化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (10): 4692-4706.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220590
侯晓松1,2,3( ), 刘晨星1,2,3, 任爱玲1,2,3, 郭斌1,2,3(
), 刘晨星1,2,3, 任爱玲1,2,3, 郭斌1,2,3( ), 郭渊明4
), 郭渊明4
收稿日期:2022-04-26
修回日期:2022-08-08
出版日期:2022-10-05
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
郭斌
作者简介:侯晓松(1995—),男,硕士研究生,15075168995@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaosong HOU1,2,3( ), Chenxing LIU1,2,3, Ailing REN1,2,3, Bin GUO1,2,3(
), Chenxing LIU1,2,3, Ailing REN1,2,3, Bin GUO1,2,3( ), Yuanming GUO4
), Yuanming GUO4
Received:2022-04-26
Revised:2022-08-08
Online:2022-10-05
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
Bin GUO
摘要:
为提高生物法净化疏水性VOCs的效率,构建了以微米级雾滴结合表面活性剂为特色的超声雾化/表面活性剂耦合生物洗涤器(ultrasonic atomization/surfactants-biological washing reactor,USBWR)。考察了USBWR对甲苯废气的去除能力及停运恢复性能,探讨USBWR最佳工艺条件及雾滴粒径分布,并分析系统中微生物群落结构,对比其与传统生物洗涤器(traditional biological washing reactor,TBWR)净化性能差异。结果表明:USBWR较TBWR系统有较高的甲苯去除能力和去除负荷,更适应企业非连续工况条件;在进气浓度2000 mg·m-3、雾化量450 ml·h-1条件下,响应曲面法优化USBWR最佳工艺条件为洗涤液pH 7.07、停留时间54.60 s、液气比0.23,USBWR去除率达97.26%;将实验室前期筛选得到的复配表面活性剂溶液(50 mg·L-1皂角苷+500 mg·L-1柠檬酸钠+200 mg·L-1柠檬酸+50 mg·L-1氯化钠)应用到超声雾化装置中,雾滴粒径均在15 μm以下,中位径为(6.911±0.326)μm,比表面积为(359.60±50.02)m2·kg-1,雾滴小而均匀,更有利于气液充分接触;USBWR系统中主要微生物细菌门为变形杆菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)和绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi),与TBWR系统相比,USBWR系统促进了优势菌种变形杆菌门(Proteobacteria)的富集生长,更有利于降解甲苯废气。
中图分类号:
侯晓松, 刘晨星, 任爱玲, 郭斌, 郭渊明. 超声雾化/表面活性剂强化吸收耦合生物洗涤净化甲苯废气[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4692-4706.
Xiaosong HOU, Chenxing LIU, Ailing REN, Bin GUO, Yuanming GUO. Study on purification of toluene waste gas by ultrasonic atomization/surfactants-enhanced absorption coupled with biological scrubbing[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4692-4706.
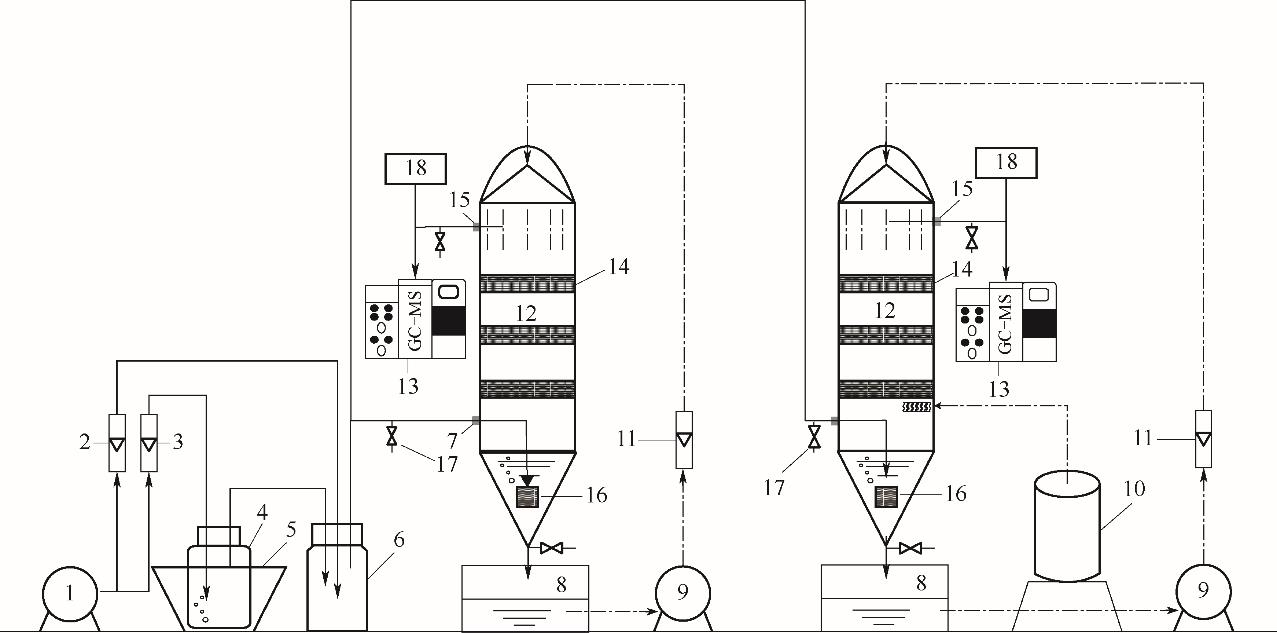
图1 实验装置流程图1—气泵;2—空气流量计;3—甲苯流量计;4—气体发生瓶;5—恒温水浴锅;6—缓冲瓶;7—进气口;8—循环液槽;9—蠕动泵;10—超声雾化吸收装置;11—液体转子流量计;12—填料洗涤塔;13—气相色谱-质谱仪;14—填料;15—出气口;16—曝气头;17—取样口;18—尾气吸收装置
Fig.1 Flow chart of test device1—air pump; 2—air flow meter; 3—toluene flow meter; 4—gas generation bottle; 5—constant temperature water bath; 6—buffer bottle; 7—gas inlet; 8—circulation liquid tank; 9—peristaltic pump; 10—ultrasonic atomization absorption device; 11—liquid rotameter; 12—packed scrubber tower; 13—gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer; 14—packing; 15—gas outlet; 16—aeration head; 17—sampling port; 18—exhaust gas absorption device
| 序号 | 工况条件 | 运行方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 临时停运事故 | 停运1 h |
| 2 | 设备故障检修 | 停运4 h |
| 3 | 生产系统故障白天检修 | 停运8 h |
| 4 | 夜间停运阶段 | 停运16 h |
| 5 | 生产系统全天停运检修 | 停运24 h |
| 6 | 双休日停运 | 停运48 h |
表1 生物洗涤系统工况条件及运行方式
Table 1 Working conditions and operation mode of biological washing system
| 序号 | 工况条件 | 运行方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 临时停运事故 | 停运1 h |
| 2 | 设备故障检修 | 停运4 h |
| 3 | 生产系统故障白天检修 | 停运8 h |
| 4 | 夜间停运阶段 | 停运16 h |
| 5 | 生产系统全天停运检修 | 停运24 h |
| 6 | 双休日停运 | 停运48 h |
