• •
王迪1( ), 李胜杰1, 崔颖晗2, 孙灵芳1, 李晓莉3(
), 李胜杰1, 崔颖晗2, 孙灵芳1, 李晓莉3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-09-10
修回日期:2025-12-10
出版日期:2025-12-11
通讯作者:
李晓莉
作者简介:王迪(1989—),男,博士,副教授,wd1989125@163.com
基金资助:
Di WANG1( ), Shengjie LI1, Yinghan CUI2, Lingfang SUN1, Xiaoli LI3(
), Shengjie LI1, Yinghan CUI2, Lingfang SUN1, Xiaoli LI3( )
)
Received:2025-09-10
Revised:2025-12-10
Online:2025-12-11
Contact:
Xiaoli LI
摘要:
随着我国“双碳”战略的深入推进,风电、光伏等间歇性可再生能源发电占比不断升高,导致电网调峰调频需求急剧增加。为显著提升传统燃煤发电机组运行灵活性,本研究提出了一种压缩超临界二氧化碳(S-CO₂)储能系统与燃煤机组耦合的方案。通过建立系统热力学模型,并基于㶲分析原理,深入研究关键运行参数对系统整体及各组成部件不可逆损失分布的影响。研究结果表明:该系统可实现68.12%的往返效率,在三种典型运行方式下的㶲效率分别为56.18%、57.84%和62.94%;S-CO₂工质流量、压缩机组入口压力及压缩机效率是对系统㶲效率影响最为显著的关键参数。研究成果可对未来建设S-CO₂储能循环工程应用奠定理论基础。
中图分类号:
王迪, 李胜杰, 崔颖晗, 孙灵芳, 李晓莉. 燃煤发电耦合压缩S-CO₂储能系统构建与热力学分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251024.
Di WANG, Shengjie LI, Yinghan CUI, Lingfang SUN, Xiaoli LI. Construction and thermodynamic analysis of a coupled compression S-CO₂ energy storage system for coal-fired power generation[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251024.
| 储能部件 | 示意图 | EF,k | EP,k | ED,k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩机 | 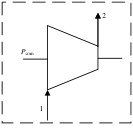 | Wcom | E2,C-E1,C | EF,C-EP,C |
| 透平 | 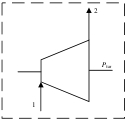 | E1,T-E2,T | Wtur | EF,T-EP,T |
| 换热器 | 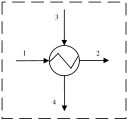 | E3,HE-E4,HE | E2,HE-E1,HE | EF,HE-EP,HE |
| 储能汽轮机 | 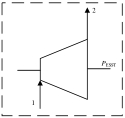 | E1,ESST-E2,ESST | WESST | EF,ESST-EP,ESST |
表1 各部件㶲分析模型
Table 1 Exergy analysis models of each component
| 储能部件 | 示意图 | EF,k | EP,k | ED,k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩机 |  | Wcom | E2,C-E1,C | EF,C-EP,C |
| 透平 |  | E1,T-E2,T | Wtur | EF,T-EP,T |
| 换热器 |  | E3,HE-E4,HE | E2,HE-E1,HE | EF,HE-EP,HE |
| 储能汽轮机 |  | E1,ESST-E2,ESST | WESST | EF,ESST-EP,ESST |
| 参数 | 设计值 | 仿真值 | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 发电机功率/MW | 350 | 355 | 1.43 |
| 汽轮机总进汽量/(kg/s) | 276.17 | 286.02 | 3.56 |
| 主蒸汽温度/℃ | 566 | 566 | 0 |
| 主蒸汽压力/MPa | 24.2 | 23.1 | 4.5 |
| 再热蒸汽温度/℃ | 566 | 566 | 0 |
| 再热蒸汽压力/MPa | 3.79 | 3.92 | 3.43 |
| 给水流量/(kg/s) | 276.17 | 286.02 | 3.56 |
| 给水温度/℃ | 276.6 | 279.91 | 1.19 |
表2 燃煤机组主要参数验证
Table 2 Verification of main parameters of coal-fired units
| 参数 | 设计值 | 仿真值 | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 发电机功率/MW | 350 | 355 | 1.43 |
| 汽轮机总进汽量/(kg/s) | 276.17 | 286.02 | 3.56 |
| 主蒸汽温度/℃ | 566 | 566 | 0 |
| 主蒸汽压力/MPa | 24.2 | 23.1 | 4.5 |
| 再热蒸汽温度/℃ | 566 | 566 | 0 |
| 再热蒸汽压力/MPa | 3.79 | 3.92 | 3.43 |
| 给水流量/(kg/s) | 276.17 | 286.02 | 3.56 |
| 给水温度/℃ | 276.6 | 279.91 | 1.19 |
| 参数 | 数值[ |
|---|---|
