化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (1): 184-197.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240582
收稿日期:2024-05-30
修回日期:2024-08-03
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-02-08
通讯作者:
刘萍
作者简介:刘萍(1978—),女,博士,教授,pingliu@mail.ustc.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ping LIU( ), Yusheng QIU, Shijing LI, Ruiqi SUN, Chen SHEN
), Yusheng QIU, Shijing LI, Ruiqi SUN, Chen SHEN
Received:2024-05-30
Revised:2024-08-03
Online:2025-01-25
Published:2025-02-08
Contact:
Ping LIU
摘要:
为提高微通道散热器的传热效率,需要对微通道进行结构优化设计。以热阻Rt和泵功Pp为目标函数,在Re=100的条件下,采用多目标遗传算法对文丘里管微通道的结构参数,如通道深度、收缩角度、喉颈宽度和扩散角度进行优化,通过遗传迭代计算得到Pareto优化解集,利用k-means聚类法对优化解集进行比较分析,通过强化传热因子
中图分类号:
刘萍, 邱雨生, 李世婧, 孙瑞奇, 申晨. 微通道内纳米流体传热流动特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 184-197.
Ping LIU, Yusheng QIU, Shijing LI, Ruiqi SUN, Chen SHEN. Heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in microchannels[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 184-197.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颜色 | 白色 |
| 热导率/(W/(m·K)) | 40 |
| 纳米颗粒直径/nm | 40 |
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 3970 |
| 比定压热容/(J/(kg | 765 |
| 模拟体积分数/% | 1~5 |
表1 Al2O3纳米颗粒参数[28]
Table 1 Al2O3 nanoparticle parameters[28]
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颜色 | 白色 |
| 热导率/(W/(m·K)) | 40 |
| 纳米颗粒直径/nm | 40 |
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 3970 |
| 比定压热容/(J/(kg | 765 |
| 模拟体积分数/% | 1~5 |
| 范围 | A/(°) | B/(°) | c/mm | h/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 40 | 14 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| 最大值 | 42 | 16 | 0.05 | 0.20 |
表2 设计变量及其范围
Table 2 Design variables and their ranges
| 范围 | A/(°) | B/(°) | c/mm | h/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 40 | 14 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| 最大值 | 42 | 16 | 0.05 | 0.20 |
| 设计序号 | 设计变量 | 目标变量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/(°) | b/(°) | c/mm | h/mm | Rt/(K/W) | Pp/(10-4 W) | |
| 1 | 40.7373 | 14.6294 | 0.0494 | 0.1997 | 14.2379 | 0.6460 |
| 2 | 40.2388 | 14.5699 | 0.0437 | 0.1920 | 14.1493 | 0.8483 |
| 3 | 41.1666 | 14.8625 | 0.0458 | 0.1926 | 14.2133 | 0.7662 |
| 4 | 40.9078 | 14.4708 | 0.0441 | 0.1985 | 14.0928 | 0.7988 |
| 5 | 41.5828 | 15.5224 | 0.0400 | 0.1804 | 14.1536 | 1.0789 |
| 6 | 41.6110 | 15.8708 | 0.0427 | 0.1992 | 14.0577 | 0.8336 |
| 7 | 41.3162 | 14.0744 | 0.0448 | 0.1905 | 14.1883 | 0.8180 |
| 8 | 40.0497 | 15.0459 | 0.0433 | 0.1806 | 14.2568 | 0.9222 |
| 9 | 40.1199 | 14.2140 | 0.0415 | 0.1957 | 14.0597 | 0.9231 |
| 10 | 40.5807 | 15.4502 | 0.0491 | 0.1821 | 14.4176 | 0.7261 |
| 11 | 41.0542 | 15.9823 | 0.0469 | 0.1815 | 14.3761 | 0.7870 |
| 12 | 41.3999 | 14.1514 | 0.0471 | 0.1930 | 14.2440 | 0.7269 |
| 13 | 40.6769 | 15.6827 | 0.0417 | 0.1848 | 14.1704 | 0.9594 |
| 14 | 41.7788 | 14.0057 | 0.0443 | 0.1875 | 14.2051 | 0.8594 |
| 15 | 41.6770 | 15.3273 | 0.0475 | 0.1892 | 14.3024 | 0.7365 |
| 16 | 41.9615 | 15.4293 | 0.0487 | 0.1899 | 14.3273 | 0.7013 |
| 17 | 41.1339 | 14.9891 | 0.0456 | 0.1889 | 14.2434 | 0.7971 |
| 18 | 40.6108 | 15.5937 | 0.0408 | 0.1938 | 14.0603 | 0.9404 |
| 19 | 40.2764 | 15.6346 | 0.0450 | 0.1830 | 14.3052 | 0.8440 |
| 20 | 41.2482 | 15.1137 | 0.0403 | 0.1831 | 14.1320 | 1.0481 |
表3 设计变量和目标变量值
Table 3 Design variables and target variable values
| 设计序号 | 设计变量 | 目标变量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/(°) | b/(°) | c/mm | h/mm | Rt/(K/W) | Pp/(10-4 W) | |
