化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (9): 4025-4033.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220351
收稿日期:2022-03-09
修回日期:2022-06-09
出版日期:2022-09-05
发布日期:2022-10-09
通讯作者:
张兴旺
作者简介:许贤伦(1996—),男,硕士研究生,578394066@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xianlun XU1( ), Yang QIAN2, Xingwang ZHANG1,2(
), Yang QIAN2, Xingwang ZHANG1,2( ), Lecheng LEI1,2
), Lecheng LEI1,2
Received:2022-03-09
Revised:2022-06-09
Online:2022-09-05
Published:2022-10-09
Contact:
Xingwang ZHANG
摘要:
针对我国土壤多环芳烃的污染问题,通过自研的介质阻挡脉冲反应器处理土壤中的芘,研究了放电电压、放电频率、土壤湿度、土壤厚度、空气流速和土壤pH等条件对降解效果的影响。结果表明,随着放电电压和放电频率增加,芘的降解率提高,空气流速和土壤湿度在适宜的范围内,有利于芘的降解,增加土壤厚度和降低pH会降低芘的降解率。最适降解条件为:放电电压12.6 kV、放电频率1.0 kHz、土壤湿度3.0%、土壤厚度1 mm、空气流速2 L/min、土壤pH≥7,芘的降解率为97.04%。通过HPLC-MS和FT-IR分析,间接证明放电产生的活性物质O3、·OH、NO x 等导致了芘的降解,提出了芘可能的降解途径。
中图分类号:
许贤伦, 钱旸, 张兴旺, 雷乐成. 高压脉冲介质阻挡放电降解土壤中芘的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4025-4033.
Xianlun XU, Yang QIAN, Xingwang ZHANG, Lecheng LEI. Study on treating soil contained pyrene by high voltage pulsed dielectric barrier discharge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4025-4033.
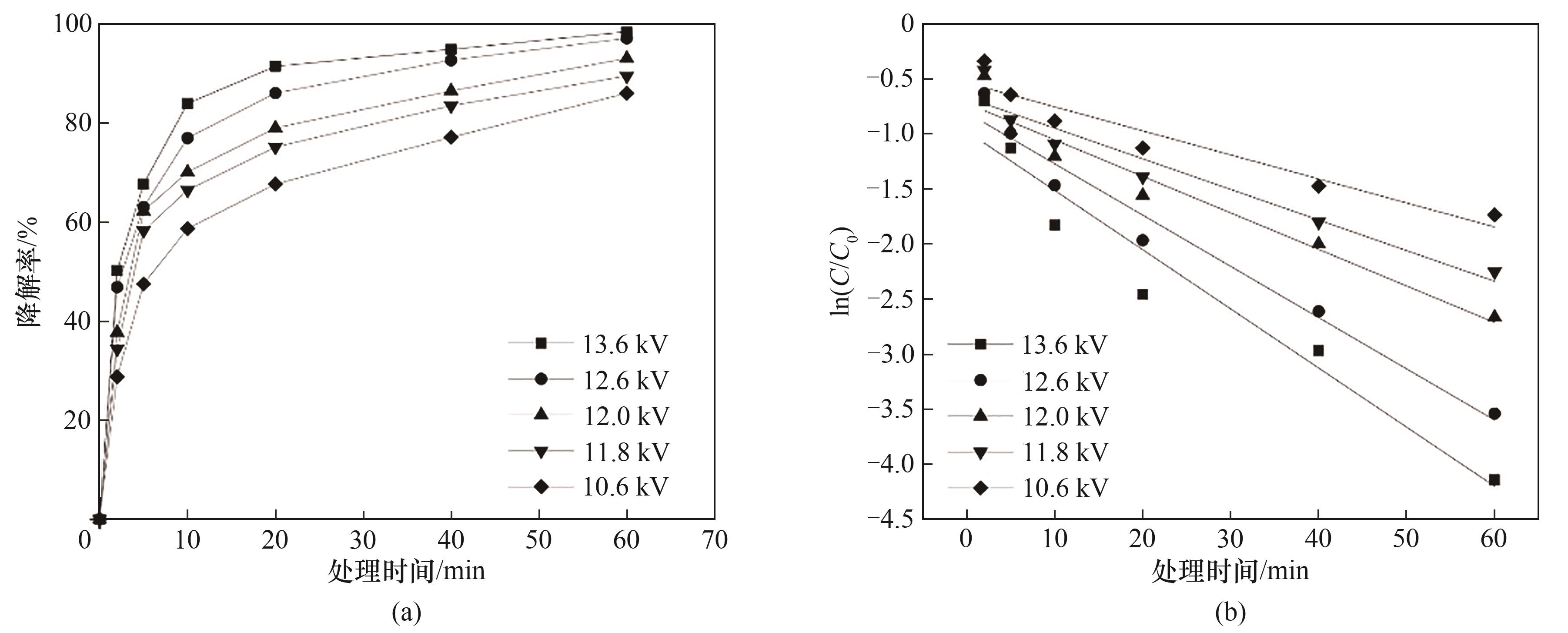
图3 放电电压的影响(a) 不同电压下的降解率; (b) 不同电压下的反应动力学
Fig.3 Effect of discharge voltage(a) degradation rates at different voltages; (b) kinetics at different voltages
| 电压/kV | k/min-1 | R2 | G/(mg/kJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.6 | 0.022 | 0.91 | 0.83 |
| 11.8 | 0.028 | 0.93 | 0.46 |
| 12.0 | 0.033 | 0.94 | 0.23 |
| 12.6 | 0.046 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| 13.6 | 0.054 | 0.94 | 0.11 |
表1 不同放电电压下芘降解动力学参数和G值
Table 1 Kinetic parameters and G values of pyrene degradation at different discharge voltages
| 电压/kV | k/min-1 | R2 | G/(mg/kJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.6 | 0.022 | 0.91 | 0.83 |
| 11.8 | 0.028 | 0.93 | 0.46 |
| 12.0 | 0.033 | 0.94 | 0.23 |
| 12.6 | 0.046 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| 13.6 | 0.054 | 0.94 | 0.11 |
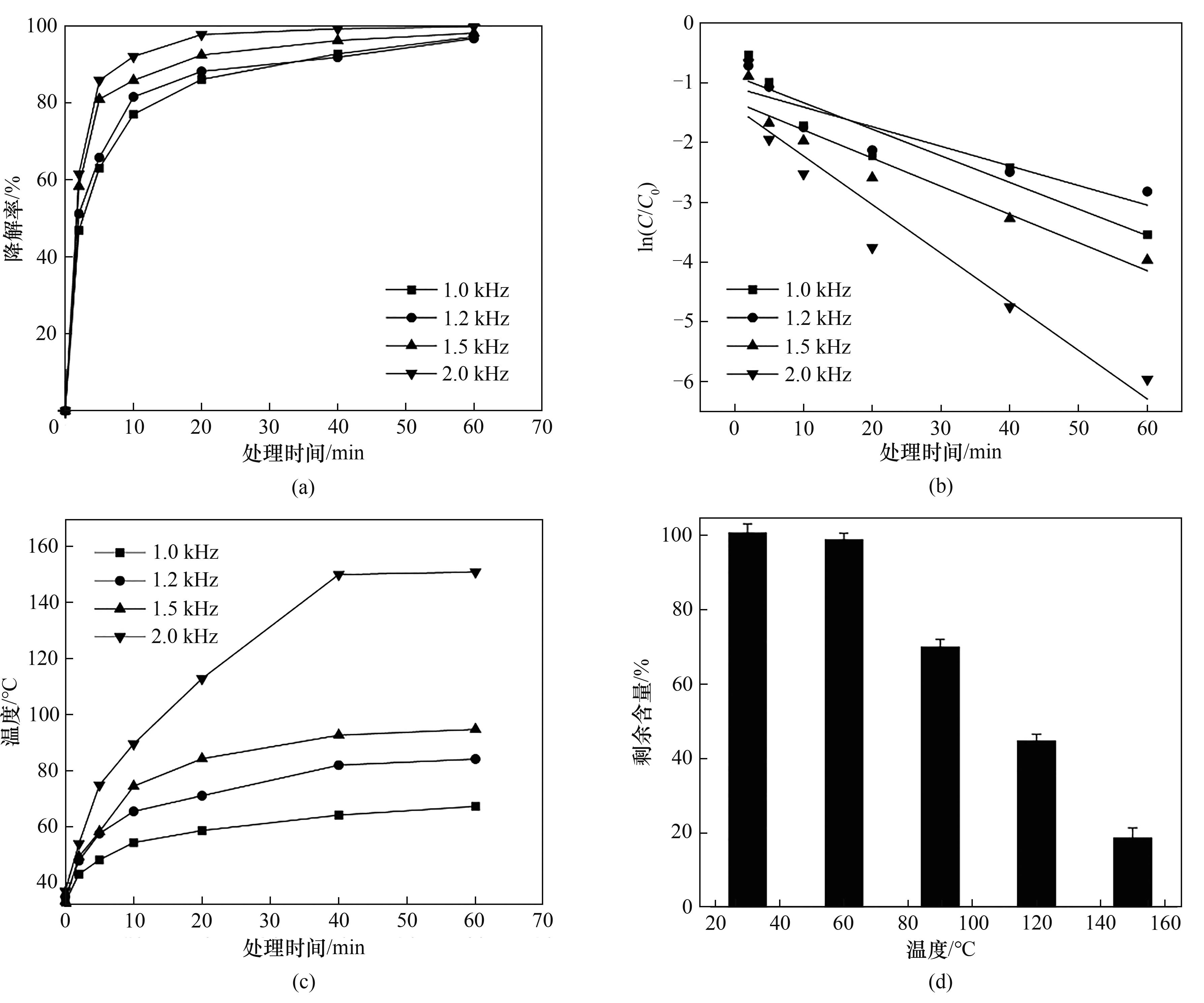
图4 放电频率的影响(a) 不同频率下的降解率; (b) 不同频率下的反应动力学; (c) 不同频率下反应器温度随时间的变化; (d) 不同温度下芘的挥发情况
Fig.4 Effect of discharge frequencies(a) degradation rates at different frequencies; (b) kinetics at different frequencies; (c) the change of temperature with time at different frequencies; (d) volatilization of pyrene at different temperatures