| 压缩机入口流量/(kg/s) | 100 |
| 压缩机入口温度/℃ | 35 |
| 压缩机入口压力/MPa | 7.8 |
| 透平入口温度/℃ | 410 |
| 透平入口压力/MPa | 29 |
表3 压缩S-CO2储能循环模型验证输入
Table 3 Input for model validation of compressed S-CO2 energy storage cycle
| 参数 | 数值[ |
|---|---|
| 压缩机入口流量/(kg/s) | 100 |
| 压缩机入口温度/℃ | 35 |
| 压缩机入口压力/MPa | 7.8 |
| 透平入口温度/℃ | 410 |
| 透平入口压力/MPa | 29 |
| 参数 | 仿真值 | 文献值[ | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩机功耗/MW | 5.13 | 4.93 | 4.1 |
| 压缩机出口温度/℃ | 116.128 | 116.2 | 0.1 |
| 透平功率/MW | 13.704 | 13.57 | 1.0 |
| 透平出口温度/℃ | 266.594 | 266.6 | 0.002 |
表4 压缩S-CO2储能循环模型验证结果
Table 4 Model validation results of the compressed S-CO2 energy storage cycle
| 参数 | 仿真值 | 文献值[ | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩机功耗/MW | 5.13 | 4.93 | 4.1 |
| 压缩机出口温度/℃ | 116.128 | 116.2 | 0.1 |
| 透平功率/MW | 13.704 | 13.57 | 1.0 |
| 透平出口温度/℃ | 266.594 | 266.6 | 0.002 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| CO2流量/(kg/s) | 50 |
| 压缩机组入口压力/MPa | 8 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 90 |
| 透平效率/% | 90 |
| 低压储气室体积/m3 | 220 |
| 高压储气室体积/m3 | 440 |
| 储热罐温度/℃ | 62 |
| 环境温度/℃ | 25 |
| 储能时间/min | 60 |
| 释能时间/min | 60 |
表5 压缩S-CO2储能循环运行主要参数
Table 5 Main operating parameters of the compressed S-CO2 energy storage cycle
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| CO2流量/(kg/s) | 50 |
| 压缩机组入口压力/MPa | 8 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 90 |
| 透平效率/% | 90 |
| 低压储气室体积/m3 | 220 |
| 高压储气室体积/m3 | 440 |
| 储热罐温度/℃ | 62 |
| 环境温度/℃ | 25 |
| 储能时间/min | 60 |
| 释能时间/min | 60 |
| 参数 | 设计值 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩机入口压力/MPa | 8 | 7.5-8 |
| 压缩机入口流量/(kg/s) | 50 | 50-100 |
| 2#压缩机入口压/MPa | 18.5 | 10-20 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 90 | 70-90 |
表6 压缩S-CO2储能循环主要参数变化范围
Table 6 Range of main parameter variations in the compressed S-CO2 energy storage cycle
| 参数 | 设计值 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩机入口压力/MPa | 8 | 7.5-8 |
| 压缩机入口流量/(kg/s) | 50 | 50-100 |
| 2#压缩机入口压/MPa | 18.5 | 10-20 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 90 | 70-90 |
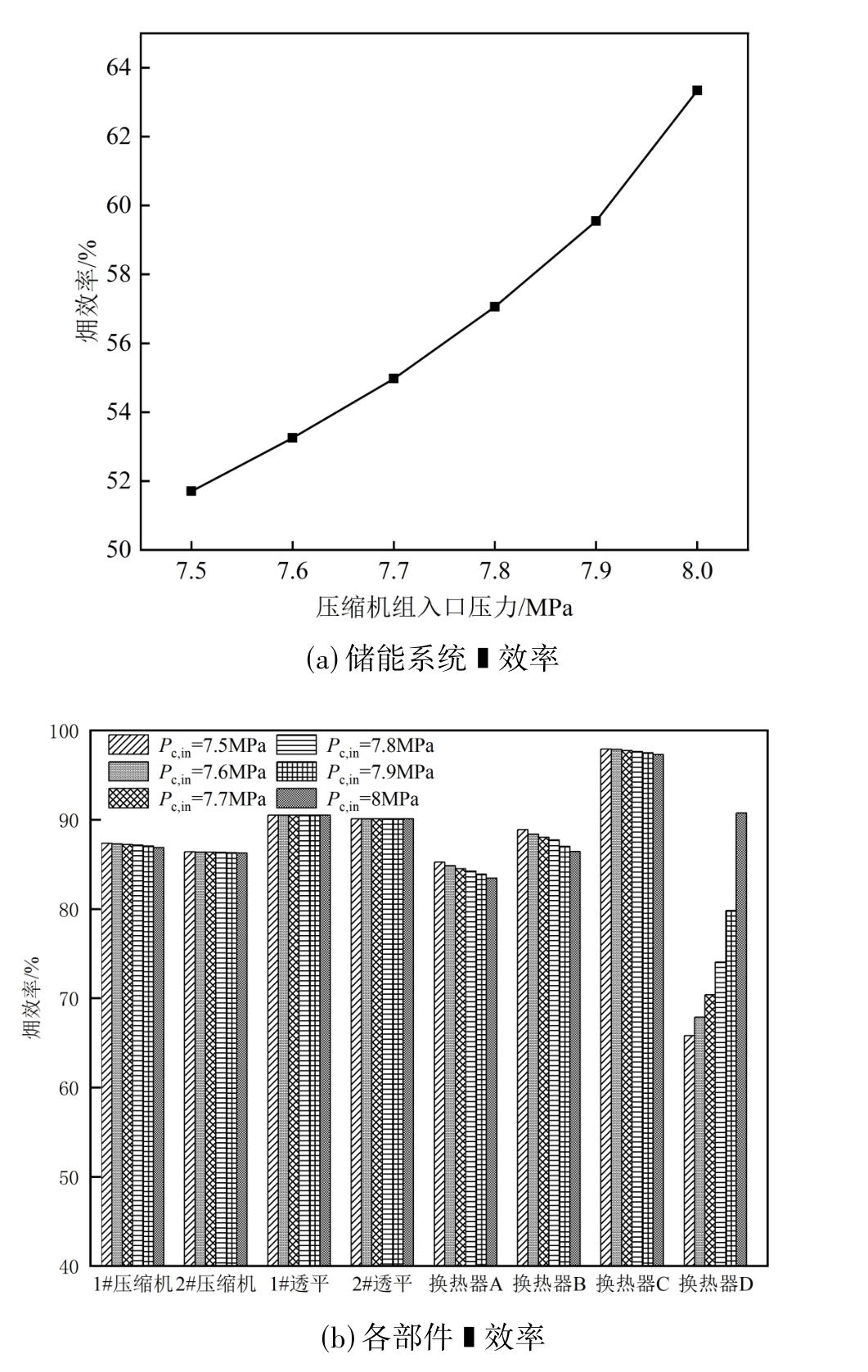
图11 压缩机组入口压力对储能系统及各部件㶲效率影响
Fig. 11 The influence of the inlet pressure of the compressor unit on the exergy efficiency of the energy storage system and its components
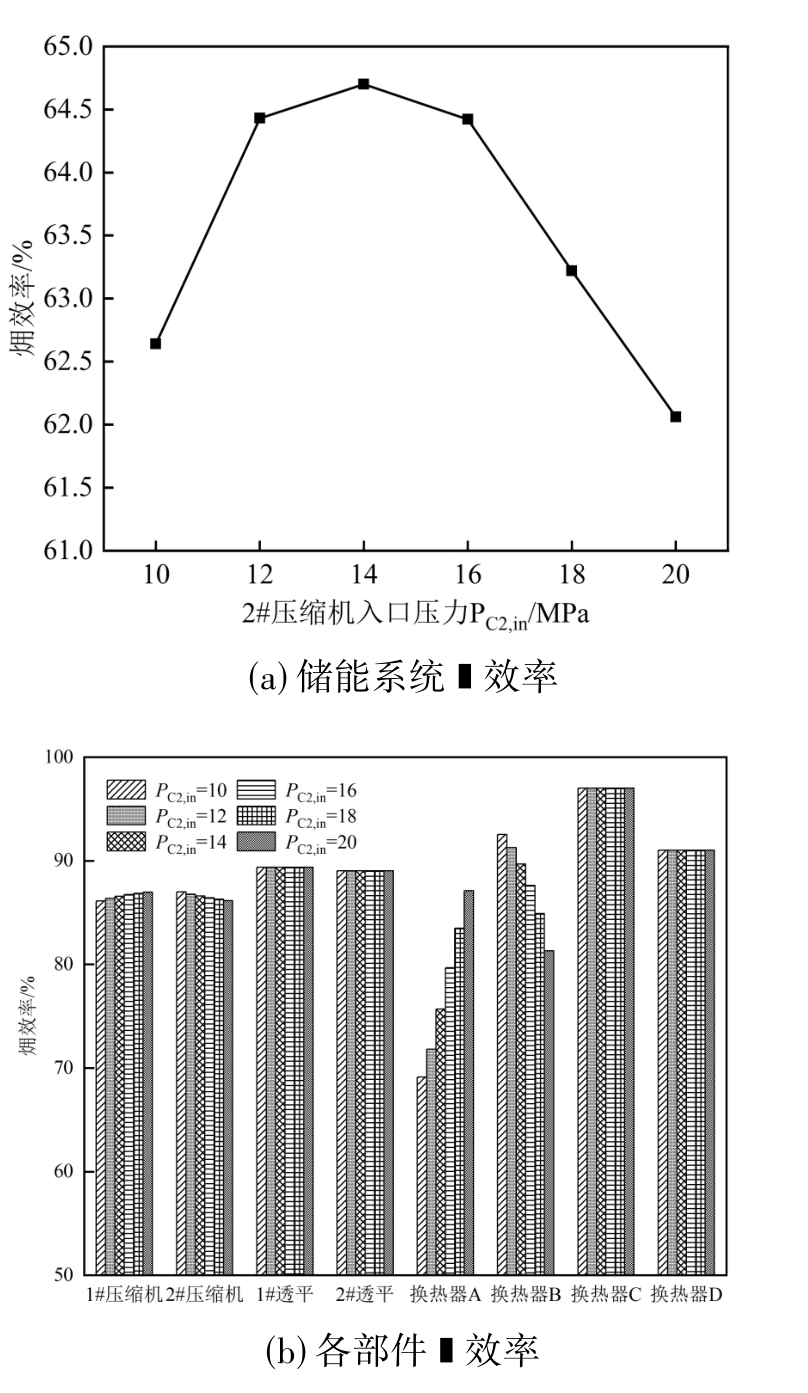
图13 2#压缩机入口压力对储能系统及各部件㶲效率影响
Fig. 13 The influence of the inlet pressure of compressor No. 2 on the exergy efficiency of the energy storage system and its components
| 储能方式 | 往返效率/% |
|---|---|
| 抽水蓄能 | 70-87 |
| 压缩空气储能 | 42-75 |
| 熔盐储能 | 39.2-83.5 |
| 本文结构 | 61-68.12 |
表7 与传统储能方式对比
Table 7 Comparison with traditional energy storage methods
