~850 | 4500 | 78 | 57 | [ | |
| Ce0.92Pb0.08O2/PbO | C3H8∶C3H6∶H2=4∶1∶1 | 1% O2/Ar | 550 | 13200 | 50 | 85 | [ | |
| Ce0.9Bi0.1O2 | C3H8∶C3H6∶H2=4∶1∶1 | 1% O2/Ar | 550 | 13200 | 33 | 77 | [ |
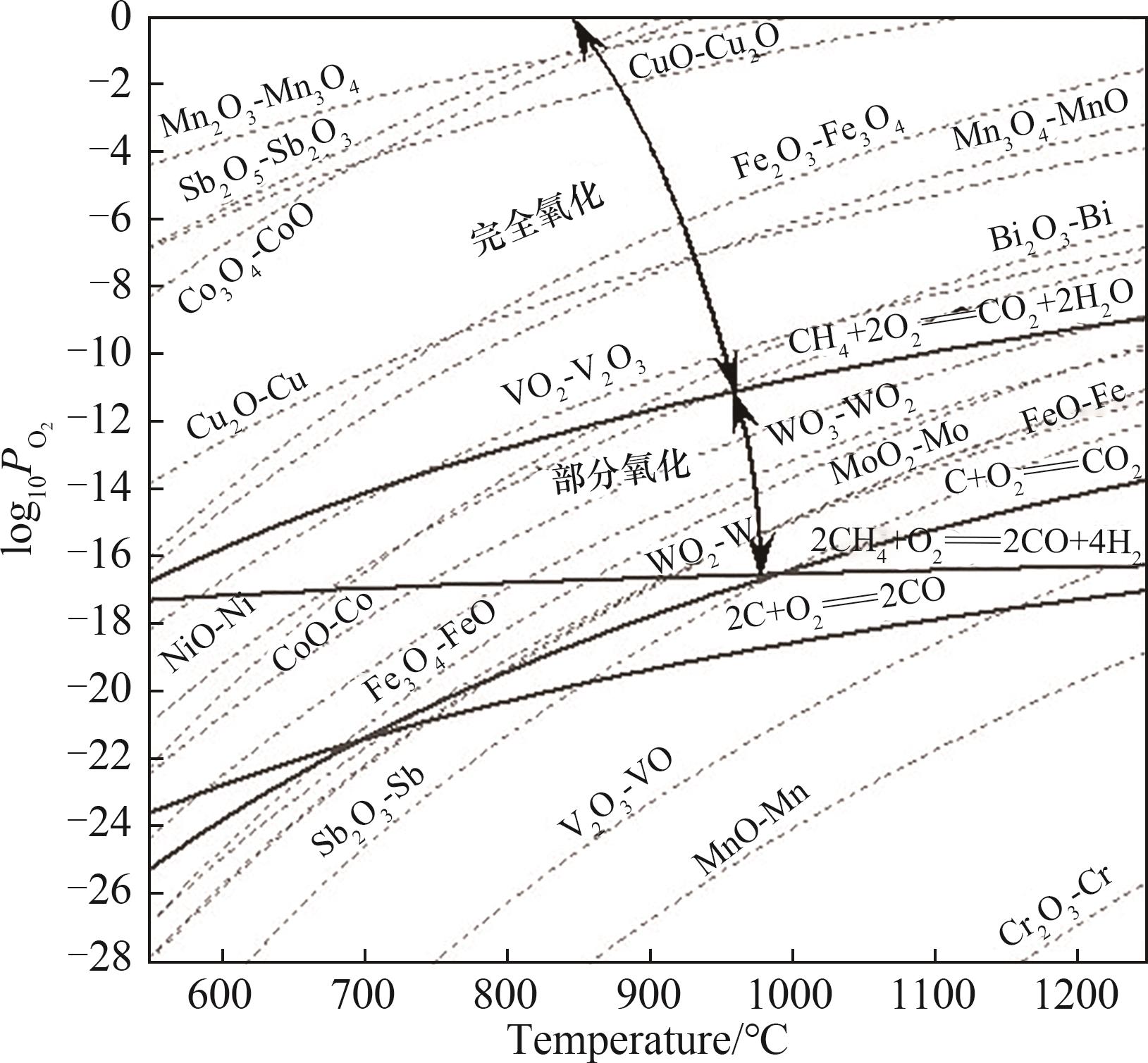
图5 用于比较金属氧化物的热力学平衡氧分压的改进Ellingham图[2]
Fig.5 Modified Ellingham diagram for comparing thermodynamic equilibrium oxygen partial pressures of metal oxides[2]

图6 利用碱/碱土金属表面修饰(a)以及惰性壳层包覆策略(b)降低表面氧通量[46-47,67-68]
Fig.6 Using alkali/alkaline earth metal surface-modification (a) and inert shell coating (b) to reduce surface oxygen flux[46-47,67-68]
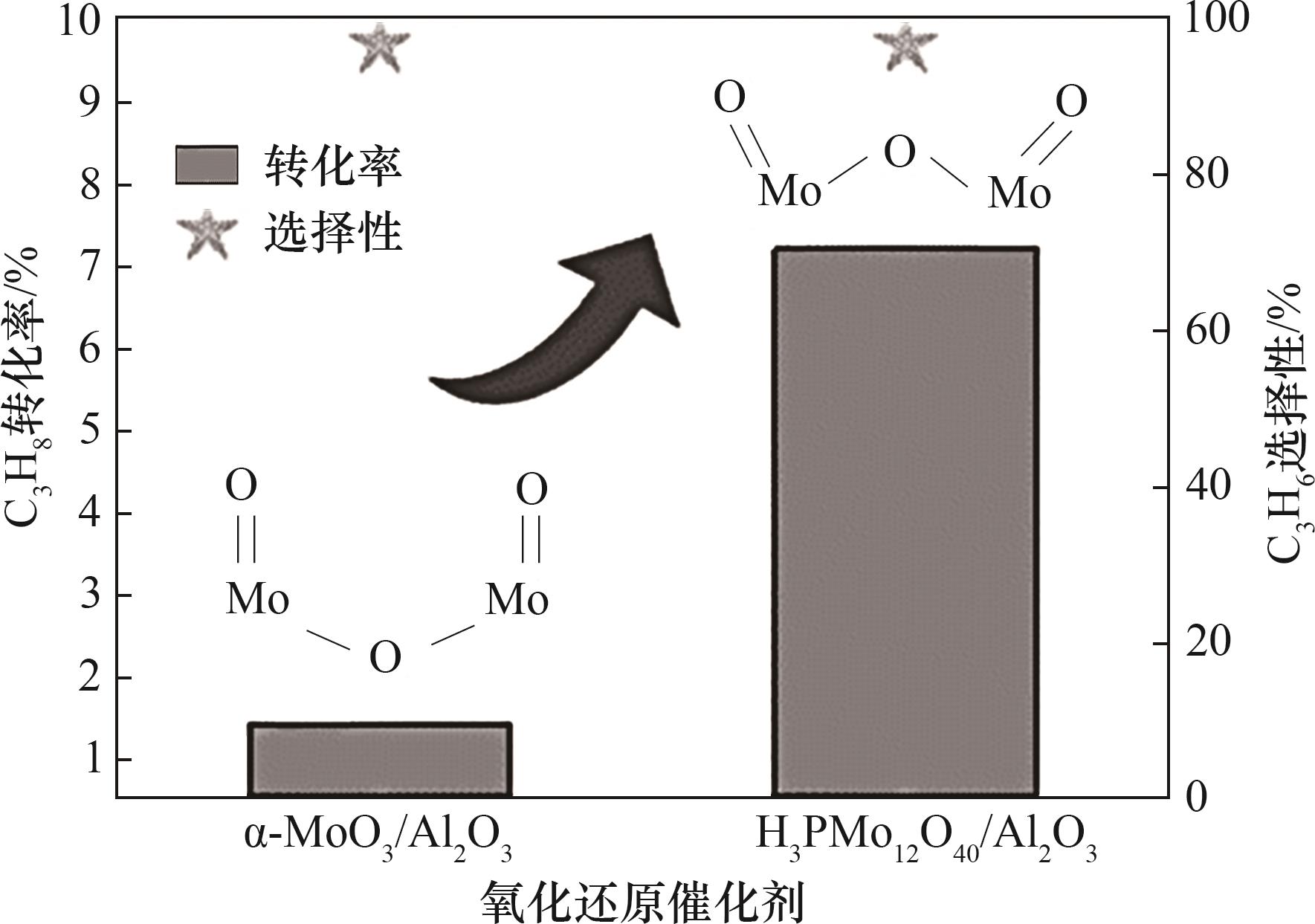
图8 具有凹曲率结构的α-MoO3/Al2O3和凸曲率结构的H3PMo12O40/Al2O3丙烷化学链脱氢反应性能对比[71]
Fig.8 Reaction performance comparison of α-MoO3/Al2O3 with concave curvature and H3PMo12O40/Al2O3 with convex curvature for chemical looping dehydrogenation of propane[71]
| 1 | Zeng L, Cheng Z, Fan J A, et al. Metal oxide redox chemistry for chemical looping processes[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2018, 2(11): 349-364. |
| 2 | Zhu X, Imtiaz Q, Donat F, et al. Chemical looping beyond combustion—a perspective[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(3): 772-804. |
| 3 | Richter H J, Knoche K F. Reversibility of combustion processes[M]//Efficiency and Costing. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1983: 71-85. |
| 4 | Mars P, van Krevelen D W. Oxidations carried out by means of vanadium oxide catalysts[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1954, 3: 41-59. |
| 5 | Coulston G W, Bare S R, Kung H, et al. The kinetic significance of V5+ in n-butane oxidation catalyzed by vanadium phosphates[J]. Science, 1997, 275(5297): 191-193. |
| 6 | Zhao X, Zhou H, Sikarwar V S, et al. Biomass-based chemical looping technologies: the good, the bad and the future[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(9): 1885-1910. |
| 7 | 冯圣, 高文波, 曹湖军, 等. 化学链合成氨研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 916-927. |
| Feng S, Gao W B, Cao H J, et al. Advances in the chemical looping ammonia synthesis[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(9): 916-927. | |
| 8 | Haribal V P, Neal L M, Li F. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane under a cyclic redox scheme—process simulations and analysis[J]. Energy, 2017, 119: 1024-1035. |
| 9 | Otsuka K, Wang Y, Sunada E, et al. Direct partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas by cerium oxide[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1998, 175(2): 152-160. |
| 10 | Tang M, Xu L, Fan M. Progress in oxygen carrier development of methane-based chemical-looping reforming: a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 151: 143-156. |
| 11 | Zhao K, He F, Huang Z, et al. Perovskite-type oxides LaFe1- x Co x O3 for chemical looping steam methane reforming to syngas and hydrogen co-production[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 168: 193-203. |
| 12 | Kang Y, Han Y, Tian M, et al. Promoted methane conversion to syngas over Fe-based garnets via chemical looping[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2020, 278: 119305. |
| 13 | Shen Q, Huang F, Tian M, et al. Effect of regeneration period on the selectivity of synthesis gas of Ba-hexaaluminates in chemical looping partial oxidation of methane[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(1): 722-731. |