| 自变量 | 编码水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 洗涤液pH(A) | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 液气比(B) | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.20 |
| 停留时间(C) | 28 | 42 | 56 |
表2 实验因素编码与水平
Table 2 Coding and level of test factors
| 自变量 | 编码水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 洗涤液pH(A) | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 液气比(B) | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.20 |
| 停留时间(C) | 28 | 42 | 56 |
| 洗涤液pH | 停留时间/s | 液气比 | 甲苯去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 预测值 | 实际值 | |||
| 7.07 | 54.60 | 0.23 | 97.71 | 97.26 |
表3 USBWR最佳工艺参数
Table 3 USBWR optimum process parameters
| 洗涤液pH | 停留时间/s | 液气比 | 甲苯去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 预测值 | 实际值 | |||
| 7.07 | 54.60 | 0.23 | 97.71 | 97.26 |
| 反应器 | 模拟方程 | 比降解速率k | R2 | 半衰期/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USBWR | ln(ct /c0)= -0.1421t+0.2719 | 0.1421 | 0.9843 | 4.88 |
| TBWR | ln(ct /c0)= -0.0834t-0.0105 | 0.0834 | 0.9662 | 8.31 |
表4 动力学拟合结果对比
Table 4 Comparison of kinetic fitting results
| 反应器 | 模拟方程 | 比降解速率k | R2 | 半衰期/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USBWR | ln(ct /c0)= -0.1421t+0.2719 | 0.1421 | 0.9843 | 4.88 |
| TBWR | ln(ct /c0)= -0.0834t-0.0105 | 0.0834 | 0.9662 | 8.31 |
| 距塔底距离/cm | 中位径(D50)/μm | 体积平均径/μm | 面积平均径/μm | 比表面积/ (m2·kg-1) | 跨度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 6.546 | 6.755 | 6.483 | 415.10 | 0.32 |
| 30 | 7.016 | 7.187 | 6.428 | 345.70 | 0.41 |
| 45 | 7.172 | 7.423 | 6.987 | 318.00 | 0.57 |
| 均值 | 6.911 | 7.122 | 6.633 | 359.60 | — |
表5 复配表面活性剂溶液在塔中不同高度的雾滴粒径分布
Table 5 Droplet size distribution of compound surfactant at different heights in the tower
| 距塔底距离/cm | 中位径(D50)/μm | 体积平均径/μm | 面积平均径/μm | 比表面积/ (m2·kg-1) | 跨度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 6.546 | 6.755 | 6.483 | 415.10 | 0.32 |
| 30 | 7.016 | 7.187 | 6.428 | 345.70 | 0.41 |
| 45 | 7.172 | 7.423 | 6.987 | 318.00 | 0.57 |
| 均值 | 6.911 | 7.122 | 6.633 | 359.60 | — |
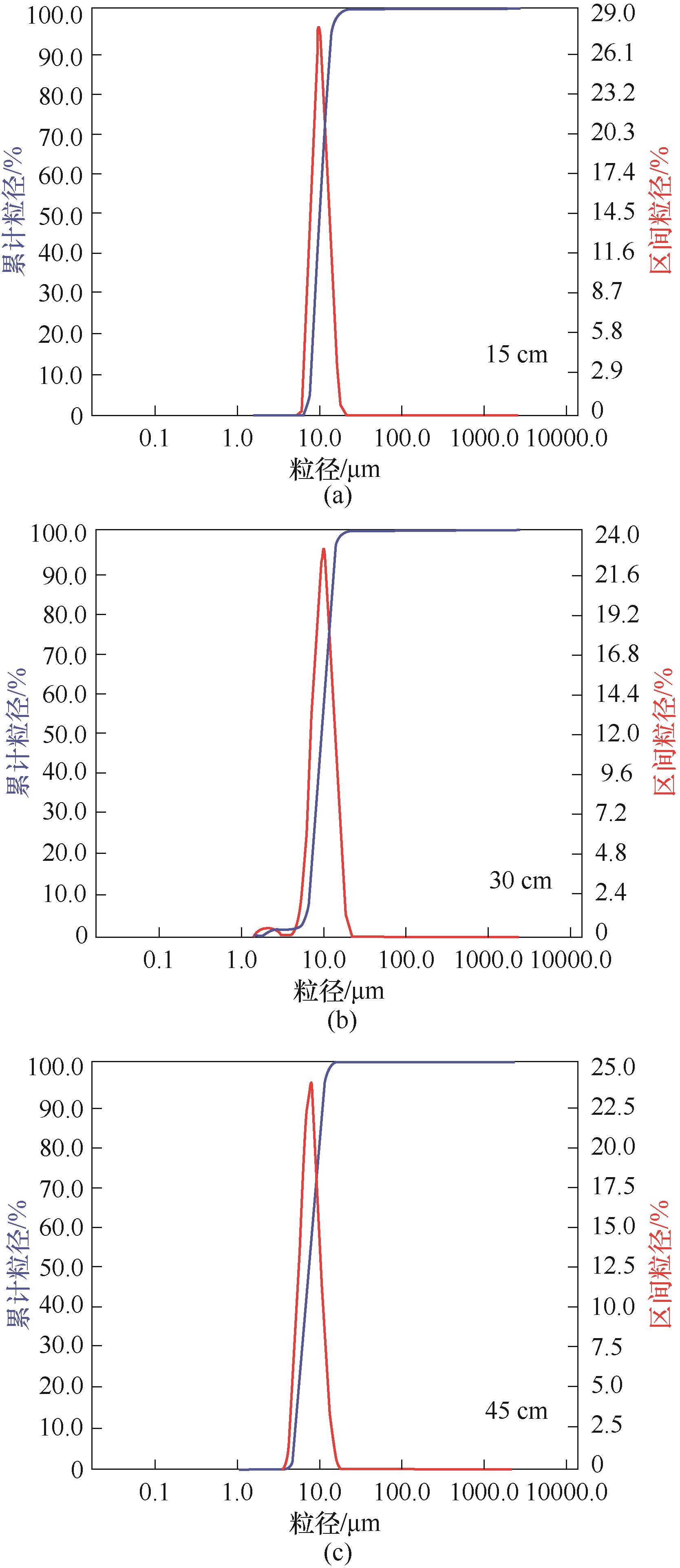
图13 皂角苷+柠檬酸钠+柠檬酸+氯化钠在塔中不同高度雾滴粒径分布曲线
Fig.13 Droplet size distribution curve of saponin + sodium citrate + citric acid + sodium chloride at different heights in the tower
| 1 | 姚维杰, 王大玮, 谢付莹, 等. 日照市夏季VOCs物种空间分布特征及其对臭氧生成的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2): 714-722. |
| Yao W J, Wang D W, Xie F Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of VOCs and its impact on ozone formation potential in Rizhao City in summer[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(2): 714-722. | |
| 2 | Wang Z W, Xiu G L, Qiao T, et al. Coupling ozone and hollow fibers membrane bioreactor for enhanced treatment of gaseous xylene mixture[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 130: 52-58. |
| 3 | 任义君, 马双良, 王思维, 等. 郑州市春季大气污染过程VOCs特征、臭氧生成潜势及源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2577-2585. |
| Ren Y J, Ma S L, Wang S W, et al. Ambient VOCs characteristics, ozone formation potential, and source apportionment of air pollution in spring in Zhengzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2577-2585. | |