| 1 | 40.7373 | 14.6294 | 0.0494 | 0.1997 | 14.2379 | 0.6460 |
| 2 | 40.2388 | 14.5699 | 0.0437 | 0.1920 | 14.1493 | 0.8483 |
| 3 | 41.1666 | 14.8625 | 0.0458 | 0.1926 | 14.2133 | 0.7662 |
| 4 | 40.9078 | 14.4708 | 0.0441 | 0.1985 | 14.0928 | 0.7988 |
| 5 | 41.5828 | 15.5224 | 0.0400 | 0.1804 | 14.1536 | 1.0789 |
| 6 | 41.6110 | 15.8708 | 0.0427 | 0.1992 | 14.0577 | 0.8336 |
| 7 | 41.3162 | 14.0744 | 0.0448 | 0.1905 | 14.1883 | 0.8180 |
| 8 | 40.0497 | 15.0459 | 0.0433 | 0.1806 | 14.2568 | 0.9222 |
| 9 | 40.1199 | 14.2140 | 0.0415 | 0.1957 | 14.0597 | 0.9231 |
| 10 | 40.5807 | 15.4502 | 0.0491 | 0.1821 | 14.4176 | 0.7261 |
| 11 | 41.0542 | 15.9823 | 0.0469 | 0.1815 | 14.3761 | 0.7870 |
| 12 | 41.3999 | 14.1514 | 0.0471 | 0.1930 | 14.2440 | 0.7269 |
| 13 | 40.6769 | 15.6827 | 0.0417 | 0.1848 | 14.1704 | 0.9594 |
| 14 | 41.7788 | 14.0057 | 0.0443 | 0.1875 | 14.2051 | 0.8594 |
| 15 | 41.6770 | 15.3273 | 0.0475 | 0.1892 | 14.3024 | 0.7365 |
| 16 | 41.9615 | 15.4293 | 0.0487 | 0.1899 | 14.3273 | 0.7013 |
| 17 | 41.1339 | 14.9891 | 0.0456 | 0.1889 | 14.2434 | 0.7971 |
| 18 | 40.6108 | 15.5937 | 0.0408 | 0.1938 | 14.0603 | 0.9404 |
| 19 | 40.2764 | 15.6346 | 0.0450 | 0.1830 | 14.3052 | 0.8440 |
| 20 | 41.2482 | 15.1137 | 0.0403 | 0.1831 | 14.1320 | 1.0481 |
| 模型 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 热阻Rt | 0.9956 | 0.9983 |
| 泵功Pp | 0.9999 | 0.9999 |
表4 模型可信度检验
Table 4 Model credibility test
| 模型 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 热阻Rt | 0.9956 | 0.9983 |
| 泵功Pp | 0.9999 | 0.9999 |
| 项目 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标变量 | a/(°) | 41.45783427 | 41.34520548 | 41.38383064 | 41.40335531 | 41.39160136 |
| b/(°) | 14.70096577 | 14.53238701 | 14.46657789 | 14.45850405 | 14.45775171 | |
| c/mm | 0.04151237 | 0.043408283 | 0.04510961 | 0.0470403 | 0.04897439 | |
| h/mm | 0.1998938 | 0.199907562 | 0.19991469 | 0.19993298 | 0.19992672 | |
| 拟合结果 | Rt/(K/W) | 14.003928 | 14.06209062 | 14.1127671 | 14.16854199 | 14.22269925 |
| Pp/(10-4 W) | 0.89170968 | 0.816684084 | 0.75664856 | 0.69696176 | 0.647391251 | |
| 模拟结果 | Rt/(K/W) | 13.97747222 | 14.0375 | 14.11241667 | 14.15291667 | 14.20372222 |
| Pp/(10-4 W) | 0.89612137 | 0.81757886 | 0.76453825 | 0.70817871 | 0.65827214 | |
| 误差 | Error(Rt)/% | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.002 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| Error(Pp)/% | 0.49 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 1.58 | 1.65 | |
表5 Pareto优化值与模拟值对比
Table 5 Comparison of Pareto optimization value and simulation value
| 项目 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标变量 | a/(°) | 41.45783427 | 41.34520548 | 41.38383064 | 41.40335531 | 41.39160136 |
| b/(°) | 14.70096577 | 14.53238701 | 14.46657789 | 14.45850405 | 14.45775171 | |
| c/mm | 0.04151237 | 0.043408283 | 0.04510961 | 0.0470403 | 0.04897439 | |
| h/mm | 0.1998938 | 0.199907562 | 0.19991469 | 0.19993298 | 0.19992672 | |
| 拟合结果 | Rt/(K/W) | 14.003928 | 14.06209062 | 14.1127671 | 14.16854199 | 14.22269925 |
| Pp/(10-4 W) | 0.89170968 | 0.816684084 | 0.75664856 | 0.69696176 | 0.647391251 | |
| 模拟结果 | Rt/(K/W) | 13.97747222 | 14.0375 | 14.11241667 | 14.15291667 | 14.20372222 |
| Pp/(10-4 W) | 0.89612137 | 0.81757886 | 0.76453825 | 0.70817871 | 0.65827214 | |
| 误差 | Error(Rt)/% | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.002 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| Error(Pp)/% | 0.49 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 1.58 | 1.65 | |
