• •
张兰河1( ), 石冰1, 刘慧2, 吴嘉明1, 张明爽1(
), 石冰1, 刘慧2, 吴嘉明1, 张明爽1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-25
修回日期:2025-12-06
出版日期:2025-12-08
通讯作者:
张明爽
作者简介:张兰河(1971—),男,博士,教授,zhanglanhe@163.com
基金资助:
Lanhe ZHANG1( ), Bing SHI1, Hui LIU2, Jiaming WU1, Mingshuang ZHANG1(
), Bing SHI1, Hui LIU2, Jiaming WU1, Mingshuang ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-07-25
Revised:2025-12-06
Online:2025-12-08
Contact:
Mingshuang ZHANG
摘要:
金属催化剂表面电子转移能力的强弱是决定反应速率的关键因素。通常情况下,金属催化剂表面的变价金属在牺牲固有电子的情况下进行电子转移,导致金属氧化物的积累和催化剂的失活。为了提高催化剂的效率,通过掺杂非变价金属Zn制备Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2催化剂(ZnCuMgSiO),以达到加速界面电子迁移和减少固有电子损失的目的;考察Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2催化剂的形貌结构,分析催化臭氧化磺胺甲噁唑(SMX)的效能,评估催化剂本身及SMX降解产物的毒性。结果表明:制备的催化剂呈多孔珊瑚网络结构,在初始pH 7、催化剂用量0.1 g·L-1、臭氧浓度2.4 mg·L-1的条件下,催化臭氧化30 min,SMX去除率达到90.39%。淬灭实验、EPR和XPS分析表明,Cu2+/Cu+和Mg2+/Mg之间的价态循环和表面羟基对O3的吸附是提高催化臭氧化效率的关键步骤,Zn2+掺杂能够提高催化剂的电子转移能力,产生的氧空位(OV)作为O3分解的活性位点。臭氧分解产生的·OH和1O2是降解SMX的活性物种,其中1O2占主导作用。结合密度泛函理论(DFT)计算和液质联用(LC-MS)分析,提出了可能的的降解途径和降解机理。通过毒性评估实验表明,ZnCuMgSiO催化剂无毒,SMX的催化臭氧化能够显著降低毒性。
中图分类号:
张兰河, 石冰, 刘慧, 吴嘉明, 张明爽. 电子传递能力强的Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2气凝胶催化剂的制备及催化臭氧化磺胺甲噁唑机理和毒性评估[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250824.
Lanhe ZHANG, Bing SHI, Hui LIU, Jiaming WU, Mingshuang ZHANG. Preparation of Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2 aerogel catalyst with strong electron transfer ability and its catalytic ozonation mechanism and toxicity evaluation on sulfamethoxazole[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250824.
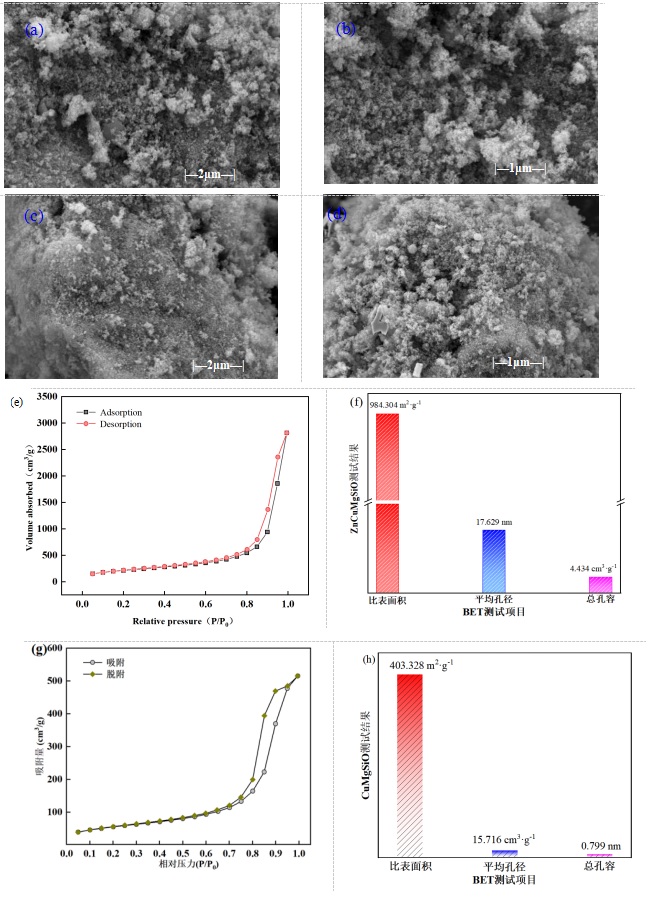
图3 催化剂的微观形貌和比表面积:(a),(b)SEM图(CuMgSiO);(c),(d)SEM图(ZnCuMgSiO);(e)ZnCuMgSiO催化剂的N2吸附脱附曲线;(f)ZnCuMgSiO催化剂的比表面积、孔径和孔容;(g)CuMgSiO催化剂的N2吸附脱附曲线;(h)CuMgSiO催化剂的比表面积、孔径和孔容
Fig. 3 Microstructure and specific surface area of the catalysts: (a), (b) SEM images of CuMgSiO; (c),(d) SEM images of ZnCuMgSiO; (e) N2 adsorption-desorption curve of ZnCuMgSiO; (f) Specific surface area, pore size, and pore volume of ZnCuMgSiO; (g) N2 adsorption-desorption curve of CuMgSiO; (h) Specific surface area, pore size, and pore volume of CuMgSiO
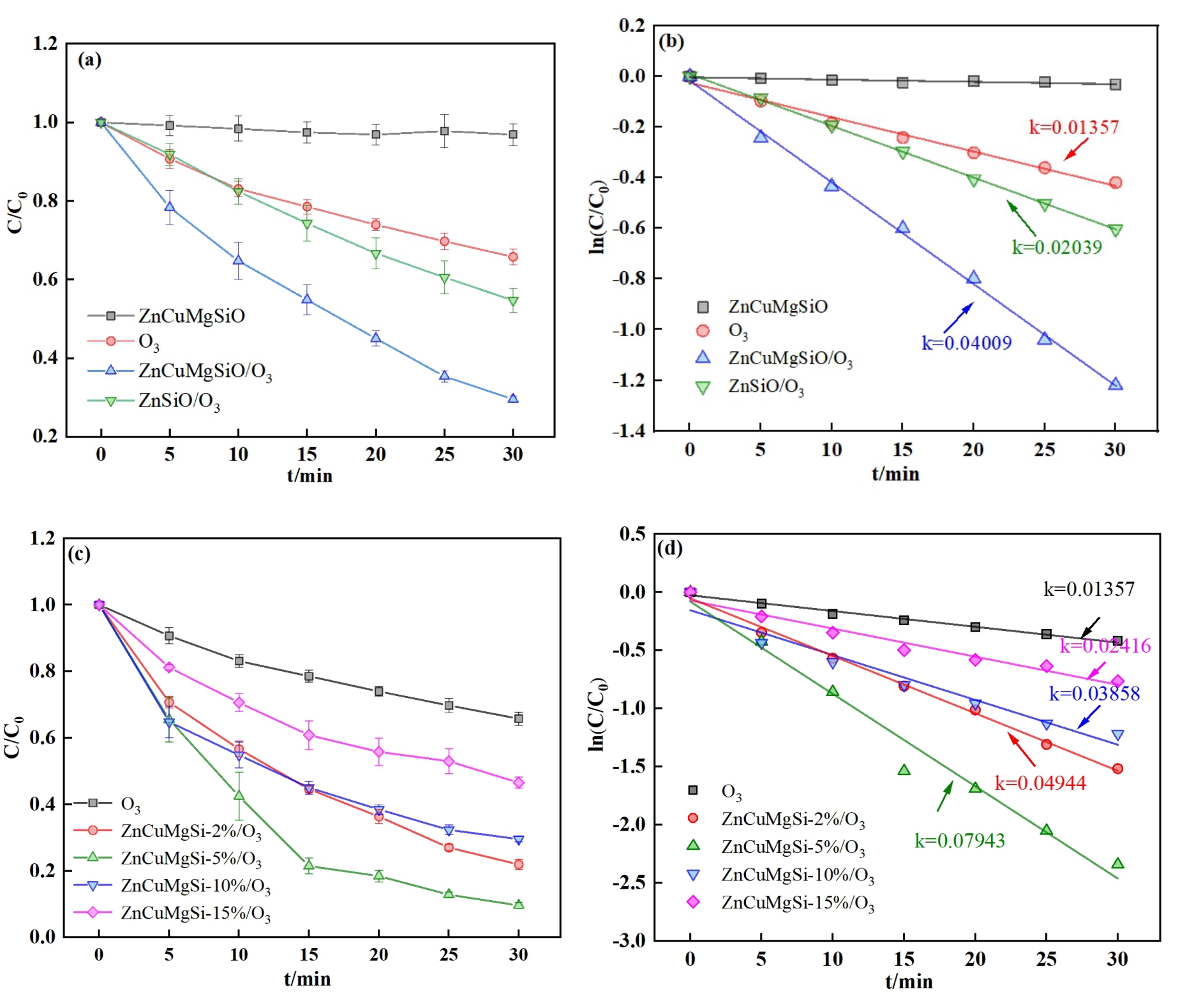
图4 不同催化剂对SMX的催化臭氧化性能:(a)不同体系对SMX去除率的影响;(c)不同掺杂比例的ZnCuMgSiO催化剂对SMX去除率的影响;(b), (d)不同体系的降解动力学注:Reaction conditions: [catalyst] = 0.1 g·L-1, [SMX] = 20 mg·L-1, pH = 7反应条件:[催化剂]=0.1 g·L-1,[SMX]=20 mg·L-1,pH=7