| 4 | 叶凯, 刘香华, 姜月, 等. 低温等离子体协同CeO2/13X催化降解甲苯[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3706-3715. |
| Ye K, Liu X H, Jiang Y, et al. Combing low-temperature plasma with CeO2/13X for toluene degradation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3706-3715. | |
| 5 | Chalupa J, Pocik O, Halecky M, et al. Thermophilic waste air treatment of an airborne ethyl acetate/toluene mixture in a bubble column reactor: stability towards temperature changes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 120744. |
| 6 | El-Naas M H, Acio J A, El Telib A E. Aerobic biodegradation of BTEX: progresses and prospects[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2014, 2(2): 1104-1122. |
| 7 | Nisola G M, Cho E, Orata J D, et al. NH3 gas absorption and bio-oxidation in a single bioscrubber system[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2009, 44(2): 161-167. |
| 8 | Kang J, Wang T, Xin H W, et al. A laboratory study of microalgae-based ammonia gas mitigation with potential application for improving air quality in animal production operations[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association (1995), 2014, 64(3): 330-339. |
| 9 | Barbusinski K, Kalemba K, Kasperczyk D, et al. Biological methods for odor treatment—a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 152: 223-241. |
| 10 | San-Valero P, Penya-roja J M, Álvarez-Hornos F J, et al. Fully aerobic bioscrubber for the desulfurization of H2S-rich biogas[J]. Fuel, 2019, 241: 884-891. |
| 11 | Marsolek M D, Torres C I, Hausner M, et al. Intimate coupling of photocatalysis and biodegradation in a photocatalytic circulating-bed biofilm reactor[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 101(1): 83-92. |
| 12 | Wei Z S, Li H Q, He J C, et al. Removal of dimethyl sulfide by the combination of non-thermal plasma and biological process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 146: 451-456. |
| 13 | Muñoz R, Daugulis A J, Hernández M, et al. Recent advances in two-phase partitioning bioreactors for the treatment of volatile organic compounds[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(6): 1707-1720. |
| 14 | Wang L, Yang C P, Cheng Y, et al. Effects of surfactant and Z n ( Ⅱ ) at various concentrations on microbial activity and ethylbenzene removal in biotricking filter[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(11): 2909-2913. |
| 15 | Tu Y H, Yang C P, Cheng Y, et al. Effect of saponins on n-hexane removal in biotrickling filters[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 175: 231-238. |
| 16 | Shao B B, Liu Z F, Zhong H, et al. Effects of rhamnolipids on microorganism characteristics and applications in composting: a review[J]. Microbiological Research, 2017, 200: 33-44. |
| 17 | Trellu C, Mousset E, Pechaud Y, et al. Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: a critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 306: 149-174. |