| 14 | Tamai K, Hosokawa S, Onishi K, et al. Dynamics of the lattice oxygen in a Ruddlesden-Popper-type Sr3Fe2O7- δ catalyst during NO oxidation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(4): 2528-2537. |
| 15 | Zhang J, Haribal V, Li F. Perovskite nanocomposites as effective CO2-splitting agents in a cyclic redox scheme[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(8): e1701184. |
| 16 | Neal L, Shafiefarhood A, LI F. Effect of core and shell compositions on MeO x @La y Sr1- y FeO3 core-shell redox catalysts for chemical looping reforming of methane[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 391-398. |
| 17 | Zhang B, Li Y, Yang B, et al. Controlling the reaction microenvironments through an embedding strategy to strengthen the chemical looping reforming of methane based on decoupling process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137061. |
| 18 | Liu Y, Qin L, Pan J, et al. SBA-16-mediated nanoparticles enabling accelerated kinetics in cyclic methane conversion to syngas at low temperatures[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(10): 9833-9840. |
| 19 | Zhang X, Xu Y, Liu Y, et al. A novel Ni-MoC x O y interfacial catalyst for syngas production via the chemical looping dry reforming of methane[J]. Chem, 2023, 9(1): 102-116. |
| 20 | Haribal V P, Wang X, Dudek R, et al. Modified ceria for “low-temperature” CO2 utilization: a chemical looping route to exploit industrial waste heat[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(41): 1901963. |
| 21 | Kousi K, Neagu D, Bekris L, et al. Endogenous nanoparticles strain perovskite host lattice providing oxygen capacity and driving oxygen exchange and CH4 conversion to syngas[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(6): 2510-2519. |
| 22 | Chen S, Zeng L, Tian H, et al. Enhanced lattice oxygen reactivity over Ni-modified WO3-based redox catalysts for chemical looping partial oxidation of methane[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(5): 3548-3559. |
| 23 | Zheng Y, Li K, Wang H, et al. Designed oxygen carriers from macroporous LaFeO3 supported CeO2 for chemical-looping reforming of methane[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2017, 202: 51-63. |
| 24 | Zhao K, Li L, Zheng A, et al. Synergistic improvements in stability and performance of the double perovskite-type oxides La2- x Sr x FeCoO6 for chemical looping steam methane reforming[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 197: 393-404. |
| 25 | Zhang X, Pei C, Chang X, et al. FeO6 octahedral distortion activates lattice oxygen in perovskite ferrite for methane partial oxidation coupled with CO2 splitting[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(26): 11540-11549. |
| 26 | Donat F, Müller C R. CO2-free conversion of CH4 to syngas using chemical looping[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2020, 278: 119328. |
| 27 | Liu R, Pei C, Zhang X, et al. Chemical looping partial oxidation over FeWO x /SiO2 catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 41(7): 1140-1151. |
| 28 | Li X, Li Z, Lu C, et al. Enhanced performance of LaFeO3 oxygen carriers by NiO for chemical looping partial oxidation of methane[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 236: 107396. |
