化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5554-5573.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250484
史博会1( ), 刘光硕1, 郭恩岐1, 史潇航1, 刘浩田2, 吴海浩1, 李晓平1, 宋尚飞1(
), 刘光硕1, 郭恩岐1, 史潇航1, 刘浩田2, 吴海浩1, 李晓平1, 宋尚飞1( ), 宫敬1
), 宫敬1
收稿日期:2025-05-06
修回日期:2025-07-01
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
宋尚飞
作者简介:史博会(1984—),女,博士,副教授,bh.shi@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Bohui SHI1( ), Guangshuo LIU1, Enqi GUO1, Xiaohang SHI1, Haotian LIU2, Haihao WU1, Xiaoping LI1, Shangfei SONG1(
), Guangshuo LIU1, Enqi GUO1, Xiaohang SHI1, Haotian LIU2, Haihao WU1, Xiaoping LI1, Shangfei SONG1( ), Jing GONG1
), Jing GONG1
Received:2025-05-06
Revised:2025-07-01
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Shangfei SONG
摘要:
在深海油气与“可燃冰”开发中,水合物浆液体系中的颗粒沉积与聚集体堵塞是流动保障的核心难题。基于CFD-DEM方法应用Fluent-EDEM软件耦合,针对水基体系水合物浆液的流动聚集与沉积过程开展数值模拟,研究不同浆液流速及体积分数的水合物颗粒流动聚集与沉积过程,比较并分析了有无颗粒条件下管道内压力变化情况。模拟结果表明,0.5 m/s时颗粒在管道内壁会形成静止沉积层,且轴向与径向聚集显著;当流速增大到1.5 m/s时,随着剪切力增强,聚集体会破碎,水合物颗粒以单颗粒或小聚集体均匀分散;当水合物体积分数从5%增至15%时,颗粒聚集程度会加剧,压降呈非线性递增,弯管中段会因沉积层发育形成压降峰值。基于模拟结果,提出弯管结构对水合物沉积的影响机理,即在低流速情况下,流体与颗粒之间相互耦合,在流场突变处的水合物聚集体发生破碎后,部分将附着在管壁沉积层上,形成黏附、破碎与再沉积的耦合堵塞机制。
中图分类号:
史博会, 刘光硕, 郭恩岐, 史潇航, 刘浩田, 吴海浩, 李晓平, 宋尚飞, 宫敬. 基于CFD-DEM的水基体系水合物流动聚集与沉积过程模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5554-5573.
Bohui SHI, Guangshuo LIU, Enqi GUO, Xiaohang SHI, Haotian LIU, Haihao WU, Xiaoping LI, Shangfei SONG, Jing GONG. Numerical study on flow aggregation and deposition processes of hydrates in water-based systems using CFD-DEM[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5554-5573.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 浆液密度/(kg/m3) | 998.2 |
| 浆液黏度/(kg/(m·s)) | 0.001 |
| 水合物颗粒粒径/mm | 1 |
| 水合物颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 900 |
| 水合物颗粒泊松比 | 0.21 |
| 水合物颗粒剪切弹性模量/(N/m2) | 1.22×107 |
| 管道材料密度/(kg/m3) | 7800 |
| 管道材料泊松比 | 0.3 |
| 管道材料剪切弹性模量/(N/m2) | 7×1010 |
| 颗粒-颗粒的恢复系数 | 0.15 |
| 颗粒-颗粒的静摩擦因数 | 0.1 |
| 颗粒-壁面的恢复系数 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒-壁面的静摩擦因数 | 0.5 |
