化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (8): 3758-3767.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220199
韩双( ), 张楠, 王慧, 张璇, 杨金栾, 张蔓琳, 张志超(
), 张楠, 王慧, 张璇, 杨金栾, 张蔓琳, 张志超( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-11
修回日期:2022-04-23
出版日期:2022-08-05
发布日期:2022-09-06
通讯作者:
张志超
作者简介:韩双(1983—),女,博士,副教授,unihanshuang@syuct.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuang HAN( ), Nan ZHANG, Hui WANG, Xuan ZHANG, Jinluan YANG, Manlin ZHANG, Zhichao ZHANG(
), Nan ZHANG, Hui WANG, Xuan ZHANG, Jinluan YANG, Manlin ZHANG, Zhichao ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-02-11
Revised:2022-04-23
Online:2022-08-05
Published:2022-09-06
Contact:
Zhichao ZHANG
摘要:
金霉素(CTC)的滥用给自然环境和人类健康带来了严重的不良影响。建立了一种简便、经济、高效的CTC分子印迹电化学传感器。该传感器的分子印迹膜由邻苯二胺在还原型氧化石墨烯-聚乙烯亚胺复合物(RGO-PEI)修饰的玻碳电极上电聚合而成。采用扫描电子显微镜、红外吸收光谱和紫外可见吸收光谱对RGO-PEI复合材料进行了表征。RGO-PEI复合材料的高比表面积和丰富的氨基基团提高了该传感器检测的灵敏度和稳定性。在优化条件下,该传感器对CTC浓度响应的线性范围为(5.0 × 10-7)~(1.0 × 10-4)mol/L,检测限为 1.67 × 10-7 mol/L (信噪比,S/N=3)。此外,该传感器对卡那霉素、土霉素和盐酸多西环素等干扰物质的响应很小,可用于实际样品中CTC的检测,回收率为102.7% ~ 104.7%,是一种简单、高效的电化学方法。
中图分类号:
韩双, 张楠, 王慧, 张璇, 杨金栾, 张蔓琳, 张志超. 金霉素分子印迹电化学传感器的制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3758-3767.
Shuang HAN, Nan ZHANG, Hui WANG, Xuan ZHANG, Jinluan YANG, Manlin ZHANG, Zhichao ZHANG. Preparation and application of chlortetracycline electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinting technique[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3758-3767.
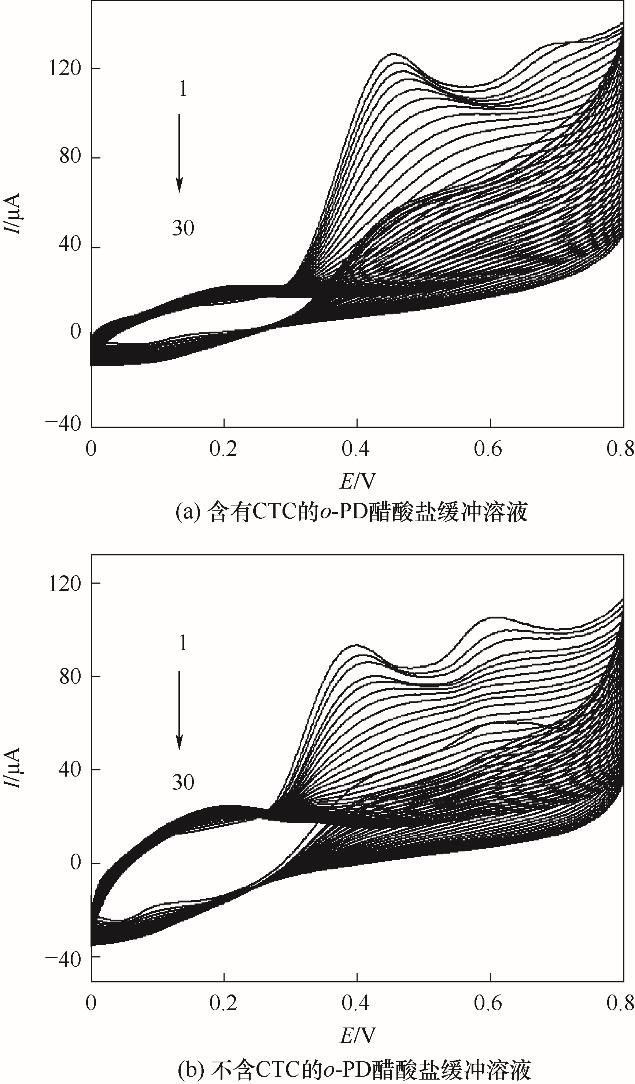
图5 5.0 mmol/L o-PD在GCE/RGO-PEI修饰电极表面电聚合的循环伏安图
Fig.5 Cyclic voltammograms for the electropolymerization of 5.0 mmol/L o-PD on GCE/RGO-PEI in the presence (a) and in the absence (b) of CTC in pH4.8 acetate buffer (scan rate: 0.050 V/s)

图6 不同电极在5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/0.1 mol/L KCl中的循环伏安图a—裸GCE; b—GCE/RGO-PEI; c—MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD; d—洗脱之后的MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD; e—重新吸附CTC的MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD
Fig.6 Cyclic voltammograms of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/0.1 mol/L KCl on the bare GCE (a), GCE/RGO-PEI (b), GCE/RGO-PEI after electropolymerization (c), MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD after the removal of CTC (d), MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD after incubation of CTC (e)

图7 不同扫描速率下MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD 在5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/0.1 mol/L KCl中的循环伏安图