| 储能方式 | 往返效率/% |
|---|---|
| 抽水蓄能 | 70-87 |
| 压缩空气储能 | 42-75 |
| 熔盐储能 | 39.2-83.5 |
| 本文结构 | 61-68.12 |
| [1] | 申融容, 玄婉玥, 张健, 等. 面向电源侧灵活性提升的热电解耦技术综述[J]. 中国能源, 2021, 43(5): 51-59. |
| Shen R R, Xuan W Y, Zhang J, et al. Summary of thermo-electrolytic coupling technology for improving power supply side flexibility[J]. Energy of China, 2021, 43(5): 51-59. | |
| [2] | 刘纹佳, 杜如雪, 王思齐, 等. 电-热转换功能型相变储热材料的研究进展及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3185-3196. |
| Liu W J, Du R X, Wang S Q, et al. Research status and application of functional phase change materials for electro-thermal conversion in thermal energy storage[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3185-3196. | |
| [3] | 严晓生, 王小东, 韩旭, 等. 液态压缩二氧化碳储能与火电机组耦合方案研究[J]. 热力发电, 2023, 52(2): 90-100. |
| Yan X S, Wang X D, Han X, et al. Study on coupling scheme of liquid compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system and thermal power unit[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2023, 52(2): 90-100. | |
| [4] | Fütterer B, Lausterer G K, Leibbrandt S R. Improved unit dynamic response using condensate stoppage[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1992, 25(1): 129-134. |
| [5] | Lausterer G K. Improved maneuverability of power plants for better grid stability[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1997, 30(17): 589-594. |
| [6] | 刘吉臻, 王耀函, 曾德良, 等. 基于凝结水节流的火电机组AGC控制优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(23): 6918-6925. |
| Liu J Z, Wang Y H, Zeng D L, et al. An AGC control method of thermal unit based on condensate throttling[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(23): 6918-6925. | |
| [7] | 李文杰, 丁宁, 陈学奇, 等. 高加旁路提升超(超)临界机组一次调频能力的研究与应用[J]. 浙江电力, 2018, 37(9): 45-49. |
| Li W J, Ding N, Chen X Q, et al. Research and application of primary frequency modulation improvement of ultra-supercritical unit through high-pressure heater bypass[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2018, 37(9): 45-49. | |
| [8] | Wang W, Jing S T, Sun Y, et al. Combined heat and power control considering thermal inertia of district heating network for flexible electric power regulation[J]. Energy, 2019, 169: 988-999. |
| [9] | 邓拓宇, 田亮, 刘吉臻. 供热机组锅炉储能与热网储能空间时间多尺度分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(2): 599-606. |
| Deng T Y, Tian L, Liu J Z. Spatial and temporal multiscale analysis on energy storage in heat supply units' boiler and heat supply nets[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(2): 599-606. | |
