化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2939-2957.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241204
刘峰1( ), 韩春硕1, 张益1(
), 韩春硕1, 张益1( ), 刘彦成2(
), 刘彦成2( ), 郁林军3, 申家伟1, 高晓泉1, 杨凯1
), 郁林军3, 申家伟1, 高晓泉1, 杨凯1
收稿日期:2024-10-30
修回日期:2024-11-28
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
张益,刘彦成
作者简介:刘峰(1984—),男,博士,副教授,xsyuliufeng@163.com
基金资助:
Feng LIU1( ), Chunshuo HAN1, Yi ZHANG1(
), Chunshuo HAN1, Yi ZHANG1( ), Yancheng LIU2(
), Yancheng LIU2( ), Linjun YU3, Jiawei SHEN1, Xiaoquan GAO1, Kai YANG1
), Linjun YU3, Jiawei SHEN1, Xiaoquan GAO1, Kai YANG1
Received:2024-10-30
Revised:2024-11-28
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Yi ZHANG, Yancheng LIU
摘要:
表面活性剂对油水界面性质具有重要影响,高温高盐油藏环境严重影响表面活性剂的界面化学特性和驱油效果。为研究不同表面活性剂结构对油水界面性质的影响。采用分子动力学模拟方法研究了阴离子表面活性剂十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)和进行基团修饰的表面活性剂SDS-B在油水界面上的微观行为和作用机理。结果表明,在SDS表面活性剂的疏水尾链中引入链烷烃改变了表面活性剂分子在油水界面的排列方式,相较于单烃链表面活性剂,双烃链结构使表面活性剂在高温高盐环境下依旧能紧密垂直于油水界面,SDS-B具有良好的分子界面行为。同时,链烷烃基团数目的增加导致SDS分子表现出轻微的弯曲,使表面活性剂分子形成多处聚集体,有利于形成多层吸附。SDS-B头基对Ca2+的排斥作用明显强于SDS,径向分布函数第一峰值降低0.89,而且SDS-B在Ca2+环境下的油水界面厚度较SDS得到改善,厚度从1.13 nm升高到1.52 nm,显著增强了界面稳定性,表明烃链的引入提高了表面活性剂的抗Ca2+盐特性。SDS-B头基易与烃链基团形成分子内氢键结构,头基水化能力提高,盐水中的阳离子受到较大的束缚力,Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+扩散系数分别降低了0.027×10-4、0.065×10-4、0.064×10-4 cm2/s。在复杂盐环境及更高离子浓度下SDS-B头基亲水性及界面行为均优于SDS。本研究对三次采油中新型表面活性剂的设计具有重要的指导意义。
中图分类号:
刘峰, 韩春硕, 张益, 刘彦成, 郁林军, 申家伟, 高晓泉, 杨凯. 高温高盐环境下单烃链和双烃链表面活性剂对油水界面性质影响的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2939-2957.
Feng LIU, Chunshuo HAN, Yi ZHANG, Yancheng LIU, Linjun YU, Jiawei SHEN, Xiaoquan GAO, Kai YANG. Micro-mechanism study on the effect of single and double hydrocarbon chain surfactants on oil-water interface properties under high temperature and high salt reservoir[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2939-2957.
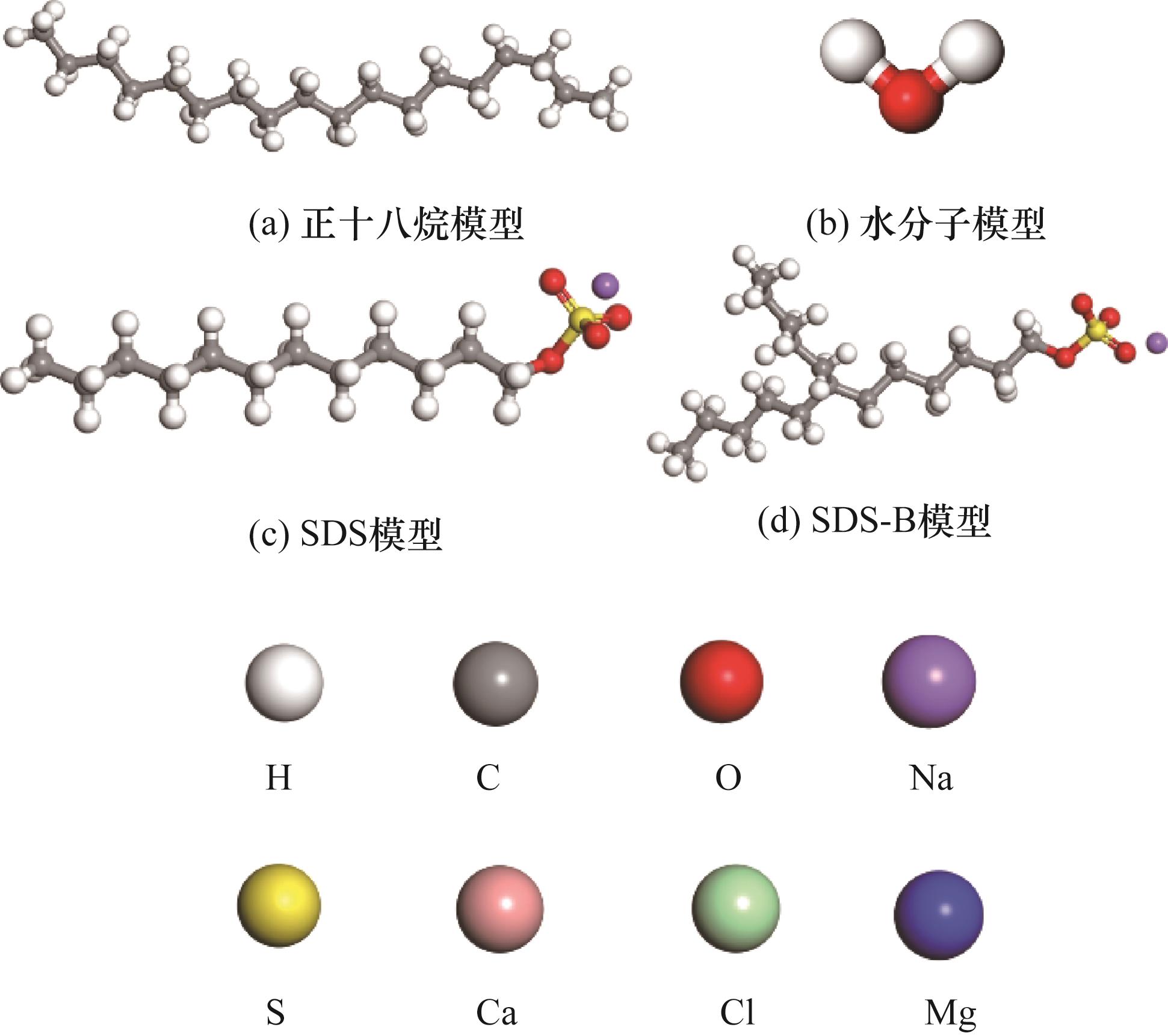
图1 油、水和表面活性剂模型(表面活性剂模型分别为SDS,以及在SDS基础上进行修饰,尾链加入一个链烷烃,新的表面活性剂命名为SDS-B;彩色球代表不同的元素)
Fig.1 Oil, water and surfactant model (surfactant model is SDS, and modified on basis of SDS, and a chain alkane is added to tail chain, new surfactant is named SDS-B, and color ball represents different elements)
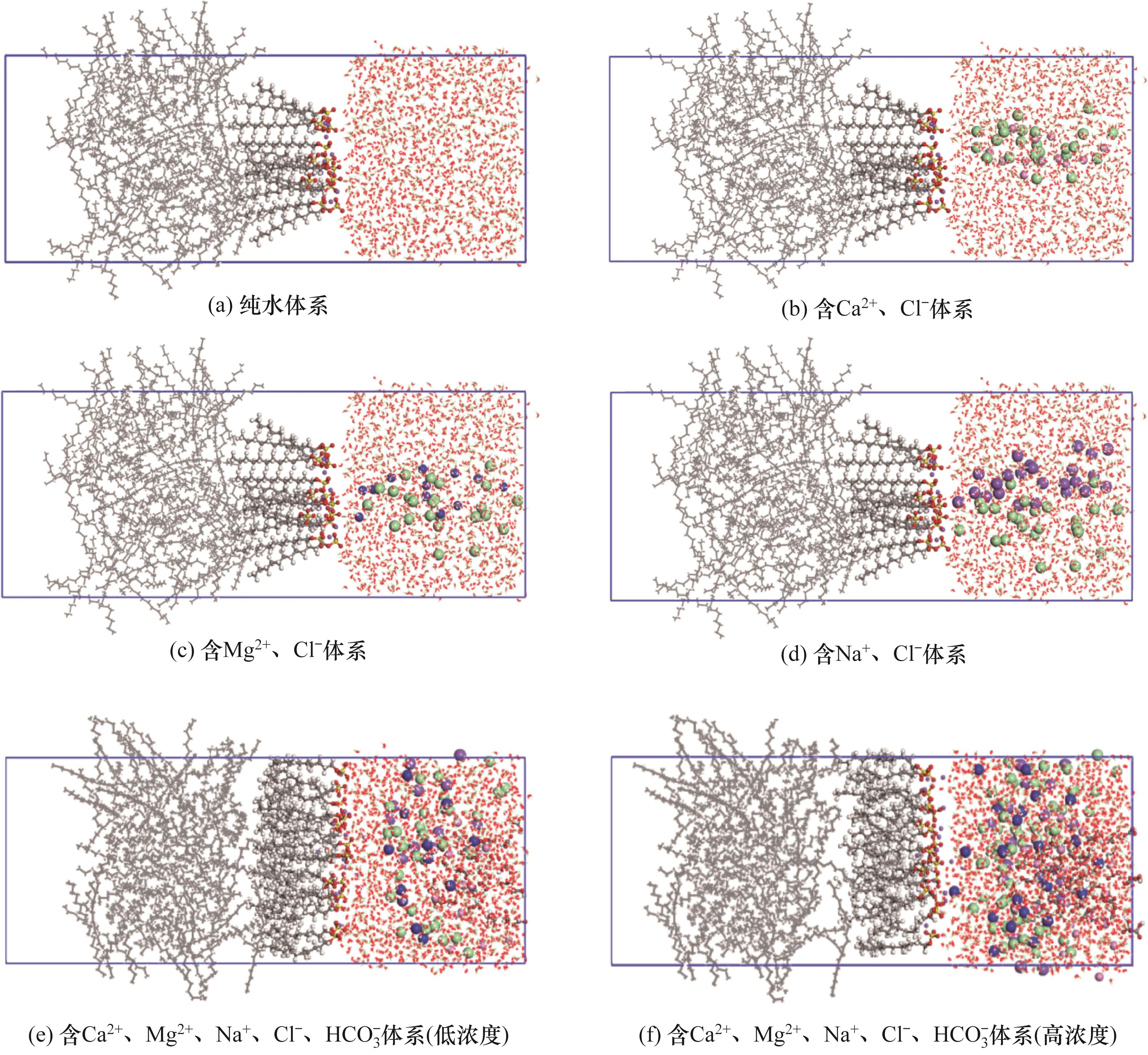
图2 5种体系初始构型[白色(氢)、灰色(碳)、红色(氧)、黄色(硫)、紫色(钠)、绿色(氯)、粉色(钙)和深蓝色(镁)]
Fig.2 Initial configurations of five systems [white (hydrogen), gray(carbon), red (oxygen), yellow (sulfur), purple (sodium), green (chlorine), pink (calcium) and dark blue (magnesium)]
| 体系 | 体系分子/离子个数 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDS | SDS-B | 正十八烷 | H2O | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl- | ||
| 体系1 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 体系2 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系3 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系4 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系5 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 30 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 30 | |