Fig.7 Cyclic voltammograms of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/0.1 mol/L KCl on the MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD at different scan rates
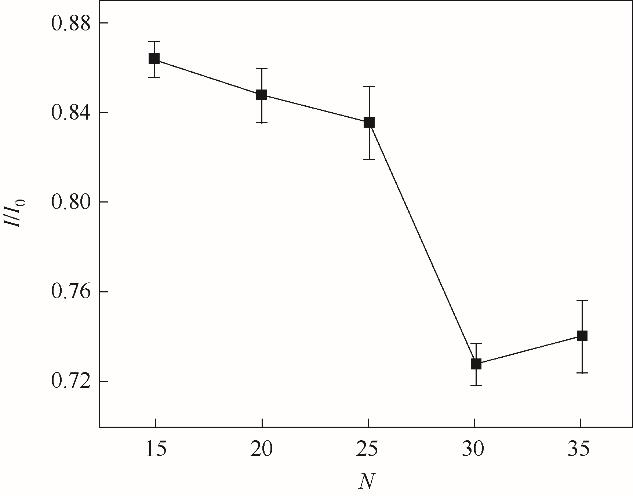
图9 电聚合圈数的优化
Fig.9 Effect of the electropolymerization cycles on the peak current of the CV response in the presence of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/ 0.1 mol/L KCl (I0 is the current of the MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD after elution; I is the current of the MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD after incubation of CTC)
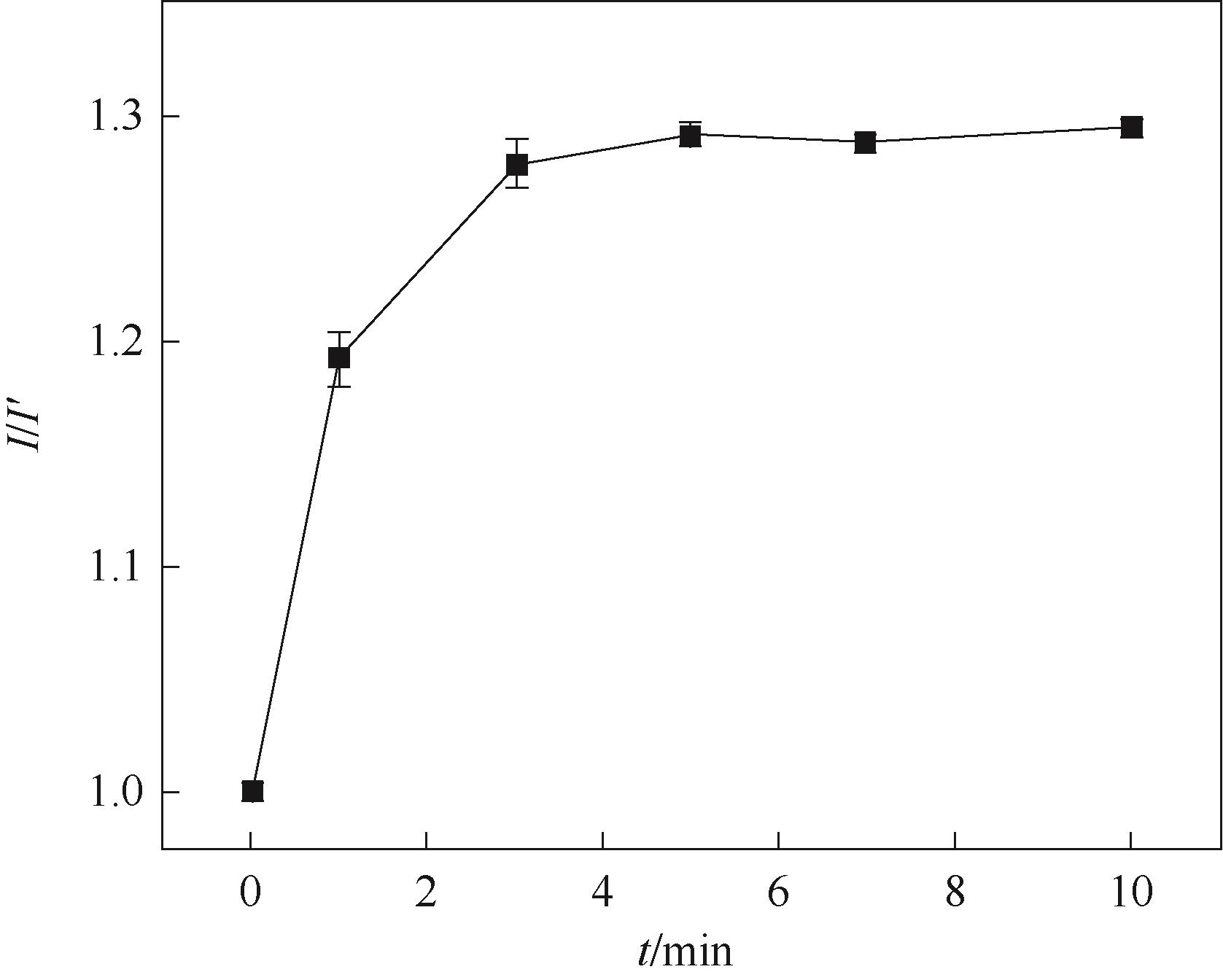
图11 洗脱时间的优化
Fig.11 Effect of elution time on the peak current of CV response in the presence of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/ 0.1 mol/L KCl (I′ is the current of the GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD after electropolymerization)
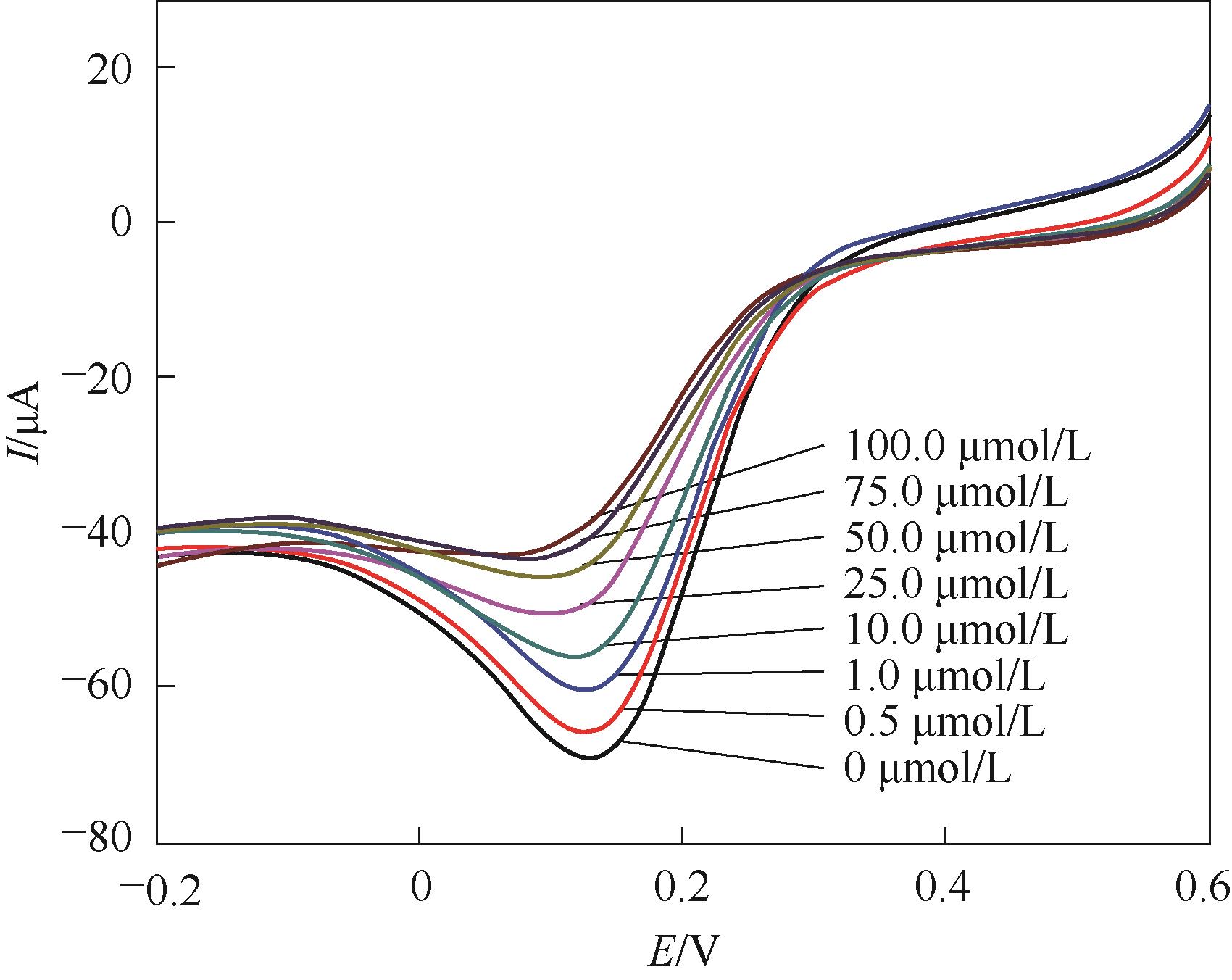
图13 MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD在不同浓度CTC标准溶液中的线性扫描伏安图
Fig.13 Linear sweep voltammograms of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/0.1 mol/L KCl at 0.050 V/s for CTC-free MIP films after rebinding CTC at different concentrations
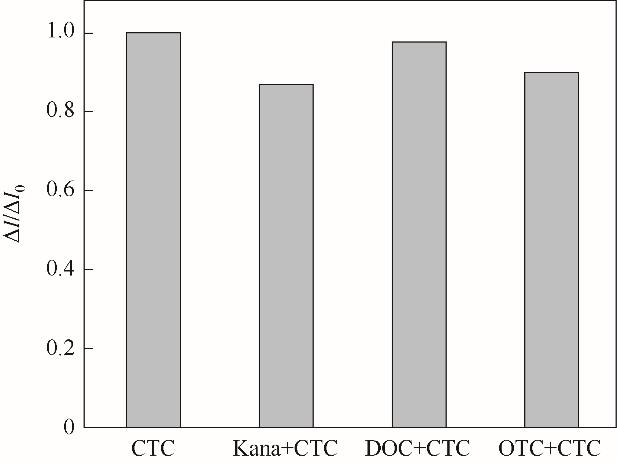
图15 MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD对其他抗生素的抗干扰能力检验
Fig.15 The the current change of MIP GCE/RGO-PEI/PPD in the presence of 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/ 0.1 mol/L KCl after incubation in 25.0 μmol/L CTC, 25.0 μmol/L CTC +100.0 μmol/L kanamycin, 25.0 μmol/L CTC + 100.0 μmol/L DOC, 25.0 μmol/L CTC + 100.0 μmol/L OTC(ΔI0 = I0 -ICTC; ΔI = I0 -ICTC+others)
| 样品 | 加入量/(μmol/L) | 测得量/(μmol/L) | 回收率/% | 平均回收率/% | RSD(n=3)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.0 | 10.51, 10.71, 10.47 | 105.1, 107.1, 104.7 | 104.7 | 1.22 |
| 2 | 50.0 | 52.61, 51.41, 50.05 | 105.2, 102.8, 100.1 | 102.7 | 2.49 |
表1 湖水样品中CTC的回收实验
Table 1 Recoveries for CTC detection in lake samples
| 样品 | 加入量/(μmol/L) | 测得量/(μmol/L) | 回收率/% | 平均回收率/% | RSD(n=3)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.0 | 10.51, 10.71, 10.47 | 105.1, 107.1, 104.7 | 104.7 | 1.22 |
| 2 | 50.0 | 52.61, 51.41, 50.05 | 105.2, 102.8, 100.1 | 102.7 | 2.49 |
| 1 | Qiao M, Ying G G, Singer A C, et al. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment[J]. Environment International, 2018, 110: 160-172. |
| 2 | Pan L X, Feng X X, Cao M, et al. Determination and distribution of pesticides and antibiotics in agricultural soils from northern China[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(28): 15686-15693. |
