化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2929-2938.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241446
收稿日期:2024-12-13
修回日期:2025-01-17
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
骆政园,温伯尧
作者简介:李品贤(2002—),男,硕士研究生,xian.2002@qq.com
基金资助:
Pinxian LI( ), Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO(
), Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO( ), Boyao WEN(
), Boyao WEN( ), Bofeng BAI
), Bofeng BAI
Received:2024-12-13
Revised:2025-01-17
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Zhengyuan LUO, Boyao WEN
摘要:
油藏开发后期液滴堵塞于微孔喉中对实际采油过程造成不利影响。纳米颗粒吸附于液滴界面降低界面张力并诱发界面黏弹性,研究其对微孔喉中液滴运移及堵塞的调控机制具有重要意义。通过微流体可视化实验,研究了纳米颗粒吸附界面对液滴在运移时发生堵塞的影响规律。通过分析液滴尺寸与临界堵塞流量以及临界堵塞毛细数的变化关系,得到纳米颗粒吸附界面对液滴堵塞行为的影响机理,即诱发界面黏弹性加剧运移液滴的堵塞,利用液滴平衡关系推导出液滴堵塞临界条件的数学模型。通过分析液滴运移及堵塞的状态分布相图,确定堵塞状态的临界转变条件,证明了纳米颗粒吸附界面具有的界面黏弹性使运移液滴更容易被微孔喉捕获而堵塞,为油藏开发中纳米驱调控技术提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
李品贤, 郭峰, 骆政园, 温伯尧, 白博峰. 纳米颗粒吸附界面对微孔喉中液滴运移及堵塞的调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2929-2938.
Pinxian LI, Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO, Boyao WEN, Bofeng BAI. Regulation of nanoparticle adsorption interface on droplet migration and blockage in micropore throat[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2929-2938.
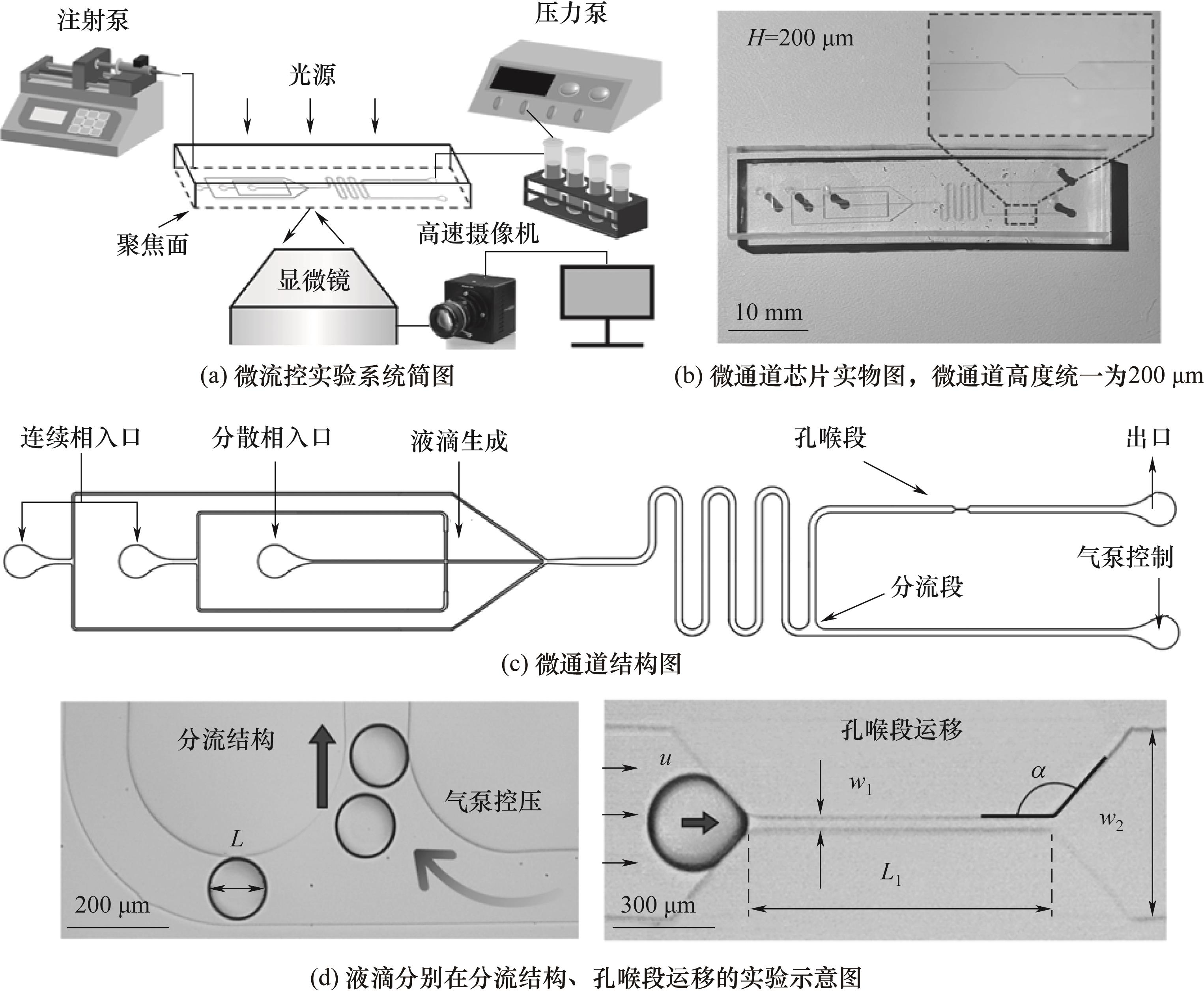
图1 实验系统、微通道结构、微通道孔喉段处液滴受限堵塞示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the experimental system, microchannel structure, and the limited blockage of droplets at the pore-throat section of the microchannel
| 试剂组别 | COOH-PS(质量分数)/% | NH2-PDMS-NH2(质量分数)/% | γ/(mN/m) | ρ/(g/cm3) | μ/(mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯水纯油 | 0 | 0 | 25.2±0.6 | — | — |
| 仅添加纳米颗粒 | 0.5 | 0 | 24.7±0.4 | — | — |
| 纳米颗粒表面活性剂 | 0.001 | 1 | 12.0±0.7 | 0.998(W)/0.963(O) | 1(W)/10O) |