| 频率/kHz | k/min-1 | R2 | G/(mg/kJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 0.046 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| 1.2 | 0.041 | 0.93 | 0.12 |
| 1.5 | 0.047 | 0.93 | 0.10 |
| 2.0 | 0.079 | 0.94 | 0.08 |
表2 不同放电频率下芘降解动力学参数和G值
Table 2 Kinetics parameters and G values of pyrene degradation with different frequencies
| 频率/kHz | k/min-1 | R2 | G/(mg/kJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 0.046 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| 1.2 | 0.041 | 0.93 | 0.12 |
| 1.5 | 0.047 | 0.93 | 0.10 |
| 2.0 | 0.079 | 0.94 | 0.08 |
| 键 | 键长 | 原子 | 偏原子电荷 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C(1)-C(2) | 1.388 | C(1) | -0.097 |
| C(2)-C(3) | 1.398 | C(2) | -0.162 |
| C(3)-C(4) | 1.422 | C(3) | 0.147 |
| C(4)-C(5) | 1.422 | C(4) | -0.021 |
| C(5)-C(6) | 1.398 | C(5) | 0.147 |
| C(3)-C(7) | 1.432 | C(6) | -0.162 |
| C(7)-C(10) | 1.355 | C(7) | -0.178 |
| C(10)-C(9) | 1.432 | C(8) | -0.021 |
| C(9)-C(8) | 1.422 | C(9) | 0.147 |
| C(8)-C(4) | 1.420 | C(10) | -0.178 |
| C(9)-C(11) | 1.398 | C(11) | -0.162 |
| C(11)-C(13) | 1.388 | C(13) | -0.097 |
| C(13)-C(14) | 1.388 | C(14) | -0.162 |
| C(14)-C(15) | 1.398 | C(15) | 0.147 |
| C(15)-C(16) | 1.432 | C(16) | -0.178 |
| C(16)-C(17) | 1.355 | C(17) | -0.178 |
| C(17)-C(5) | 1.432 | H(12) | -0.102 |
| C(11)-H(12) | 1.083 | H(18) | 0.097 |
| C(13)-H(25) | 1.083 | H(19) | 0.097 |
| C(14)-H(26) | 1.083 | H(20) | 0.097 |
| C(16)-H(19) | 1.083 | H(21) | 0.106 |
| C(17)-H(18) | 1.083 | H(22) | 0.102 |
| C(6)-H(23) | 1.083 | H(23) | 0.102 |
| C(1)-H(21) | 1.083 | H(24) | 0.097 |
| C(2)-H(22) | 1.083 | H(25) | 0.106 |
| C(7)-H(20) | 1.083 | H(26) | 0.102 |
| C(10)-H(24) | 1.083 |
表3 Pyr分子的键长和偏原子电荷
Table 3 Main bond lengths and atomic charges of Pyr
| 键 | 键长 | 原子 | 偏原子电荷 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C(1)-C(2) | 1.388 | C(1) | -0.097 |
| C(2)-C(3) | 1.398 | C(2) | -0.162 |
| C(3)-C(4) | 1.422 | C(3) | 0.147 |
| C(4)-C(5) | 1.422 | C(4) | -0.021 |
| C(5)-C(6) | 1.398 | C(5) | 0.147 |
| C(3)-C(7) | 1.432 | C(6) | -0.162 |
| C(7)-C(10) | 1.355 | C(7) | -0.178 |
| C(10)-C(9) | 1.432 | C(8) | -0.021 |
| C(9)-C(8) | 1.422 | C(9) | 0.147 |
| C(8)-C(4) | 1.420 | C(10) | -0.178 |
| C(9)-C(11) | 1.398 | C(11) | -0.162 |
| C(11)-C(13) | 1.388 | C(13) | -0.097 |
| C(13)-C(14) | 1.388 | C(14) | -0.162 |
| C(14)-C(15) | 1.398 | C(15) | 0.147 |
| C(15)-C(16) | 1.432 | C(16) | -0.178 |
| C(16)-C(17) | 1.355 | C(17) | -0.178 |
| C(17)-C(5) | 1.432 | H(12) | -0.102 |