| 29 | Zheng Y, Marek E J, Scott S A. H2 production from a plasma-assisted chemical looping system from the partial oxidation of CH4 at mild temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122197. |
| 30 | Yang L, Zhang J, Wei J. Highly active La0.35Sr0.35Ba0.3Fe1- x Co x O3 oxygen carriers with the anchored nanoparticles for chemical looping dry reforming of methane[J]. Fuel, 2023, 349: 128771. |
| 31 | Shafiefarhood A, Zhang J, Neal L M, et al. Rh-promoted mixed oxides for “low-temperature” methane partial oxidation in the absence of gaseous oxidants[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(23): 11930-11939. |
| 32 | Kousi K, Tang C, Metcalfe I S, et al. Emergence and future of exsolved materials[J]. Small, 2021, 17(21): 2006479. |
| 33 | Yuan K, Zheng Y, Li K, et al. Enhanced resistance to carbon deposition over La x Ce1- x Fe x Ni1- x O3 oxygen carrier for chemical looping reforming[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(19): 15867-15878. |
| 34 | Zhao K, Zhang R, Gao Y, et al. High syngas selectivity and near pure hydrogen production in perovskite oxygen carriers for chemical looping steam methane reforming[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 236: 107398. |
| 35 | Iftikhar S, Martin W, Gao Y, et al. LaNi x Fe1- x O3 as flexible oxygen or carbon carriers for tunable syngas production and CO2 utilization[J]. Catalysis Today, 2023, 416: 113854. |
| 36 | Li X, Pei C, Gong J. Shale gas revolution: catalytic conversion of C1—C3 light alkanes to value-added chemicals[J]. Chem, 2021, 7(7): 1755-1801. |
| 37 | Chen S, Chang X, Sun G, et al. Propane dehydrogenation: catalyst development, new chemistry, and emerging technologies[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(5): 3315-3354. |
| 38 | 孙嘉辰, 裴春雷, 陈赛, 等. 化学链低碳烷烃氧化脱氢技术进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 205-223. |
| Sun J C, Pei C L, Chen S, et al. Advances in chemical-looping oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkanes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 205-223. | |
| 39 | Dou J, Funderburg J, Yang K, et al. Ce x Zr1- x O2-supported CrO x catalysts for CO2-assisted oxidative dehydrogenation of propane─probing the active sites and strategies for enhanced stability[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(1): 213-223. |
| 40 | Neal L M, Haribal V P, Li F. Intensified ethylene production via chemical looping through an exergetically efficient redox scheme[J]. iScience, 2019, 19: 894-904. |
| 41 | Dudek R B, Li F. Selective hydrogen combustion as an effective approach for intensified chemical production via the chemical looping strategy[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 218: 106827. |
| 42 | Tian X, Zheng C, Zhao H. Ce-modified SrFeO3-δ for ethane oxidative dehydrogenation coupled with CO2 splitting via a chemical looping scheme[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2022, 303: 120894. |
| 43 | Jeong M H, Lee D H, Moon J W, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane and subsequent CO2 activation on Ce-incorporated FeTiO x metal oxides[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 134621. |
| 44 | Tian X, Zheng C, Li F, et al. Co and Mo co-doped Fe2O3 for selective ethylene production via chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(23): 8002-8011. |