| 3 | Cai C Y, Li J Y, Wu D, et al. Spatial distribution, emission source and health risk of parent PAHs and derivatives in surface soils from the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 178: 301-308. |
| 4 | Lv J, Zhang L, Chen Y Y, et al. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in raw, finished, and drinking water from seven large river basins in China[J]. Journal of Water and Health, 2019, 17(3): 477-489. |
| 5 | Han S, Li B Q, Song Z, et al. A kanamycin sensor based on an electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine film on a single-walled carbon nanohorn modified glassy carbon electrode[J]. Analyst, 2016, 142(1): 218-223. |
| 6 | Han S, Zhang X, Sun H D, et al. Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of chloramphenicol and doxycycline using a glassy carbon electrode modified with single-walled carbon nanohorns[J]. Electroanalysis, 2022, 34(4): 735-742. |
| 7 | Pulicharla R, Brar S K, Rouissi T, et al. Degradation of chlortetracycline in wastewater sludge by ultrasonication, Fenton oxidation, and Ferro-sonication[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 34: 332-342. |
| 8 | Meng L, Lan C W, Liu Z H, et al. A novel ratiometric fluorescence probe for highly sensitive and specific detection of chlorotetracycline among tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1089: 144-151. |
| 9 | Zhou Y T, Niu L L, Zhu S Y, et al. Occurrence, abundance, and distribution of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in agricultural soils across China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 1977-1983. |
| 10 | Pulicharla R, Das R K, Brar S K, et al. Toxicity of chlortetracycline and its metal complexes to model microorganisms in wastewater sludge[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532: 669-675. |
| 11 | Han J, Jiang D, Chen T S, et al. Simultaneous determination of olaquindox, oxytetracycline and chlorotetracycline in feeds by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and fluorescence detection adopting online synchronous derivation and separation[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2020, 1152: 122253. |
| 12 | Weng R, Sun L S, Jiang L P, et al. Electrospun graphene oxide-doped nanofiber-based solid phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of tetracycline antibiotic residues in food samples[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(7): 1594-1603. |