| C(11)-H(12) | 1.083 | H(18) | 0.097 |
| C(13)-H(25) | 1.083 | H(19) | 0.097 |
| C(14)-H(26) | 1.083 | H(20) | 0.097 |
| C(16)-H(19) | 1.083 | H(21) | 0.106 |
| C(17)-H(18) | 1.083 | H(22) | 0.102 |
| C(6)-H(23) | 1.083 | H(23) | 0.102 |
| C(1)-H(21) | 1.083 | H(24) | 0.097 |
| C(2)-H(22) | 1.083 | H(25) | 0.106 |
| C(7)-H(20) | 1.083 | H(26) | 0.102 |
| C(10)-H(24) | 1.083 |
| 1 | Wilson S C, Jones K C. Bioremediation of soil contaminated with polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 1993, 81(3): 229-249. |
| 2 | Haritash A K, Kaushik C P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 169(1/2/3): 1-15. |
| 3 | Dong T T T, Lee B K. Characteristics, toxicity, and source apportionment of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Ulsan, Korea[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 74(9): 1245-1253. |
| 4 | Li X J, Wang X, Ren Z J, et al. Sand amendment enhances bioelectrochemical remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 141: 62-70. |
| 5 | Kim K H, Jahan S A, Kabir E, et al. A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects[J]. Environment International, 2013, 60: 71-80. |
| 6 | Waigi M G, Kang F X, Goikavi C, et al. Phenanthrene biodegradation by sphingomonads and its application in the contaminated soils and sediments: a review[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2015, 104: 333-349. |
| 7 | Falciglia P P, de Guidi G, Catalfo A, et al. Remediation of soils contaminated with PAHs and nitro-PAHs using microwave irradiation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 296: 162-172. |
| 8 | Li G C, Xia X H, Yang Z F, et al. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 144(3): 985-993. |
| 9 | Chen L G, Ran Y, Xing B S, et al. Contents and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in vegetable soils of Guangzhou, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 60(7): 879-890. |
| 10 | Feng C L, Xia X H, Shen Z Y, et al. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2007, 133(1/2/3): 447-458. |
| 11 | Bayat B, Sari B. Comparative evaluation of microbial and chemical leaching processes for heavy metal removal from dewatered metal plating sludge[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1/2/3): 763-769. |
| 12 | Jin Y S, Jiang T, Yang Y B, et al. Removal of phosphorus from iron ores by chemical leaching[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(6): 673-677. |
