化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3424-3436.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240480
收稿日期:2024-04-30
修回日期:2024-06-13
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
马学虎
作者简介:王禹丹(1999—),女,硕士研究生,wangyudan_0427@163.com
基金资助:
Yudan WANG1( ), Chen XU2, Da RUAN1, Jiang CHUN1, Xuehu MA1(
), Chen XU2, Da RUAN1, Jiang CHUN1, Xuehu MA1( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Revised:2024-06-13
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Xuehu MA
摘要:
利用V形沟槽纳米线团簇表面的毛细抽吸和补液特征,结合实验观测和建模分析对表面的薄液膜蒸发进行研究。探究了表面结构参数和沟槽液位对蒸发性能的影响,建立薄液膜蒸发模型求解纳米线团簇和V形沟槽中的液膜轮廓方程并分析传热性能。结果表明,随着纳米线直径减小和高度增大,薄液膜蒸发传热系数增大,最高可达369 kW/(m2·K)。团簇内液膜在毛细力驱动下具有极高的爬升速度,使得小持液量下液膜仍位于团簇顶端蒸发。沟槽液膜完全润湿沟槽且与团簇顶端液膜相连通,为团簇蒸发补液,沟槽液位下降不影响团簇顶端蒸发,能够延伸薄液膜长度并减薄沟槽侧壁液膜厚度,进一步强化传热。纳米线团簇中液膜宏观传热系数显著高于沟槽,证明了团簇在整体蒸发中的决定性贡献,阐明了V形沟槽纳米线团簇表面薄液膜蒸发微观机制。
中图分类号:
王禹丹, 徐晨, 阮达, 春江, 马学虎. V形沟槽纳米线团簇表面的毛细抽吸-补液蒸发传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3424-3436.
Yudan WANG, Chen XU, Da RUAN, Jiang CHUN, Xuehu MA. Heat transfer characteristics of capillary pumping-replenishment evaporation on nanowire clusters surfaces with V-grooves[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3424-3436.
| 表面类型 | p/nm | d/nm | h/μm | a/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW-A1 | 450 | 140 | 10 | 4.25 |
| NW-A2 | 450 | 140 | 20 | 7.25 |
| NW-A3 | 450 | 140 | 30 | 9.75 |
| NW-B1 | 450 | 200 | 10 | 5.25 |
| NW-B2 | 450 | 200 | 20 | 9.35 |
| NW-B3 | 450 | 200 | 30 | 15.50 |
| NW-C1 | 450 | 250 | 10 | 5.75 |
| NW-C2 | 450 | 250 | 20 | 14.75 |
| NW-C3 | 450 | 250 | 30 | 17.75 |
表1 V形沟槽纳米线团簇表面及其结构参数
Table 1 Nanowire clusters surfaces with V-grooves and corresponding structural parameters
| 表面类型 | p/nm | d/nm | h/μm | a/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW-A1 | 450 | 140 | 10 | 4.25 |
| NW-A2 | 450 | 140 | 20 | 7.25 |
| NW-A3 | 450 | 140 | 30 | 9.75 |
| NW-B1 | 450 | 200 | 10 | 5.25 |
| NW-B2 | 450 | 200 | 20 | 9.35 |
| NW-B3 | 450 | 200 | 30 | 15.50 |
| NW-C1 | 450 | 250 | 10 | 5.75 |
| NW-C2 | 450 | 250 | 20 | 14.75 |
| NW-C3 | 450 | 250 | 30 | 17.75 |
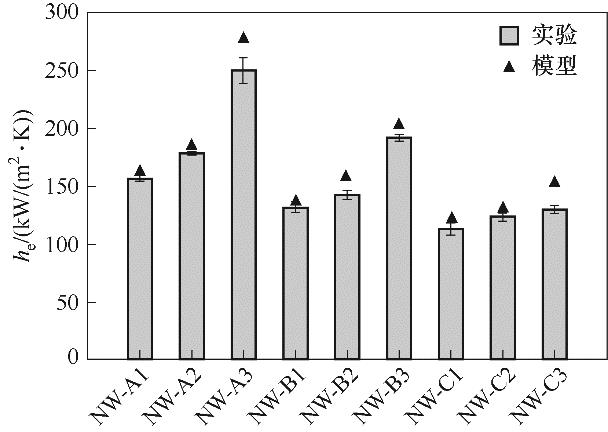
图14 沟槽充满时薄液膜蒸发总传热系数模型预测值与实验结果对比
Fig.14 Comparison between model predicted and experimental results of total heat transfer coefficient for thin liquid film evaporation when the grooves are filled
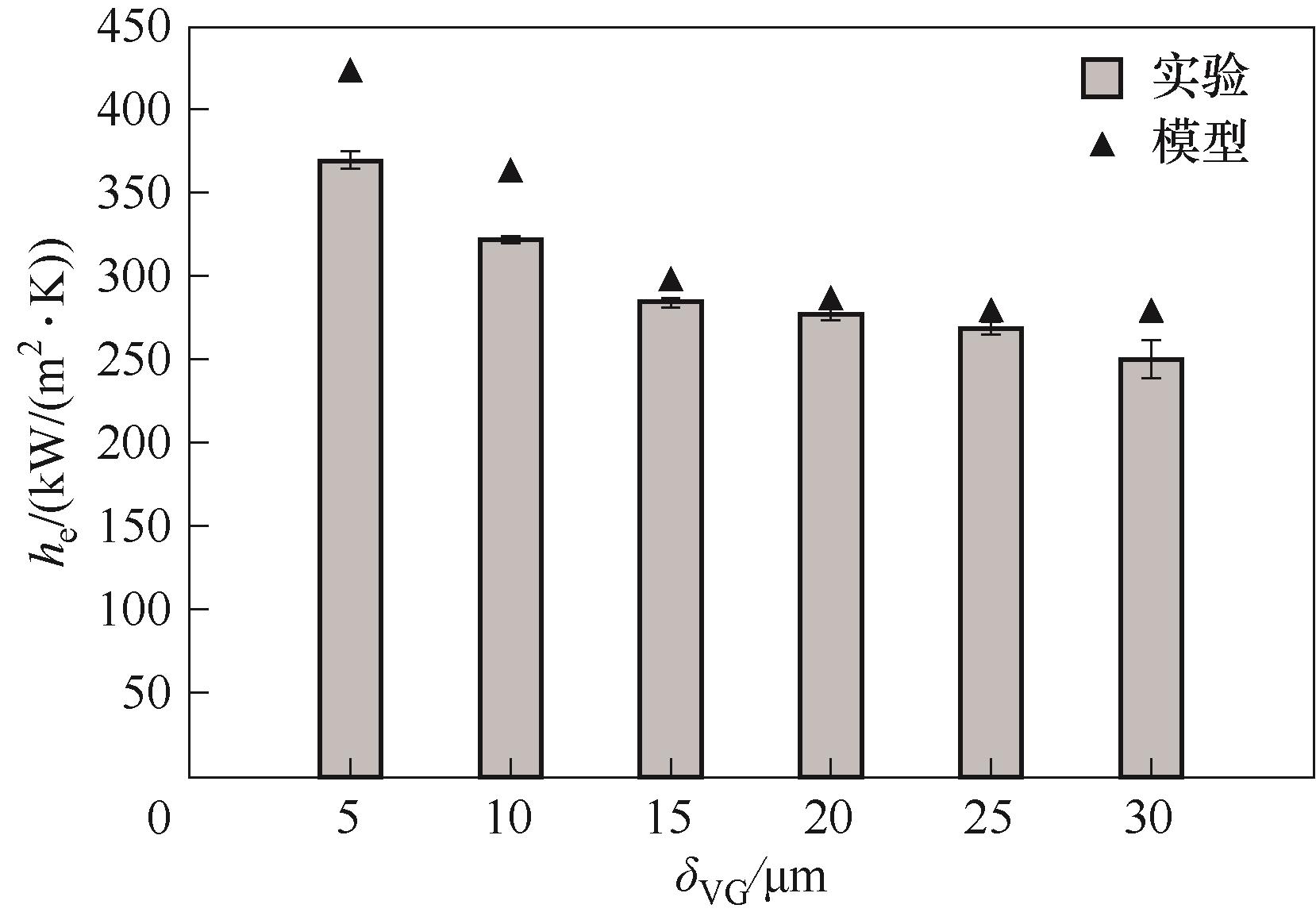
图16 沟槽液位不同时NW-A3表面液膜蒸发总传热系数模型预测值与实验结果对比
Fig.16 Comparison between model predicted and experimental results of total heat transfer coefficient for thin liquid film evaporation on the NW-A3 surface at different groove liquid levels
| 1 | Zheng Y, Ma X H, Li Y, et al. Experimental study of falling film evaporation heat transfer on superhydrophilic horizontal-tubes at low spray density[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 111: 1548-1556. |
| 2 | Zeraatkardevin A, Jowkar S, Morad M R, et al. A three dimensional simulation of spray cooling and its evaporating liquid film generated on patterned surfaces[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2022, 155: 104174. |