| 45 | Li M, Gao Y, Zhao K, et al. Mg-doped La1.6Sr0.4FeCoO6 for anaerobic oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane using surface-absorbed oxygen with tuned electronic structure[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 216: 106771. |
| 46 | Ding W, Zhao K, Jiang S, et al. Alkali-metal enhanced LaMnO3 perovskite oxides for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Applied Catalysis A-General, 2021, 609: 117910. |
| 47 | Gao Y, Wang X, Liu J, et al. A molten carbonate shell modified perovskite redox catalyst for anaerobic oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(17): eaaz9339. |
| 48 | Chen S, Zeng L, Mu R, et al. Modulating lattice oxygen in dual-functional Mo-V-O mixed oxides for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(47): 18653-18657. |
| 49 | Gao Y, Wang X, Corolla N, et al. Alkali metal halide-coated perovskite redox catalysts for anaerobic oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butane[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(30): eabo7343. |
| 50 | Wang C, Yang B, Gu Q, et al. Near 100% ethene selectivity achieved by tailoring dual active sites to isolate dehydrogenation and oxidation[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5447. |
| 51 | Tian Y, Dudek R B, Westmoreland P R, et al. Effect of sodium tungstate promoter on the reduction kinetics of CaMn0.9Fe0.1O3 for chemical looping-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 398: 125583. |
| 52 | Yusuf S, Neal L, Bao Z, et al. Effects of sodium and tungsten promoters on Mg6MnO8-based core-shell redox catalysts for chemical looping—oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(4): 3174-3186. |
| 53 | Yusuf S, Neal L M, Li F. Effect of promoters on manganese-containing mixed metal oxides for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane via a cyclic redox scheme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(8): 5163-5173. |
| 54 | Beckers J, Rothenberg G. Lead-containing solid “oxygen reservoirs” for selective hydrogen combustion[J]. Green Chemistry, 2009, 11(10): 1550-1554. |
| 55 | Beckers J, Lee A F, Rothenberg G. Bismuth-doped ceria, Ce0.90Bi0.10O2: a selective and stable catalyst for clean hydrogen combustion[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2009, 351(10): 1557-1566. |
| 56 | Sun W, Zhao G, Gao Y, et al. An oxygen carrier catalyst toward efficient chemical looping-oxidative coupling of methane[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2022, 304: 120948. |
| 57 | Damasceno S, Trindade F J, Fonseca F C, et al. Oxidative coupling of methane in chemical looping design[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 231: 107255. |
| 58 | Al-ghamdi S, Volpe M, Hossain M M, et al. VO x /c-Al2O3 catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane to ethylene: desorption kinetics and catalytic activity[J]. Applied Catalysis A-General, 2013, 450: 120-130. |
| 59 | Al-ghamdi S A, Hossain M M, de Lasa H I. Kinetic modeling of ethane oxidative dehydrogenation over VO x /Al2O3 catalyst in a fluidized-bed riser simulator[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(14): 5235-5244. |