| 13 | Du F Y, Zheng X, Sun L, et al. Development and validation of polymerized high internal phase emulsion monoliths coupled with HPLC and fluorescence detection for the determination of trace tetracycline antibiotics in environmental water samples[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2015, 38(21): 3774-3780. |
| 14 | Valverde R S, Pérez I S, Franceschelli F, et al. Determination of photoirradiated tetracyclines in water by high-performance liquid chromatography with chemiluminescence detection based reaction of Rhodamine B with cerium (Ⅳ)[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, 1167(1): 85-94. |
| 15 | Gajda A, Antczak M, Mitrowska K, et al. Development, validation and application to real samples of a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of tetracyclines in beeswax[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2018, 41(20): 3821-3829. |
| 16 | Tong L, Liu H, Xie C, et al. Quantitative analysis of antibiotics in aquifer sediments by liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1452: 58-66. |
| 17 | Jiao Z, Zhang S L, Chen H W. Determination of tetracycline antibiotics in fatty food samples by selective pressurized liquid extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2015, 38(1): 115-120. |
| 18 | Pamreddy A, Hidalgo M, Havel J, et al. Determination of antibiotics (tetracyclines and sulfonamides) in biosolids by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1298: 68-75. |
| 19 | Chang X S, Meyer M T, Liu X Y, et al. Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(5): 1444-1450. |
| 20 | Patyra E, Kowalczyk E, Grelik A, et al. Screening method for the determination of tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones in animal drinking water by liquid chromatography with diode array detector[J]. Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 2015, 18(2): 283-289. |
| 21 | Patyra E, Kowalczyk E, Kwiatek K. Screening method for the determination of selected tetracyclines in water by liquid chromatography with diode array detector[J]. Bulletin of the Veterinary Institute in Pulawy, 2014, 58(1): 65-70. |
| 22 | Karageorgou E, Armeni M, Moschou I, et al. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive extraction for the high pressure liquid chromatographic determination of tetracyclines residues in milk with diode array detection[J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 150: 328-334. |
| 23 | Patyra E, Kowalczyk E, Kwiatek K. Development and validation method for the determination of selected tetracyclines in animal medicated feedingstuffs with the use of micellar liquid chromatography[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 405(21): 6799-6806. |