Fig. 4 Catalytic ozonation performance of SMX under different catalysts: (a) Effects of different systems on removal efficiencies of SMX; (c) Effects of different doping ratios of ZnCuMgSiO catalysts on removal efficiencies of SMX; (b), (d) Degradation kinetics of SMX in different systems
| 催化剂种类 | 催化剂用量 (g·L-1) | 污染物 (mg⋅L-1) | 反应时间 (min) | 去除率 (%) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeSO | 1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 89.0 | [ |
| Bi2WO6/TiO2 | 0.2 | SMX (10) | 60 | 89.1 | [ |
| Mn@CNM | 1 | SMX (20) | 420 | 81.3 | [ |
| CuOx/MgO-SiO2 | 0.1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 87.9 | [ |
| Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2 | 0.1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 90.39 | 本研究 |
表1 本研究与其他催化剂降解SMX效能对比
Table 1 Comparison of SMX degradation efficiency between this study and other catalysts
| 催化剂种类 | 催化剂用量 (g·L-1) | 污染物 (mg⋅L-1) | 反应时间 (min) | 去除率 (%) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeSO | 1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 89.0 | [ |
| Bi2WO6/TiO2 | 0.2 | SMX (10) | 60 | 89.1 | [ |
| Mn@CNM | 1 | SMX (20) | 420 | 81.3 | [ |
| CuOx/MgO-SiO2 | 0.1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 87.9 | [ |
| Zn-CuOx/MgO-SiO2 | 0.1 | SMX (20) | 30 | 90.39 | 本研究 |
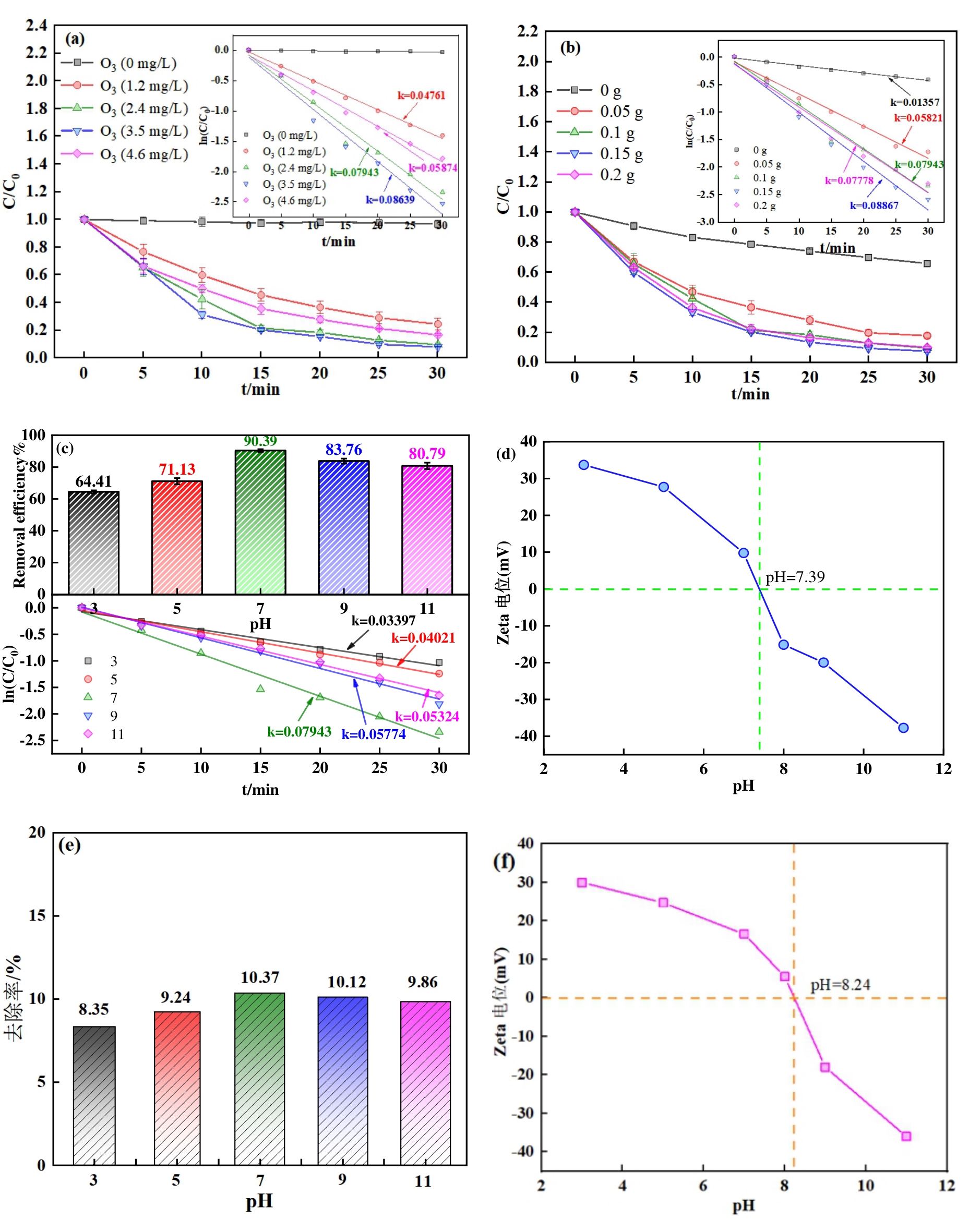
图5 不同因素对SMX去除率的影响和反应的Kobs:(a)O3 浓度;(b)催化剂投加量;(c)初始pH(反应条件:(a),(c)[催化剂]=0.1 g·L-1,(b),(c)[O3]=2.96 mg·L-1,(a),(b)pH=7);(d)ZnCuMgSiO的Zeta电位与pH值的关系;(e)ZnCuMgSiO在不同pH下对SMX的吸附;(f)CuMgSiO的Zeta电位与pH值的关系
Fig. 5 Effects of various factors on SMX removal efficiency and reaction parameters Kobs: (a) O3 concentration; (b) catalyst dosage; (c) initial pH (Reaction conditions: (a), (c) [catalyst] = 0.1 g L-1, (b), (c) [O3] = 2.96 mg L-1, (a), (b) pH = 7); (d) Zeta potential of ZnCuMgSiO versus pH; (e) SMX adsorption by ZnCuMgSiO at different pH levels; (f) Zeta potential of CuMgSiO versus pH
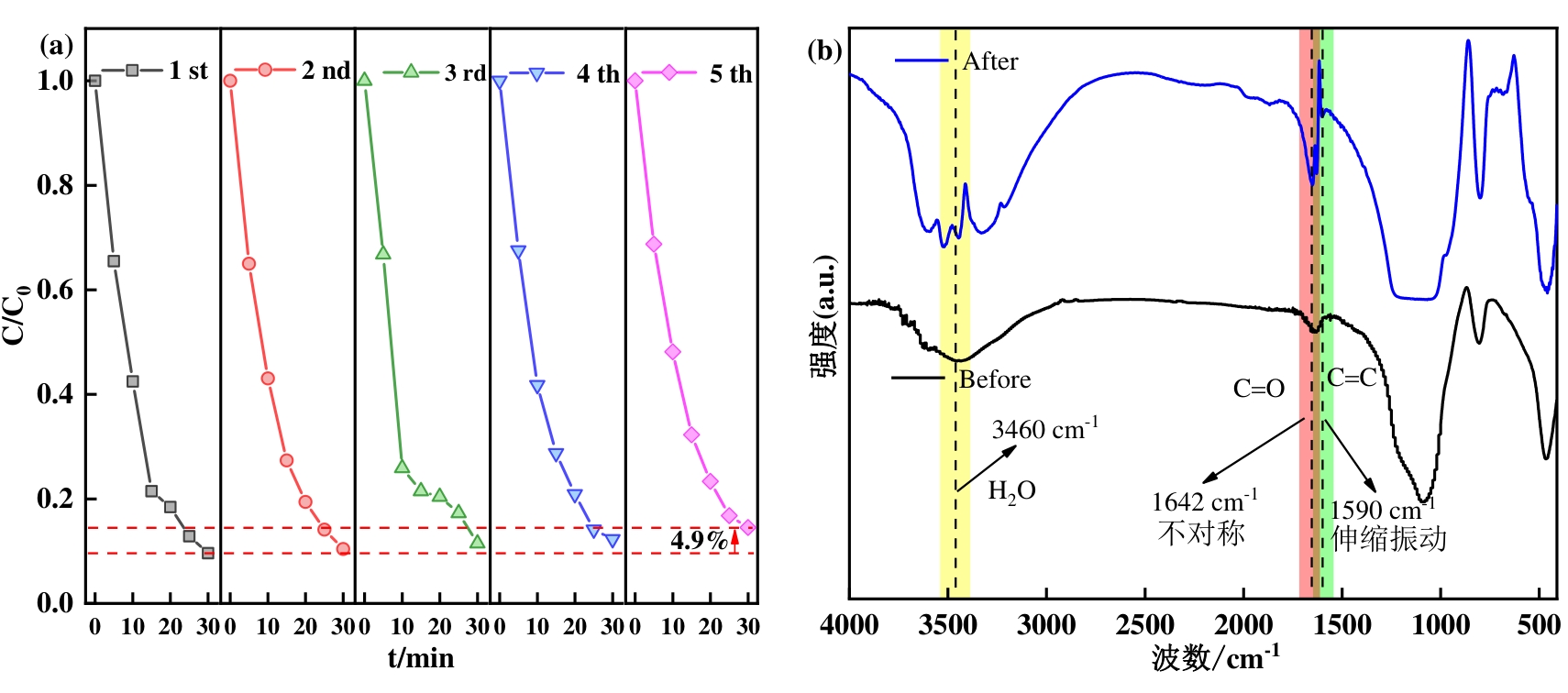
图6(a) ZnCuMgSiO催化剂的循环实验;(b)ZnCuMgSiO催化剂使用前后的FTIR谱图(反应条件:[催化剂]=0.1 g·L-1,[O3]=2.4 mg·L-1,[SMX]=20 mg·L-1,pH=7)
Fig. 6 (a) The cyclic test results of ZnCuMgSiO catalyst; (b) FTIR spectra before and after ZnCuMgSiO catalyst was utilized (Reaction conditions: [catalyst] = 0.1 g L-1, [O3] = 2.4 mg L-1, [SMX] = 20 mg L-1, pH = 7)
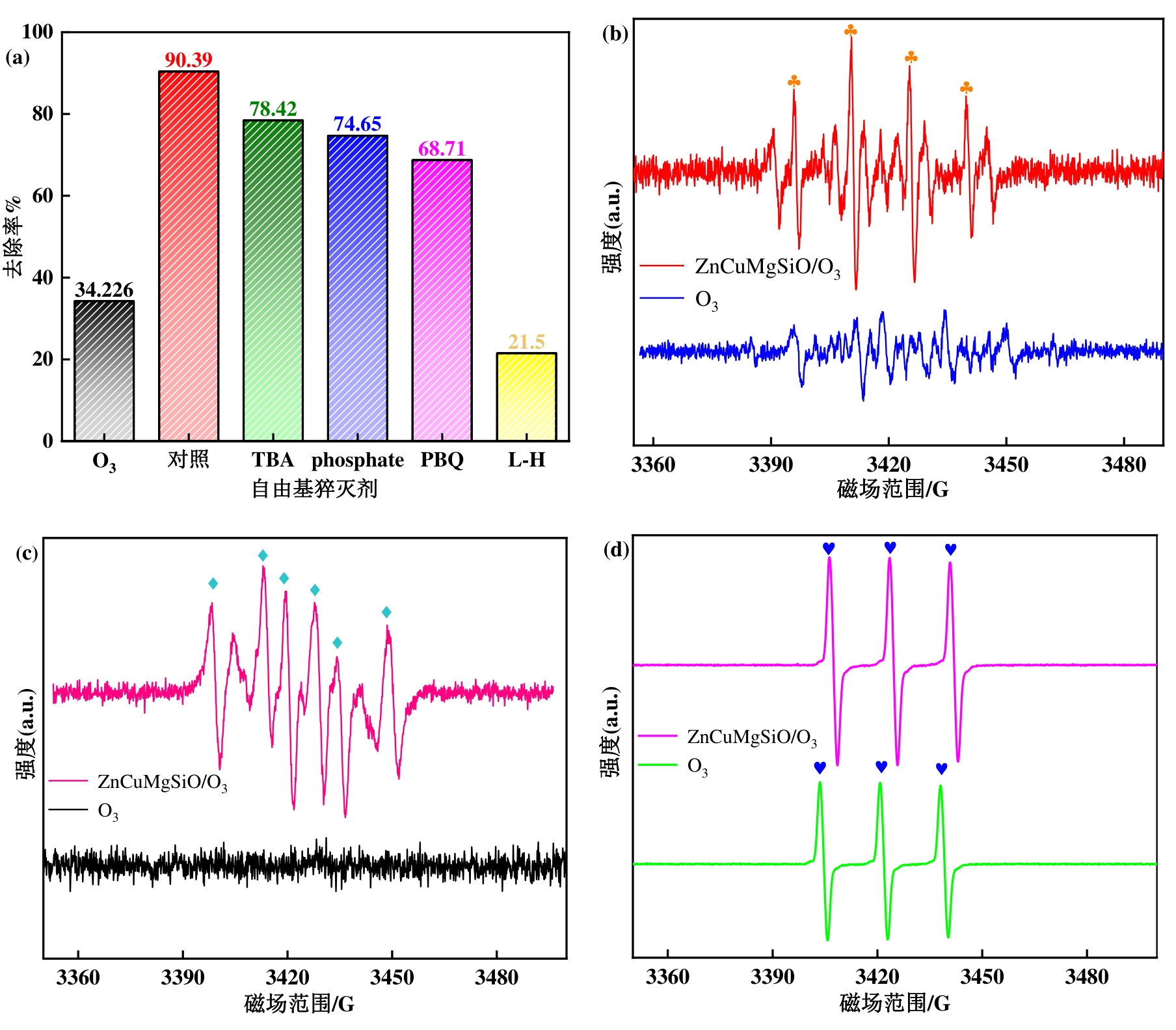
图7(a) 淬灭剂对SMX降解的影响;(b)~(d)CuMgSiO/O3体系的EPR谱图(反应条件:[催化剂]=0.1 g·L-1,[O3]=2.4 mg·L-1,[SMX]=20 mg·L-1,pH=7)
