化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (4): 1668-1678.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231251
周康1( ), 王建新2, 于海1, 魏朝良1, 范丰奇1, 车昕昊2, 张磊2(
), 王建新2, 于海1, 魏朝良1, 范丰奇1, 车昕昊2, 张磊2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-27
修回日期:2024-01-12
出版日期:2024-04-25
发布日期:2024-06-06
通讯作者:
张磊
作者简介:周康(1987—),男,硕士,高级工程师, zhoukang_rhy@petrochina.com.cn
基金资助:
Kang ZHOU1( ), Jianxin WANG2, Hai YU1, Chaoliang WEI1, Fengqi FAN1, Xinhao CHE2, Lei ZHANG2(
), Jianxin WANG2, Hai YU1, Chaoliang WEI1, Fengqi FAN1, Xinhao CHE2, Lei ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2023-11-27
Revised:2024-01-12
Online:2024-04-25
Published:2024-06-06
Contact:
Lei ZHANG
摘要:
润滑油中的泡沫会增加设备间的磨损,减少油品中的泡沫可以有效降低能源消耗。选用四种矿物型基础油的代表性烃类组分构建了泡沫液膜的分子模拟体系,通过分子动力学模拟分析了液膜破裂过程的微观机理,并计算了单组分及混合组分液膜的破裂时间作为液膜稳定性的评价指标。在此基础上,研究了基础油结构与添加剂、抗泡剂的加入对油基泡沫液膜破裂时间的影响。结果显示,在液膜破裂的过程中,初始孔洞的出现,会显著加快液膜破裂进程,在各基础油体系中加入添加剂、抗泡剂后,液膜破裂时间变化与扩散系数的变化一致,符合泡沫破裂的排液机理。提出的研究方法可从分子层面深入分析油基泡沫的稳定性及破裂机理,探索减少润滑油品泡沫的方法。
中图分类号:
周康, 王建新, 于海, 魏朝良, 范丰奇, 车昕昊, 张磊. 基于分子动力学模拟的矿物基础油泡沫破裂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1668-1678.
Kang ZHOU, Jianxin WANG, Hai YU, Chaoliang WEI, Fengqi FAN, Xinhao CHE, Lei ZHANG. Foam rupture properties of mineral base oils based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1668-1678.
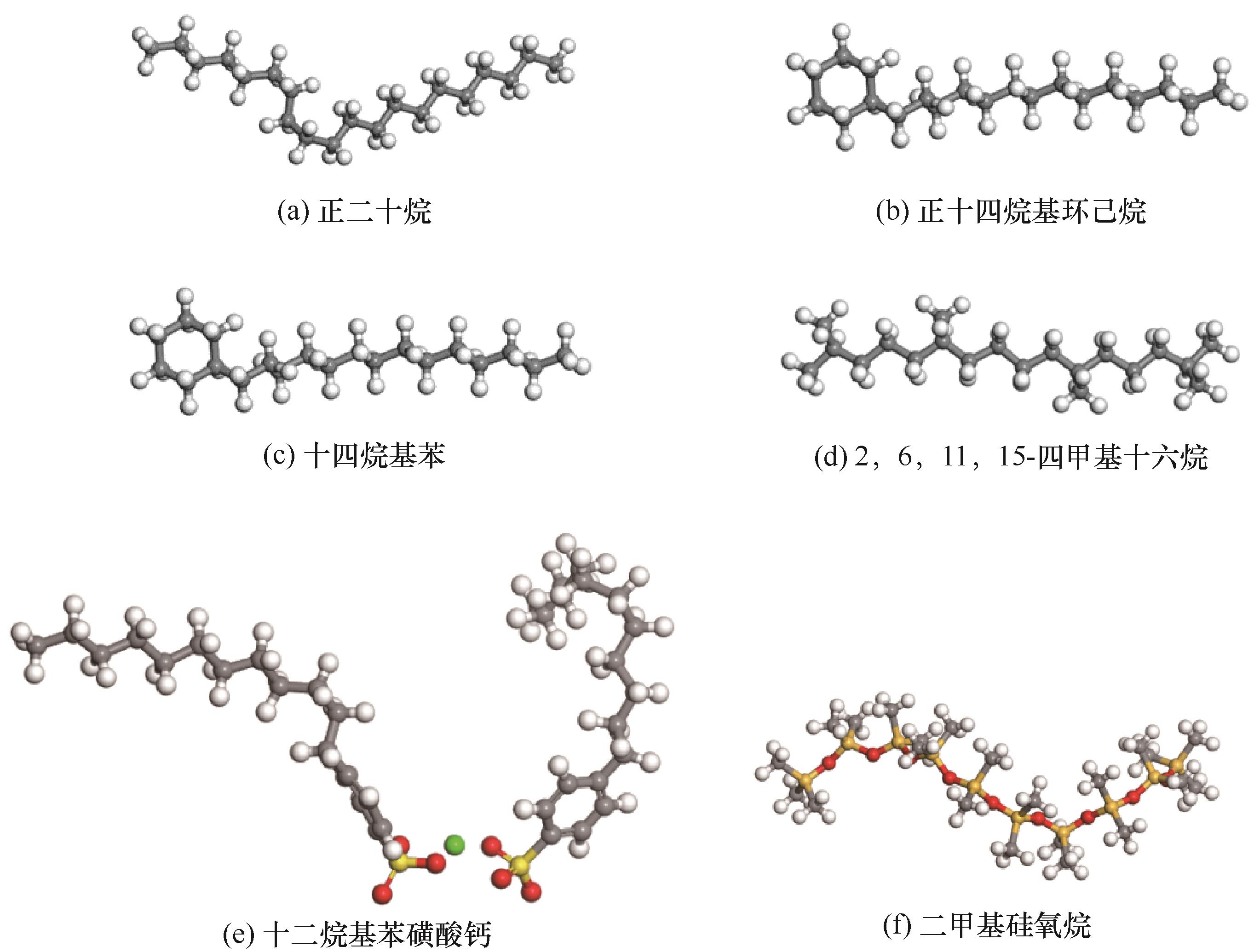
图1 用于构建泡沫膜体系的代表性基础油、添加剂及抗泡剂的分子结构
Fig.1 The molecular structures of the representative base oil, additive and antifoam agent used to construct the foam film system
| 基础油 | 密度/(g/cm3) | |
|---|---|---|
| 模拟值 | 实验值 | |
| 2,6,11,15-四甲基十六烷 | 0.7990 | 0.7853(298 K) |
| 正十四烷基环己烷 | 0.8301 | 0.8258(293 K) |
| 十四烷基苯 | 0.8617 | 0.8570(296.8 K) |
| 正二十烷 | 0.8145 | 0.7889(293 K) |
表1 基础油密度模拟结果与实验值的比较
Table 1 Comparison of base oil density simulation results with experimental values
| 基础油 | 密度/(g/cm3) | |
|---|---|---|
| 模拟值 | 实验值 | |
| 2,6,11,15-四甲基十六烷 | 0.7990 | 0.7853(298 K) |
| 正十四烷基环己烷 | 0.8301 | 0.8258(293 K) |
| 十四烷基苯 | 0.8617 | 0.8570(296.8 K) |
| 正二十烷 | 0.8145 | 0.7889(293 K) |
| 模拟体系 | 扩散系数/(10-5 cm2/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 十四烷基苯 | 正十四烷基环己烷 | 2,6,11,15-四甲基十六烷 | 正二十烷 | |
| 加入十二烷基苯磺酸钙 | 1.01 | 2.17 | 2.46 | 2.02 |
| 同时加入十二烷基苯磺酸钙+二甲基硅氧烷 | 3.29 | 3.76 | 3.95 | 1.96 |
表2 不同体系下基础油的扩散系数
Table 2 Diffusion coefficient of base oil molecules in different systems
| 模拟体系 | 扩散系数/(10-5 cm2/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 十四烷基苯 | 正十四烷基环己烷 | 2,6,11,15-四甲基十六烷 | 正二十烷 | |
| 加入十二烷基苯磺酸钙 | 1.01 | 2.17 | 2.46 | 2.02 |
| 同时加入十二烷基苯磺酸钙+二甲基硅氧烷 | 3.29 | 3.76 | 3.95 | 1.96 |
| 1 | Zhou Y, Qu J. Ionic liquids as lubricant additives: a review[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(4): 3209-3222. |