| 60 | Novotný P, Yusuf S, Li F, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane using MoO3/Fe2O3 catalysts in a cyclic redox mode[J]. Catalysis Today, 2018, 317: 50-55. |
| 61 | Weckhuysen B M, Schoonheydt R A. Alkane dehydrogenation over supported chromium oxide catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 1999, 51(2): 223-232. |
| 62 | Khan M Y, Al-Ghamdi S, Razzak S A, et al. Fluidized bed oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane to ethylene over VO x /Ce-γ-Al2O3 catalysts: reduction kinetics and catalyst activity[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2017, 443: 78-91. |
| 63 | Ayandiran A A, Bakare I A, Binous H, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propylene over VO x /CaO-γ-Al2O3 using lattice oxygen[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(13): 5154-5167. |
| 64 | Hossain M M. Kinetics of oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propylene using lattice oxygen of VO x /CaO/γ-Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(15): 4309-4318. |
| 65 | Kang K H, Kim T H, Choi W C, et al. Dehydrogenation of propane to propylene over CrO y -CeO2-K2O/γ-Al2O3 catalysts: effect of cerium content[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2015, 72: 68-72. |
| 66 | Royer S, Duprez D, Can F, et al. Perovskites as substitutes of noble metals for heterogeneous catalysis: dream or reality[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(20): 10292-10368. |
| 67 | Gao Y, Haeri F, He F, et al. Alkali metal-promoted La x Sr2- x FeO4- δ redox catalysts for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(3): 1757-1766. |
| 68 | Gao Y, Neal L M, Li F. Li-promoted La x Sr2- x FeO4- δ core-shell redox catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane under a cyclic redox scheme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(11): 7293-7302. |
| 69 | Wang X, Gao Y, Krzystowczyk E, et al. High-throughput oxygen chemical potential engineering of perovskite oxides for chemical looping applications[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(4): 1512-1528. |
| 70 | Jiang C, Song H, Sun G, et al. Data-driven interpretable descriptors for the structure-activity relationship of surface lattice oxygen on doped vanadium oxides[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(35): e202206758. |
| 71 | Jiang C, Chang X, Wang X, et al. Enhanced C—H bond activation by tuning the local environment of surface lattice oxygen of MoO3 [J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(25): 7468-7474. |
| 72 | Tsikoyiannis J G, Stern D L, Grasselli R K. Metal oxides as selective hydrogen combustion (SHC) catalysts and their potential in light paraffin dehydrogenation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 184(1): 77-86. |
| 73 | Sattler J J H B, Ruiz-Martinez J, Santillan-Jimenez E, et al. Catalytic dehydrogenation of light alkanes on metals and metal oxides[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(20): 10613-10653. |
| 74 | van der Zande L M, de Graaf E A, Rothenberg G. Design and parallel synthesis of novel selective hydrogen oxidation catalysts and their application in alkane dehydrogenation[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2002, 344(8): 884-889. |
| 75 | de Graaf E A, Andreini A, Hensen E J M, et al. Selective hydrogen oxidation in a mixture with ethane/ethene using cerium zirconium oxide[J]. Applied Catalysis A-General, 2004, 262(2): 201-206. |