Fig. 7 (a) Effect of quencher on SMX degradation; (b)-(d) EPR spectra of CuMgSiO/O3 system (Reaction conditions: [catalyst] = 0.1 g L-1, [O3] = 2.4 mg L-1, [SMX] = 20 mg L-1, pH = 7)

图8 ZnCuMgSiO催化剂反应前后的XPS谱图;(a)Cu元素分峰图;(b)Mg元素分峰图;(c)Zn元素分峰图;(d)O元素分峰图;(e)ZnCuMgSiO催化剂的CV曲线;(f)催化剂的EIS曲线
Fig. 8 XPS spectra of ZnCuMgSiO catalyst before and after the reaction: (a) Cu; (b) Mg; (c) Zn; (d) O; (e) CV curve; (f) EIS curve
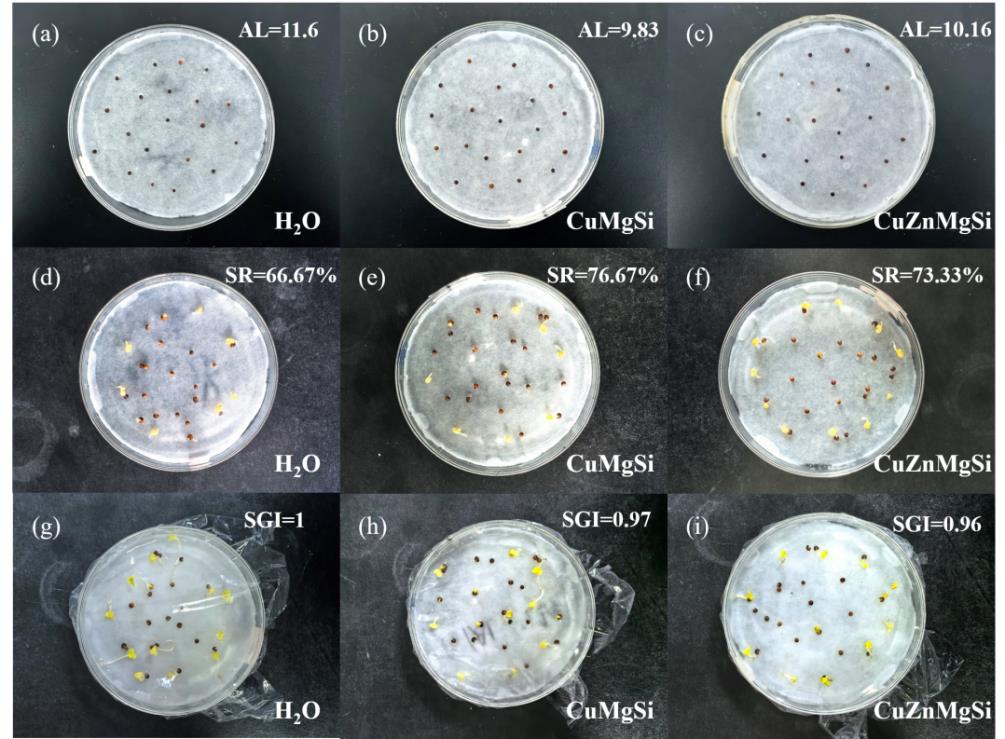
图11 植物毒性:(a)~(c)发芽0 d;(d)~(f)发芽2 d;(g)~(i)发芽3 d
Fig. 11 Plant toxicity: (a)-(c) germination for 0 d; (d)-(f) germination for 2 d; (g)-(i) germination for 3 d
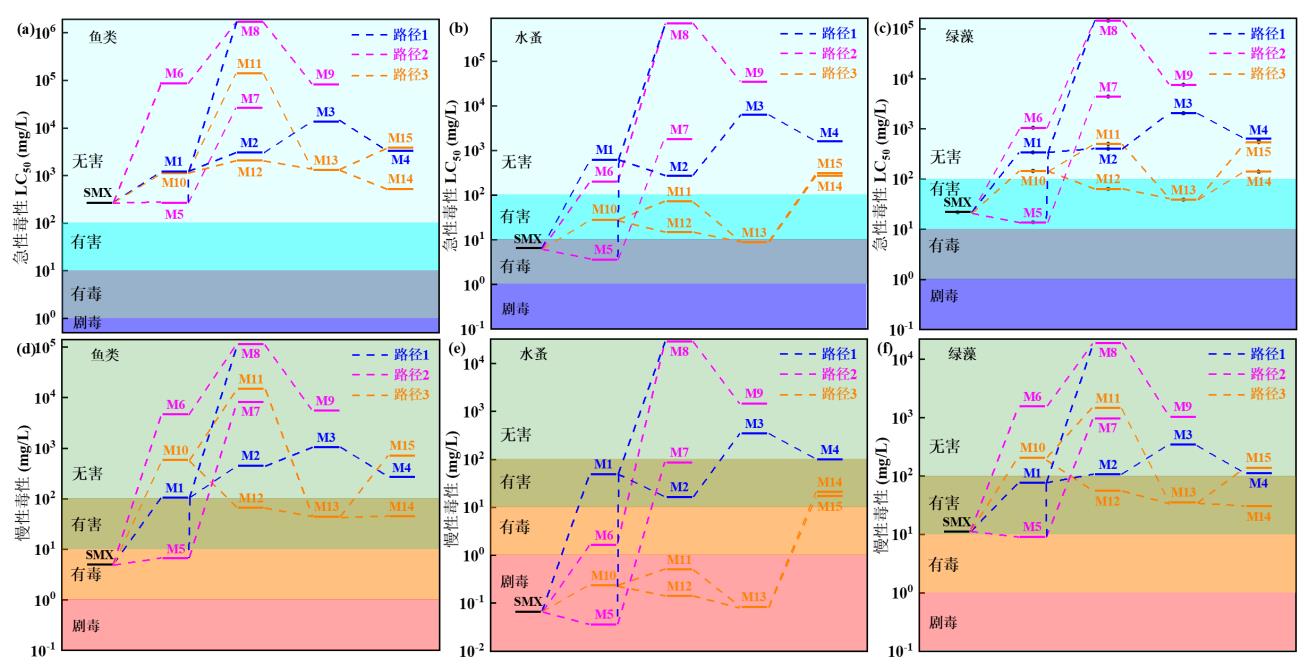
图12 急性毒性:(a)鱼类;(b)水蚤;(c)绿藻;慢性毒性:(d)鱼类;(e)水蚤;(f)绿藻
Fig. 12 Acute toxicity: (a) fish; (b) water fleas; (c) green algae; chronic toxicity: (d) fish; (e) water fleas; (f) green algae
| 产物 | m/z | 分子式 | 结构式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMX | 254 | C10H11N3O3S | 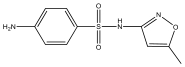 | |
| M1 | 284 | C10H9N3O5S | 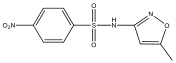 | |
| M2 | 317 | C10H11N3O7S | 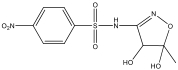 | |
| M3 | 187 | C6H5NO4S | 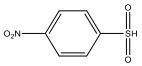 | |
| M4 | 108 | C6H4O2 | 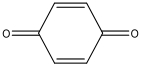 | |
| M5 | 98 | C4H6N2O | 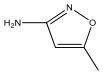 | |
| M6 | 173 | C6H7NO3S | 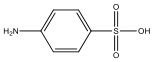 | |
| M7 | 102 | C4H10N2O | 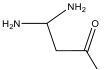 | |
| M8 | 203 | C6H5NO5S | 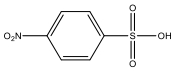 | |
| M9 | 143 | C6H6O2S | 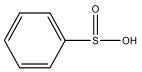 | |
| M10 | 255 | C10H11N3O3S | 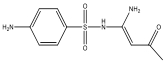 | |
| M11 | 249 | C7H10N3O4S | 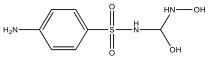 | |
| M12 | 274 | C10H13N3O4S | 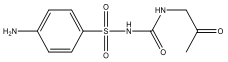 | |
| M13 | 159 | C6H7NO2S | 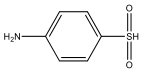 | |
| M14 | 93 | C6H7N | 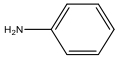 | |
| M15 | 127 | C6H9NO2 | 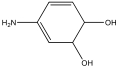 | |
| 丙酮酸 | 88 | C3H4O3 | 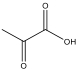 | |
| 草氨酸 | 89 | C2H3NO3 |  | |
 | ||||
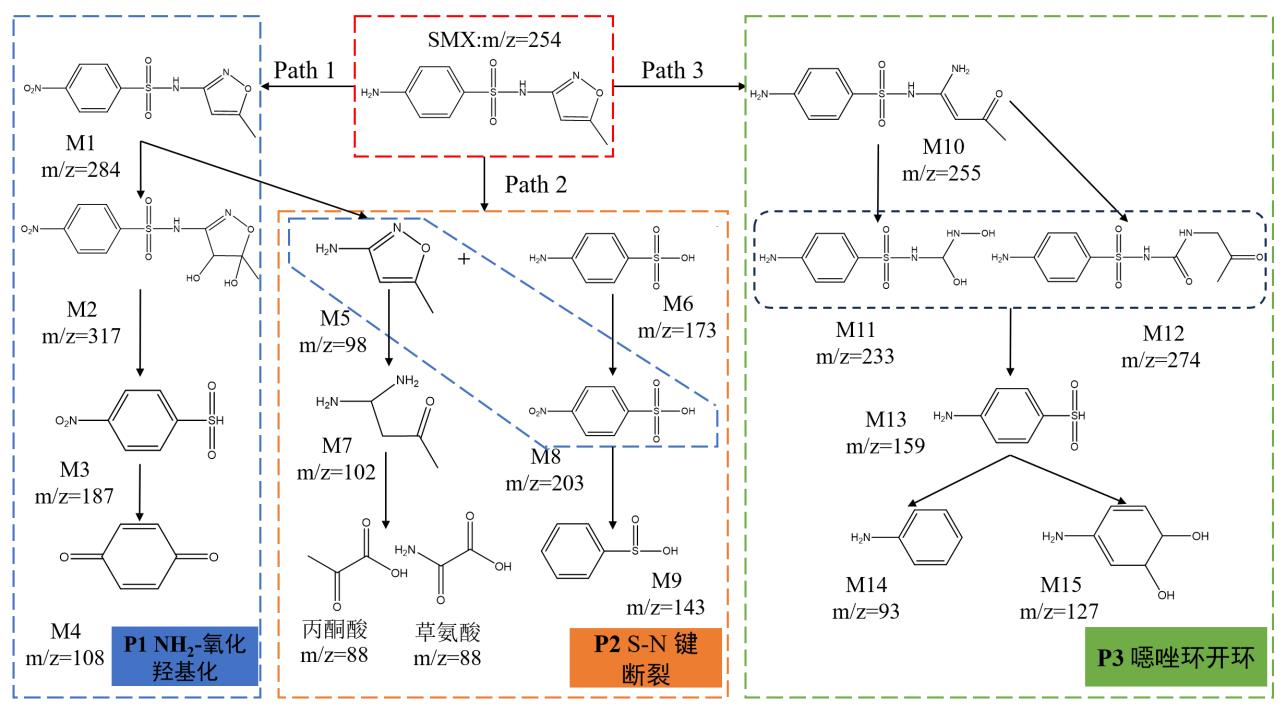 | ||||
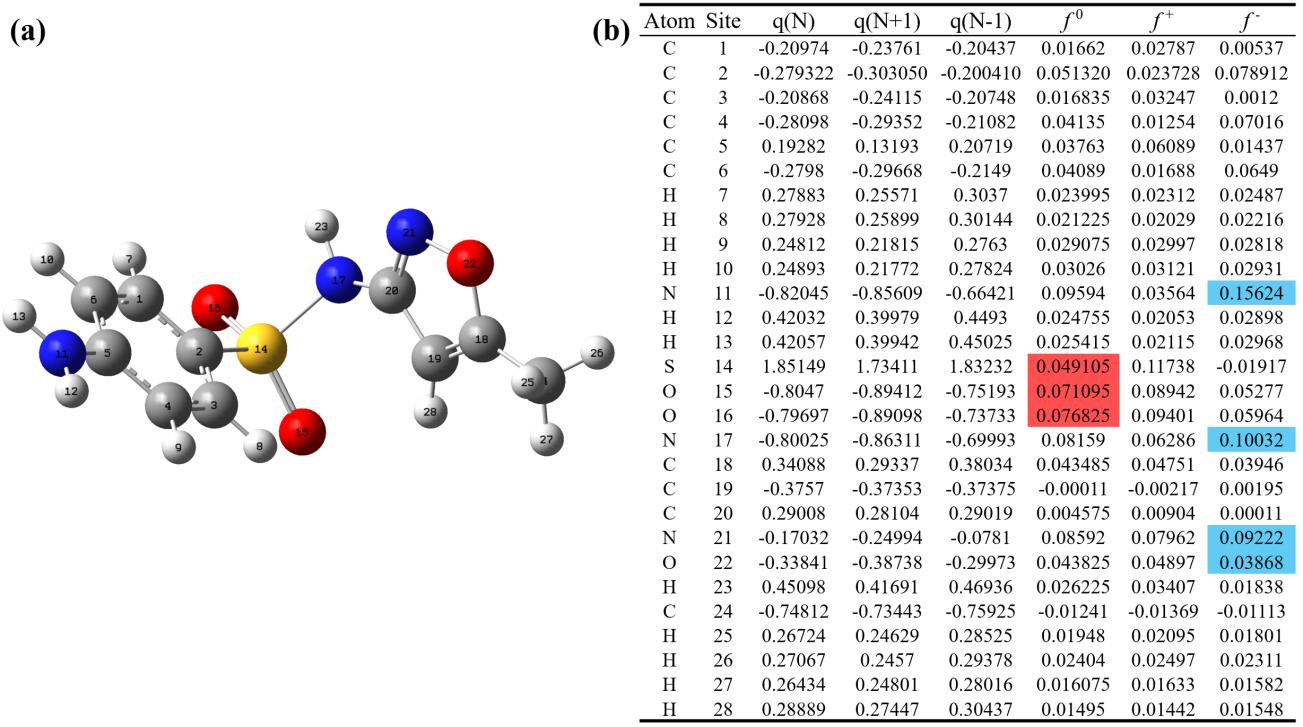
图10 (a)SMX分子结构;(b)Fukui指数;(c)SMX的降解路径 Fig. 10 (a) SMX molecular structure; (b) Fukui index; (c) Degradation pathway of SMX | ||||
表2 SMX降解中间产物
Table 2 Degradation intermediates of SMX