| 2 | Holmberg K, Erdemir A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions[J]. Friction, 2017, 5(3): 263-284. |
| 3 | 常俊辉. 齿轮油泡沫问题研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2015. |
| Chang J H. Study on the problems of gear oil bubble properties[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2015. | |
| 4 | Rudnick L R. Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications[M]. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 337-392. |
| 5 | Prolić T Ć, Lepušić A. Effect of foaming on the antiwear properties of lubricating oils[J]. Goriv I Mazira, 2012, 51(1): 29-46. |
| 6 | 杨俊杰, 王雷, 兰奕. 中国基础油市场五个趋势[J]. 润滑油, 2020, 35(5): 1-5, 15. |
| Yang J J, Wang L, Lan Y. Five trends in China's base oil market[J]. Lubricating Oil, 2020, 35(5): 1-5, 15. | |
| 7 | Bart J C J, Gucciardi E, Cavallaro S. Lubricants: properties and characteristics[M]//Biolubricants. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013: 24-73. |
| 8 | 李紫恬. 润滑油抗泡剂机理及特点探讨[J]. 合成润滑材料, 2020, 47(2): 38-41. |
| Li Z T. Discussion on the mechanism and characteristics of antifoaming agents for lubricating oils[J]. Synthetic Lubricants, 2020, 47(2): 38-41. | |
| 9 | Carey E, Stubenrauch C. Foaming properties of mixtures of a non-ionic (C12DMPO) and an ionic surfactant (C12TAB)[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 346(2): 414-423. |
| 10 | 朱超亮. 含油多相介质起泡与液膜排液机制的分子动力学模拟[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2022. |
| Zhu C L. Molecular dynamics simulation of foaming and liquid film drainage in multiphase medium[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2022. | |
| 11 | 王军超, 李国胜, 邓丽君, 等. 阳离子型表面活性剂CTAB的泡沫性能研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2018, 50(1): 113-116. |
| Wang J C, Li G S, Deng L J, et al. Study on foaming properties of CTAB cationic surfactant[J]. Coal Engineering, 2018, 50(1): 113-116. | |
| 12 | 孙元宝, 阮少军, 姜旭峰, 等. 某型国产与进口航空发动机润滑油泡沫特性对比研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2020, 45(9): 108-112. |
| Sun Y B, Ruan S J, Jiang X F, et al. Comparative study on foam characteristics of domestic and imported aircraft engine lubricants[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2020, 45(9): 108-112. | |
| 13 | Onoghwarite O E, Okeoghene E A, Ovonomo O, et al. Performance evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane-solvent blends as defoamer for crude oil foam[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 413: 012047. |
| 14 | Wu J W, Yi M R, Han X Y, et al. Effect of an amine phosphate addition on the foaming characteristics in turbine base oil[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2019, 37(8): 863-868. |