| 24 | Loetanantawong B, Suracheep C, Somasundrum M, et al. Electrocatalytic tetracycline oxidation at a mixed-valent ruthenium oxide: ruthenium cyanide-modified glassy carbon electrode and determination of tetracyclines by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 76(8): 2266-2272. |
| 25 | Wu X Y, Xu Z Q, Huang Z, et al. Large volume sample stacking of cationic tetracycline antibiotics toward 10 ppb level analysis by capillary electrophoresis with UV detection[J]. Electrophoresis, 2016, 37(22): 2963-2969. |
| 26 | Guo Y X, Meng L, Zhang Y H, et al. Sensitive determination of four tetracycline antibiotics in pig plasma by field-amplified sample stacking open-tubular capillary electrochromatography with dimethylethanolamine aminated polychloromethyl styrene nano-latex coated capillary column[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2013, 942/943: 151-157. |
| 27 | Wangfuengkanagul N, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O. A flow injection method for the analysis of tetracycline antibiotics in pharmaceutical formulations using electrochemical detection at anodized boron-doped diamond thin film electrode[J]. Talanta, 2004, 64(5): 1183-1188. |
| 28 | Si X J, Wang H L, Wu T H, et al. Novel methods for the rapid detection of trace tetracyclines based on the fluorescence behaviours of Maillard reaction fluorescent nanoparticles[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(71): 43256-43261. |
| 29 | Gan T, Lv Z, Liu N, et al. Electrochemical detection method for chlorotetracycline based on enhancement of yolk–shell structured carbon sphere@MnO2 [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(4): H200-H205. |
| 30 | Ni Y N, Li S Z, Kokot S. Simultaneous voltammetric analysis of tetracycline antibiotics in foods[J]. Food Chemistry, 2011, 124(3): 1157-1163. |
| 31 | Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li J H, et al. Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(30): 2100543. |
| 32 | Tarannum N, Khatoon S, Dzantiev B B. Perspective and application of molecular imprinting approach for antibiotic detection in food and environmental samples: a critical review[J]. Food Control, 2020, 118: 107381. |
| 33 | Li S P, Guan H M, Xu G B, et al. Progress in molecular imprinting electrochemiluminescence analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(2): 294-299. |
| 34 | Li W, Zheng Y P, Zhang T W, et al. A surface plasmon resonance-based optical fiber probe fabricated with electropolymerized molecular imprinting film for melamine detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 828. |