| 13 | Schmidt U. Enhancing phytoextraction: the effect of chemical soil manipulation on mobility, plant accumulation, and leaching of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2003, 32(6): 1939-1954. |
| 14 | Zhao C, Dong Y, Feng Y P, et al. Thermal desorption for remediation of contaminated soil: a review[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 221: 841-855. |
| 15 | Vinegar H J, Stegemeier G L. Low cost, self regulating heater for use in an in situ thermal desorption soil remediation system: US6485232[P]. 2002-11-26. |
| 16 | 吴作军, 卢滇楠, 张敏莲, 等. 微生物分子生态学技术及其在石油污染土壤修复中的应用现状与展望[J]. 化工进展, 2010, 29(5): 789-795. |
| Wu Z J, Lu D N, Zhang M L, et al. Progress in applications of microbiological molecular ecology in bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2010, 29(5): 789-795. | |
| 17 | Kulik N, Goi A, Trapido M, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by combined chemical pre-oxidation and bioremediation in creosote contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2006, 78(4): 382-391. |
| 18 | Kang N, Hua I. Enhanced chemical oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons in soil systems[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 61(7): 909-922. |
| 19 | Oonnittan A, Shrestha R A, Sillanpää M. Removal of hexachlorobenzene from soil by electrokinetically enhanced chemical oxidation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2/3): 989-993. |
| 20 | Andreozzi R, Caprio V, Insola A, et al. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery[J]. Catalysis Today, 1999, 53(1): 51-59. |
| 21 | 严琼, 杨俊. 综述高级氧化技术在废水处理中的应用[J]. 净水技术, 2013, 32(3): 5-7. |
| Yan Q, Yang J. An overview of application for advanced oxidation processes in wastewater treatment[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2013, 32(3): 5-7. | |
| 22 | Gao Y Z, Gai K, Lu Q F, et al. Plasma induced degradation of aniline in aqueous solution[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2002, 4(2): 1243-1251. |
| 23 | Ren J Y, Zhen Y Z, Wang J, et al. Catalytic degradation of caffeic acid by DBD plasma and Mn doped cobalt oxyhydroxide catalyst[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 275: 130101. |
| 24 | 叶凯, 刘香华, 姜月, 等. 低温等离子体协同CeO2/13X催化降解甲苯[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3706-3715. |
| Ye K, Liu X H, Jiang Y, et al. Combing low-temperature plasma with CeO2/13X for toluene degradation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3706-3715. | |