| 76 | Blank J H, Beckers J, Collignon P F, et al. Redox kinetics of ceria-based mixed oxides in selective hydrogen combustion[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2007, 8(17): 2490-2497. |
| 77 | Beckers J, Drost R, van Zandvoort I, et al. Selective hydrogen oxidation in the presence of C3 hydrocarbons using perovskite oxygen reservoirs[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2008, 9(7): 1062-1068. |
| 78 | Wang W, Chen S, Pei C, et al. Tandem propane dehydrogenation and surface oxidation catalysts for selective propylene synthesis[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6660): 886-890. |
| 79 | Dudek R B, Gao Y, Zhang J, et al. Manganese-containing redox catalysts for selective hydrogen combustion under a cyclic redox scheme[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(8): 3141-3150. |
| 80 | Yusuf S, Neal L, Haribal V, et al. Manganese silicate based redox catalysts for greener ethylene production via chemical looping-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2018, 232: 77-85. |
| 81 | Yusuf S, Haribal V, Jackson D, et al. Mixed iron-manganese oxides as redox catalysts for chemical looping—oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane with tailorable heat of reactions[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2019, 257: 117885. |
| 82 | Lin C H, Lee K C, Wan B Z. Development of catalyst system for selective combustion of hydrogen[J]. Applied Catalysis A-General, 1997, 164(1): 59-67. |
| 83 | 段一菲, 陈存壮, 张军社, 等. 化学链小分子转化研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2020, 50(3): 337-365. |
| Duan Y F, Chen C Z, Zhang J S, et al. Progress in chemical looping-based transformations of small molecules[J]. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2020, 50(3): 337-365. | |
| 84 | Spivey J J, Hutchings G. Catalytic aromatization of methane[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(3): 792-803. |
| 85 | Ji X, Liu Y, Liu J, et al. Na2WO4-tuned manganese ore as a high-effective redox catalyst for selective hydrogen combustion in the presence of methane and benzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2022, 307: 121194. |
| 86 | Kim S, Annamalai L, Lobo R F. Silica-encapsulated Fe2O3 oxygen carriers for selective chemical looping combustion of hydrogen[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140919. |
| 87 | Brady C, Murphy B, Xu B. Enhanced methane dehydroaromatization via coupling with chemical looping[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(6): 3924-3928. |
| 88 | Brady C, Debruyne Q, Majumder A, et al. An integrated methane dehydroaromatization and chemical looping process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 127168. |
| 89 | Zhang Y, Jiang H. A novel route to improve methane aromatization by using a simple composite catalyst[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(73): 10343-10346. |
| 90 | Ravi M, Sushkevich V L, Knorpp A J, et al. Misconceptions and challenges in methane-to-methanol over transition-metal-exchanged zeolites[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(6): 485-494. |