表1 模拟参数设定
Table 1 Simulation parameter setting
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 浆液密度/(kg/m3) | 998.2 |
| 浆液黏度/(kg/(m·s)) | 0.001 |
| 水合物颗粒粒径/mm | 1 |
| 水合物颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 900 |
| 水合物颗粒泊松比 | 0.21 |
| 水合物颗粒剪切弹性模量/(N/m2) | 1.22×107 |
| 管道材料密度/(kg/m3) | 7800 |
| 管道材料泊松比 | 0.3 |
| 管道材料剪切弹性模量/(N/m2) | 7×1010 |
| 颗粒-颗粒的恢复系数 | 0.15 |
| 颗粒-颗粒的静摩擦因数 | 0.1 |
| 颗粒-壁面的恢复系数 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒-壁面的静摩擦因数 | 0.5 |
| 工况 | 压力/MPa | 入口流速/(m/s) | 水合物体积分数/% | 实验单位压降/(Pa/m) | 模拟单位压降/(Pa/m) | 偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.45 | 0.202 | 5 | 285.13 | 336.32 | 17.6 |
| 2 | 6.45 | 0.569 | 2 | 261.79 | 301.49 | 15.2 |
| 3 | 6.45 | 0.690 | 4 | 328.12 | 351.66 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 6.45 | 0.320 | 8 | 296.45 | 338.43 | 14.2 |
| 5 | 6.45 | 0.910 | 9 | 685.32 | 802.66 | 17.1 |
| 6 | 5.15 | 0.550 | 2.5 | 283.21 | 324.41 | 14.5 |
| 7 | 5.15 | 0.618 | 3 | 365.28 | 380.03 | 3.8 |
| 8 | 5.15 | 0.323 | 8 | 2944.67 | 325.13 | 10.6 |
| 9 | 5.15 | 0.234 | 10 | 306.53 | 361.65 | 18.0 |
| 10 | 5.15 | 0.750 | 10 | 429.31 | 405.62 | 10.6 |
表2 实验及模拟水合物单位压降对比
Table 2 Experimental and simulation comparison of hydrate unit pressure drop
| 工况 | 压力/MPa | 入口流速/(m/s) | 水合物体积分数/% | 实验单位压降/(Pa/m) | 模拟单位压降/(Pa/m) | 偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.45 | 0.202 | 5 | 285.13 | 336.32 | 17.6 |
| 2 | 6.45 | 0.569 | 2 | 261.79 | 301.49 | 15.2 |
| 3 | 6.45 | 0.690 | 4 | 328.12 | 351.66 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 6.45 | 0.320 | 8 | 296.45 | 338.43 | 14.2 |
| 5 | 6.45 | 0.910 | 9 | 685.32 | 802.66 | 17.1 |
| 6 | 5.15 | 0.550 | 2.5 | 283.21 | 324.41 | 14.5 |
| 7 | 5.15 | 0.618 | 3 | 365.28 | 380.03 | 3.8 |
| 8 | 5.15 | 0.323 | 8 | 2944.67 | 325.13 | 10.6 |
| 9 | 5.15 | 0.234 | 10 | 306.53 | 361.65 | 18.0 |
| 10 | 5.15 | 0.750 | 10 | 429.31 | 405.62 | 10.6 |