| [10] | Zhao Y L, Wang C Y, Liu M, et al. Improving operational flexibility by regulating extraction steam of high-pressure heaters on a 660 MW supercritical coal-fired power plant: a dynamic simulation[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 212: 1295-1309. |
| [11] | Zhou Y L, Wang D. An improved coordinated control technology for coal-fired boiler-turbine plant based on flexible steam extraction system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 1047-1060. |
| [12] | Liu M, Zhang X W, Yang K X, et al. Comparison and sensitivity analysis of the efficiency enhancements of coal-fired power plants integrated with supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle and steam Rankine cycle[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 198: 111918. |
| [13] | 李建林, 袁晓冬, 郁正纲, 等. 利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(8): 15-24. |
| Li J L, Yuan X D, Yu Z G, et al. Comments on power quality enhancement research for power grid by energy storage system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(8): 15-24. | |
| [14] | 王辉, 李峻, 祝培旺, 等. 应用于火电机组深度调峰的百兆瓦级熔盐储能技术[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(5): 1760-1767. |
| Wang H, Li J, Zhu P W, et al. Hundred-megawatt molten salt heat storage system for deep peak shaving of thermal power plant[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(5): 1760-1767. | |
| [15] | 梁志宏, 刘吉臻, 洪烽, 等. 电力级大功率飞轮储能系统耦合火电机组调频技术研究及工程应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44(21): 8518-8531. |
| Liang Z H, Liu J Z, Hong F, et al. Research and engineering application of frequency modulation technology of power-level high-power flywheel energy storage system coupled with thermal power unit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44(21): 8518-8531. | |
| [16] | Sun Y, Wang L, Xu C, et al. Enhancing the operational flexibility of thermal power plants by coupling high-temperature power-to-gas[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 263: 114608. |
| [17] | Avgerinou H, Braimakis K, Roumpedakis T C, et al. Thermodynamic modeling and techno-economic assessment of hydrogen fuelled diabatic compressed air energy storage configurations[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2025, 278: 127325. |
| [18] | Li T Y, Chen L J, Liu H C, et al. Configuration optimization for advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage considering thermal coupling characteristics[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2025, 131: 117249. |
| [19] | Jiang Z R, Zhang S S, Hu Z B, et al. Analysis of compressed air energy storage system coupled with thermal storage and photothermal[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2025, 3011(1): 012008. |