| 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 60 | 60 | |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 60 | 60 | |
表1 体系所含分子/离子个数
Table 1 Number of molecules/ions in system
| 体系 | 体系分子/离子个数 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDS | SDS-B | 正十八烷 | H2O | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl- | ||
| 体系1 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 体系2 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系3 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系4 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| 体系5 | 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 30 |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 30 | |
| 16 | 0 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 60 | 60 | |
| 0 | 16 | 80 | 1600 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 60 | 60 | |
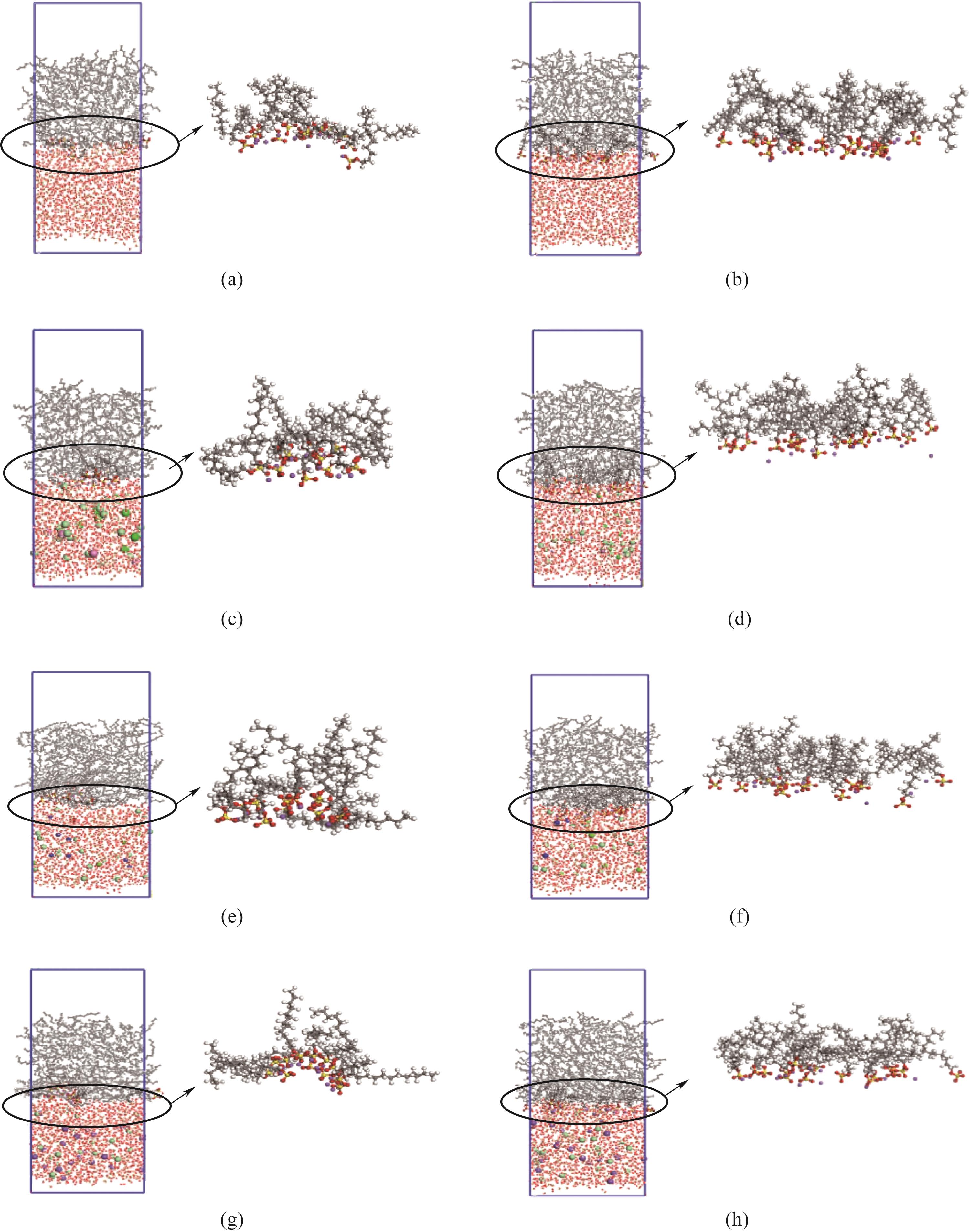
图4 300 K下表面活性剂在油水界面的分布形态:(a)、(c)、(e)、(g)分别代表SDS在纯水体系、含Ca2+体系、含Mg2+体系,含Na+体系的快照;(b)、(d)、(f)、(h)分别代表SDS-B在纯水体系、含Ca2+体系、含Mg2+体系、含Na+体系的快照
Fig.4 Distribution of surfactants at oil-water interface at 300 K: (a), (c), (e), (g) represents snapshots of SDS in pure water system, Ca2+-containing system, Mg2+-containing system and Na+ -containing system, respectively; (b), (d), (f), (h) represents snapshots of SDS-B in pure water system, Ca2+-containing system, Mg2+ -containing system and Na+ -containing system, respectively
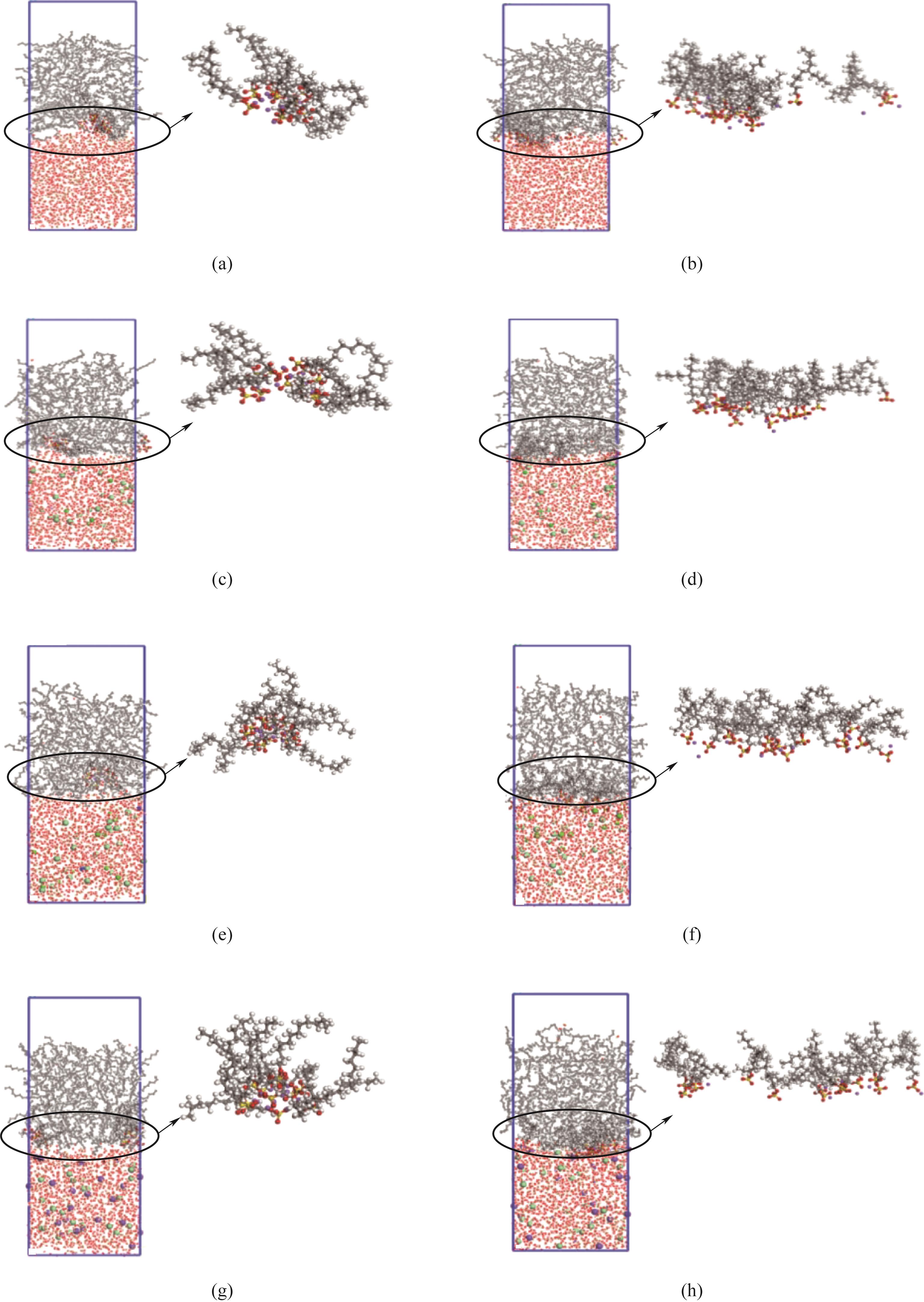
图5 390 K下表面活性剂在油水界面的分布形态:(a)、(c)、(e)、(g)分别代表SDS在纯水体系、含Ca2+体系、含Mg2+体系,含Na+体系的快照;(b)、(d)、(f)、(h)分别代表SDS-B在纯水体系、含Ca2+体系、含Mg2+体系、含Na+体系的快照
Fig.5 Distribution of surfactants at the oil-water interface at 390 K: (a), (c), (e), (g) represents snapshot of SDS in pure water system, Ca2+-containing system, Mg2+-containing system and Na+-containing system, respectively: (b), (d), (f), (h) represents snapshots of SDS-B in pure water system, Ca2+-containing system, Mg2+-containing system and Na+-containing system, respectively

图6 盐离子密度分布曲线:(a)~(d)为含SDS的盐离子密度分布,温度分别为300、330、360、390 K;(e)~(h)为含SDS-B的盐离子密度分布,温度分别为300、330、360、390 K。System2代表Ca2+,System3代表Mg2+,System4代表Na+
Fig.6 Salt ion density distribution curve: (a)—(d) is salt ion density distribution containing SDS, and temperature from (a) to (d) is 300, 330, 360, 390 K, respectively; (e)—(h) is salt ion density distribution containing SDS-B, and temperatures from (e) to (h) are 300, 330, 360, 390 K, respectively. System2 represents Ca2+, System3 represents Mg2+, System4 represents Na+

图8 不同体系中油水界面构型:(a)~(d)为SDS在4种体系中的油水界面分布构型;(e)~(h)为SDS-B在4种体系中的油水界面分布构型(4种体系分别为纯水体系、含Ca2+体系、含Mg2+体系和含Na+体系)
Fig.8 Oil-water interface configuration in different systems: (a)—(d) is the oil-water interface distribution configuration of SDS in four systems, (e)—(h) is the oil-water interface distribution configuration of SDS-B in four systems, which are pure water system, Ca2+-containing system, Mg2+-containing system and Na+-containing system