| 工况 | 纯水单相流动模拟的单位压降/(Pa/m) | 含水合物颗粒浆液流动模拟相比纯水单相流动模拟单位压降的增幅倍数 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.34 | 65.7 |
| 2 | 21.53 | 12.2 |
| 3 | 30.78 | 10.7 |
| 4 | 7.52 | 39.4 |
| 5 | 47.81 | 14.3 |
| 6 | 20.25 | 14.0 |
| 7 | 25.18 | 14.5 |
| 8 | 7.25 | 40.6 |
| 9 | 7.26 | 42.2 |
| 10 | 35.43 | 12.1 |
表3 纯水及含水合物颗粒浆液模拟单位压降对比
Table 3 Pure water and hydrate particle-laden simulations comparison of unit pressure drop
| 工况 | 纯水单相流动模拟的单位压降/(Pa/m) | 含水合物颗粒浆液流动模拟相比纯水单相流动模拟单位压降的增幅倍数 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.34 | 65.7 |
| 2 | 21.53 | 12.2 |
| 3 | 30.78 | 10.7 |
| 4 | 7.52 | 39.4 |
| 5 | 47.81 | 14.3 |
| 6 | 20.25 | 14.0 |
| 7 | 25.18 | 14.5 |
| 8 | 7.25 | 40.6 |
| 9 | 7.26 | 42.2 |
| 10 | 35.43 | 12.1 |
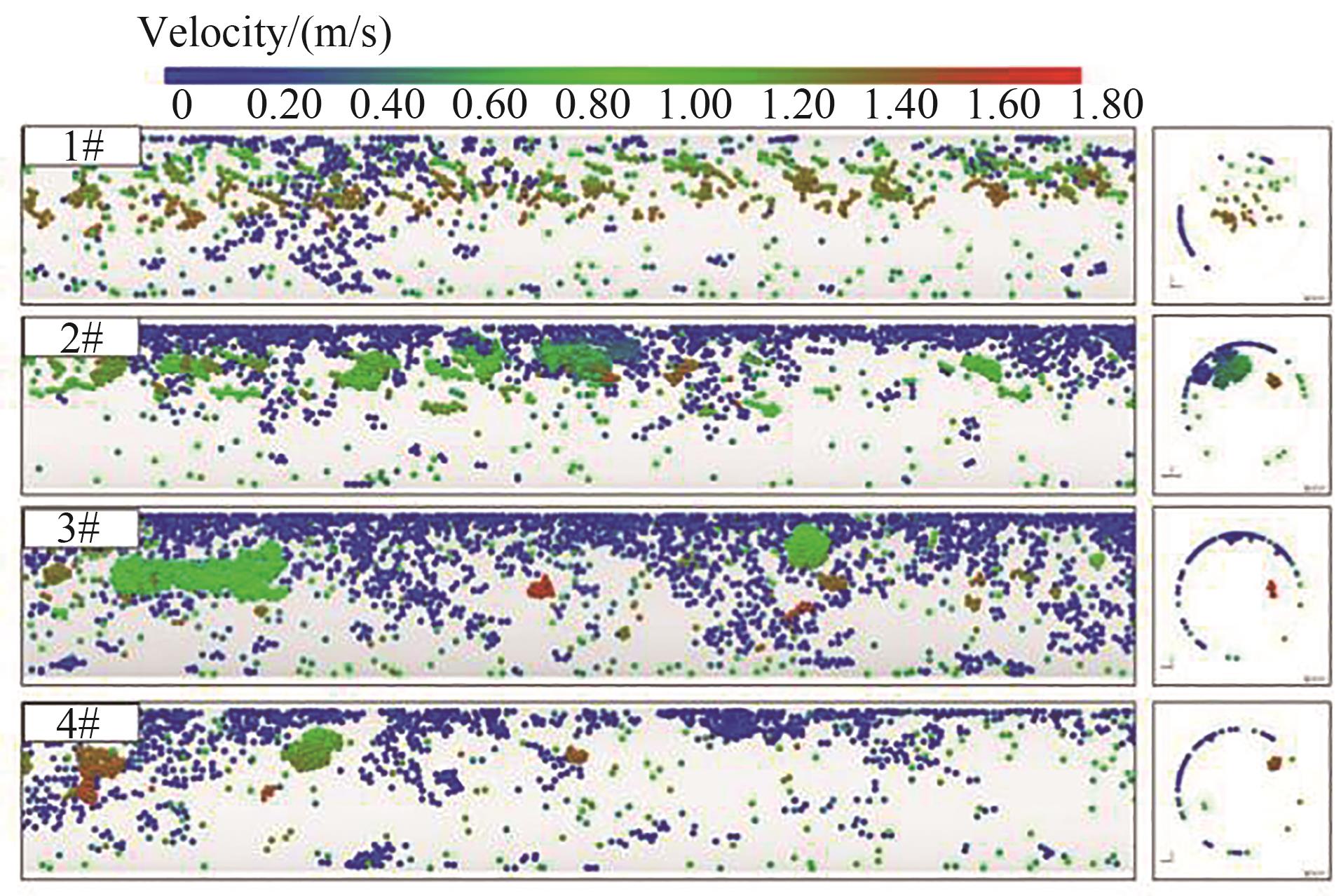
图6 四个典型截面附近管路轴截面速度云图及对应截面横截面速度云图
Fig.6 Velocity distributions in axial and cross view at four cross-sectional positions under different hydrate volume fractions
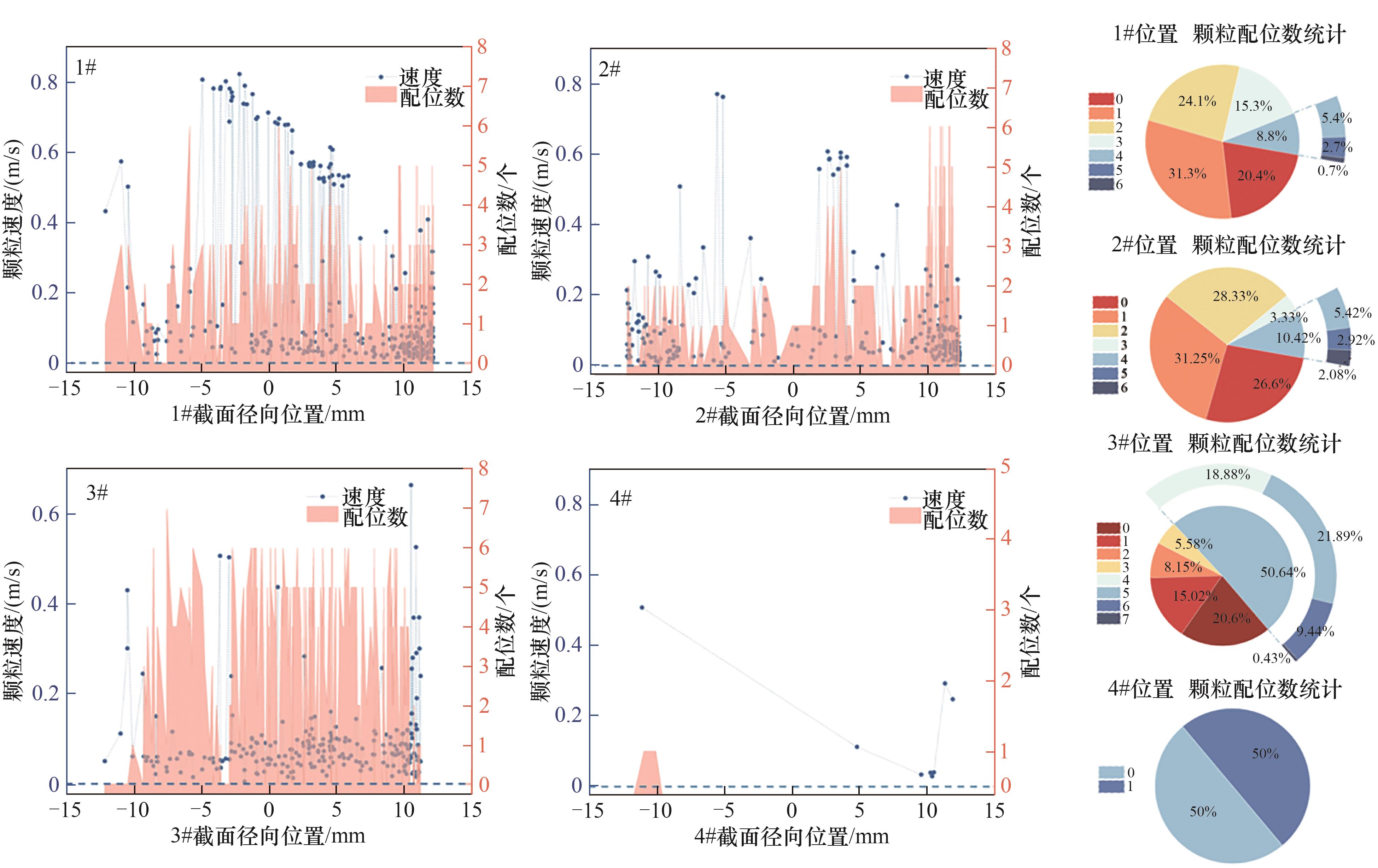
图7 四个典型截面水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.7 Distribution of hydrate particle velocity and particle coordination number statistics of four cross-sections along the radial direction
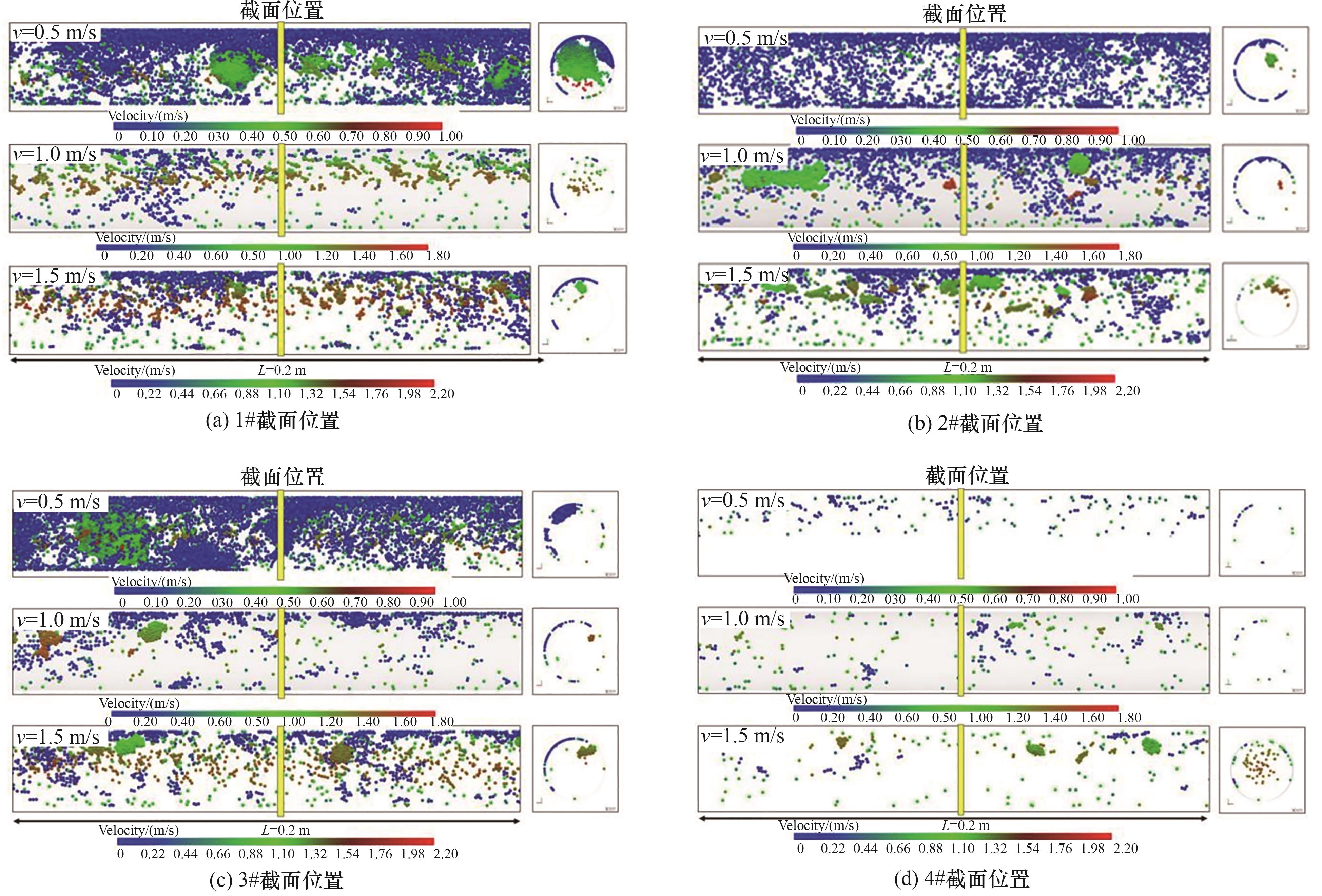
图8 不同流速下四个典型截面附近管路轴截面速度云图及对应截面横截面速度云图
Fig.8 Velocity distributions in axial and cross view at four cross-sectional positions under different hydrate volume fractions
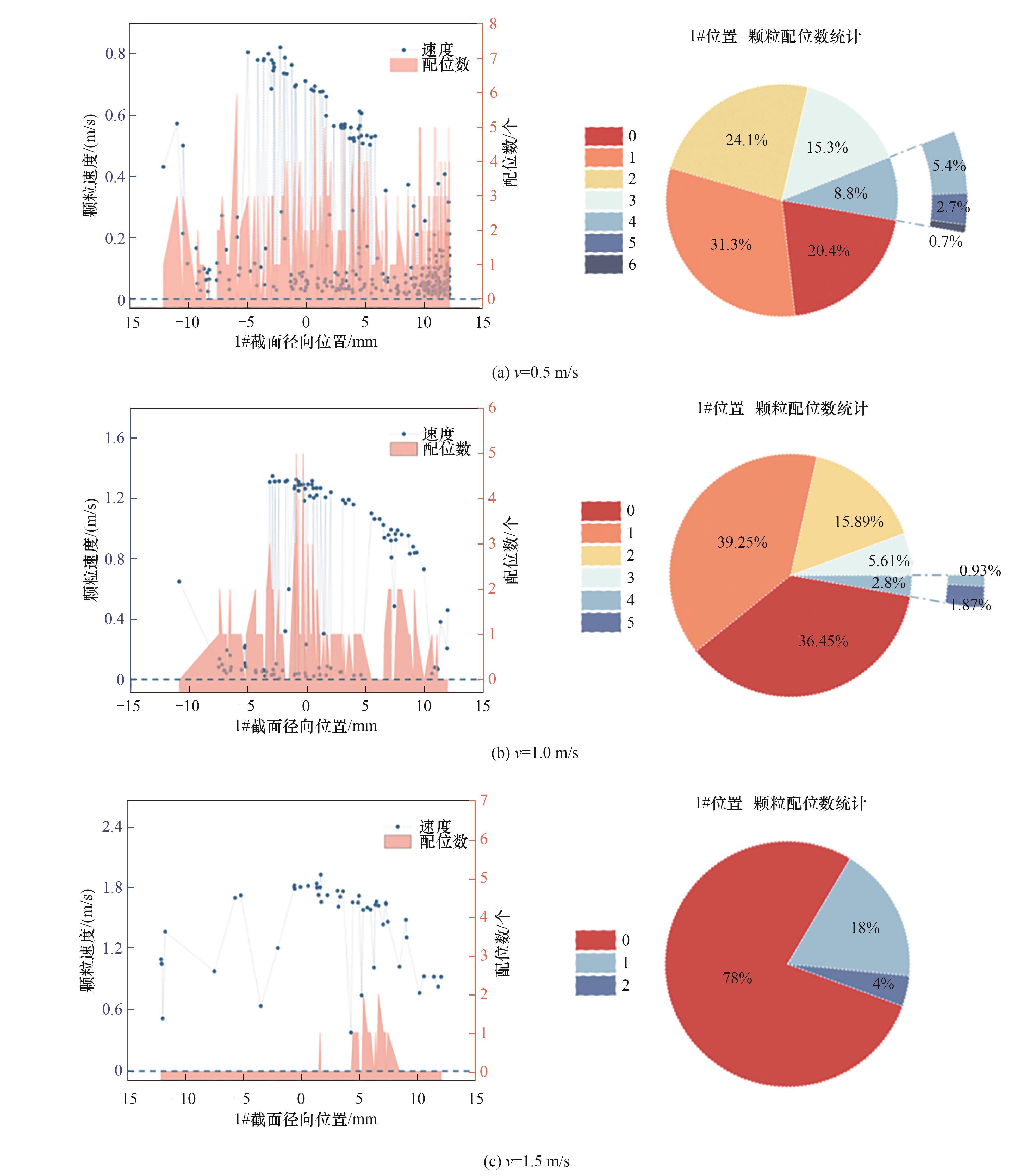
图9 不同流速下1#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.9 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 1# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate velocity
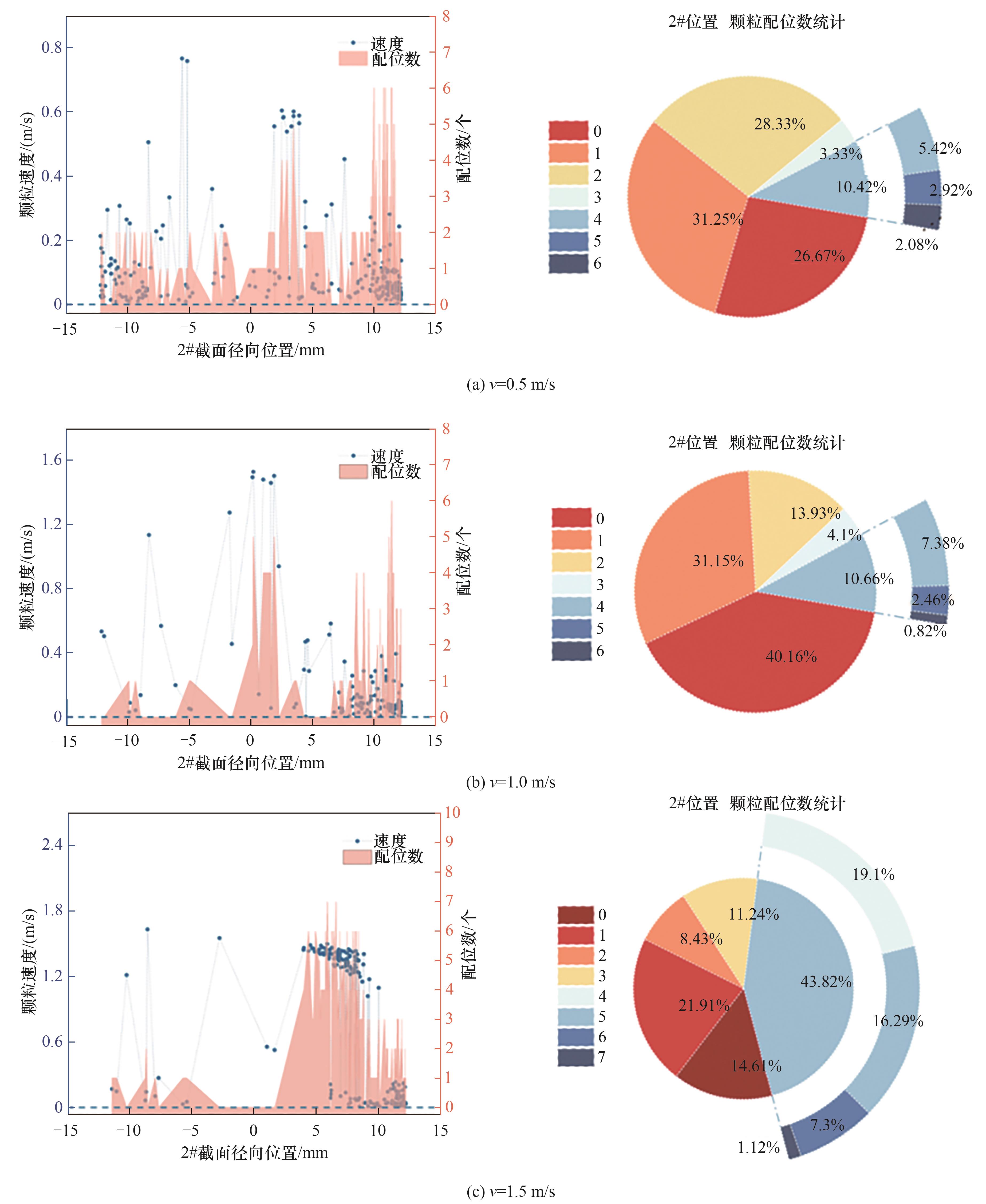
图10 不同流速下2#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.10 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 2# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate velocity
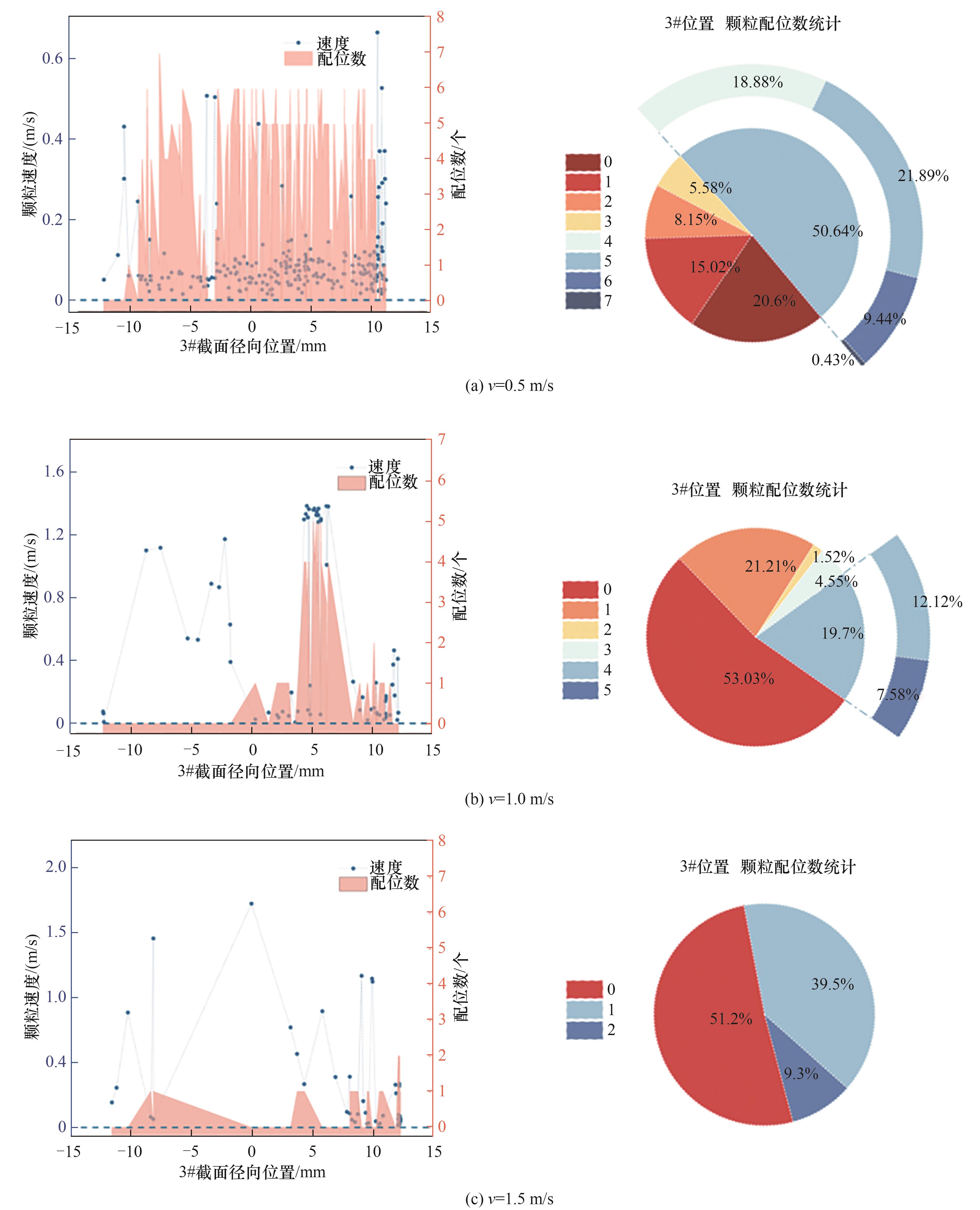
图11 不同流速下3#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.11 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 3# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate velocity