| 15 | 谢娟, 贺文, 赵勖丞,等. 分子动力学模拟在沥青体系中的应用研究进展[J].化工进展, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-1235 . |
| Xie J, He W, Zhao X C, et al. Research progress on the application of molecular dynamics simulation in asphalt systems[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-1235 . | |
| 16 | Jabbarzadeh A, Atkinson J D, Tanner R I. The effect of branching on slip and rheological properties of lubricants in molecular dynamics simulation of Couette shear flow[J]. Tribology International, 2002, 35(1): 35-46. |
| 17 | 李义雅, 龙军, 段庆华, 等. 分子动力学模拟研究矿物基础油润滑性能[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2017, 33(4): 619-625. |
| Li Y Y, Long J, Duan Q H, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation on the lubricating property of mineral base oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2017, 33(4): 619-625. | |
| 18 | Qiu F, Song H, Feng W M, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of the interaction between graphene and lubricating oil molecules[J]. Tribology Letters, 2023, 71(2): 33. |
| 19 | Tang H F, Song J M, Zha M L, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation on the structure-activity relationship between the Gemini surfactant and foam properties[J]. AIChE Journal, 2022, 68(5): e17625. |
| 20 | Zhang Z Y, Qiao M, Zhao H X, et al. Effect of sodium alkyl sulfate chain length on foam stability: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 656: 130394. |
| 21 | Yang W H, Wu R L, Kong B, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of film rupture in water/surfactant systems[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2009, 113(24): 8332-8338. |
| 22 | Peng T F, Chang T M. Molecular processes of ion effects on aqueous nanofilm rupture[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2014, 193: 139-151. |
| 23 | Peng T F, Nguyen A V, Peng H, et al. Quantitative analysis of aqueous nanofilm rupture by molecular dynamic simulation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2012, 116(3): 1035-1042. |
| 24 | 王秀文, 陈文艺, 邹恺. 润滑油基础油结构组成与性能关系研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2014, 43(3): 539-542. |
| Wang X W, Chen W Y, Zou K. The progress of the relation between composition and character of lube base oil[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2014, 43(3): 539-542. | |
| 25 | Klitzing R V, Müller H J. Film stability control[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2002, 7(1/2): 42-49. |
| 26 | Boecker J, Brickmann J, Bopp P. Molecular dynamics simulation study of an n-decyltrimethylammonium chloride micelle in water[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1994, 98(2): 712-717. |