| 18 | Rezaei M, Moussavi G, Naddafi K, et al. Enhanced biodegradation of styrene vapors in the biotrickling filter inoculated with biosurfactant-generating bacteria under H2O2 stimulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135325. |
| 19 | 王光旭, 徐国栋, 刘文婧, 等. 应用电声换能超声波雾化方法提高超细颗粒捕集效率[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(1): 294-300. |
| Wang G X, Xu G D, Liu W J, et al. Improvement of ultrafine particles separation efficiency by electro-acoustic ultrasonic nebulizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(1): 294-300. | |
| 20 | 陈卓楷, 陈凡植, 周炜煌, 等. 超声雾化水雾在除尘试验中的应用[J]. 广东化工, 2006, 33(10): 74-77. |
| Chen Z K, Chen F Z, Zhou W H, et al. The application of atomization water made by ultrasonic technique in dust removal experiment[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2006, 33(10): 74-77. | |
| 21 | 陈泊豪. 超声波雾化除尘机理的实验探究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014. |
| Chen B H. Experimental study on the mechanism of the fine particles separation by the ultrasonic nebulizer[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2014. | |
| 22 | 陈泊豪, 於进, 周万利, 等. 电声换能超声波雾化方法捕集细颗粒物的强化实验研究[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(6): 78-82. |
| Chen B H, Yu J, Zhou W L, et al. Experimental study on enhanced performance of the fine particles separation by the electro-acoustic ultrasonic nebulizer[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(6): 78-82. | |
| 23 | 郑德康. 基于超声波雾化法的船舶废气NaClO2气雾脱硝实验研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2018. |
| Zheng D K. Study on NO removal from marine flue gas by NaClO2 mist based on ultrasonic atomization[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2018. | |
| 24 | Wei J Q, Gu J J, Guo J H, et al. Simultaneous removal of nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide using ultrasonically atomized hydrogen peroxide[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(22): 22351-22361. |
| 25 | 孙嘉祺, 郭斌, 侯晓松. 新型填料喷雾塔强化吸收甲醇废气的应用[J]. 化学工程, 2020, 48(7): 33-38. |
| Sun J Q, Guo B, Hou X S. Application of new packed spray tower to intensify absorption of methanol waste gas[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2020, 48(7): 33-38. | |
| 26 | Shah A, Shahzad S, Munir A, et al. Micelles as soil and water decontamination agents[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(10): 6042-6074. |
| 27 | 涂燕红. 表面活性剂强化生物滴滤器处理正己烷废气的净化效果及机理[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2015. |
| Tu Y H. Enhancement and mechamisms of surfactants on n-hexane removal in biotrickling filters[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2015. | |
| 28 | Ono Y, Sekiguchi K, Sankoda K, et al. Improved ultrasonic degradation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic aldehydes in water by combined use of atomization and UV irradiation onto the mist surface[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2020, 60: 104766. |
| 29 | 李远啸. 生物洗涤法净化含苯废气及其强化技术研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019. |