| 0.005 | 1 | 10.3±0.7 | — | — | |
| 0.05 | 1 | 6.4±0.8 | — | — |
表1 不同流体系统的相关参数
Table 1 The relative parameters for three different fluid systems
| 试剂组别 | COOH-PS(质量分数)/% | NH2-PDMS-NH2(质量分数)/% | γ/(mN/m) | ρ/(g/cm3) | μ/(mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯水纯油 | 0 | 0 | 25.2±0.6 | — | — |
| 仅添加纳米颗粒 | 0.5 | 0 | 24.7±0.4 | — | — |
| 纳米颗粒表面活性剂 | 0.001 | 1 | 12.0±0.7 | 0.998(W)/0.963(O) | 1(W)/10O) |
| 0.005 | 1 | 10.3±0.7 | — | — | |
| 0.05 | 1 | 6.4±0.8 | — | — |
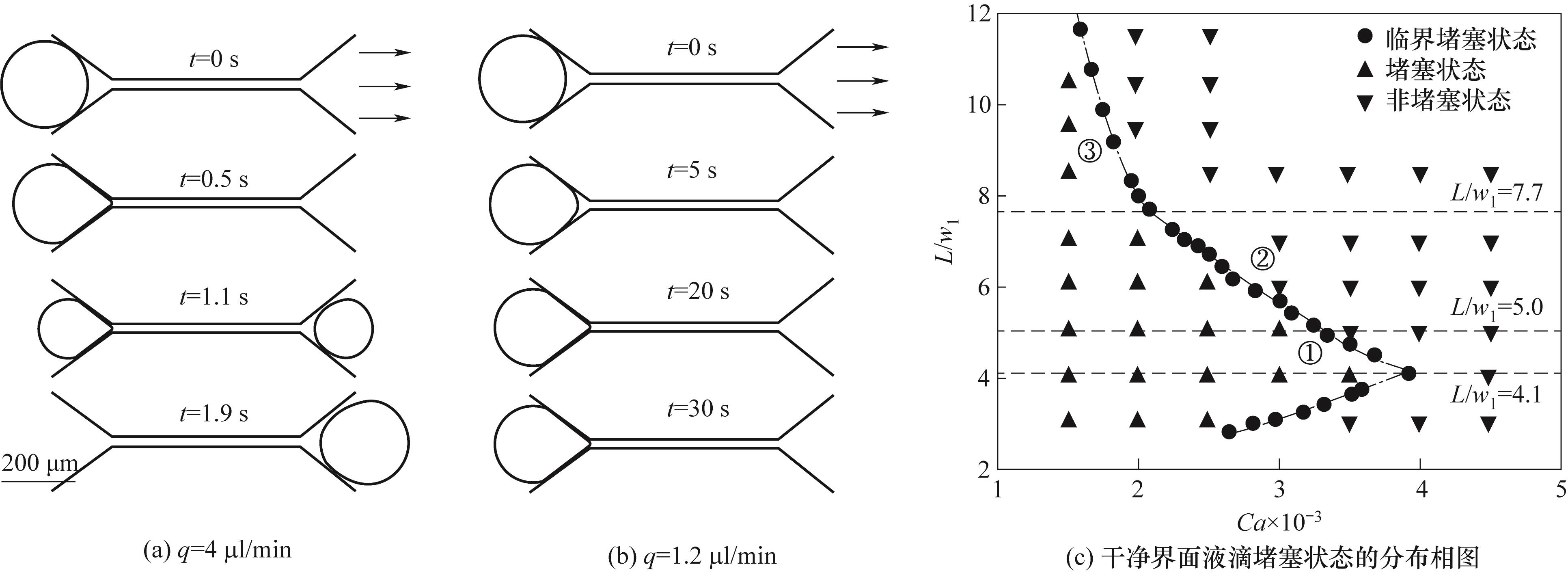
图2 相同尺寸液滴(L/w1 = 6.5)在不同流量下经过孔喉结构的时间序列图(a)、(b);及干净界面液滴堵塞状态的分布相图(c)(点划线代表堵塞状态与非堵塞状态的理论预测)
Fig.2 Time evolution of the same size droplet (L/w1 = 6.5) passing through the pore-throat structure under different flow rates (a)、(b); the distribution phase diagram of the blocked state of the clean interface droplet (c) (The dotted line represents the theoretical prediction of the blocked state and the non-blocked state)
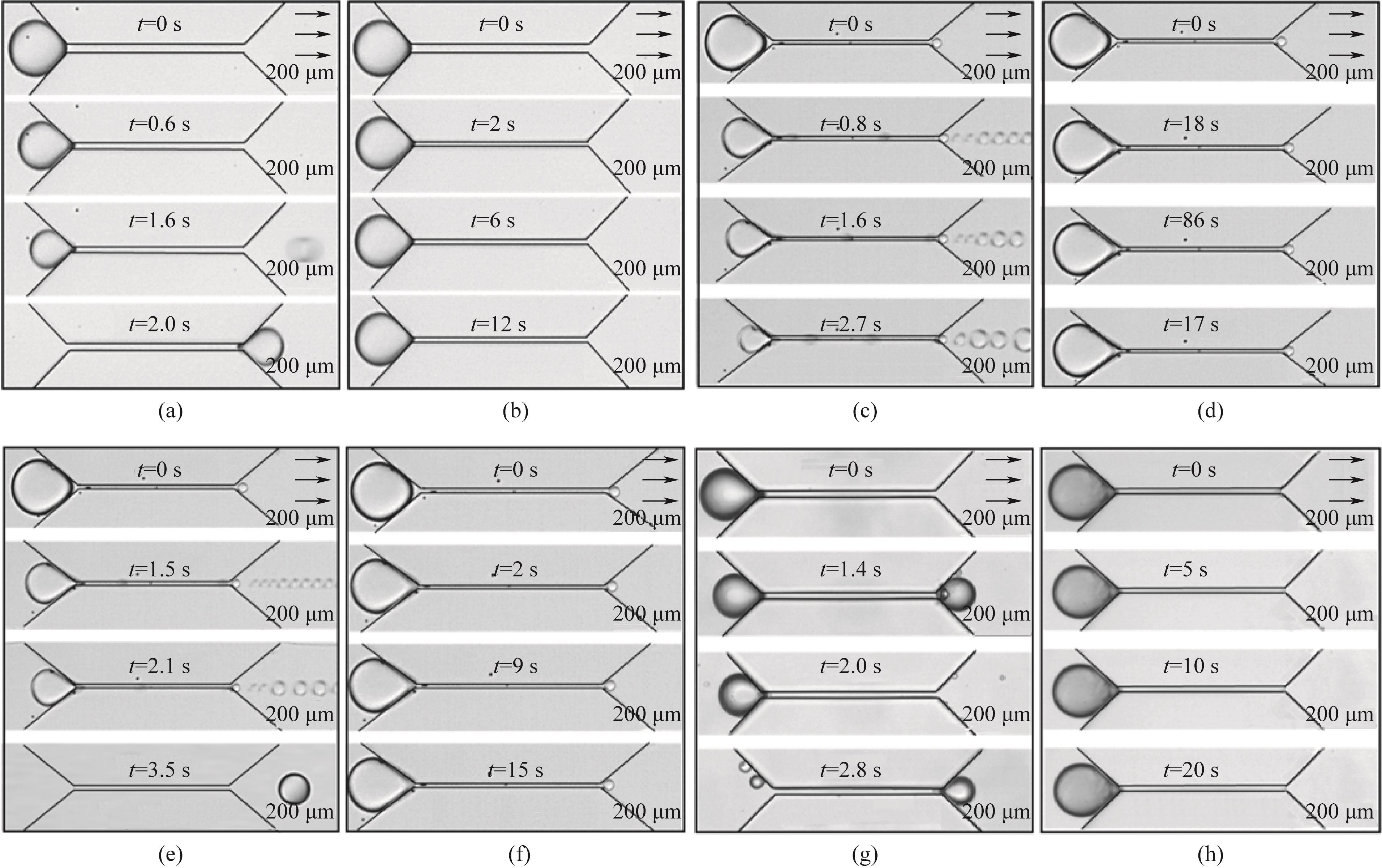
图4 不同试剂作用下运移液滴(相同大小L/w1 = 3.5)经过微孔喉的时间序列图。 (a) 纯水纯油组别,流量q = 4.0 μl·min-1;(b) 纯水纯油组别,流量q = 2.9 μl·min-1;(c) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.5%,流量q = 3.5 μl·min-1;(d) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.5%,流量q = 3.1 μl·min-1;(e) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.005%,聚合物表活剂浓度为1%,流量q = 1.6 μl·min-1;(f) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.005%,聚合物表活剂浓度为1%,流量q = 0.9 μl·min-1;(g) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.5%,聚合物表活剂浓度为1%,流量q = 1.5 μl·min-1;(h) 纳米颗粒浓度为0.005%,聚合物表活剂浓度为1%,流量q = 1.0 μl·min-1