| 25 | Du Z H, Lin X. Research progress in application of low temperature plasma technology for wastewater treatment[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 512(1): 012031. |
| 26 | 战佳勋, 张艾, 李振宇, 等. 低温等离子体降解土壤中的石油类污染物的研究[C]// 中国土壤学会土壤环境专业委员会第二十次会议暨农田土壤污染与修复研讨会. 2018: 184-185. |
| Zhan J X, Zhang A, Li Z Y, et al. Study on degradation of petroleum pollutants in soil by low temperature plasma[C]// The 20th Meeting of Soil Environment Professional Committee of Chinese Soil Society and Seminar on Farmland Soil Pollution and Remediation. 2018: 184-185. | |
| 27 | Abbas Y, Lu W J, Dai H X, et al. Remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soil with double dielectric barrier discharge plasma technology: influencing parameters[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 394: 124858. |
| 28 | Mu R W, Liu Y N, Li R, et al. Remediation of pyrene-contaminated soil by active species generated from flat-plate dielectric barrier discharge[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 296: 356-365. |
| 29 | Sun B, Sato M, Clements J S. Oxidative processes occurring when pulsed high voltage discharges degrade phenol in aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(3): 509-513. |
| 30 | 柯梁建, 卢秀圆, 王兴权, 等. 介质阻挡放电低温等离子体降解水中吡虫啉、啶虫脒和三唑磷的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(7): 262-272. |
| Ke L J, Lu X Y, Wang X Q, et al. Degradation of imidacloprid, acetamiprid and triazophos in aqueous solution by dielectric barrier discharge low-temperature plasma[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(7): 262-272. | |
| 31 | 于政, 李杰, 姜楠, 等. 淋土式介质阻挡放电等离子体修复阿特拉津污染土壤[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(12): 212-219. |
| Yu Z, Li J, Jiang N, et al. Remediation of atrazine contaminated soil by dielectric barrier discharge plasma with soil sprinkle mode[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(12): 212-219. | |
| 32 | Zhang H, Ma D Y, Qiu R L, et al. Non-thermal plasma technology for organic contaminated soil remediation: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313: 157-170. |
| 33 | Wang T C, Lu N, Li J, et al. Plasma-TiO2 catalytic method for high-efficiency remediation of p-nitrophenol contaminated soil in pulsed discharge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9301-9307. |
