化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (2): 818-829.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221022
何仁初1( ), 张朝晖1, 杨明磊1(
), 张朝晖1, 杨明磊1( ), 王聪1, 奚桢浩2
), 王聪1, 奚桢浩2
收稿日期:2022-07-15
修回日期:2022-08-24
出版日期:2023-02-05
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
杨明磊
作者简介:何仁初(1978—),男,博士,副教授,renchuhe@ecust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Renchu HE1( ), Zhaohui ZHANG1, Minglei YANG1(
), Zhaohui ZHANG1, Minglei YANG1( ), Cong WANG1, Zhenhao XI2
), Cong WANG1, Zhenhao XI2
Received:2022-07-15
Revised:2022-08-24
Online:2023-02-05
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
Minglei YANG
摘要:
针对国家“双碳”战略目标要求,以炼化企业汽油调合在线优化为研究对象,分析了国Ⅵ汽油新标准下被控属性更多、更严、调合效率要求更高等特点,以及由此带来的调合组分油调整导致调合成品汽油携带碳排放量的变化情况。考虑到传统的汽油调合在线优化一般只考虑调合成本、质量卡边等目标,首先建立了非线性的汽油调合辛烷值、蒸气压和馏程等软测量模型,然后构建了基于调合效应的汽油调合优化模型,优化目标中引入调合成品油二氧化碳排放最低化目标,开发了一种融合携带碳排放特征的汽油调合优化模型。为满足在线调合优化需求,优化模型中考虑了实际累积调合过程,将调合工艺过程中储罐汽油属性合格转化成调合头属性区间合格,利用调合头处优化的属性补偿已调合体积和罐底油的属性偏差。仿真结果表明,设计的考虑碳排放因素汽油累积调合优化技术能很好地满足汽油调合在线优化需求,为国Ⅵ标准和碳交易背景下汽油调合工艺设计及在线优化控制提供了技术支撑。
中图分类号:
何仁初, 张朝晖, 杨明磊, 王聪, 奚桢浩. 考虑碳排放因素的汽油调合在线优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 818-829.
Renchu HE, Zhaohui ZHANG, Minglei YANG, Cong WANG, Zhenhao XI. Online optimization of gasoline blending considering carbon emissions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 818-829.
| 属性名称 | 苯含量/% (体积) | 芳烃含量/% (体积) | 烯烃含量/% (体积) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 车用汽油国Ⅴ标准 | 1.0 | 40 | 24 |
| 车用汽油国Ⅵ(B)标准 | 0.8 | 35 | 15 |
| 属性值变化量 | 0.2 | 5 | 9 |
表1 国Ⅵ(B)与国Ⅴ标准的质量指标变化(GB 17930—2016)
Table 1 Changes in the quality index of the national Ⅵ(B) standard compared to the national Ⅴ standard (GB 17930—2016)
| 属性名称 | 苯含量/% (体积) | 芳烃含量/% (体积) | 烯烃含量/% (体积) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 车用汽油国Ⅴ标准 | 1.0 | 40 | 24 |
| 车用汽油国Ⅵ(B)标准 | 0.8 | 35 | 15 |
| 属性值变化量 | 0.2 | 5 | 9 |
| 组分油 | 单价/(CNY·t-1) | 研究法辛烷值(RON) | 烯烃 含量/% (体积) | 芳烃 含量/% (体积) | 苯 含量/% (体积) | 氧 含量/% (质量) | 10% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 50% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 90% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 终馏点/℃ | 密度(20℃)/(kg·m-3) | 硫含量/(mg·kg-1) | 蒸气压①/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 催化裂化汽油 | 4300 | 90.0 | 39.0 | 20.0 | 0.55 | 0 | 43 | 82 | 170 | 207 | 736 | 30.0 | 68 |
| 烷基化油 | 5300 | 96.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 104 | 120 | 186 | 692 | 1.2 | 54 |
| 重整汽油 | 5000 | 100.0 | 0.3 | 72.0 | 0.49 | 0 | 99 | 121 | 154 | 197 | 760 | 0.1 | 45 |
| MTBE | 6000 | 110.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18.3 | 30 | 50 | 140 | 170 | 727 | 0 | 44 |
| 加氢裂化轻石脑油 | 4400 | 78.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 1.40 | 0 | 42 | 54 | 75 | 96 | 661 | 1.0 | 84 |
表2 国Ⅵ(B)汽油调合池组分油属性
Table 2 Composition properties of national Ⅵ(B) gasoline blending pool
| 组分油 | 单价/(CNY·t-1) | 研究法辛烷值(RON) | 烯烃 含量/% (体积) | 芳烃 含量/% (体积) | 苯 含量/% (体积) | 氧 含量/% (质量) | 10% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 50% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 90% 蒸发 温度/℃ | 终馏点/℃ | 密度(20℃)/(kg·m-3) | 硫含量/(mg·kg-1) | 蒸气压①/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 催化裂化汽油 | 4300 | 90.0 | 39.0 | 20.0 | 0.55 | 0 | 43 | 82 | 170 | 207 | 736 | 30.0 | 68 |