| 3 | Hu C Z, Pei Z X, Shi L, et al. Phase transition properties of thin liquid films with various thickness on different wettability surfaces[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 135: 106125. |
| 4 | Wang J X, Li Y Z, Liu X D, et al. Recent active thermal management technologies for the development of energy-optimized aerospace vehicles in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(2): 1-27. |
| 5 | Lu Z M, Salamon T R, Narayanan S, et al. Design and modeling of membrane-based evaporative cooling devices for thermal management of high heat fluxes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 6(7): 1056-1065. |
| 6 | 中国科学院. 中国学科发展战略——电子设备热管理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022. |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences. China's Discipline Development Strategy—Thermal Management of Electronic Devices[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022. | |
| 7 | Hanks D F, Lu Z M, Sircar J, et al. Nanoporous membrane device for ultra high heat flux thermal management[J]. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2018, 4: 1. |
| 8 | Ishikawa H, Ookawara S, Yoshikawa S, et al. Numerical study on mass transfer in a falling film on structured plates with micro-baffles[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2022, 175: 108903. |
| 9 | Liang Q Q, Bu Y F, Men Z W, et al. Taylor flow bubble transport characteristics of low partial pressure CO2 absorption in a serpentine micro contactor[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2022, 181: 109168. |
| 10 | Ye X, Hao T T, Chen Y S, et al. Liquid film transport around Taylor bubble in a microchannel with gas cavities[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2020, 148: 107828. |
| 11 | Maroo S C, Chung J N. Heat transfer characteristics and pressure variation in a nanoscale evaporating meniscus[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(15/16): 3335-3345. |
| 12 | Yan C J, Ma H B. Analytical solutions of heat transfer and film thickness in thin-film evaporation[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2013, 135(3): 031501. |
| 13 | Xiao R, Wang E N. Microscale liquid dynamics and the effect on macroscale propagation in pillar arrays[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(17): 10360-10364. |
| 14 | Alhosani M H, Zhang T J. Dynamics of microscale liquid propagation in micropillar arrays[J]. Langmuir, 2017, 33(26): 6620-6629. |
| 15 | McClure E R, Carey V P. Nanoscale and macroscale effects of mineral deposition during water evaporation on nanoporous surfaces[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(23): 26350-26359. |
| 16 | Mai T T, Lai C Q, Zheng H, et al. Dynamics of wicking in silicon nanopillars fabricated with interference lithography and metal-assisted chemical etching[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(31): 11465-11471. |