Fig.4 Time evolution of migration droplets (the same size L/w1 = 3.5) passing through the micropore throat under the action of different reagents. (a) Pure liquid group, flow rate q = 4.0 μl·min-1; (b) Pure liquid group, flow rate q = 2.9 μl·min-1; (c) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, and the flow rate q = 3.5 μl·min-1; (d) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, and the flow rate q = 3.1 μl·min-1; (e) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate was 1.6 μl·min-1; (f) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 0.9 μl·min-1; (g) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 1.5 μl·min-1; (h) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 1.0 μl·min-1
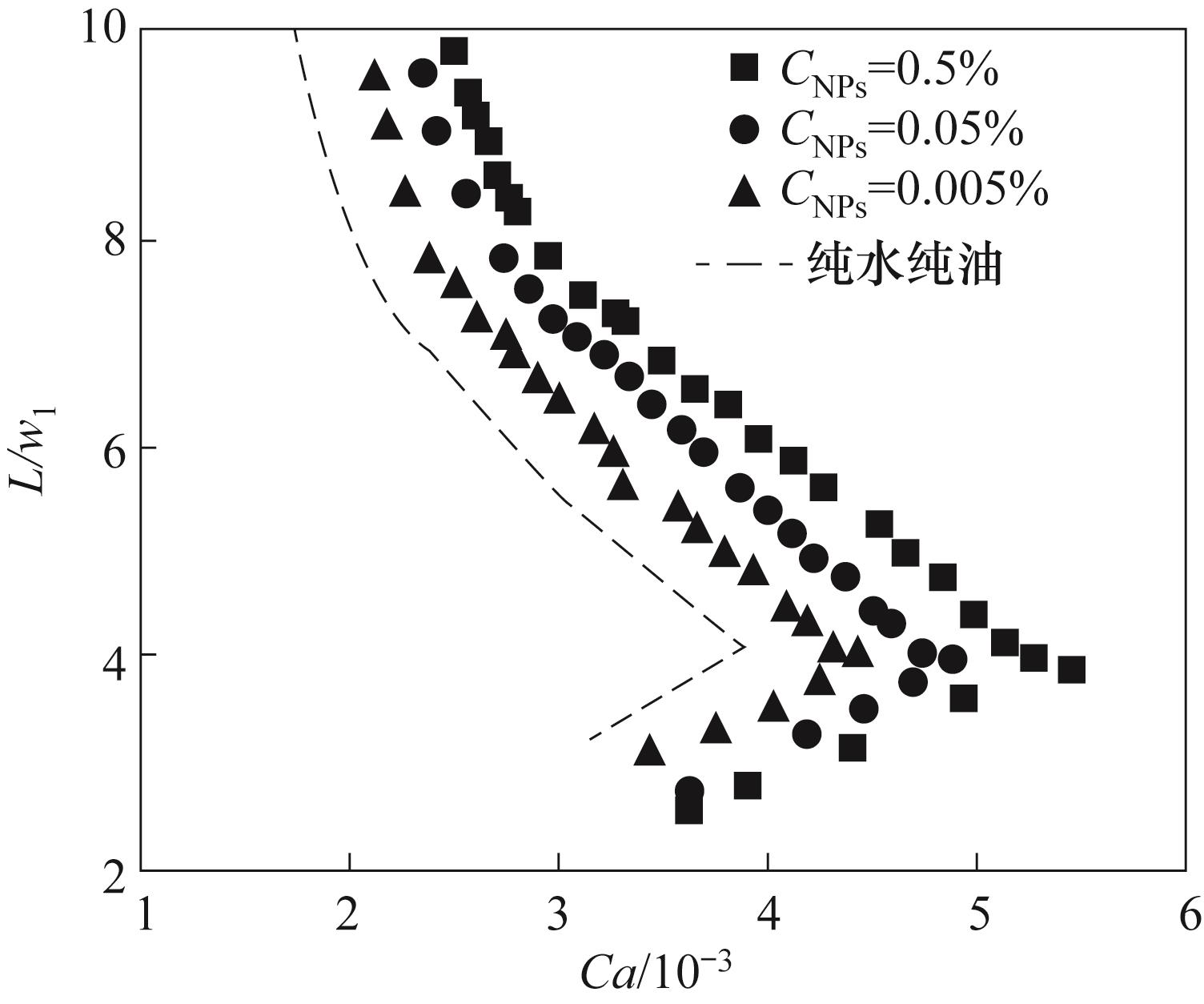
图6 不同浓度纳米颗粒表面活性剂对液滴临界堵塞毛细数的影响
Fig.6 Effect of different concentrations of nanoparticles surfactant on the critical blocking capillary number of droplets
| [1] | Du S H, Shi Y M. Concise extraction and characterization of the pore-throat network in unconventional hydrocarbon reservoirs: a new perspective[J]. Petroleum Science, 2024, 21(3): 1474-1487. |
| [2] | Singh K, Jung M, Brinkmann M, et al. Capillary-dominated fluid displacement in porous media[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 51: 429-449. |
| [3] | 罗莉涛, 廖广志, 刘卫东, 等. Marangoni对流启动残余油微观机理[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9): 1127-1134. |
| Luo L T, Liao G Z, Liu W D, et al. Micromechanism of residual oil mobilization by Marangoni convection[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1127-1134. | |
| [4] | Lai J, Wang G W, Wang Z Y, et al. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 436-457. |
| [5] | 吴飞鹏, 李娜, 杨维, 等. 水力脉动波驱动微观剩余油实验与机理分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(6): 1217-1226. |
| Wu F P, Li N, Yang W, et al. Experimental characterization and mechanism analysis of hydraulic pulsation waves driving microscopic residual oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(6): 1217-1226. | |