图9 不同体系中表面活性剂头基RDF:(a)~(d)为SDS的头基与水分子中的氢的径向分布函数曲线;(e)~(h)为SDS-B的头基与水分子中的氢的径向分布函数曲线,温度分别为300、330、360、390 K
Fig.9 Surfactant head group RDF in different systems: (a)—(d) is radial distribution function curve of SDS head group and hydrogen in water molecules, (e)—(h) is radial distribution function curve of SDS-B head group and hydrogen in water molecules; temperatures are 300, 330, 360, 390 K, respectively
| Cation type | Cation diffusion coefficient in SDS/(10-4 cm2/s) | Cation diffusion coefficient in SDS-B/(10-4 cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 0.169 | 0.142 |
| Mg2+ | 0.127 | 0.062 |
| Na+ | 0.276 | 0.212 |
表2 含盐体系中阳离子扩散系数
Table 2 Cation diffusion coefficient in salt system
| Cation type | Cation diffusion coefficient in SDS/(10-4 cm2/s) | Cation diffusion coefficient in SDS-B/(10-4 cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 0.169 | 0.142 |
| Mg2+ | 0.127 | 0.062 |
| Na+ | 0.276 | 0.212 |
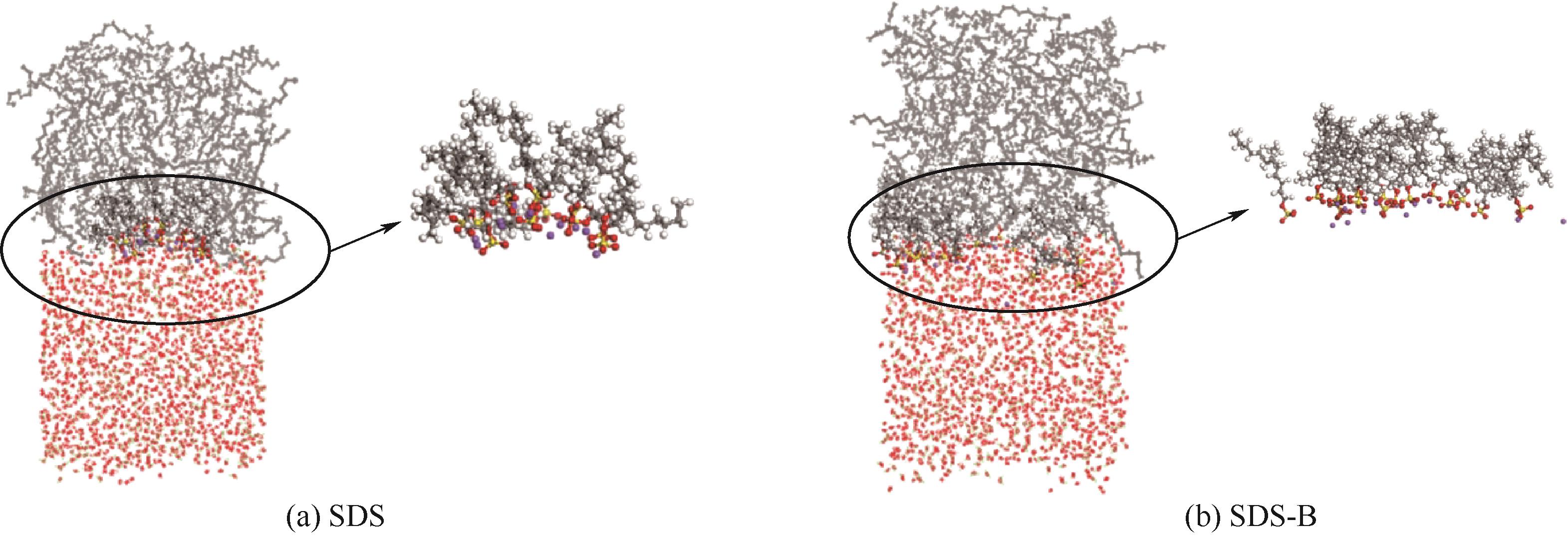
图11 SDS和SDS-B在更高浓度钙盐环境下的界面形态分布快照
Fig.11 Snapshots of interfacial morphology distribution of SDS and SDS-B in higher concentration calcium salt environments

图15 SDS和SDS-B在复杂含盐环境中的油水界面分布快照:(a)SDS在低浓度复杂含盐环境下的油水界面快照;(b)SDS在高浓度复杂含盐环境下的油水界面快照;(c)SDS-B在低浓度复杂含盐环境下的油水界面快照;(d)SDS-B在高浓度复杂含盐环境下的油水界面快照
Fig.15 Snapshots of oil-water interfacial distribution of SDS and SDS-B in complex saline environments: (a) snapshot of oil-water interface of SDS in low concentration complex salt environment; (b) snapshot of oil-water interface of SDS in high concentration complex salt environment; (c) snapshot of oil-water interface of SDS-B in low concentration complex salt environment; (d) snapshot of oil-water interface of SDS-B in high concentration complex salt environment
| [1] | 姚远, 成萌, 张剑. 分子动力学模拟在表面活性剂界面行为研究中的应用[J]. 化学通报, 2024, 87(10): 1169-1180. |
| Yao Y, Cheng M, Zhang J. Application of molecular dynamics simulation in the study of surfactant interface behavior[J]. Chemistry, 2024, 87(10): 1169-1180. | |
| [2] | Lu N, Dong X H, Liu H Q, et al. Molecular insights into the synergistic mechanisms of hybrid CO2-surfactant thermal systems at heavy oil-water interfaces[J]. Energy, 2024, 286: 129476. |
| [3] | 王凤娇, 孟详昊, 刘义坤, 等. 致密储层压驱焖井阶段渗吸机理分子模拟研究[J]. 力学学报, 2024, 56(6): 1624-1634. |
| Wang F J, Meng X H, Liu Y K, et al. The shut-in imbibition mechanism of hydraulic fracturing-assisted oil displacement in tight reservoirs based on molecular simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2024, 56(6): 1624-1634. | |
| [4] | 耿铁, 赵春花, 刘雪婧, 等. 表面活性剂分子在油/水界面聚集行为: 分子模拟研究进展[J]. 日用化学工业, 2019, 49(8): 537-544. |
| Geng T, Zhao C H, Liu X J, et al. Molecular simulations for aggregation behavior of surfactant molecules at oil/water interface[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(8): 537-544. | |
| [5] | Xue Z H, Feng Y L, Li H R. Enhancement mechanism of polysorbate surfactant at solid/liquid and gas/liquid interfaces in magnesite tailings flotation desilication via MD and DFT calculations[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(4): 113085. |