| 产物 | m/z | 分子式 | 结构式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMX | 254 | C10H11N3O3S |  | |
| M1 | 284 | C10H9N3O5S |  | |
| M2 | 317 | C10H11N3O7S |  | |
| M3 | 187 | C6H5NO4S |  | |
| M4 | 108 | C6H4O2 |  | |
| M5 | 98 | C4H6N2O |  | |
| M6 | 173 | C6H7NO3S |  | |
| M7 | 102 | C4H10N2O |  | |
| M8 | 203 | C6H5NO5S |  | |
| M9 | 143 | C6H6O2S |  | |
| M10 | 255 | C10H11N3O3S |  | |
| M11 | 249 | C7H10N3O4S |  | |
| M12 | 274 | C10H13N3O4S |  | |
| M13 | 159 | C6H7NO2S |  | |
| M14 | 93 | C6H7N |  | |
| M15 | 127 | C6H9NO2 |  | |
| 丙酮酸 | 88 | C3H4O3 |  | |
| 草氨酸 | 89 | C2H3NO3 |  | |
 | ||||
 | ||||
图10 (a)SMX分子结构;(b)Fukui指数;(c)SMX的降解路径 Fig. 10 (a) SMX molecular structure; (b) Fukui index; (c) Degradation pathway of SMX | ||||
| 样品 | AL(mm) | SR(%) | SGI |
|---|---|---|---|
| DW | 11.6 | 66.67 | 1 |
| CuMgSi | 9.83 | 76.67 | 0.97 |
| CuZnMgSi | 10.16 | 73.33 | 0.96 |
表3 大白菜种子在不同培养液中的AL、SR和SGI
Table 3 AL, SR, and SGI of Chinese cabbage seeds in different culture media
| 样品 | AL(mm) | SR(%) | SGI |
|---|---|---|---|
| DW | 11.6 | 66.67 | 1 |
| CuMgSi | 9.83 | 76.67 | 0.97 |
| CuZnMgSi | 10.16 | 73.33 | 0.96 |
| 化合物 | m/z | 急性毒性 | 慢性毒性 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鱼类 | 水蚤 | 绿藻 | 鱼类 | 水蚤 | 绿藻 | ||
| (96 h-LC50) | (48 h-LC50) | (96 h-EC50) | (ChV) | (ChV) | (ChV) | ||
| SMX | 254 | 267 | 6.43 | 21.8 | 5.00 | 0.068 | 11.1 |
| M1 | 284 | 1170 | 619 | 342 | 105 | 49.3 | 76.2 |
| M2 | 317 | 3070 | 271 | 405 | 448 | 16.6 | 108 |
| M3 | 187 | 13600 | 6310 | 2060 | 1050 | 353 | 345 |
| M4 | 108 | 3330 | 1610 | 614 | 269 | 100 | 112 |
| M5 | 98 | 270 | 3.63 | 13.8 | 6.59 | 0.036 | 9.116 |
| M6 | 173 | 86300 | 200 | 1060 | 4650 | 1.67 | 1570 |
| M7 | 102 | 26300 | 1800 | 4440 | 8260 | 86.4 | 989 |
| M8 | 203 | 1690000 | 706000 | 146000 | 115000 | 29100 | 19300 |
| M9 | 143 | 81600 | 34600 | 7690 | 5650 | 1490 | 1050 |
| M10 | 255 | 1120 | 28.1 | 146 | 584 | 0.236 | 209 |
| M11 | 249 | 140000 | 71.8 | 505 | 14900 | 0.510 | 1480 |
| M12 | 274 | 2080 | 15.0 | 64.1 | 67.3 | 0.141 | 56.6 |
| M13 | 159 | 1330 | 9.05 | 39.0 | 44.0 | 0.084 | 35.4 |
| M14 | 93 | 517 | 270 | 141 | 45.7 | 20.7 | 30.6 |
| M15 | 127 | 3820 | 309 | 549 | 726 | 17.4 | 138 |
表4 SMX降解产物的ECOSAR毒性分析结果
Table 4 ECOSAR toxicity analysis results of SMX degradation products
| 化合物 | m/z | 急性毒性 | 慢性毒性 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鱼类 | 水蚤 | 绿藻 | 鱼类 | 水蚤 | 绿藻 | ||