| 34 | Czaplicka M, Kaczmarczyk B. Infrared study of chlorophenols and products of their photodegradation[J]. Talanta, 2006, 70(5): 940-949. |
| 35 | Mangun C L, Benak K R, Economy J, et al. Surface chemistry, pore sizes and adsorption properties of activated carbon fibers and precursors treated with ammonia[J]. Carbon, 2001, 39(12): 1809-1820. |
| 36 | Park D P, Davis K, Gilani S, et al. Reactive nitrogen species produced in water by non-equilibrium plasma increase plant growth rate and nutritional yield[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2013, 13: S19-S29. |
| 37 | San N, Hatipoğlu A, Koçtürk G, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol in aqueous TiO2 suspensions: theoretical prediction of the intermediates[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2002, 146(3): 189-197. |
| [1] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [2] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [3] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [4] | 谢煜, 张民, 胡卫国, 王玉军, 骆广生. 利用膜分散微反应器高效溶解D-7-ACA的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 748-755. |
| [5] | 李彩风, 王晓, 李岗建, 林军章, 汪卫东, 束青林, 曹嫣镔, 肖盟. 嗜烃乳化菌SL-1与内源菌协同驱油的菌群作用关系研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4095-4102. |
| [6] | 靳文章, 张玉玲, 贾晓宇. 电化学高级氧化对HEDP的降解效能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4062-4069. |
| [7] | 徐振和, 李泓江, 高雨, 礼峥, 张含烟, 徐宝彤, 丁茯, 孙亚光. In2O3/Ag:ZnIn2S4“Type Ⅱ”型异质结构材料的制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3625-3635. |
| [8] | 黄仕元, 邓简, 袁瀚钦, 王国华, 吴兴良. 钴强化铁磁体活化过一硫酸盐的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3045-3056. |
| [9] | 贾艳萍, 丁雪, 刚健, 佟泽为, 张海丰, 张兰河. Mn强化Fe/C微电解工艺条件优化及降解油墨废水机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2183-2193. |
| [10] | 韩雪, 高生旺, 王国英, 夏训峰. 铈掺杂强化碳纳米管活化过一硫酸盐实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1743-1753. |
| [11] | 王小西, 李笑艳, 王保伟. 介质阻挡放电微等离子体分解二氧化碳研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1343-1350. |
| [12] | 万丽, 梁德青. 一种可生物降解水合物动力学抑制剂的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 894-903. |
| [13] | 石秀娟, 梁文俊, 尹国彬, 王金柱. 低温等离子体协同Mn基催化剂降解氯苯研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4472-4483. |
| [14] | 侯晓松, 刘晨星, 任爱玲, 郭斌, 郭渊明. 超声雾化/表面活性剂强化吸收耦合生物洗涤净化甲苯废气[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4692-4706. |
| [15] | 朱振林, 王松林, 姜冰雪, 李家旭, 邓维, 吴海强, 杨轩, 刘平伟, 王文俊. 聚酯生物降解及评价方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 110-121. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号