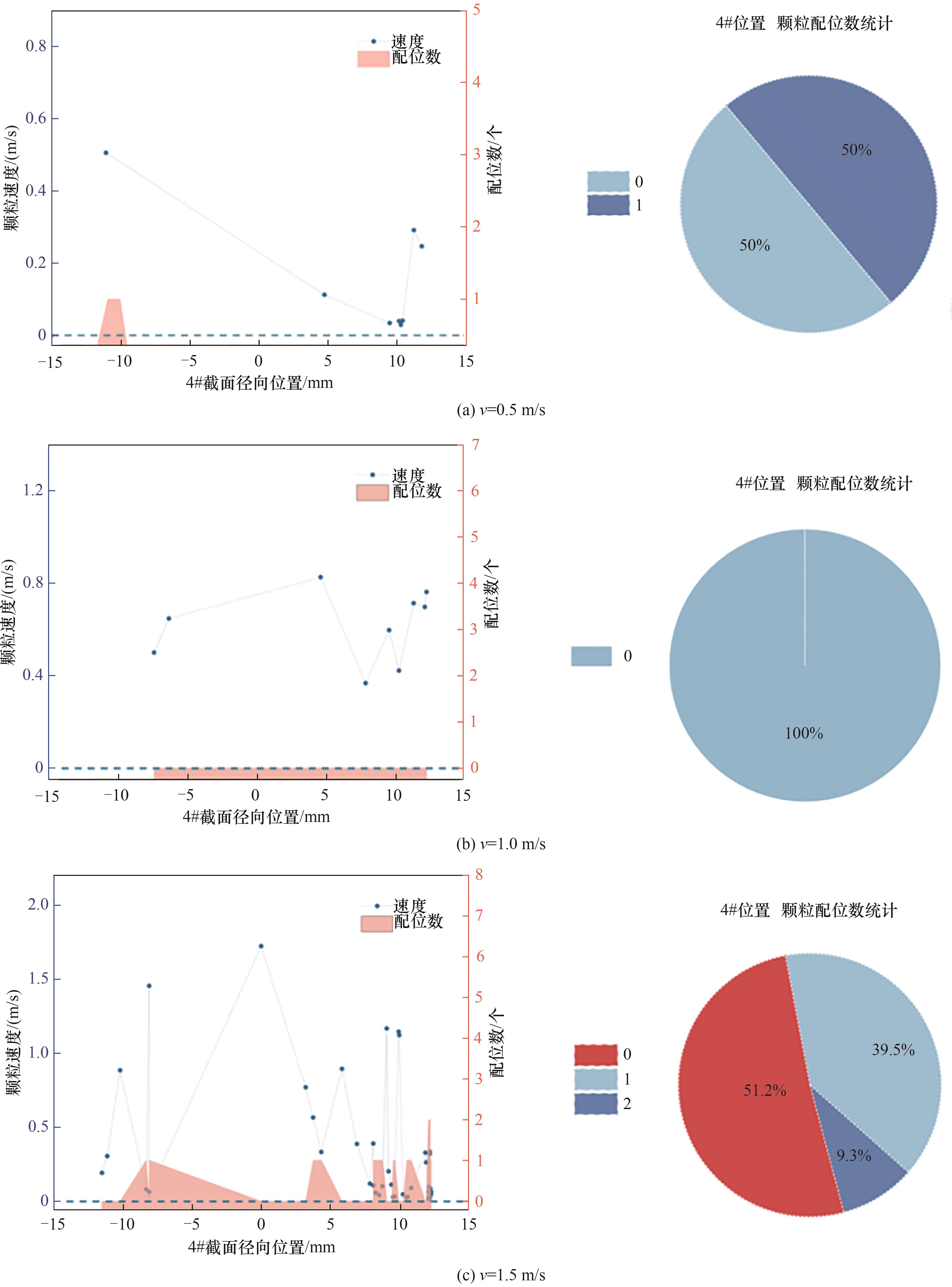
图12 不同流速下4#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.12 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 4# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate velocity
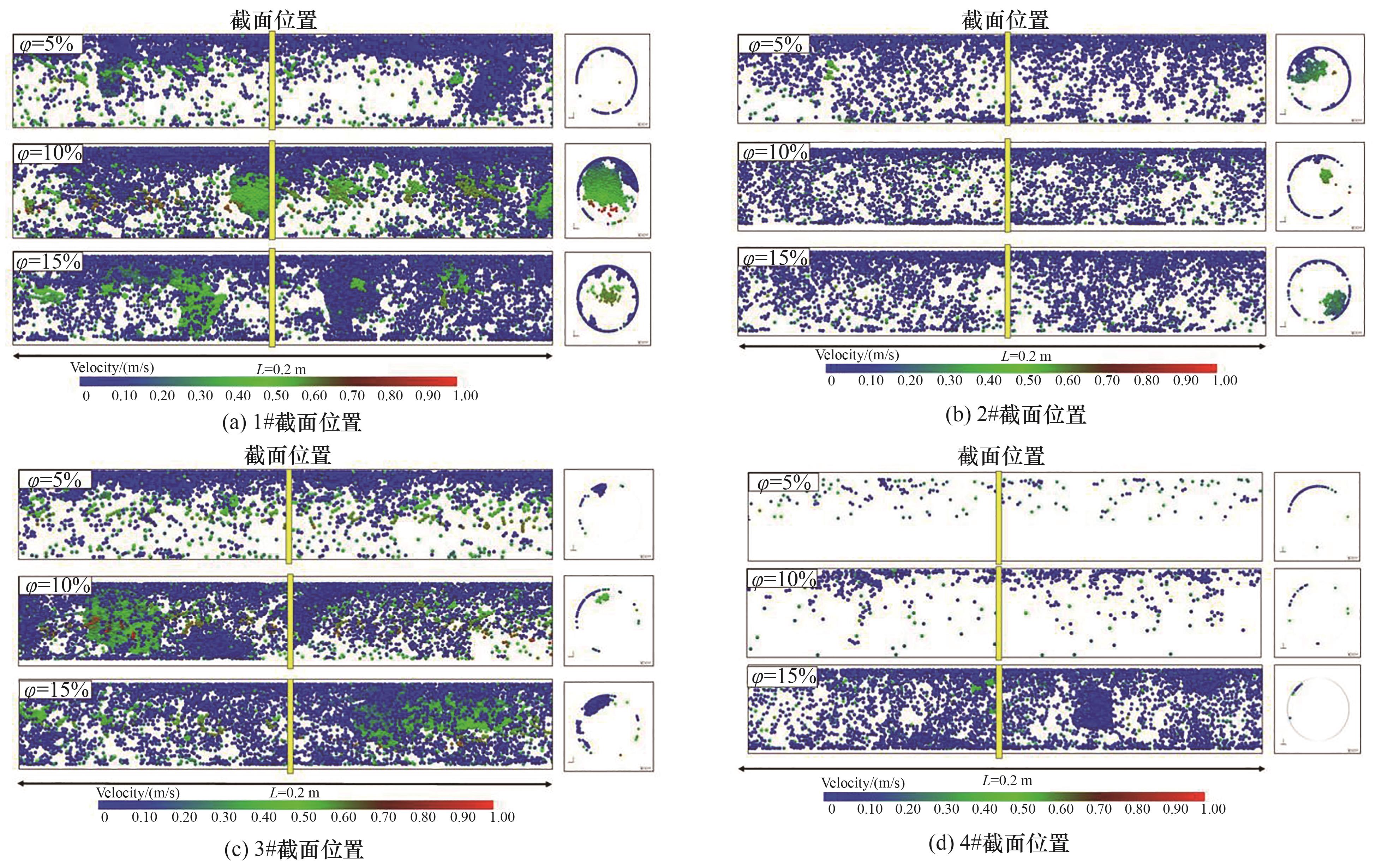
图14 不同颗粒体积分数下四个典型截面附近管路轴截面速度云图及对应截面的横截面速度云图
Fig.14 Velocity distributions in axial and cross view at four cross-sectional positions under different hydrate volume fractions
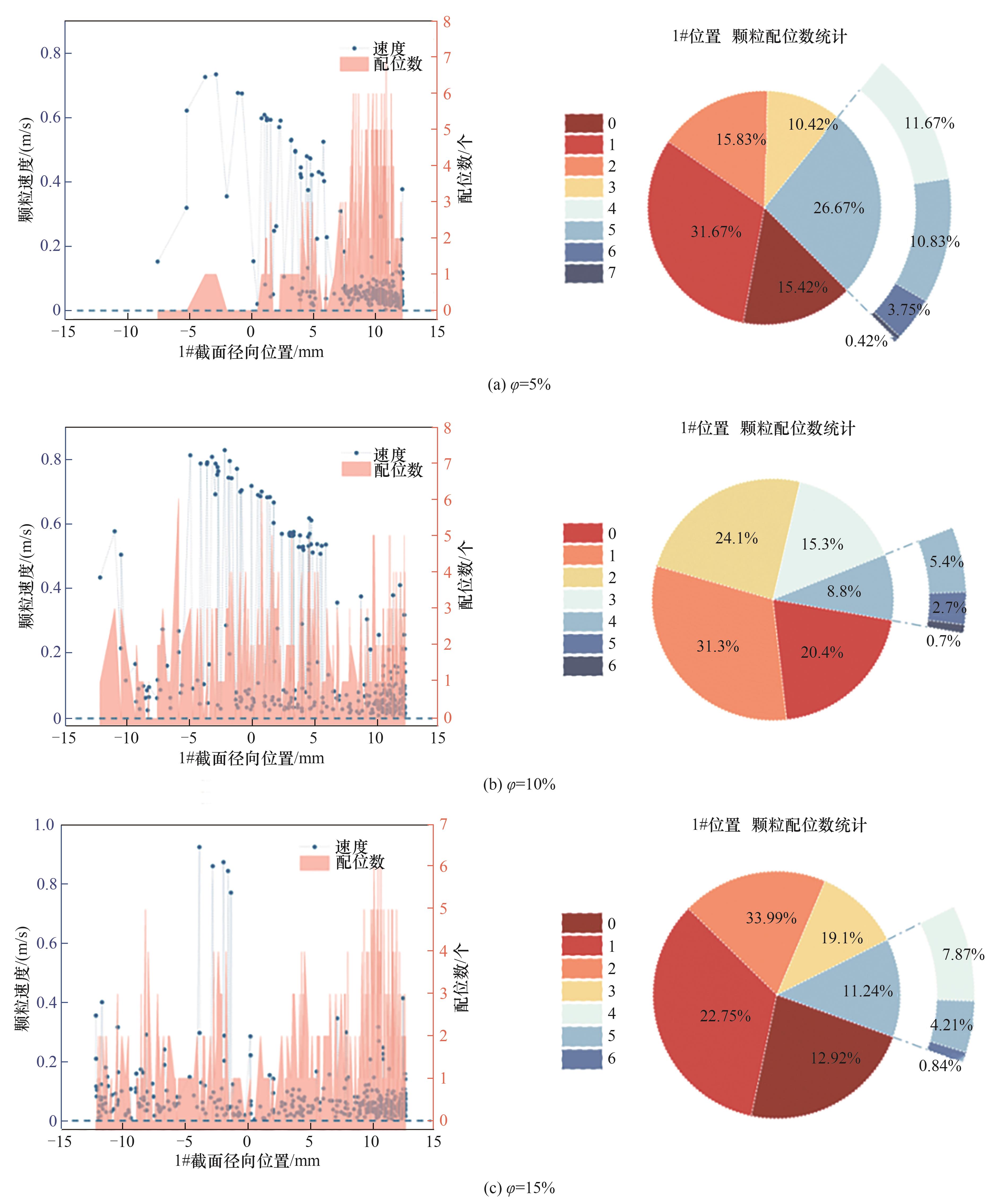
图15 不同颗粒体积分数下1#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.15 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 1# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate volume fractions
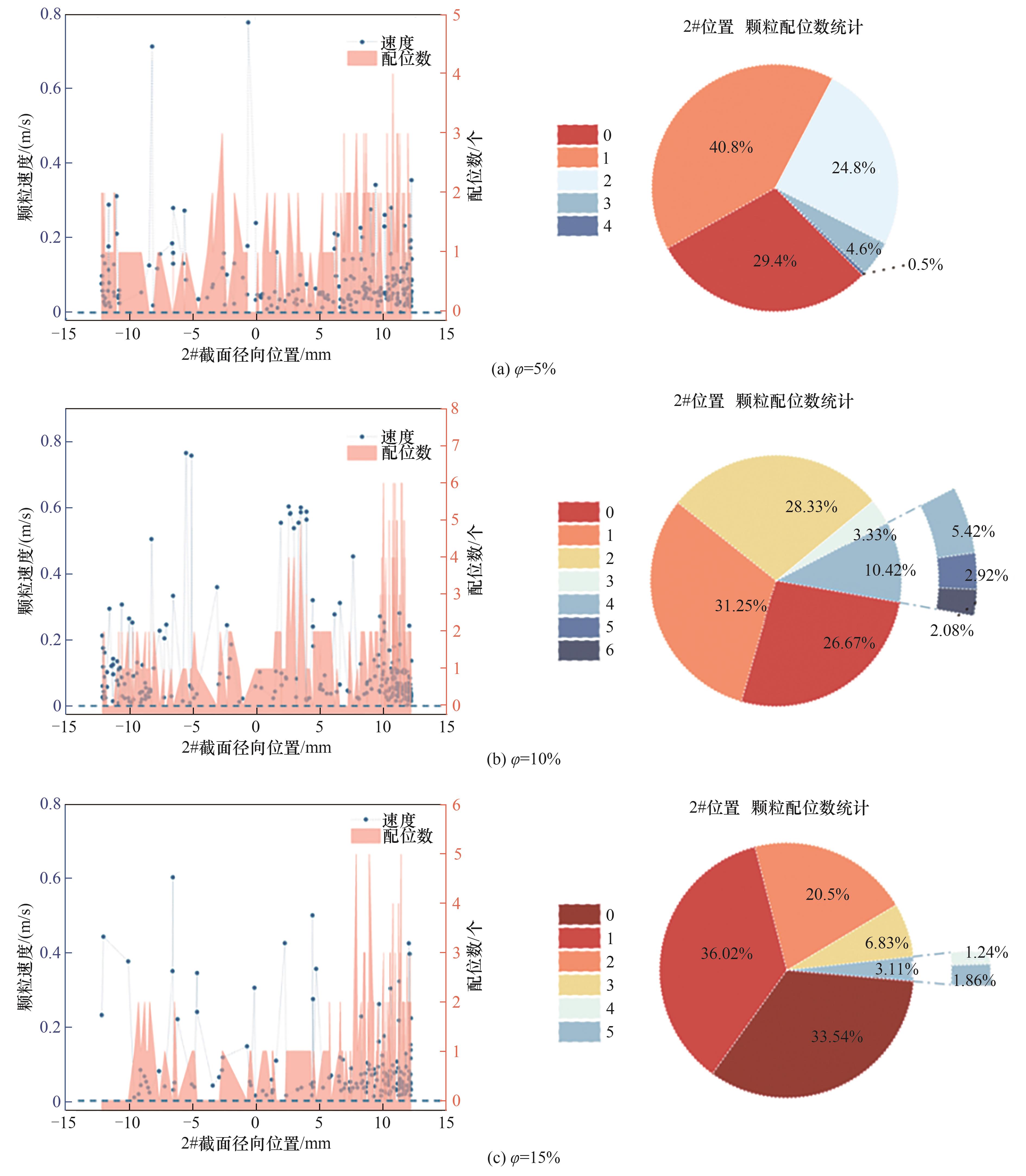
图16 不同颗粒体积分数下2#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.16 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 2# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate volume fractions
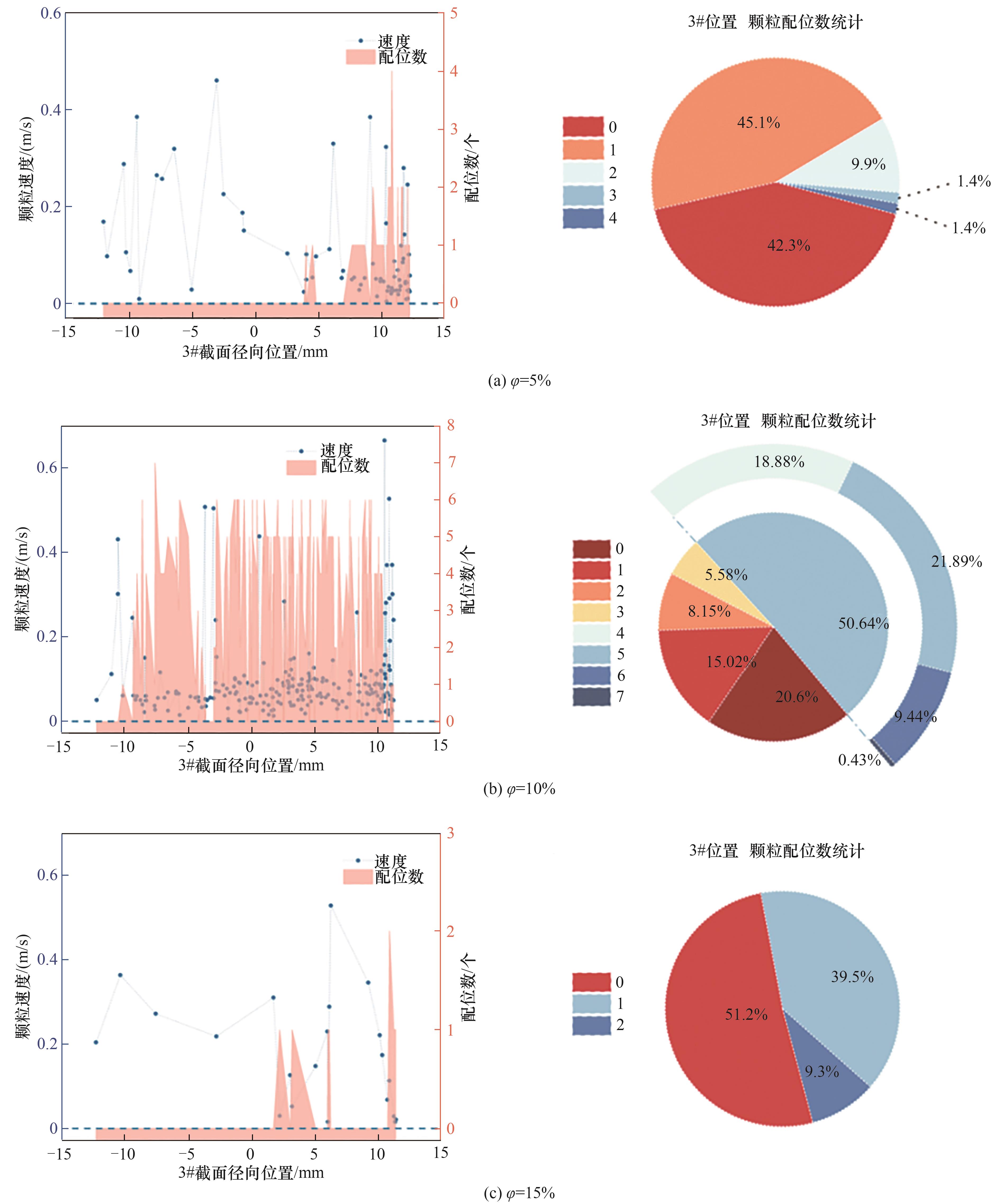
图17 不同颗粒体积分数下3#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.17 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 3# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate volume fractions
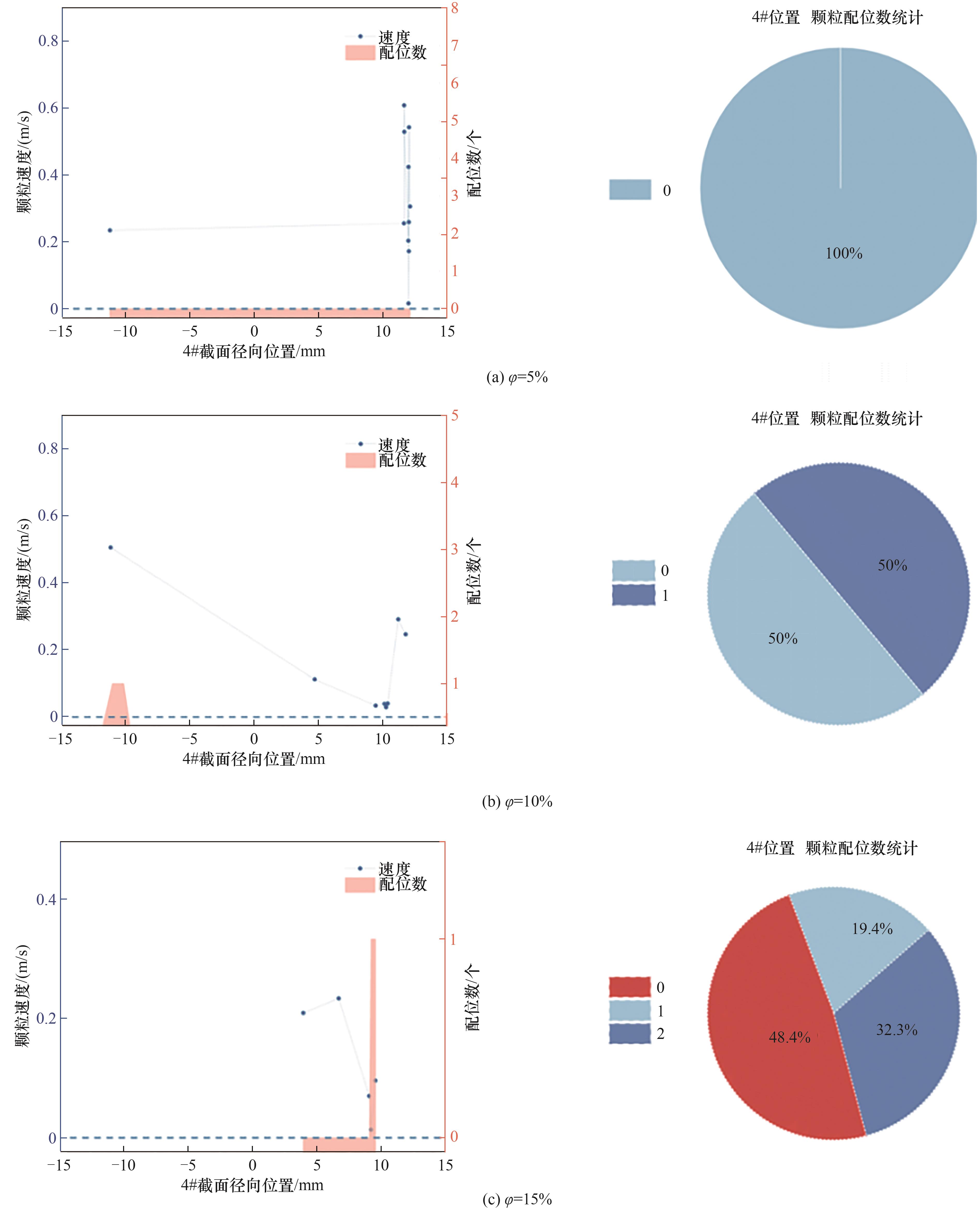
图18 不同颗粒体积分数下4#截面位置水合物颗粒速度随截面径向分布及颗粒配位数统计
Fig.18 Distribution of velocity and coordination number values at 4# cross-sectional locations under varying hydrate volume fractions
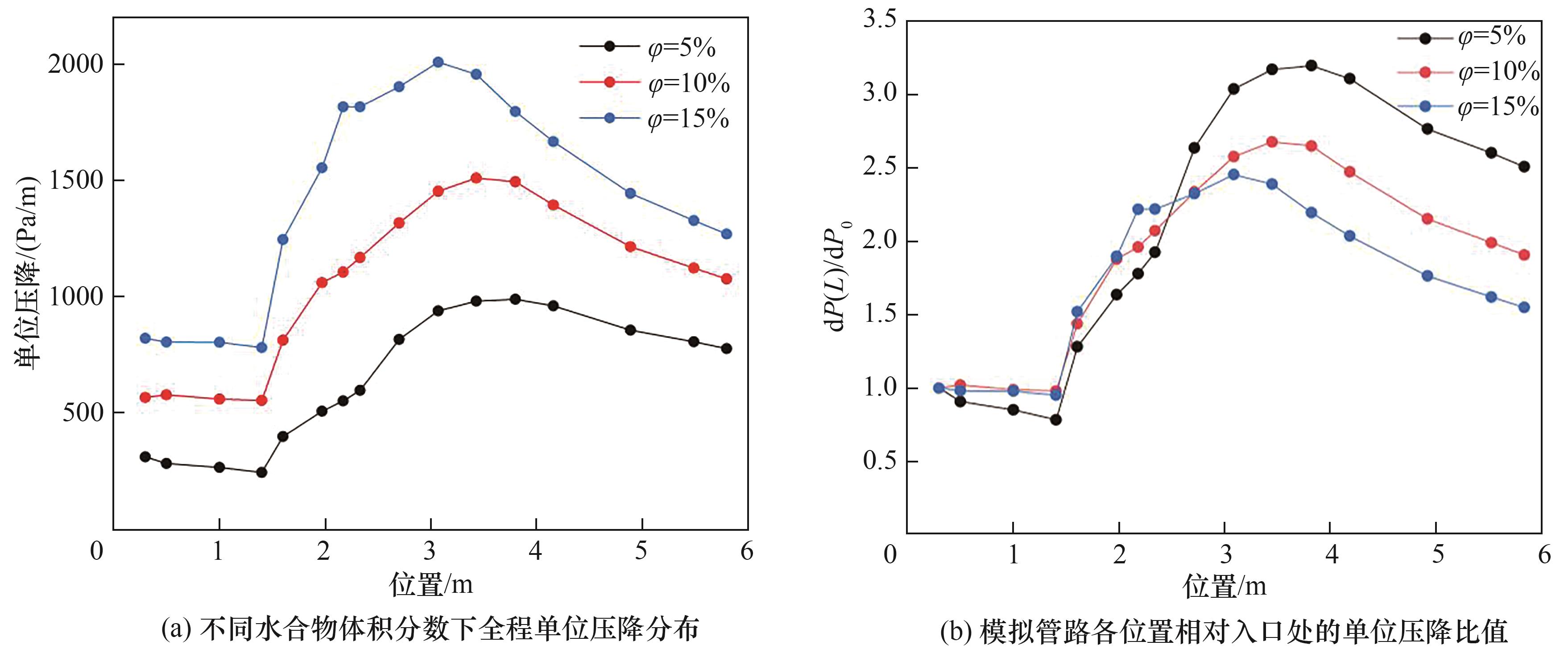
图19 不同水合物体积分数下水合物浆液流动的单位压降分布特征
Fig.19 Distribution characteristics of unit pressure drop in hydrate slurry flow under different hydrate volume fractions
| [1] | 李清平, 周守为, 赵佳飞, 等. 天然气水合物开采技术研究现状与展望[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(3): 214-224. |
| Li Q P, Zhou S W, Zhao J F, et al. Research status and prospects of natural gas hydrate exploitation technology[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(3): 214-224. | |
| [2] | 邓乐洋, 王雨婷, 王春辉, 等. 油气输送管道水合物堵塞机理、特性及其检测研究进展[J]. 油气与新能源, 2025, 37(2): 47-55. |