| 17 | Lu L S, Sun J W, Liu Q P, et al. Influence of electrochemical deposition parameters on capillary performance of a rectangular grooved wick with a porous layer[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 737-745. |
| 18 | Lee J, Suh Y, Dubey P P, et al. Capillary wicking in hierarchically textured copper nanowire arrays[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(1): 1546-1554. |
| 19 | Wang X F, Huang Z, Miao D Y, et al. Biomimetic fibrous Murray membranes with ultrafast water transport and evaporation for smart moisture-wicking fabrics[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 1060-1070. |
| 20 | Poudel S, Zou A, Maroo S C. Wicking in cross-connected buried nanochannels[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(38): 23529-23534. |
| 21 | Luo J L, Mo D C, Wang Y Q, et al. Biomimetic copper forest wick enables high thermal conductivity ultrathin heat pipe[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(4): 6614-6621. |
| 22 | Antao D S, Adera S, Zhu Y Y, et al. Dynamic evolution of the evaporating liquid-vapor interface in micropillar arrays[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(2): 519-526. |
| 23 | Arends A A, Germain T M, Owens J F, et al. Simultaneous reflectometry and interferometry for measuring thin-film thickness and curvature[J]. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(5): 055117. |
| 24 | Ong W L, Rupich S M, Talapin D V, et al. Surface chemistry mediates thermal transport in three-dimensional nanocrystal arrays[J]. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(5): 410-415. |
| 25 | Chen H B, Wang W Z, Ge X Y, et al. Pixel-dependent laser-induced fluorescence method for determining thin liquid film thickness distribution[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(1): 012111. |
| 26 | Che Z X, Wang T, Sun F Y, et al. Research on heat transfer capability of liquid film in three-phase contact line area[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 195: 123158. |
| 27 | Wang X M, Ghaffarizadeh S A, He X, et al. Ultrahigh evaporative heat transfer measured locally in submicron water films[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 22353. |
| 28 | Wang H, Garimella S V, Murthy J Y. Characteristics of an evaporating thin film in a microchannel[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(19/20): 3933-3942. |
| 29 | Adera S, Antao D, Raj R, et al. Design of micropillar wicks for thin-film evaporation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 101: 280-294. |
| 30 | Mei X K, Xie Y X, Chai S T, et al. Analysis of liquid film evaporation in porous particles: toward optimal wick parameters for heat transfer in heat pipes[J]. ASME Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 145(11): 111003. |
| 31 | Chun J, Xu C, Zhang Y F, et al. Fast capillary wicking on hierarchical copper nanowired surfaces with interconnected V-grooves: implications for thermal management[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(5): 5360-5371. |