| Li Y X. Study on purification of benzene containing waste gas by biscrubber and its strengthening technology[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| 30 | Skjevrak I, Lund V, Ormerod K, et al. Volatile organic compounds in natural biofilm in polyethylene pipes supplied with lake water and treated water from the distribution network[J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(17): 4133-4141. |
| 31 | 凌丹. 挥发性有机物多技术联合治理研究进展[J]. 绿色科技, 2020(12): 147-149. |
| Ling D. Research progress in multi-technology combined treatment technology of volatile organic compounds organic compounds[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2020(12): 147-149. | |
| 32 | 刘烁. 两相分配生物反应器降解苯乙烯废气的实验研究及CFD模拟[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2020. |
| Liu S. Study on using two phase partitioning bioreactor to remove styrene: experiment and CFD simulation[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2020. | |
| 33 | Hasan H A, Abdullah S R S, Kamarudin S K, et al. Response surface methodology for optimization of simultaneous COD, N H 4 + -N and Mn2+ removal from drinking water by biological aerated filter[J]. Desalination, 2011, 275(1/2/3): 50-61. |
| 34 | 朱连燕, 王玉明, 周幸福. 响应曲面法优化电催化降解染料废水工艺的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1335-1342. |
| Zhu L Y, Wang Y M, Zhou X F. Application of response surface methodology in optimizing electrocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1335-1342. | |
| 35 | Li J W, Han Z W. A modeling study of severe winter haze events in Beijing and its neighboring regions[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2016, 170: 87-97. |
| 36 | 任爱玲, 刘烁, 谷丹丹, 等. 两相分配生物反应器降解苯乙烯废气的研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(3): 1551-1558. |
| Ren A L, Liu S, Gu D D, et al. Study on using two-phase partitioning bioreactor to remove styrene[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(3): 1551-1558. | |
| 37 | Littlejohns J V, McAuley K B, Daugulis A J. Model for a solid-liquid stirred tank two-phase partitioning bioscrubber for the treatment of BTEX[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1/2/3): 872-882. |
| 38 | 姜岩, 张哲. 不同亲水特性VOCs在生物滴滤工艺中的作用规律[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 2973-2982. |
| Jiang Y, Zhang Z. Interaction of VOCs with different hydrophilic properties in biotrickling filters[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 2973-2982. | |
| 39 | 姜岩, 张晓华, 杨颖, 等. 基于约氏不动杆菌的萘生物降解特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(9): 3981-3987. |
| Jiang Y, Zhang X H, Yang Y, et al. Naphthalene biodegradation by Acinetobacter johnsonii [J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(9): 3981-3987. | |
| 40 | Kan E, Deshusses M. Modeling of a foamed emulsion bioreactor(Ⅰ): Model development and experimental validation[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 99(5): 1096-1106. |
| 41 | Fazaelipoor M H. Analysis of a dual liquid phase biofilter for the removal of hydrophobic organic compounds from airstreams[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 147(2/3): 110-116. |
| 42 | Yeom S H. A simplified steady-state model of a hybrid bioreactor composed of a bubble column bioreactor and biofilter compartments[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2007, 42(4): 554-560. |