| 91 | Shen K, Kumari S, Huang Y C, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of methane to methanol on electrodeposited transition metal oxides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(12): 6927-6943. |
| 92 | An B, Li Z, Wang Z, et al. Direct photo-oxidation of methane to methanol over a mono-iron hydroxyl site[J]. Nature Materials, 2022, 21(8): 932-938. |
| 93 | Groothaert M H, Smeets P J, Sels B F, et al. Selective oxidation of methane by the bis(μ-oxo)dicopper core stabilized on ZSM-5 and mordenite zeolites[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(5): 1394-1395. |
| 94 | Balasubramanian R, Smith S M, Rawat S, et al. Oxidation of methane by a biological dicopper centre[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7294): 115-119. |
| 95 | Sushkevich V L, Palagin D, Ranocchiari M, et al. Selective anaerobic oxidation of methane enables direct synthesis of methanol[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6337): 523-527. |
| 96 | Meyet J, Searles K, Newton M A, et al. Monomeric copper(Ⅱ) sites supported on alumina selectively convert methane to methanol[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(29): 9841-9845. |
| 97 | Vanelderen P, Snyder B E R, Tsai M L, et al. Spectroscopic definition of the copper active sites in mordenite: selective methane oxidation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(19): 6383-6392. |
| 98 | Ipek B, Wulfers M J, Kim H, et al. Formation of [Cu2O2]2+ and [Cu2O]2+ toward C—H bond activation in Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SSZ-39[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(7): 4291-4303. |
| 99 | Sushkevich V L, Artsiusheuski M, Klose D, et al. Identification of kinetic and spectroscopic signatures of copper sites for direct oxidation of methane to methanol[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(29): 15944-15953. |
| 100 | Meyet J, van Bavel A P, Horton A D, et al. Selective oxidation of methane to methanol on dispersed copper on alumina from readily available copper(Ⅱ) formate[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(16): 5484-5490. |
| 101 | Knorpp A J, Pinar A B, Baerlocher C, et al. Paired copper monomers in zeolite omega: the active site for methane-to-methanol conversion[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(11): 5854-5858. |
| 102 | Artiglia L, Sushkevich V L, Palagin D, et al. In situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy detects multiple active sites involved in the selective anaerobic oxidation of methane in copper-exchanged zeolites[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(8): 6728-6737. |
| 103 | Lange J P, Sushkevich V L, Knorpp A J, et al. Methane-to-methanol via chemical looping: economic potential and guidance for future research[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(20): 8674-8680. |
| 104 | Chan M S C, Marek E, Scott S A, et al. Chemical looping epoxidation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 359: 1-7. |
| 105 | Gabra S, Marek E J, Poulston S, et al. The use of strontium ferrite perovskite as an oxygen carrier in the chemical looping epoxidation of ethylene[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2021, 286: 119821. |
| 106 | Marek E J, Conde E G C. Effect of catalyst preparation and storage on chemical looping epoxidation of ethylene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 127981. |