| Deng L Y, Wang Y T, Wang C H, et al. Research progress on hydrate plugging mechanism, characteristics and detection of oil and gas pipeline[J]. Petroleum and New Energy, 2025, 37(2): 47-55. | |
| [3] | 宫敬, 史博会, 陈玉川, 等. 含天然气水合物的海底多相管输及其堵塞风险管控[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(12): 133-142. |
| Gong J, Shi B H, Chen Y C, et al. Submarine multiphase pipeline transport containing natural gas hydrate and its plugging risk prevention and control[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(12): 133-142. | |
| [4] | 陈光进, 孙长宇, 马庆兰. 气体水合物科学与技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| Chen G J, Sun C Y, Ma Q L. Gas Hydrate Science and Technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. | |
| [5] | Doron P, Barnea D. A three-layer model for solid-liquid flow in horizontal pipes[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1993, 19(6): 1029-1043. |
| [6] | Balakin B V, Lo S, Kosinski P, et al. Modelling agglomeration and deposition of gas hydrates in industrial pipelines with combined CFD-PBM technique[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 153: 45-57. |
| [7] | Shi B H, Wang J Q, Yu Y F, et al. Investigation on the transition criterion of smooth stratified flow to other flow patterns for gas-hydrate slurry flow[J]. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 2017: 9846507. |
| [8] | Shi B H, Gong J, Sun C Y, et al. An inward and outward natural gas hydrates growth shell model considering intrinsic kinetics, mass and heat transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 171(3): 1308-1316. |
| [9] | Wang W C, Fan S S, Liang D Q, et al. Experimental study on flow characteristics of tetrahydrofuran hydrate slurry in pipelines[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry, 2010, 19(3): 318-322. |
| [10] | Bu Y H, Lu Z L, Lu C, et al. Molecular design and evaluation of hydrate dissociation inhibitors used in cementing slurry based on molecular dynamic simulations[J]. Fuel, 2023, 354: 129317. |