| [6] | Liu Z X, Liang Y, Wang Q, et al. Status and progress of worldwide EOR field applications[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 193: 107449. |
| [7] | Habib S H, Yunus R, Zakaria R, et al. Chemical enhanced oil recovery: synergetic mechanism of alkali, surfactant and polymer with overview of methyl ester sulfonate as a green alternative for EOR surfactant[J]. Fuel, 2024, 363: 130957. |
| [8] | Mir H, Siavashi M. Whole-time scenario optimization of steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) with temperature, pressure, and rate control using an efficient hybrid optimization technique[J]. Energy, 2022, 239: 122149. |
| [9] | Tan Y S, Li Q, Xu L, et al. A critical review of carbon dioxide enhanced oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Fuel, 2022, 328: 125256. |
| [10] | Shi N, Mohibullah M, Easley C J. Active flow control and dynamic analysis in droplet microfluidics[J]. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 14(1): 133-153. |
| [11] | Padmanabhan S, Misteli T, DeVoe D L. Controlled droplet discretization and manipulation using membrane displacement traps[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(21): 3717-3724. |
| [12] | Rambach R W, Biswas P, Yadav A, et al. Fast selective trapping and release of picoliter droplets in a 3D microfluidic PDMS multi-trap system with bubbles[J]. The Analyst, 2018, 143(4): 843-849. |
| [13] | Carreras M P, Wang S H. A multifunctional microfluidic platform for generation, trapping and release of droplets in a double laminar flow[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 251: 106-111. |
| [14] | Courtney M, Chen X M, Chan S, et al. Droplet microfluidic system with on-demand trapping and releasing of droplet for drug screening applications[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(1): 910-915. |