| (96 h-LC50) | (48 h-LC50) | (96 h-EC50) | (ChV) | (ChV) | (ChV) | ||
| SMX | 254 | 267 | 6.43 | 21.8 | 5.00 | 0.068 | 11.1 |
| M1 | 284 | 1170 | 619 | 342 | 105 | 49.3 | 76.2 |
| M2 | 317 | 3070 | 271 | 405 | 448 | 16.6 | 108 |
| M3 | 187 | 13600 | 6310 | 2060 | 1050 | 353 | 345 |
| M4 | 108 | 3330 | 1610 | 614 | 269 | 100 | 112 |
| M5 | 98 | 270 | 3.63 | 13.8 | 6.59 | 0.036 | 9.116 |
| M6 | 173 | 86300 | 200 | 1060 | 4650 | 1.67 | 1570 |
| M7 | 102 | 26300 | 1800 | 4440 | 8260 | 86.4 | 989 |
| M8 | 203 | 1690000 | 706000 | 146000 | 115000 | 29100 | 19300 |
| M9 | 143 | 81600 | 34600 | 7690 | 5650 | 1490 | 1050 |
| M10 | 255 | 1120 | 28.1 | 146 | 584 | 0.236 | 209 |
| M11 | 249 | 140000 | 71.8 | 505 | 14900 | 0.510 | 1480 |
| M12 | 274 | 2080 | 15.0 | 64.1 | 67.3 | 0.141 | 56.6 |
| M13 | 159 | 1330 | 9.05 | 39.0 | 44.0 | 0.084 | 35.4 |
| M14 | 93 | 517 | 270 | 141 | 45.7 | 20.7 | 30.6 |
| M15 | 127 | 3820 | 309 | 549 | 726 | 17.4 | 138 |
| [1] | Craig C R, Stitzel R E. Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications[M]. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004. |
| [2] | Pelalak R, Heidari Z, Forouzesh M, et al. High performance ozone based advanced oxidation processes catalyzed with novel argon plasma treated iron oxyhydroxide hydrate for phenazopyridine degradation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 964. |
| [3] | Pang C K, Joseph C G, Farm Y Y. Magnetically recoverable copper ferrite for catalytic ozonation of surfactant-containing simulated laundry wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(6): 111203. |
| [4] | Turkay O, Inan H, Dimoglo A. Experimental and theoretical investigations of CuO-catalyzed ozonation of humic acid[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2014, 134: 110-116. |
| [5] | Ma G J, Tang W X, Wang A Q, et al. Heterojunctioned CuO/Cu2O catalyst for highly efficient ozone removal[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 125: 340-348. |
| [6] | Ghuge S P, Saroha A K. Ozonation of Reactive Orange 4 dye aqueous solution using mesoporous Cu/SBA-15 catalytic material[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2018, 23: 217-229. |
| [7] | Zhang F Z, Wei C H, Hu Y, et al. Zinc ferrite catalysts for ozonation of aqueous organic contaminants: phenol and bio-treated coking wastewater[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 156: 625-635. |