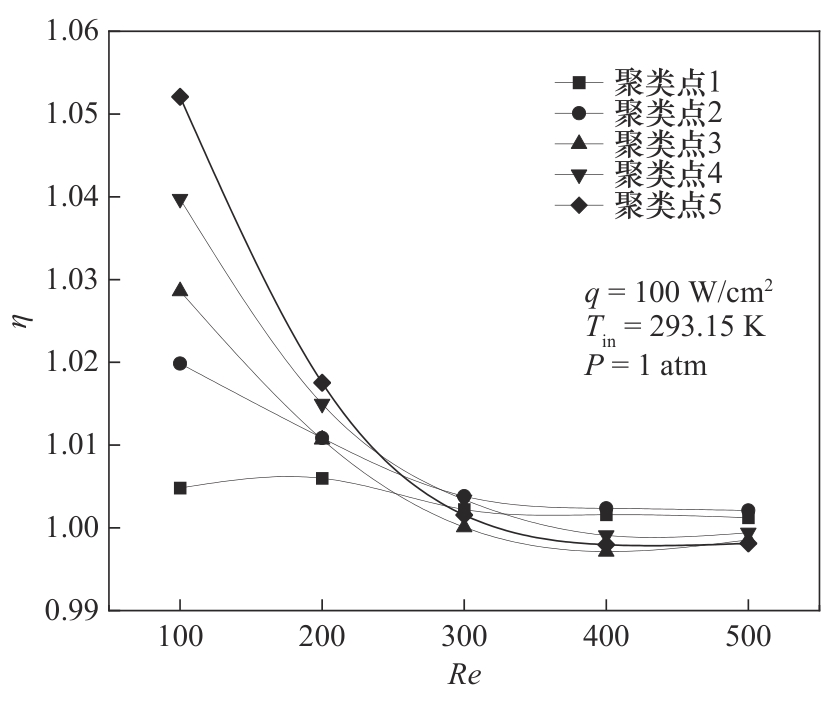
图4 不同聚类点的强化传热因子η随Reynolds数的变化(1 atm=101.325 kPa)
Fig.4 The change of heat transfer enhancement factor of different clustering points with Reynolds number
| 网格数/个 | Nu | f | 相对误差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nu | f | |||
| 105450 | 18.23633 | 11.70182 | 7.91 | 6.78 |
| 203823 | 18.26503 | 12.19808 | 8.08 | 2.83 |
| 512410 | 17.69948 | 12.34234 | 4.73 | 1.68 |
| 1156491 | 17.23667 | 12.43544 | 1.99 | 0.93 |
| 1640613 | 16.89959 | 12.55278 | — | — |
表6 网格无关性验证
Table 6 Grid independence verification
| 网格数/个 | Nu | f | 相对误差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nu | f | |||
| 105450 | 18.23633 | 11.70182 | 7.91 | 6.78 |
| 203823 | 18.26503 | 12.19808 | 8.08 | 2.83 |
| 512410 | 17.69948 | 12.34234 | 4.73 | 1.68 |
| 1156491 | 17.23667 | 12.43544 | 1.99 | 0.93 |
| 1640613 | 16.89959 | 12.55278 | — | — |
| 1 | Mohammadi R, Shahkarami N. Performance improvement of rectangular microchannel heat sinks using nanofluids and wavy channels[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A. Applications: An International Journal of Computation and Methodology, 2022, 82(10): 619-639. |
| 2 | Sakanova A, Keian C C, Zhao J Y. Performance improvements of microchannel heat sink using wavy channel and nanofluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 89: 59-74. |
| 3 | Wang S L, Zhu J F, An D, et al. Heat transfer enhancement of symmetric and parallel wavy microchannel heat sinks with secondary branch design[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2022, 171: 107229. |
| 4 | Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Hassani S M, Mazloumi S-H. Performance enhancement of straight and wavy miniature heat sinks using pin-fin interruptions and nanofluids[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2017, 122: 90-108. |
| 5 | 张海佳, 李惟毅, 云海涛. TiO2-蒸馏水纳米流体在内螺纹铜管内表面传热试验研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2012,48(12): 150-155. |
| Zhang H J, Li W Y, Yun H T. Experimental study of TiO2-distilled-water nanofluids surface heat transfer in internally ribbed copper tube[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(12): 150-155. | |
| 6 | 刘冉, 夏国栋, 杜墨. 三角形微通道内纳米流体流动与换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(12): 4936-4943. |
| Liu R, Xia G D, Du M. Characteristics of convective heat transfer in triangular microchannel heat sink using different nanofluids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(12): 4936-4943. | |
| 7 | Ebrahimi A, Rikhtegar F, Sabaghan A, et al. Heat transfer and entropy generation in a microchannel with longitudinal vortex generators using nanofluids[J]. Energy, 2016, 101: 190-201. |
| 8 | Alnaqi A A, Alsarraf J, Al-rashed A A A A, et al. Thermal-hydraulic analysis and irreversibility of the MWCNTs-SiO2/EG-H2O non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluids inside a zigzag micro-channels heat sink[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 122(5): 105158. |
| 9 | Mohammadpour J, Salehi F, Lee A, et al. Nanofluid heat transfer in a microchannel heat sink with multiple synthetic jets and protrusions[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2022, 179: 107642. |
| 10 | Zhang H N, Shao S Q, Xu H B, et al. Heat transfer and flow features of Al2O3-water nanofluids flowing through a circular microchannel-experimental results and correlations[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 61(2): 86-92. |