| [15] | Zhang Z F, Drapaca C, Chen X L, et al. Droplet squeezing through a narrow constriction: minimum impulse and critical velocity[J]. 2017, 29(7): 072102. |
| [16] | Liang M C, Yang S S, Miao T J, et al. Minimum applied pressure for a drop through an abruptly constricted capillary[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2015, 19(1): 1-8. |
| [17] | Zhang Z F, Drapaca C, Gritsenko D, et al. Pressure of a viscous droplet squeezing through a short circular constriction: an analytical model[J]. 2018, 30(10): 102004. |
| [18] | He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F. Release of a trapped droplet in a single micro pore throat[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 554: 1-8. |
| [19] | Imani G, Zhang L, Xu C, et al. Finite droplets vs long droplets: discrepancy in release conditions in a microscopic constricted channel[J]. 2023, 35(3): 032101. |
| [20] | Wen B Y, Sun C Z, Bai B F. Nanoparticle-induced ion-sensitive reduction in decane-water interfacial tension[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(35): 22796-22804. |
| [21] | 赵赫, 费滢洁, 朱春英, 等. 高黏体系中纳米颗粒稳定气泡的形变及破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| Zhao H, Fei Y J, Zhu C Y, et al. Deformation and breakup behavior of nanoparticle-stabilized bubbles in high-viscosity systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. | |
| [22] | Xu K, Zhu P X, Huh C, et al. Microfluidic investigation of nanoparticles' role in mobilizing trapped oil droplets in porous media[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(51): 13673-13679. |
| [23] | Frijters S, Günther F, Harting J. Effects of nanoparticles and surfactant on droplets in shear flow[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(24): 6542-6556. |