| [6] | Liu B J M, Lei X T, Ahmadi M, et al. Molecular insights into oil detachment from hydrophobic quartz surfaces in clay-hosted nanopores during steam-surfactant co-injection[J]. Petroleum Science, 2024, 21(4): 2457-2468. |
| [7] | Schneck E, Reed J, Seki T, et al. Experimental and simulation-based characterization of surfactant adsorption layers at fluid interfaces[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 331: 103237. |
| [8] | 吕冬梅, 吴慧君, 陈健朋, 等. 分子动力学模拟在分散剂/表面活性剂在煤颗粒表面吸附机理方面的研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文), 2024, 52(3): 452-460. |
| Lü D M, Wu H J, Chen J P, et al. Research progress of molecular dynamics simulation on adsorption mechanisms of dispersants/surfactants on the surface of coal particles[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2024, 52(3): 452-460. | |
| [9] | Wang Y D, Li S Y, Zhang Y W, et al. Effect of electric field on coalescence of an oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by surfactant: a molecular dynamics study[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(47): 30658-30669. |
| [10] | Ren Y, Zhang Q, Yang N, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of surfactant adsorption at oil/water interface under shear flow[J]. Particuology, 2019, 44: 36-43. |
| [11] | Zhou L X, Yan Y G, Li S C, et al. Molecular dynamic simulation study on formation of water channel in oil film detachment process controlled by surfactant polarity[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2021, 771: 138502. |
| [12] | Li L, Liu Z. The role of the interface on surfactant transport to crude oil-water liquid-liquid interface[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 395: 123849. |
| [13] | Zhou W N, Jiang L, Liu X L, et al. Molecular insights into the effect of anionic-nonionic and cationic surfactant mixtures on interfacial properties of oil-water interface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 637: 128259. |
| [14] | Sun X Y, Zeng H B, Tang T. Effect of salinity on water/oil interface with model asphaltene and non-ionic surfactant: insights from molecular simulations[J]. Fuel, 2023, 339: 126944. |
| [15] | 吕耀东, 徐娜, 刘子璐. 湍流减阻型聚/表复配体系分子自组装结构及机理的介观分子动力学模拟[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2022, 36(5): 665-674. |
| Lyu Y D, Xu N, Liu Z L. Mesoscopic molecular dynamic simulation on the molecular self-assembly structure and mechanism of the polymer/surfactant compound system using as the turbulent drag-reduction additives[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2022, 36(5): 665-674. | |
| [16] | Li N, Sun Z Q, Pang Y H, et al. Microscopic mechanism for electrocoalescence of water droplets in water-in-oil emulsions containing surfactant: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 289: 120756. |
| [17] | Barbosa G D, Manske C L, Tavares F W, et al. A molecular simulation study of ethoxylated surfactant effects on bulk and water/crude-oil interfacial asphaltenes[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2023, 575: 113925. |