| 11 | Alkasmoul F S, Asaker M, Almogbel A, et al. Combined effect of thermal and hydraulic performance of different nanofluids on their cooling efficiency in microchannel heat sink[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2022, 30: 101776. |
| 12 | Chu Y M, Farooq U, Mishra N K, et al. CFD analysis of hybrid nanofluid-based microchannel heat sink for electronic chips cooling: applications in nano-energy thermal devices[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2023, 44: 102818. |
| 13 | Yang D, Sun B, Xu T K, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the flow and heat transfer characteristic of nanofluid in the recirculation zone of backward-facing step microchannels[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 199: 117527. |
| 14 | Wang H L, Chen X Y. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and flow of Al2O3-water nanofluid in microchannel heat sink with cantor fractal structure based on genetic algorithm[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2022, 1221: 339927. |
| 15 | 王江, 翟玉玲, 姚沛滔,等. 基于多目标遗传算法的微通道结构优化[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2020, 34(4): 1034-1043. |
| Wang J, Zhai Y L, Yao P T, et al. Structural optimization of microchannels based on multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2020, 34(4): 1034-1043. | |
| 16 | 史晓军, 李珊, 魏亚东,等. 纳米流体矩形微通道热沉结构参数多目标优化[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2018, 52(5): 56-61, 132. |
| Shi X J, Li S, Wei Y D, et al. Multi-objective optimization on the geometrical parameters of a nanofluid-cooled rectangular microchannel heat sink[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(5): 56-61, 132. | |
| 17 | 张帅, 欧阳峥嵘. 基于遗传算法的板翅式换热器优化策略[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2021, 42(11): 2919-2925. |
| Zhang S, Ouyang Z R. Optimization strategy of plate-fin heat exchanger based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2021, 42(11): 2919-2925. | |
| 18 | Mohd-Ghazali N, Jong-Taek O, Chien B N, et al. Optimization of square and circular ammonia-cooled microchannel heat sink with genetic algorithm[J]. Energy Procedia, 2014, 61: 55-58. |
| 19 | 郝晓红, 胡争光, 侯琼, 等. 基于多目标遗传算法的串联通道水冷散热器优化设计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(10): 151-155. |
| Hao X H, Hu Z G, Hou Q, et al. Optimization of serpentine channel heat sink based on multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(10): 151-155. | |
| 20 | Yu F, Ding W, Luo X P, et al. Multi-objective optimization of fractal-tree microchannels in a rectangular heat sink by a distributed-adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 217: 124672. |
| 21 | Jahanbakhshi A, Nadooshan A A, Bayareh M. Multi-objective optimization of microchannel heatsink with wavy microtube by combining response surface method and genetic algorithm[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 2022, 140: 12-31. |
| 22 | Kose H A, Yildizeli A, Cadirci S. Parametric study and optimization of microchannel heat sinks with various shapes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 211: 118368. |
| 23 | Majmader F B, Hasan M J. Multi-objective hydrothermal performance optimization of a microchannel heat sink equipped with delta winglet vortex generators using NSGA-Ⅱ genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2024, 201: 109046. |