| 烷基化油 | 5300 | 96.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 104 | 120 | 186 | 692 | 1.2 | 54 |
| 重整汽油 | 5000 | 100.0 | 0.3 | 72.0 | 0.49 | 0 | 99 | 121 | 154 | 197 | 760 | 0.1 | 45 |
| MTBE | 6000 | 110.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18.3 | 30 | 50 | 140 | 170 | 727 | 0 | 44 |
| 加氢裂化轻石脑油 | 4400 | 78.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 1.40 | 0 | 42 | 54 | 75 | 96 | 661 | 1.0 | 84 |
| 组分油 | 碳排放携带量/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|
| 催化裂化汽油 | 241 |
| 烷基化油 | 969 |
| 重整汽油 | 529 |
| MTBE | 500 |
| 加氢裂化轻石脑油 | 126 |
表3 组分油的碳排放携带量
Table 3 Carrying capacity of component oil carbon emissions
| 组分油 | 碳排放携带量/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|
| 催化裂化汽油 | 241 |
| 烷基化油 | 969 |
| 重整汽油 | 529 |
| MTBE | 500 |
| 加氢裂化轻石脑油 | 126 |
| 项目 | 成品汽油碳排放携带量/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|
| 国Ⅴ标准下的汽油调合 | 385.8 |
| 国Ⅵ(B)标准下的汽油调合 | 487.1 |
| 差值 | 101.3 |
表4 国Ⅴ和国Ⅵ(B)标准下的成品汽油碳排放携带量对比
Table 4 Comparison of carbon emission carrying capacity of gasoline under national Ⅴ and national Ⅵ(B)
| 项目 | 成品汽油碳排放携带量/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|
| 国Ⅴ标准下的汽油调合 | 385.8 |
| 国Ⅵ(B)标准下的汽油调合 | 487.1 |
| 差值 | 101.3 |
| 情景 | 碳排放成本/(CNY·t-1) |
|---|---|
| (1) | 58 |
| (2) | 345 |
| (3) | 1050 |
表5 不同情景下的碳排放成本
Table 5 Cost of carbon emissions under different scenarios
| 情景 | 碳排放成本/(CNY·t-1) |
|---|---|
| (1) | 58 |
| (2) | 345 |
| (3) | 1050 |
| 在线调合优化 | Cb/ (CNY·t-1) | Cc/ (CNY·t-1) | Ce/ (CNY·t-1) | Eb/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不考虑碳排放因素 | 4867.6 | 4839.3 | 28.3 | 487.1 |
| 考虑碳排放因素 | 4863.1 | 4840.6 | 22.5 | 388.0 |
| 差值 | -4.5 | 1.3 | -5.8 | -99.1 |
表6 情景(1)下的优化结果对比
Table 6 Comparison of optimization results under scenario(1)
| 在线调合优化 | Cb/ (CNY·t-1) | Cc/ (CNY·t-1) | Ce/ (CNY·t-1) | Eb/(kg·t-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不考虑碳排放因素 | 4867.6 | 4839.3 | 28.3 | 487.1 |
| 考虑碳排放因素 | 4863.1 | 4840.6 | 22.5 | 388.0 |
| 差值 | -4.5 | 1.3 | -5.8 | -99.1 |
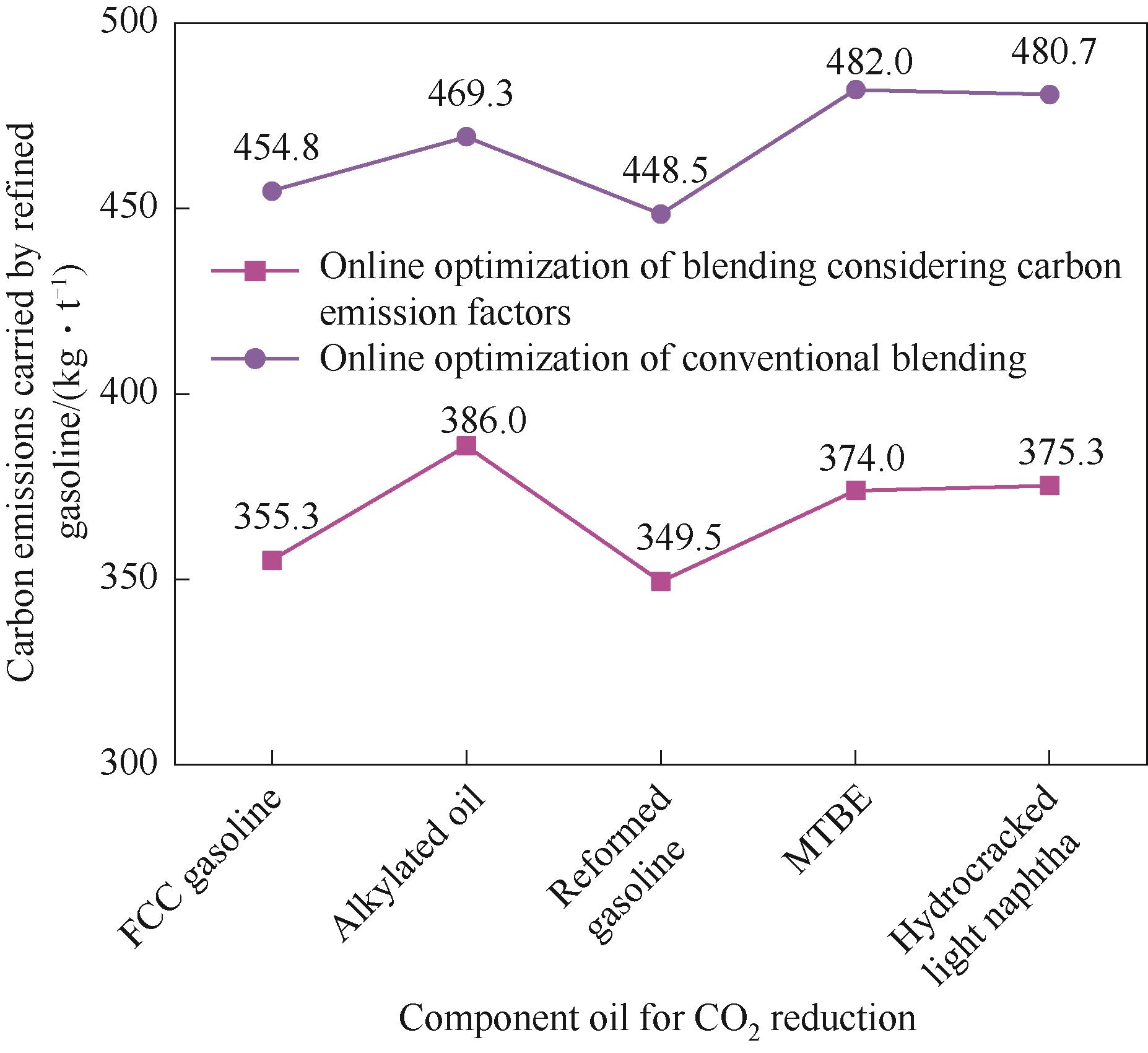
图8 定量减少某一组分油碳排放携带量对成品汽油碳排放携带量的影响
Fig.8 The effect of quantitatively reducing the carbon emission carried by a certain component oil on the carbon emission carried by refined gasoline
| 1 | 刘学之, 黄敬, 郑燕燕, 等. 碳交易背景下中国石化行业2020年碳减排目标情景分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27(10): 103-114. |
| Liu X Z, Huang J, Zheng Y Y, et al. Scenario analysis of carbon emission reduction target on China's petrochemical industry in 2020 under carbon trading background based on PCCGE model[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2017, 27(10): 103-114. | |
| 2 | Elkamel A, Ba-Shammakh M, Douglas P, et al. An optimization approach for integrating planning and CO2 emission reduction in the petroleum refining industry[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(3): 760-776. |