| [18] | Wen Z, Xiao P W, Wang P M, et al. Effect of Gemini surfactant structure on water/oil interfacial properties: a dissipative particle dynamics study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 251: 117466. |
| [19] | 燕友果, 郝羽键, 伊卓, 等. 改性聚丙烯酰胺降低油水界面张力行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(3): 215-220. |
| Yan Y G, Hao Y J, Yi Z, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation study on behavior of modified polyacrylamide reducing oil-water interfacial tension[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2024, 48(3): 215-220. | |
| [20] | Huang S M, Jiang G C, Guo C P, et al. Experimental study of adsorption/desorption and enhanced recovery of shale oil and gas by zwitterionic surfactants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 487: 150628. |
| [21] | Palanisamy T, Tabatabai S A A, Zhang T, et al. Role of surfactants in cleaning of PVDF ultrafiltration membranes fouled by emulsified cutting oil[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 40: 101923. |
| [22] | 孙浩玉, 张琰, 高阳, 等. NaSal/2SHNC对R14HTAB体系自组装行为的影响机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6): 171-176. |
| Sun H Y, Zhang Y, Gao Y, et al. Effecting mechanism of organic salts NaSal/2SHNC on self-assembly of cationic surfactant R14HTAB[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2019, 43(6): 171-176. | |
| [23] | Tanis-Kanbur M B, Velioğlu S, Tanudjaja H J, et al. Understanding membrane fouling by oil-in-water emulsion via experiments and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 566: 140-150. |
| [24] | Lu C Y, Xu X Y, Yuan Z Y, et al. Effects of structural changes of PPO and PEO of nonionic surfactants on oil-water interface properties: a molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Chemical Physics, 2024, 586: 112397. |
| [25] | Jia H, Song J Y, Sun Y Q, et al. Molecular insight into the effect of the number of introduced ethoxy groups on the calcium resistance of anionic-nonionic surfactants at the oil/water interface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 667: 131382. |
| [26] | Zeighami A, Kargozarfard Z, Khiabani N P, et al. Salt-acid-surfactant synergistic effects on interfacial characteristics of water/oil systems: a molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 396: 123996. |
| [27] | Jiang S S, Li X Y, Gao S T, et al. Opposite effect of cyclic and chain-like hydrocarbons on the trend of self-assembly transition in catanionic surfactant systems[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 648: 129231. |
| [28] | Hasanov E E, Rahimov R A, Ahmadova G A, et al. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation and experimental studies of pseudo-gemini surfactants with different hydrophobic chain lengths[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 411: 125766. |