| 107 | Jin F, Gao Y, Jin Y, et al. High-yield reduction of carbon dioxide into formic acid by zero-valent metal/metal oxide redox cycles[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(3): 881-884. |
| 108 | Yu X, Zholobenko V L, Moldovan S, et al. Stoichiometric methane conversion to ethane using photochemical looping at ambient temperature[J]. Nature Energy, 2020, 5(7): 511-519. |
| 109 | Huo S, Chen H, Zuo W. Selective chlorination of methane photochemically mediated by ferric chloride at ambient temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 41(4): 1683. |
| 110 | He X, Zhang L, Chen J, et al. Photo-driven aerobic methane nitration[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2023, 62(26): 10343-10350. |
| 111 | He X, Li Z, Hu H, et al. Chemical looping conversion of ethane to ethanol via photo-assisted nitration of ethane[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2021, 2(7): 100481. |
| 112 | Feng S, Gao W, Guo J, et al. Electrodriven chemical looping ammonia synthesis mediated by lithium imide[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(3): 1567-1574. |
| 113 | Li X, Wang R, Na J, et al. Reversible reaction-assisted intensification process for separating the azeotropic mixture of ethanediol and 1,2-butanediol: reactants screening[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(2): 710-717. |
| [1] | 周小文, 杜杰, 张战国, 许光文. 基于甲烷脉冲法的Fe2O3-Al2O3载氧体还原特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2611-2623. |
| [2] | 张金鹏, 王强, 王艳美, 严舒, 吴建波, 张慧, 白红存. 镍基载氧体化学链燃烧过程中宁夏QH和YCW煤分子结构演化特征及对比分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4252-4266. |
| [3] | 何笑, 刘晶晶, 李文瑶, 刘永卓, 郭庆杰. 玉米秸秆化学链热解过程铁基复合载氧体的载氧-催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4153-4163. |
| [4] | 杨柳青, 赵子瑞, 张军社, 魏进家. 钡含量对(La0.5Sr0.5)1-x Ba x Fe0.6Co0.4O3化学链甲烷干重整性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4286-4301. |
| [5] | 孙嘉辰, 裴春雷, 陈赛, 赵志坚, 何盛宝, 巩金龙. 化学链低碳烷烃氧化脱氢技术进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 205-223. |
| [6] | 袁妮妮, 郭拓, 白红存, 何育荣, 袁永宁, 马晶晶, 郭庆杰. 化学链燃烧过程Fe2O3/Al2O3载氧体表面CH4反应:ReaxFF-MD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4054-4061. |
| [7] | 郭丹, 方雨洁, 许一寒, 李致远, 黄守莹, 王胜平, 马新宾. 乙烷和二氧化碳催化转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3406-3416. |
| [8] | 王保文, 张港, 刘同庆, 李炜光, 王梦家, 林德顺, 马晶晶. CeO2/CuFe2O4氧载体CH4化学链重整耦合CO2热催化还原研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5414-5426. |
| [9] | 武鹏, 王芳, 曾玺, 战洪仁, 岳君容, 王婷婷, 许光文. 微型流化床中焦油热裂解和水蒸气重整的反应特性及动力学对比[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 362-375. |
| [10] | 赵旭, 卜昌盛, 王昕晔, 张鑫, 程晓磊, 王乃继, 朴桂林. 铁基载氧体辅助无烟煤焦富氧燃烧动力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 384-392. |
| [11] | 陈晨, 王明明, 王志刚, 谭小耀. 镍基非对称中空纤维膜用于乙醇自热重整制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 482-493. |
| [12] | 赵林洲, 郑燕娥, 李孔斋, 王亚明, 蒋丽红, 范浩熙, 王雅静, 祝星, 魏永刚. Ce1-xNixOy氧载体在化学链甲烷重整耦合CO2还原中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4371-4380. |
| [13] | 刘一君, 陈时熠, 胡骏, 周威, 向文国. 化学链反应器研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2392-2412. |
| [14] | 钮朝阳, 江南, 沈圆辉, 吴统波, 刘冰, 张东辉. 快速变压吸附制氢工艺的模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 1036-1046. |
| [15] | 孙晓明, 沙琪昊, 王陈伟, 周道金. 用于甲醇重整制氢的铜基催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5975-6001. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号