| 24 | 朱汝凯, 程潇, 刘金亚, 等. 针翅式多孔倾斜射流微通道流动传热特性与多目标优化[J]. 化工进展, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-2297 . |
| Zhu R K, Cheng X, Liu J Y, et al. Flow and heat transfer characteristics and multi-objective optimization of pin-fin multi inclined jet microchannels[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-2297 . | |
| 25 | Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, et al. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows(part Ⅰ): Fundamental and theory[J]. Physics Reports, 2019, 790: 1-48. |
| 26 | Xuan Y M, Roetzel W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2000, 43(19): 3701-3707. |
| 27 | 贾玉婷, 夏国栋, 马丹丹, 等. 水滴型凹穴微通道流动与传热的熵产分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(4): 141-148. |
| Jia Y T, Xia G D, Ma D D, et al. Entropy generation analysis of flow and heat transfer in microchannel with droplet reentrant cavities[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(4): 141-148. | |
| 28 | Mukherjee S, Wciślik S, Khadanga V, et al. Influence of nanofluids on the thermal performance and entropy generation of varied geometry microchannel heat sink[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2023, 49: 103241. |
| 29 | Kalteh M, Abbassi A, Saffar-Avval M, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluid forced convection inside a wide microchannel heat sink[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 36: 260-268. |
| 30 | 王楠, 陈俊, 安青松, 等. 纳米流体分散稳定性的分子动力学研究初探[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2011, 32(7): 1107-1110. |
| Wang N, Chen J, An Q S, et al. Elementary research on the dispersion and stability of nanofluids by molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2011, 32(7): 1107-1110. |
| [1] | 王瀚彬, 胡帅, 毕丰雷, 李隽森, 贺来宾. 新型波纹翅片金属氢化物反应器的放氢性能有限元分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 221-230. |
| [2] | 高羡明, 杨汶轩, 卢少辉, 任晓松, 卢方财. 双槽道结构对超疏水表面液滴合并弹跳的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 208-220. |
| [3] | 韩启沃, 刘永峰, 裴普成, 张璐, 姚圣卓. 工作温度对PEMFC水分布、质子传输及性能影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 374-384. |
| [4] | 邓志诚, 杨欢, 王斯民, 王家瑞. 微混燃烧器中微管结构对氢燃料掺混效果与燃烧性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 335-347. |
| [5] | 杨晔, 卢建刚. 基于融合Transformer的门尼系数预测建模研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 266-282. |
| [6] | 张俊杰, 陈源, 李运堂, 李孝禄, 王冰清, 彭旭东. 超椭圆织构浮动坝箔片端面气膜密封动态性能分析与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 296-310. |
| [7] | 韩志敏, 周相宇, 张宏宇, 徐志明. 不同粗糙元结构下CaCO3污垢局部沉积特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 151-160. |
| [8] | 李雨诗, 陈源, 李运堂, 彭旭东, 王冰清, 李孝禄. 新型柔性坝箔片端面气膜密封变形协调分析及性能智能优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 324-334. |
| [9] | 李海东, 张奇琪, 杨路, AKRAM Naeem, 常承林, 莫文龙, 申威峰. 采用智能进化算法的管壳式换热器详细设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 241-255. |
| [10] | 董新宇, 边龙飞, 杨怡怡, 张宇轩, 刘璐, 王腾. 冷却条件下倾斜上升管S-CO2流动与传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [11] | 郭骐瑞, 任丽媛, 陈康, 黄翔宇, 马卫华, 肖乐勤, 周伟良. 用于HTPB推进剂浆料的静态混合管数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [12] | 李匡奚, 于佩潜, 王江云, 魏浩然, 郑志刚, 冯留海. 微气泡旋流气浮装置内流动分析与结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [13] | 汪张洲, 唐天琪, 夏嘉俊, 何玉荣. 基于复合相变材料的电池热管理性能模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [14] | 李雨霜, 王兴成, 温伯尧, 骆政园, 白博峰. 多孔介质中乳状液驱油的两相流动过程及其影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 56-66. |
| [15] | 刘律, 刘洁茹, 范亮亮, 赵亮. 基于层流效应的被动式颗粒分离微流控方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 67-75. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号