| [8] | Pospelova V, Aubrecht J, Pacultová K, et al. Does the structure of CuZn hydroxycarbonate precursors affect the intrinsic hydrogenolysis activity of CuZn catalysts?[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(10): 3303-3314. |
| [9] | Mazumder P, Khwairakpam M, Kalamdhad A S. Bio-inherent attributes of water hyacinth procured from contaminated water body–effect of its compost on seed germination and radicle growth[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 257: 109990. |
| [10] | Kopanja L, Milosevic I, Panjan M, et al. Sol–gel combustion synthesis, particle shape analysis and magnetic properties of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles embedded in an amorphous silica matrix[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 362: 380-386. |
| [11] | Meng F Y, Zhang S L, Zhang M J, et al. The mechanism of Ce-MCM-41 catalyzed peroxone reaction into •OH and •O2 - radicals for enhanced NO oxidation[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 518: 112110. |
| [12] | Zhou X Q, Jawad A, Luo M Y, et al. Regulating activation pathway of Cu/persulfate through the incorporation of unreducible metal oxides: Pivotal role of surface oxygen vacancies[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 286: 119914. |
| [13] | Karuppusamy I, Samuel M S, Selvarajan E, et al. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of mixed calcium magnesium oxide (CaMgO2) nanoflakes for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 584: 770-778. |
| [14] | Hessien M, Da'na E, AL-Amer K, et al. Nano ZnO (hexagonal wurtzite) of different shapes under various conditions: fabrication and characterization[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(8): 085057. |
| [15] | Yang Y L, Fu W Y, Chen X X, et al. Ceramic nanofiber membrane anchoring nanosized Mn2O3 catalytic ozonation of sulfamethoxazole in water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 436: 129168. |
| [16] | 魏健, 徐晓月, 郭壮, 等. 全氟辛酸光催化材料应用及降解机理研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(3): 1127-1138. |
| Wei J, Xu X Y, Guo Z, et al. Research progress in the application and degradation mechanism of perfluorooctanoic acid photocatalytic materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023, 13(3): 1127-1138. | |