| [29] | Khalil R A, Saadoon F A. Effect of presence of benzene ring in surfactant hydrophobic chain on the transformation towards one dimensional aggregate[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2015, 19(4): 423-428. |
| [30] | Cao X W, Qin X, Chen J W, et al. Adsorption kinetics investigation of surfactant molecules at the short-chain alkane-water interface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 660: 130867. |
| [31] | Fu L P, Gu F, Liao K L, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of enhancing surfactant flooding performance by using SiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 367: 120404. |
| [32] | 李杰训, 许云飞, 王志华. 剪切流场中油-水界面成膜的影响因素及微观机制[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(8): 1244-1256. |
| Li J X, Xu Y F, Wang Z H. Influencing factors and micromechanisms of film formation at oil-water interface in shear flow field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(8): 1244-1256. | |
| [33] | 宋瑛, 田宜灵, 肖衍繁, 等. 二元液液系统界面张力[J]. 化工学报, 1999, 50(5): 620-628. |
| Song Y, Tian Y L, Xiao Y F, et al. Interfacial tensions of binary liquid-liquid systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 1999, 50(5): 620-628. | |
| [34] | Ahmadi M, Hou Q F, Wang Y Y, et al. Spotlight on reversible emulsification and demulsification of tetradecane-water mixtures using CO2/N2 switchable surfactants: molecular dynamics (MD) simulation[J]. Energy, 2023, 279: 128100. |
| [35] | Zhang Z Q, Tao Z, Zhang Y, et al. Molecular dynamics study on the interaction of phosphorus building gypsum/surfactant composites[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 2024, 126: 108650. |
| [36] | 刘峰, 韩春硕, 郁林军, 等. 分子动力学模拟表面活性剂驱油的研究进展与展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(3): 78-87. |
| Liu F, Han C S, Yu L J, et al. Research progress and prospects of surfactant flooding in molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(3): 78-87. | |
| [37] | Liu Z L, Gao Y H, Shi D, et al. Selective solubilization of organic molecules into vesicles formed by Gemini surfactants: a dissipative particle dynamics study[J]. Fuel, 2024, 375: 132591. |
| [38] | Jia H, Wei X, Sun Y Q, et al. Effects of surfactant with different injection times on asphaltene adsorption behaviors on the kaolinite surfaces: a molecular simulation study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 639: 158167. |
| [39] | Li B, Su D, Zhang L, et al. Mechanisms of N2 molecule adsorption and accumulation on surfactant-modified substrates: a molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 411: 125679. |
| [40] | Wang K, Xu M, Zhou B, et al. Study on the effects of inorganic salts and ionic surfactants on the wettability of coal based on the experimental and molecular dynamics investigations[J]. Energy, 2024, 300: 131610. |
| [41] | Yuan M Y, Nie W, Zhou W W, et al. Determining the effect of the non-ionic surfactant AEO9 on lignite adsorption and wetting via molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and experiment comparisons[J]. Fuel, 2020, 278: 118339. |