| [11] | Li L X, Liang Q Y, Yu Y J, et al. Microbial self-healing cementing slurry: a promising technology in deepwater with gas hydrate formations[J]. Gas Science and Engineering, 2025, 139: 205637. |
| [12] | Liu X, Yuan A, Li Y X, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrate slurry flow and deposit behavior based on openfoam-IATE[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122426. |
| [13] | Lv X F, Zhang J, Liu Y, et al. Simulation study of natural gas hydrate slurry flow characteristics in a high-pressure flow loop[J]. Fuel, 2022, 316: 123332. |
| [14] | Lv X F, Xu K Y, Liu Y, et al. Numerical simulation analysis of stable flow of hydrate slurry in gas-liquid-solid multiphase flow[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 300: 117336. |
| [15] | Song G C, Li Y X, Wang W C, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrate slurry flow behavior in oil-water systems based on hydrate agglomeration modelling[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 169: 393-404. |
| [16] | Balakin B V, Chang Y F, Øynes M, et al. Plugging of pipes by cohesive particles. Computed tomography investigation and theoretical analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 296: 120214. |
| [17] | Sontti S G, Zhang X H. Numerical insights from a population balance model into the distribution of bitumen residues in industrial horizontal pipes during the hydrotransport of oil sands tailings[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(1): 691-705. |
| [18] | Pei J H, Shen J Y, Wang Z Y, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrate flow in gas-dominated undulating pipes considering nucleation and deposition behaviors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2025, 301: 120735. |
| [19] | Ma H Q, Zhou L Y, Liu Z H, et al. A review of recent development for the CFD-DEM investigations of non-spherical particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 412: 117972. |