| [17] | Shen T D, Su W T, Yang Q Q, et al. Synergetic mechanism for basic and acid sites of MgMxOy (M = Fe, Mn) double oxides in catalytic ozonation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and acetic acid[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 279: 119346. |
| [18] | Guo Y, Zhang Y X, Yu G, et al. Revisiting the role of reactive oxygen species for pollutant abatement during catalytic ozonation: The probe approach versus the scavenger approach[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 280: 119418. |
| [19] | Luo R, Li M Q, Wang C H, et al. Singlet oxygen-dominated non-radical oxidation process for efficient degradation of bisphenol A under high salinity condition[J]. Water Research, 2019, 148: 416-424. |
| [20] | Fanaei F, Moussavi G, Srivastava V, et al. The enhanced catalytic potential of sulfur-doped MgO (S-MgO) nanoparticles in activation of peroxysulfates for advanced oxidation of acetaminophen[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 404-413. |
| [21] | Zhang L S, Meng G H, Liu B H, et al. Heterogeneous photocatalytic ozonation of sulfamethoxazole by Z-scheme Bi2WO6/TiO2 heterojunction: Performance, mechanism and degradation pathway[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 360: 119427. |
| [22] | Zhang L H, Wu J M, Zhang J, et al. Catalytic ozonation of sulfamethoxazole using loaded CuOx/MgO-SiO2 silica aerogel catalyst: Performance, mechanisms and toxicity[J]. Environmental Research, 2025, 272: 121155. |
| [23] | Liu X H, Li H P, Fang Y, et al. Heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of sulfamethazine in aqueous solution using maghemite-supported manganese oxides[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 274: 118945. |
| [24] | Huang Y X, Liang M L, Ma L M, et al. Ozonation catalysed by ferrosilicon for the degradation of ibuprofen in water[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115722. |
| [25] | 景凌云, 张泽强, 刘莎莎, 等. TiO2/g-C3N4高效固定漆酶光酶协同催化降解毒死蜱[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2024, 14(6): 1847-1856. |
| Jing L Y, Zhang Z Q, Liu S S, et al. Effective immobilization of laccase on TiO2/g-C3N4 for enhanced chlorpyrifos degradation via photo-enzyme synergistic catalysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2024, 14(6): 1847-1856. | |
| [26] | Zeng Y Q, Wang T X, Zhang S L, et al. Sol–gel synthesis of CuO-TiO2 catalyst with high dispersion CuO species for selective catalytic oxidation of NO[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 411: 227-234. |