| [42] | Meng J Q, Yin F F, Li S C, et al. Effect of different concentrations of surfactant on the wettability of coal by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2019, 29(4): 577-584. |
| [43] | 张雪龄, 谷军恒, 叶强, 等. 分子模拟技术在页岩油气吸附和流动特性研究中的应用进展[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(3): 103-115. |
| Zhang X L, Gu J H, Ye Q, et al. Application progress of molecular simulation technology in the study of adsorption and flow characteristics of shale oil and gas[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(3): 103-115. | |
| [44] | Gurina D L, Budkov Y A. The self-assembly of water reverse micelles with imidazolium ionic liquids in supercritical carbon dioxide: a molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2024, 695: 134209. |
| [45] | Ahmad Bhat I, Roy B, Hazra P, et al. Conformational and solution dynamics of hemoglobin (Hb) in presence of a cleavable gemini surfactant: insights from spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, molecular docking and density functional theory[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 538: 489-498. |
| [46] | Kanduč M, Reed J, Schlaich A, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations as support for experimental studies on surfactant interfacial layers[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2024, 72: 101816. |
| [47] | Jin H, Zhang Y S, Dong H T, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations and experimental study of the effects of an ionic surfactant on the wettability of low-rank coal[J]. Fuel, 2022, 320: 123951. |
| [48] | Hu G Y, Cui K X, Jin S M, et al. Effect of surfactant on dynamics and gas-liquid mass transfer for single carbon dioxide bubbles[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 453: 142148. |
| [49] | Farkas E, Dóra Kovács K, Szekacs I, et al. Kinetic monitoring of molecular interactions during surfactant-driven self-propelled droplet motion by high spatial resolution waveguide sensing[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 677: 352-364. |
| [50] | Li G L, Xu X J, Zuo Y Y. Phase transitions of the pulmonary surfactant film at the perfluorocarbon-water interface[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2023, 122(10): 1772-1780. |
| [51] | Pegg J C, Eastoe J. Solid mesostructured polymer-surfactant films at the air-liquid interface[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 222: 564-572. |
| [52] | Liang M Y, Ma C, Qin W Q, et al. A synergetic binary system of waste cooking oil-derived bio-based surfactants and its interfacial performance for enhanced oil recovery[J]. Colloids and Surfaces C: Environmental Aspects, 2024, 2: 100039. |
| [53] | Guo P, Zhou R, Tian Z K, et al. High-efficiency mechanism of enhancement of spreading performance of oil involving surfactant-laden oil droplet spreading over water surface[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 388: 122723. |