| [24] | Cui M M, Emrick T, Russell T P. Stabilizing liquid drops in nonequilibrium shapes by the interfacial jamming of nanoparticles[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6157): 460-463. |
| [25] | Toor A, Helms B A, Russell T P. Effect of nanoparticle surfactants on the breakup of free-falling water jets during continuous processing of reconfigurable structured liquid droplets[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(5): 3119-3125. |
| [26] | Toor A, Lamb S, Helms B A, et al. Reconfigurable microfluidic droplets stabilized by nanoparticle surfactants[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(3): 2365-2372. |
| [27] | Chai Y, Lukito A, Jiang Y, et al. Fine-tuning nanoparticle packing at water-oil interfaces using ionic strength[J]. Nano letters, 2017, 17(10): 6453-6457. |
| [28] | Subramanian R S. The Stokes force on a droplet in an unbounded fluid medium due to capillary effects[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1985, 153: 389-400. |
| [29] | He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F. Breakup of pancake droplets flowing through a microfluidic constriction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 220: 115649. |
| [30] | Shi S W, Russell T P. Nanoparticle assembly at liquid–liquid interfaces: from the nanoscale to mesoscale[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(44): 1800714. |
| [31] | Wang B B, Yin B Q, Zhang Z, et al. The assembly and jamming of nanoparticle surfactants at liquid-liquid interfaces[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(10): e202114936. |
| [32] | Luo Y Z, Yang Y, Wang Y K, et al. Reconfigurable liquids constructed by pillar [6] arene-based nanoparticle surfactants[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(33): e202207199. |