| 3 | Al Dhaheri N, Diabat A. A mathematical programming approach to reducing carbon dioxide emissions in the petroleum refining industry[C]//2010 Second International Conference on Engineering System Management and Applications. Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2010. |
| 4 | Gezehei I, Almehrezi A. Mathematical model development with emissions considerations in oil refinery[C]//Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management (IESM). Agdal, Morocco: IEEE, 2013. |
| 5 | Liu N B, Kayyali D, Yousef S. Integration of CO2 management within oil refinery planning[C]//Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management (IESM). Agdal, Morocco: IEEE, 2013. |
| 6 | Kangas I, Nikolopoulou C, Attiya M. Modeling & optimization of the FCC unit to maximize gasoline production and reduce carbon dioxide emissions in the presence of CO2 emissions trading scheme[C]//Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management (IESM). Agdal, Morocco: IEEE, 2013. |
| 7 | Abdul-Manan A F N, Arfaj A, Babiker H. Oil refining in a CO2 constrained world: effects of carbon pricing on refineries globally[J]. Energy, 2017, 121: 264-275. |
| 8 | Chan W N, Walter A, Sugiyama M I, et al. Assessment of CO2 emission mitigation for a Brazilian oil refinery[J]. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 33(4): 835-850. |
| 9 | Taqvi S, Almansoori A, Elkamel A. Optimal renewable energy integration into the process industry using multi-energy hub approach with economic and environmental considerations: refinery-wide case study[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2021, 151: 107345. |
| 10 | 王玉梅, 程辉, 钱锋. 改进生物地理学优化算法及其在汽油调合调度中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(3): 773-778. |
| Wang Y M, Cheng H, Qian F. Improved biogeography-based optimization algorithm and its application in gasoline blending scheduling[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(3): 773-778. | |
| 11 | 袁奇, 程辉, 钟伟民, 等. 全局群搜索优化算法及其在汽油调合中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(12): 4427-4433. |
| Yuan Q, Cheng H, Zhong W M, et al. Improved group search optimizer and application on gasoline blending process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(12): 4427-4433. | |
| 12 | Wang C, Zhong W M, He R C, et al. A scenario-based chance-constrained program for gasoline blending under uncertainty[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(15): 5215-5226. |
| 13 | Long J, Jiang S Y, Liu T B, et al. Modified hybrid strategy integrating online adjustable oil property characterization and data-driven robust optimization under uncertainty: application in gasoline blending[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(12): 6581-6596. |
| 14 | Zhou K L, Li Y W. Carbon finance and carbon market in China: progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 214: 536-549. |
| 15 | Ji C J, Hu Y J, Tang B J, et al. Price drivers in the carbon emissions trading scheme: evidence from Chinese emissions trading scheme pilots[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 123469. |