| [27] | Zhang L H, Shi B, Liu H, et al. Charge-engineered 2D layered magnetic Cl-CaFe2O4/g-C3N4 catalyst for catalytic ozonation of norfloxacin: performance, mechanism and ecotoxicological assessment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 525: 170440. |
| [28] | Zhao J J, Li F C, Wei H X, et al. Superior performance of ZnCoOx/peroxymonosulfate system for organic pollutants removal by enhancing singlet oxygen generation: The effect of oxygen vacancies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128150. |
| [29] | Li S Y, Wang J, Ye Y Y, et al. Composite Si-O-metal network catalysts with uneven electron distribution: Enhanced activity and electron transfer for catalytic ozonation of carbamazepine[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 263: 118311. |
| [30] | Liu W, Li Y Y, Liu F Y, et al. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by carbon quantum dots modified porous g-C3N4: Mechanisms, degradation pathway and DFT calculation[J]. Water Research, 2019, 151: 8-19. |
| [31] | Chen H, Wang J L. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by ozonation combined with ionizing radiation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 407: 124377. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [3] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [4] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [5] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [6] | 张淇栋, 艾立强, 马原, 吴胜宝, 王磊, 厉彦忠. 基于一维漂移流模型的低温管路预冷过程两相流动与换热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3842-3852. |
| [7] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [8] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [9] | 陆学瑞, 周帼彦, 方琦, 俞孟正, 张秀成, 涂善东. 固体氧化物燃料电池外重整器积炭效应数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| [10] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [11] | 李愽龙, 蒋雨希, 任傲天, 秦雯琪, 傅杰, 吕秀阳. TS-1/In-TS-1催化果糖一步法醇解制备乳酸甲酯连续化试验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2678-2686. |
| [12] | 孙文浩, 田君, 张锟, 刘娜, 曹宝森, 梁晓嫱. 锂离子电池用高热稳定性新型隔膜的研究新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2524-2543. |
| [13] | 李子阳, 申沛鑫, 张孝阿, 王成忠, 史翎, 张军营. α, ω-端羟基苯基/亚苯基高乙烯基聚硅氧烷的合成及热稳定性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3041-3052. |
| [14] | 杨浩杰, 刘春雨, 李雪娇, 于亮, 吕兴才. 低旋流配置下氨-甲烷-空气预混旋流火焰稳定性和排放特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3029-3040. |
| [15] | 何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号