| [20] | 姜文, 黄乐清, 张松航, 等. 压缩空气储能地下储气库地质评价研究进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2025, 53(8): 62-75. |
| Jiang W, Huang L Q, Zhang S H, et al. Advances in research on geological evaluation of compressed air energy storage in underground gas storage facilities[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2025, 53(8): 62-75. | |
| [21] | 徐进良, 刘超, 孙恩慧, 等. 超临界二氧化碳动力循环研究进展及展望[J]. 热力发电, 2020, 49(10): 1-10. |
| Xu J L, Liu C, Sun E H, et al. Review and perspective of supercritical carbon dioxide power cycles[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2020, 49(10): 1-10. | |
| [22] | Morandin M, Mercangöz M, Hemrle J, et al. Thermoeconomic design optimization of a thermo-electric energy storage system based on transcritical CO2 cycles[J]. Energy, 2013, 58: 571-587. |
| [23] | Budt M, Wolf D, Span R, et al. A review on compressed air energy storage: Basic principles, past milestones and recent developments[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 170: 250-268. |
| [24] | Yang D L, Tang G H, Luo K H, et al. Integration and conversion of supercritical carbon dioxide coal-fired power cycle and high-efficiency energy storage cycle: Feasibility analysis based on a three-step strategy[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 269: 116074. |
| [25] | Yin L, Ju Y L, Lin Q G. An integrated solution of energy storage and CO2 reduction: Trans-critical CO2 energy storage system combining carbon capture with LNG cold energy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 482: 144228. |
| [26] | 李源, 赵明智, 徐玉杰, 等. 液态二氧化碳储能系统变工况运行特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2761-2771. |
| Li Y, Zhao M Z, Xu Y J, et al. Variable-operating-condition operational characteristics of liquid carbon dioxide energy storage systems[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(7): 2761-2771. | |
| [27] | He Q, Liu H, Hao Y P, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of a novel supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system through advanced exergy analysis[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 127: 835-849. |
| [28] | Xu W P, Zhao P, Ma N, et al. Design and performance analysis of a combined cooling, heating and power system: Integration of an isobaric compressed CO2 energy storage and heat pump cycle[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 91: 112146. |
| [29] | Liu Y F, Wang Y J, Zhang Y P, et al. Design and performance analysis of compressed CO2 energy storage of a solar power tower generation system based on the S-CO2 Brayton cycle[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 249: 114856. |