| 35 | Tlili A, Attia G, Khaoulani S, et al. Contribution to the understanding of the interaction between a polydopamine molecular imprint and a protein model: ionic strength and pH effect investigation[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(2): 619. |
| 36 | Tang X S, Zhang D, Zhou T S, et al. Fe3O4@Au sphere molecular imprinting with self-assembled monolayer for the recognition of parathion-methyl[J]. Analytical Methods, 2011, 3(10): 2313. |
| 37 | Yu Y J, Zhang Q, Buscaglia J, et al. Quantitative real-time detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) from pancreatic cyst fluid using 3-D surface molecular imprinting[J]. The Analyst, 2016, 141(14): 4424-4431. |
| 38 | Yin D X, Ulbricht M. Protein-selective adsorbers by molecular imprinting via a novel two-step surface grafting method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(25): 3209. |
| 39 | Zhao M, Chen X J, Zhang H T, et al. Well-defined hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for efficient molecular recognition in real biological samples by facile RAFT coupling chemistry[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15(5): 1663-1675. |
| 40 | Blanco-López M C, Lobo-Castañón M J, Miranda-Ordieres A J, et al. Voltammetric sensor for vanillylmandelic acid based on molecularly imprinted polymer-modified electrodes[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2003, 18(4): 353-362. |
| 41 | Li H D, Guan H M, Dai H, et al. An amperometric sensor for the determination of benzophenone in food packaging materials based on the electropolymerized molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine film[J]. Talanta, 2012, 99: 811-815. |
| 42 | Wu S X, He Q Y, Tan C L, et al. Graphene-based electrochemical sensors[J]. Small, 2013, 9(8): 1160-1172. |
| 43 | Chen D, Feng H B, Li J H. Graphene oxide: preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(11): 6027-6053. |
| 44 | Geim A K, Novoselov K S. The rise of graphene[J]. Nature Materials, 2007, 6(3): 183-191. |
| 45 | Lawal A T. Graphene-based nano composites and their applications. A review[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2019, 141: 111384. |
| 46 | Huang X, Qi X Y, Boey F, et al. Graphene-based composites[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(2): 666-686. |
| 47 | Atar N, Yola M L, Eren T. Sensitive determination of citrinin based on molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 362(1): 315-322. |