| [20] | Wang J A, Li Y, Zhao J F, et al. Simulation of the effect of hydrate adhesion properties on flow safety in solid fluidization exploitation[J]. Petroleum, 2023, 9(3): 403-411. |
| [21] | Duan X, Shi B H, Wang J N, et al. Simulation of the hydrate blockage process in a water-dominated system via the CFD-DEM method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 96: 104241. |
| [22] | Tang Y, Xie N, He Y F, et al. Study on the performance of downhole spiral-cyclone coupling separator for natural gas hydrate[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2024, 35(10): 104638. |
| [23] | Katagiri J, Yoneda J, Tenma N. Multiobjective optimization of the particle aspect ratio for gravel pack in a methane-hydrate reservoir using pore scale simulation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 35: 920-927. |
| [24] | Li X, Li C P, Ruan Z E, et al. Analysis of particle migration and agglomeration in paste mixing based on discrete element method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 352: 129007. |
| [25] | Qin S, Xu T, Zhou W H, et al. Infiltration behaviour and microstructure of filter cake from sand-modified bentonite slurry[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2023, 40: 100963. |
| [26] | Ren W L, Zhang X H, Zhang Y, et al. The impact of particle size and concentration on the characteristics of solid-fluid two-phase flow in vertical pipe under pulsating flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500: 156398. |
| [27] | Dai Y, Zhang Y Y, Li X Y. Numerical and experimental investigations on pipeline internal solid-liquid mixed fluid for deep ocean mining[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 220: 108411. |
| [28] | Fan J C, Zhang S M, Yao B C, et al. Numerical simulation of the motion of polypropylene-particles in a horizontal straight pipe[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 88: 103854. |