| 16 | Hua Y F, Dong F. China's carbon market development and carbon market connection: a literature review[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(9): 1663. |
| 17 | 王伟. 国Ⅵ标准汽油质量升级方案分析[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2019, 50(8): 6-12. |
| Wang W. Analysis of national standard Ⅵ gasoline upgrading processes[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2019, 50(8): 6-12. | |
| 18 | 程冬茹. 汽柴油全生命周期碳排放计算[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016. |
| Cheng D R. Carbon emissions calculation of gasoline and diesel fuel based on life cycle assessment[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2016. | |
| 19 | 贾曌, 施大鹏. 炼油过程碳排放量化模型构建及汽油质量升级碳排放测算[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2021, 52(5): 98-102. |
| Jia Z, Shi D P. Modeling of carbon emission in refining process and estimation of carbon emission from gasoline quality upgrading[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2021, 52(5): 98-102. | |
| 20 | Pasadakis N, Gaganis V, Foteinopoulos C. Octane number prediction for gasoline blends[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2006, 87(6): 505-509. |
| 21 | 佟新宇. 优化控制及近红外技术在汽油调合中应用的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2005. |
| Tong X Y. Research on application of optimal control and near-infrared technology in gasoline blending[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2005. | |
| 22 | 程辉, 刘朝, 钱锋. 新的汽油调合辛烷值模型及其现场应用[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2010, 27(10): 1317-1320. |
| Cheng H, Liu Z, Qian F. A novel octane number model for gasoline blending and its application[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2010, 27(10): 1317-1320. | |
| 23 | 竺柏康. 油品储运[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 1999. |
| Zhu B K. Oil Storage and Transportation[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 1999. | |
| 24 | 李祖奎. 油品调合优化与控制研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2005. |
| Li Z K. Research on optimization and control of oil blending[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2005. | |
| 25 | Hao H, Liu F Q, Liu Z W, et al. Compression ignition of low-octane gasoline: life cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 181: 391-398. |
| 26 | 何仁初, 陈海泉, 张卫东, 等. 基于严格约束的汽油调合双调合头协调优化方法[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2019, 35(2): 337-347. |
| He R C, Chen H Q, Zhang W D, et al. Coordinated optimization method of dual head gasoline blending under strict constraint conditions[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2019, 35(2): 337-347. | |
| 27 | 何仁初, 陈海泉, 杨超文. 面向国Ⅵ标准的汽油调合优化技术探讨与分析[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(3): 962-969. |
| He R C, Chen H Q, Yang C W. Discussion and analysis on optimization technology of gasoline blending for Chinese national standard Ⅵ[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(3): 962-969. | |
| 28 | 贺宗江, 房韦华, 王锋, 等. 汽油调合累积过程在线控制与优化[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2012, 29(7): 895-899. |