| [54] | Lee S, Lee G, Ryu J, et al. Surfactant-free, spray-assisted water droplet templating for efficient fabrication of ultraviolet-curable polydimethylsiloxane sponge as a reusable oil cleanup sorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150958. |
| [55] | Okamura S, Aono K, Yokoyama M, et al. Influence of dialkyl chains of sulfosuccinate sodium salt surfactant on interfacial tension between hydrophobic material and water[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2024, 681: 132770. |
| [56] | 王贤君, 张明慧. 双链表面活性剂压裂液研究及应用[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2015, 34(5): 77-80. |
| Wang X J, Zhang M H. Researches and application of double-chain surfactant fracturing fluid[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2015, 34(5): 77-80. | |
| [57] | Yang D L, He D Y, Huang Y, et al. Real-time and quantitative investigation of zwitterionic surfactant interaction at oil-water interface: interferometry experimental and MD simulation insights[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 398: 124265. |
| [58] | Lei X T, Liu B, Hou Q F, et al. Switchability and synergistic effect of a CO2-responsive surfactant with co-surfactants at an O/W interface: a molecular insight[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 405: 125051. |
| [59] | Yong W, Wei Z J, Zhou Y F. Molecular dynamics simulation of oil displacement using surfactant in a nano-silica pore[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2024, 684: 133165. |
| [60] | Zahariev T K, Tadjer A V, Ivanova A N. Transfer of non-ionic surfactants across the water-oil interface: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 506: 20-31. |
| [61] | Gassin P M, Champory R, Martin-Gassin G, et al. Surfactant transfer across a water/oil interface: a diffusion/kinetics model for the interfacial tension evolution[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 436: 1103-1110. |
| [62] | McMillin R E, Nowaczyk J, Centofanti K, et al. Effect of small molecule surfactant structure on the stability of water-in-lubricating oil emulsions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 652: 825-835. |
| [63] | 张扬. 阴离子表面活性剂耐盐性能的实验和理论研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2013. |
| Zhang Y. Experimental and theoretical study on salt tolerance of anionic surfactants[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2013. |
| [1] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [6] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [12] | 卓森庆, 陈华, 陈伟, 尚彬, 刘恒恒, 古汤汤, 白韡, 王龙炎, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 多联式空调系统APF性能仿真的模型开发与软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 370-376. |
| [13] | 何永宁, 曹文良, 王苏澳, 赵希航, 邢林芬, 吴学红. 低GWP工质高温热泵系统应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3009-3017. |
| [14] | 向晓彤, 段旭东, 王斯民. 多目标优化驱动的PEM电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2626-2637. |
| [15] | 包兴, 郭雪岩. 圆柱颗粒结构修饰对填充床内流动和换热特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2603-2615. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号