| 27 | Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin E G, et al. PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009, 30(13): 2157-2164. |
| 28 | Abraham M J, Murtola T, Schulz R, et al. GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers[J]. SoftwareX, 2015, 1/2: 19-25. |
| 29 | Wang J M, Wolf R M, Caldwell J W, et al. Development and testing of a general amber force field[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2004, 25(9): 1157-1174. |
| 30 | Bayly C I, Cieplak P, Cornell W, et al. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: the RESP model[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1993, 97(40): 10269-10280. |
| 31 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 32 | 胡松伟, 郭庆洲, 夏国富, 等. 异构脱蜡润滑油基础油组成对其性质的影响[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2015, 31(4): 831-835. |
| Hu S W, Guo Q Z, Xia G F, et al. Influence of composition on properties of lube base oils produced by hydroisomerization dewaxing process[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2015, 31(4): 831-835. |
| [1] | 刘东飞, 张帆, 刘铮, 卢滇楠. 机器学习势及其在分子模拟中的应用综述[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1241-1255. |
| [2] | 张政, 汪妩琼, 张雅静, 王康军, 吉远辉. 理论计算在药物制剂设计中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1429-1438. |
| [3] | 吴凡, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 孟祥铠, 梁杨杨. 分子动力学模拟预测天然气密度和黏度的可行性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 450-462. |
| [4] | 宋明昊, 赵霏, 刘淑晴, 李国选, 杨声, 雷志刚. 离子液体脱除模拟油中挥发酚的多尺度模拟与研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [5] | 胡建波, 刘洪超, 胡齐, 黄美英, 宋先雨, 赵双良. 有机笼跨细胞膜易位行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [6] | 赵佳佳, 田世祥, 李鹏, 谢洪高. SiO2-H2O纳米流体强化煤尘润湿性的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [7] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | 陈吉, 洪泽, 雷昭, 凌强, 赵志刚, 彭陈辉, 崔平. 基于分子动力学的焦炭溶损反应及其机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [9] | 邢美波, 张中天, 景栋梁, 张洪发. 磁调控水基碳纳米管协同多孔材料强化相变储/释能特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [10] | 董明, 徐进良, 刘广林. 超临界水非均质特性分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [11] | 刘远超, 蒋旭浩, 邵钶, 徐一帆, 钟建斌, 李耑. 几何尺寸及缺陷对石墨炔纳米带热输运特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [12] | 顾浩, 张福建, 刘珍, 周文轩, 张鹏, 张忠强. 力电耦合作用下多孔石墨烯膜时间维度的脱盐性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [13] | 李辰鑫, 潘艳秋, 何流, 牛亚宾, 俞路. 基于碳微晶结构的炭膜模型及其气体分离模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [14] | 王帅, 杨富凯, 徐新宇. 阻燃型全生物基多元醇聚氨酯泡沫的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1399-1408. |
| [15] | 赵焕娟, 刘婧, 周冬雷, 林敏. 多孔材料对氢气爆轰的抑制作用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 968-976. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号