| He Z J, Fang W, Wang F, et al. On-line control and optimization of the heap process in the gasoline blending[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2012, 29(7): 895-899. | |
| 29 | 伍叶露, 刘潇潇. 基于动态成本模型的石化企业碳排放压力及对策分析[J]. 当代石油石化, 2020, 28(11): 16-22. |
| Wu Y L, Liu X X. Analysis on carbon emission pressure and countermeasures of petrochemical enterprises based on dynamic cost model[J]. Petroleum & Petrochemical Today, 2020, 28(11): 16-22. | |
| 30 | 董晓梅. 我国碳减排的成本和效益分析[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2013. |
| Dong X M. Analysis of cost and benefit of carbon emission reduction in China[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2013. | |
| 31 | 吴慧娟, 张智光. 中国碳市场价格特征及其成因分析:高低性、均衡性与稳定性[J]. 世界林业研究, 2021, 34(3): 123-128. |
| Wu H J, Zhang Z G. Price characteristics and its causes in China's carbon market: level, equilibrium and stability[J]. World Forestry Research, 2021, 34(3): 123-128. | |
| 32 | Tang B J, Ji C J, Hu Y J, et al. Optimal carbon allowance price in China's carbon emission trading system: perspective from the multi-sectoral marginal abatement cost[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 253: 119945. |
| 33 | 周艳春, 刘明浩. 基于DDF分析模型的石油行业边际碳减排成本估算研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2018, 43(3): 10-14. |
| Zhou Y C, Liu M H. Estimation of marginal carbon emission of petroleum industry based on DDF model[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2018, 43(3): 10-14. | |
| 34 | Zhao X G, Jiang G W, Nie D, et al. How to improve the market efficiency of carbon trading: a perspective of China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 59: 1229-1245. |
| 35 | Zhou X, Fan L W, Zhou P. Marginal CO2 abatement costs: findings from alternative shadow price estimates for Shanghai industrial sectors[J]. Energy Policy, 2015, 77: 109-117. |
| [1] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [2] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [3] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [5] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [6] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [7] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [8] | 蔺彩虹, 王丽, 吴瑜, 刘鹏, 杨江峰, 李晋平. 沸石中碱金属阳离子对CO2/N2O吸附分离性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| [9] | 李晨曦, 刘永峰, 张璐, 刘海峰, 宋金瓯, 何旭. O2/CO2氛围下正庚烷的燃烧机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2157-2169. |
| [10] | 王皓, 唐思扬, 钟山, 梁斌. MEA吸收CO2富液解吸过程中固体颗粒表面的强化作用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1539-1548. |
| [11] | 朱兵国, 何吉祥, 徐进良, 彭斌. 冷却条件下渐扩/渐缩管内超临界压力二氧化碳的传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1062-1072. |
| [12] | 王煦清, 严圣林, 朱礼涛, 张希宝, 罗正鸿. 填料塔中有机胺吸收CO2气液传质的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 237-256. |
| [13] | 李鑫, 曾少娟, 彭奎霖, 袁磊, 张香平. CO2电催化还原制合成气研究进展及趋势[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 313-329. |
| [14] | 沈辰阳, 孙楷航, 张月萍, 刘昌俊. 二氧化碳加氢合成甲醇氧化铟及其负载金属催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 145-156. |
| [15] | 李沐紫, 贾国伟, 赵砚珑, 张鑫, 李建荣. 金属有机框架材料对非二氧化碳温室气体捕捉研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 365-379. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号