| 32 | 春江. 超亲水表面液膜快速铺展及其强化机理的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2022. |
| Chun J. Enhancing mechanism of liquid film fast spreading on superhydrophilic surfaces[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2022. | |
| 33 | Chun J, Xu C, Li Q F, et al. Microscopic observation of preferential capillary pumping in hollow nanowire bundles[J]. Langmuir, 2022, 38(1): 352-362. |
| 34 | Wen R F, Li Q, Wu J F, et al. Hydrophobic copper nanowires for enhancing condensation heat transfer[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 33: 177-183. |
| 35 | Moffat R J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 1988, 1(1): 3-17. |
| 36 | Xu C, Zeng T, Chun J, et al. Capillary spreading of ethanol-water on hierarchical nanowire surfaces with interconnected V-groove[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 658: 130786. |
| 37 | Hu H, Sun Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of disjoining pressure effect in ultra-thin water film on a metal surface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(26): 263110. |
| 38 | Xu X, Carey V P. Film evaporation from a micro-grooved surface—an approximate heat transfer model and its comparison with experimental data[J]. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 1990, 4(4): 512-520. |
| [1] | 陈超伟, 柳洋, 杜文静, 李金波, 史大阔, 辛公明. 局部热点下微肋通道流动传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3113-3121. |
| [2] | 朱子良, 王爽, 姜宇昂, 林梅, 王秋旺. 欧拉-拉格朗日迭代固-液相变算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [3] | 王倩倩, 李冰, 郑伟波, 崔国民, 赵兵涛, 明平文. 氢燃料电池局部动态特征三维模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [4] | 毛宇飞, 曹飞, 上官燕琴. 超临界压力流体管内湍流对流传热的计算方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2821-2830. |
| [5] | 李倩, 张蓉民, 林子杰, 战琪, 蔡伟华. 基于机器学习的印刷电路板式换热器流动换热预测与仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2852-2864. |
| [6] | 董可豪, 周敬之, 周峰, 陈海家, 淮秀兰, 李栋. 超薄空间复杂边界条件下气体流动压降实验[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2505-2521. |
| [7] | 杨锦蕊, 郑宏飞, 马兴龙, 金日辉, 梁深. 两级叠置式加湿除湿海水淡化装置性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2446-2454. |
| [8] | 余清杰, 杨洪海, 刘玉浩, 方海洲, 何伟琪, 王军, 卢心诚. 脉动热管温度信号的小波分析及流型识别[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2497-2504. |
| [9] | 罗小平, 侯云天, 范一杰. 逆流相分离结构微细通道流动沸腾传热与均温性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2474-2485. |
| [10] | 徐嘉宇, 陈飞国, 徐骥, 葛蔚. 颗粒体系的多尺度混合指数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2214-2221. |
| [11] | 李新泽, 张双星, 杨洪海, 杜文静. 基于电池冷却用新型脉动热管性能的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2222-2232. |
| [12] | 李娟, 曹耀文, 朱章钰, 石雷, 李佳. 仿生正形尾鳍结构微通道流动与传热特性数值研究及结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1802-1815. |
| [13] | 关朝阳, 黄国庆, 张一喃, 陈宏霞, 杜小泽. 泡沫铜导离气泡强化流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1765-1776. |
| [14] | 王金山, 王世学, 朱禹. 冷却表面温差对高温质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2026-2035. |
| [15] | 李怡菲, 董新宇, 王为术, 刘璐, 赵一璠. 微肋板表面干冰升华喷雾冷却传热数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1830-1842. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号