| 43 | England E, Fitch M W, Mormile M, et al. Toluene removal in membrane bioreactors under recirculating and non-recirculating liquid conditions[J]. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 2005, 7(4): 259-269. |
| 44 | 肖建军, 李亚龙, 杨琦. 苯降解菌的筛选及其对苯的降解研究[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(6): 159-162. |
| Xiao J J, Li Y L, Yang Q. Isolation and characterization of benzene degrading bacterium[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(6): 159-162. | |
| 45 | Majeau J A, Brar S K, Tyagi R D. Laccases for removal of recalcitrant and emerging pollutants[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2331-2350. |
| 46 | Wang L, Ji G D, Huang S Q. Contribution of the Kodama and 4S pathways to the dibenzothiophene biodegradation in different coastal wetlands under different C/N ratios[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 76: 217-226. |
| 47 | Wang J, Tian Z, Huo Y B, et al. Monitoring of 943 organic micropollutants in wastewater from municipal wastewater treatment plants with secondary and advanced treatment processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 67: 309-317. |
| 48 | 苏俊朋. 鼠李糖脂强化生物滴滤塔去除VOCs效能及其机理研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2018. |
| Su J P. Study on the efficiency and mechanism of the removal of VOCs by rhamnolipid enhanced biotrickling filter[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2018. |
| [1] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [2] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [3] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [4] | 张媛媛, 曲江源, 苏欣欣, 杨静, 张锴. 循环流化床燃煤机组SNCR脱硝过程气液传质和反应特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [5] | 朱理想, 罗默也, 张晓东, 龙涛, 余冉. 醌指纹法指示三氯乙烯污染土功能微生物活性应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2647-2654. |
| [6] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [7] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [8] | 王皓, 唐思扬, 钟山, 梁斌. MEA吸收CO2富液解吸过程中固体颗粒表面的强化作用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1539-1548. |
| [9] | 黄玉龙, 吕凡, 仇俊杰, 章骅, 何品晶. 易腐垃圾厌氧消化沼液理化性质及VOCs分子特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1275-1285. |
| [10] | 钱志广, 樊越, 王世学, 岳利可, 王金山, 朱禹. 吹扫条件对PEMFC阻抗弛豫现象和低温启动的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1286-1293. |
| [11] | 何洋, 高森虎, 吴青云, 张明理, 龙涛, 牛佩, 高景辉, 孟颖琪. 析湿工况下平直开缝翅片传热传质特性的数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1073-1081. |
| [12] | 贾露凡, 王艺颖, 董钰漫, 李沁园, 谢鑫, 苑昊, 孟涛. 微流控双水相贴壁液滴流动强化酶促反应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [13] | 何万媛, 陈一宇, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. 阵列凸起微通道内气液两相传质特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| [14] | 谢煜, 张民, 胡卫国, 王玉军, 骆广生. 利用膜分散微反应器高效溶解D-7-ACA的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 748-755. |
| [15] | 王煦清, 严圣林, 朱礼涛, 张希宝, 罗正鸿. 填料塔中有机胺吸收CO2气液传质的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 237-256. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号