| 48 | Yola M L, Eren T, Atar N. A sensitive molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide: application to selective determination of tyrosine in milk[J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 2015, 210: 149-157. |
| 49 | Zhou X H, Chen Z X, Yan D H, et al. Deposition of Fe-Ni nanoparticles on polyethyleneimine-decorated graphene oxide and application in catalytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(27): 13506. |
| 50 | Gan S Y, Zhong L J, Han D X, et al. Probing bio-nano interactions between blood proteins and monolayer-stabilized graphene sheets[J]. Small, 2015, 11(43): 5814-5825. |
| 51 | Kim H, Namgung R, Singha K, et al. Graphene oxide-polyethylenimine nanoconstruct as a gene delivery vector and bioimaging tool[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2011, 22(12): 2558-2567. |
| 52 | Guo H L, Wang X F, Qian Q Y, et al. A green approach to the synthesis of graphene nanosheets[J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(9): 2653-2659. |
| 53 | Zhang Y, Chen B, Zhang L M, et al. Controlled assembly of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on graphene oxide[J]. Nanoscale, 2011, 3(4): 1446-1450. |
| 54 | Yang S, Yue W B, Huang D Z, et al. A facile green strategy for rapid reduction of graphene oxide by metallic zinc[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(23): 8827-8832. |
| 55 | Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L, et al. Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 368(1): 540-546. |
| [1] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [3] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [5] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [6] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [7] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [9] | 王承泽, 顾凯丽, 张晋华, 石建轩, 刘艺娓, 李锦祥. 硫化协同老化零价铁增效去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)的作用机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206. |
| [10] | 郭旭, 张永政, 夏厚兵, 杨娜, 朱真珍, 齐晶瑶. 碳基材料电氧化去除水体污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [11] | 顾浩, 张福建, 刘珍, 周文轩, 张鹏, 张忠强. 力电耦合作用下多孔石墨烯膜时间维度的脱盐性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [12] | 张正, 何永平, 孙海东, 张荣子, 孙正平, 陈金兰, 郑一璇, 杜晓, 郝晓刚. 蛇形流场电控离子交换装置用于选择性提锂[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| [13] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [14] | 刘瑞琪, 周栖桐, 张悦, 贺莹, 高静, 马丽. 基于金纳米颗粒修饰二氧化硅纳米花的生物传感器构建及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| [15] | 程伟江, 汪何琦, 高翔, 李娜, 马赛男. 锂离子电池硅基负极电解液成膜添加剂的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号