| [1] | 陈巨辉, 陈轲, 李丹, 杨天一, ZHURAVKOV Michael, LAPATSIN Siarhel, 姜文锐. 基于多组分DQMOM模型的FCC辅助纳米颗粒混合体系流化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2616-2625. |
| [2] | 蔡本安, 张建新, 龙城君, 杜乔琛, 车勋建, 张义迎, 蔡伟华. 喷雾闪蒸制备微纳米颗粒[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1334-1345. |
| [3] | 赵赫, 费滢洁, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 马友光. 高黏体系中纳米颗粒稳定气泡的形变及破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| [4] | 刘梦绮, 王凯, 骆广生. 基于人工智能的微分散基础研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1096-1104. |
| [5] | 阮达, 侯静静, 薄紫一, 张帅帅, 马学虎. 微通道内环状流薄液膜厚度及波动实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4178-4187. |
| [6] | 颜诗宇, 高姣姣, 杨太顺, 谢尚志, 杨艳娟, 徐晶. 钌基催化剂配位环境对聚乙烯氢解性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3588-3599. |
| [7] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [8] | 何宣志, 何永清, 闻桂叶, 焦凤. 磁液液滴颈部自相似破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [9] | 陈巨辉, 张谦, 舒崚峰, 李丹, 徐鑫, 刘晓刚, 赵晨希, 曹希峰. 基于DEM方法的旋转流化床纳米颗粒流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2374-2381. |
| [10] | 张银宁, 王进卿, 冯致, 詹明秀, 徐旭, 张光学, 池作和. 升温条件下多孔介质内气泡的生长和聚并行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1509-1518. |
| [11] | 张童, 杨扬, 叶丁丁, 陈蓉, 朱恂, 廖强. 催化剂分布对可渗透阳极微流体燃料电池性能特性影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4156-4162. |
| [12] | 艾承燚, 乔金硕, 王振华, 孙旺, 孙克宁. 原位析出纳米合金的PrBaFe2O6-δ 基阳极构筑及其在固体碳燃料电池中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [13] | 童海航, 石德智, 刘嘉宇, 蔡桦伊, 罗丹, 陈飞. 金属纳米颗粒辅助木质纤维素暗发酵生物制氢的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1417-1435. |
| [14] | 王之豪, 宋欣, 殷亚然, 张先明. 微流控纺丝中凝胶速率对螺旋纤维形貌的调控机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166. |
| [15] | 高文莉, 辛忠. Fe对Ni/SBA-16催化CO低温甲烷化促进作用的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 241-254. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号