| [30] | He Z, Xu X X, Hao Y Y, et al. Investigation on dynamic characteristics of a novel isochoric-isobaric discharging compressed CO2 energy storage system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2025, 343: 120149. |
| [31] | Su W, Jiao K Q, Jin X, et al. Performance analysis of a novel solar-assisted liquid CO2 energy storage system with flexible cooling, heating and power outputs: Energy, exergy, economic, and environmental aspects[J]. Energy, 2025, 324: 136010. |
| [32] | 郝佳豪, 郑平洋, 越云凯, 等. 一种耦合光热的超临界二氧化碳储能发电系统性能分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45(14): 5369-5381. |
| Hao J H, Zheng P Y, Yue Y K, et al. Performance analysis of a supercritical carbon dioxide energy storageand power generation system with integrated photothermal unit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45(14): 5369-5381. | |
| [33] | He T Y, Cao Y, Si F Q, Thermodynamic analysis and optimization of a compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system coupled with a combined heating and power unit[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2023, 277: 116618. |
| [34] | Zheng Q Y, Zhang Z T, Yang J L, et al. Thermodynamic and economic analysis of compressed carbon dioxide energy storage systems based on different storage modes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 243: 122669. |
| [35] | Wang C Y, Liu M, Li B X, et al. Thermodynamic analysis on the transient cycling of coal-fired power plants: Simulation study of a 660 MW supercritical unit[J]. Energy, 2017, 122: 505-527. |
| [36] | Xu C, Zhang Q, Yang Z P, et al. An improved supercritical coal-fired power generation system incorporating a supplementary supercritical CO2 cycle[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 1319-1329. |
| [37] | Rehman S, Al-Hadhrami L M, Alam M M. Pumped hydro energy storage system: a technological review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 44: 586-598. |
| [38] | Pérez-Díaz J I, Chazarra M, García-González J, et al. Trends and challenges in the operation of pumped-storage hydropower plants[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 44: 767-784. |
| [39] | Kong Y G, Kong Z G, Liu Z Q, et al. Pumped storage power stations in China: The past, the present, and the future[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 71: 720-731. |
| [40] | Jankowski M, Pałac A, Sornek K, et al. Status and development perspectives of the compressed air energy storage (CAES) technologies: a literature review[J]. Energies, 2024, 17(9): 2064. |
| [41] | Miao X X, Zhang K, Wang J G, et al. Coupled thermodynamic and thermomechanical modelling for compressed air energy storage in underground mine tunnels[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2024, 176: 105717. |