| [29] | Hayashi K, Watano S. Novel population balance model for granule aggregation and breakage in fluidized bed granulation and drying[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 342: 664-675. |
| [30] | Johnson K L, Kendall K, Roberts A D. Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1971, 324(1558): 301-313. |
| [1] | 刘卓龙, 甘云华, 屈可扬, 陈宁光, 潘铭晖. 均匀电场对生物柴油小尺度射流扩散燃烧特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4800-4808. |
| [2] | 李云昊, 徐纯刚, 李小森, 付骏, 王屹, 陈朝阳. 固液复配型促进剂对盐水体系CO2水合物形成影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4228-4238. |
| [3] | 周航, 张斯婧, 刘剑, 张小松. 小通道内非共沸工质流动沸腾换热数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3864-3872. |
| [4] | 刘建海, 王磊, 鲁朝金, 白志山, 张平雨. 耦合电化学与多相流模型的电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3885-3893. |
| [5] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [6] | 马永丽, 安澍, 杨捷, 刘明言. 气液固流化床直接数值模拟研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788. |
| [7] | 周臣儒, 刘陈伟, 王志远, 綦民辉, 董三宝, 王翔宇, 李明忠. 甲醇和乙二醇对甲烷水合物黏附强度的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3596-3604. |
| [8] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [9] | 颜成辉, 谢应明, 庞治海, 翁盛乔. 泡沫多孔材料对R134a水合物蓄冷的强化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3084-3092. |
| [10] | 郭江悦, 常守金, 胡海涛. 水平管内甲醇流动冷凝数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2580-2588. |
| [11] | 王令颁, 孙漪霏, 卜禹豪, 许振彬, 孙贤, 邵瀚锋, 孙长宇, 陈光进. 大尺度扇柱形反应釜内甲烷水合物降压开采规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2958-2973. |
| [12] | 贾文龙, 肖欢, 冷翔宇, 黄巧竞, 刘程玮, 吴瑕. 原油储罐重质沉积物超声波空化微射流清洗实验及数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1288-1296. |
| [13] | 张鑫源, 何呈祥, 李亚婷, 朱春英, 马友光, 付涛涛. 微通道内液液非均相传质的模拟和实验研究方法进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 484-503. |
| [14] | 方筑, 廖亚琴, 张乾, 张易阳, 李水清. 基于随机弹道沉积方法的黏附性椭球颗粒疏松堆积极限的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5533-5543. |
| [15] | 武顺杰, 蔡容容, Eliseev A.A., 张立志. 磁性纳米流体颗粒定向排布与各向异性导热的数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5709-5719. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号