| [42] | Rabi A M, Radulovic J, Buick J M. Comprehensive review of compressed air energy storage (CAES) technologies[J]. Thermo, 2023, 3(1): 104-126. |
| [43] | Zhu C, Zhang G M, Zhu K Y, et al. A molten salt energy storage integrated with combined heat and power system: Scheme design and performance analysis[J]. Energy, 2024, 313: 133755. |
| [44] | Ladkany S, Culbreth W, Loyd N. Molten salts and applications III: worldwide molten salt technology developments in energy production and storage[J]. Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, 2018, 12(11): 533-544. |
| [45] | Xu J, Liu W H, Wang Z P, et al. Comparative investigation on the thermodynamic performance of coal-fired power plant integrating with the molten salt thermal storage system[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 89: 111738. |
| [1] | 杨语晴, 李银龙, 晏刚. 采用低GWP制冷剂的级联加热自复叠高温热泵循环热力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 43-53. |
| [2] | 肖鑫, 杨耿, 王云峰. 基于TRNSYS的太阳能梯级蓄热热泵系统模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 393-400. |
| [3] | 周有苗, 刘晔, 余锋, 罗小钰, 王斌辉. 双源压缩-喷射复合热泵系统构建及特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 36-42. |
| [4] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [5] | 刘辉, 王佳, 赵晶, 李传常, 吕又付. 大容量储能电池产热行为特性及容量衰减研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4903-4912. |
| [6] | 刘璐, 王文玥, 王腾, 王太, 董新宇, 汤建成, 王少恒. 基于双混合工质深冷的氢液化工艺优化与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4933-4943. |
| [7] | 董泽明, 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰, 赵攀. 含余热回收的超临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3477-3486. |
| [8] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [9] | 吴罗长, 杨泽宇, 颜建国, 朱旭涛, 陈阳, 王子辰. 微小方形通道内近超临界压力二氧化碳流动换热特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1583-1594. |
| [10] | 产文, 余万, 王岗, 苏华山, 黄芬霞, 胡涛. 改进回热布局的Allam循环热力、经济性能分析和双目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1680-1692. |
| [11] | 王光磊, 刘晓玲, 徐震, 李琳. 面向压缩空气储能的气-水直接接触换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1595-1603. |
| [12] | 翟祥瑞, 张伟, 张倩倩, 曲玖哲, 杨绪飞, 邓雅军, 宇波. 基于外场扰动的固液相变储能主动强化换热技术[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1432-1446. |
| [13] | 伏遥, 邵应娟, 钟文琪. TiO2掺杂钙基材料加压碳酸化循环储热性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1180-1190. |
| [14] | 宫政, 高秀鲁, 赵玲, 胡冬冬. 超临界CO2发泡PBAT/PLA复合材料及其形状记忆性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 888-896. |
| [15] | 翟庆伟, 林锦辉, 李彦锋, 韩东旭, 吴小华, 王鹏, 陈宇杰, 宇波. 新型泵-热协同增压液氢加氢站系统㶲分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5390-5401. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号