化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (6): 2306-2317.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220211
收稿日期:2022-03-01
修回日期:2022-05-09
出版日期:2022-06-05
发布日期:2022-06-30
通讯作者:
汪伟
作者简介:潘大伟(1991—),男,博士,副研究员,基金资助:
Dawei PAN( ),Wei WANG(
),Wei WANG( ),Rui XIE,Xiaojie JU,Zhuang LIU,Liangyin CHU
),Rui XIE,Xiaojie JU,Zhuang LIU,Liangyin CHU
Received:2022-03-01
Revised:2022-05-09
Online:2022-06-05
Published:2022-06-30
Contact:
Wei WANG
摘要:
功能微颗粒材料因其微型化和多功能化等优点而在诸多领域具有广泛的应用。微流控技术可控制备的多样化乳液液滴体系为功能微颗粒材料的创新设计与可控制备提供了优良而独特的模板。深入研究乳液模板法构建功能微颗粒材料过程中介尺度结构的形成与演变规律,以及液滴界面介尺度结构与乳液动力学行为、界面传质与反应耦合对微颗粒介尺度结构的影响规律等,对于实现乳液模板结构调控与新型功能微颗粒材料创新制备具有重要意义。本文主要综述了微流控乳液模板法构建功能微颗粒过程中介尺度结构定向调控的研究进展,着重涵盖了两方面内容:(1)微流控法可控制备乳液模板的过程中,液滴界面两亲分子聚集态介尺度结构的调控与液滴运动、吞并、融合、相界面定向演变等动力学行为之间的相互影响关系和调控机制,以及上述调控对液滴形貌、结构和组成的影响规律;(2)乳液模板制备功能微颗粒的过程中,界面传质、反应,及两者耦合对微颗粒介尺度结构的定向调控,以期为新型功能微颗粒材料的高效制备与性能强化提供科学指导。
中图分类号:
潘大伟, 汪伟, 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 刘壮, 褚良银. 微流控乳液模板法构建功能微颗粒过程中介尺度结构定向调控的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2306-2317.
Dawei PAN, Wei WANG, Rui XIE, Xiaojie JU, Zhuang LIU, Liangyin CHU. Progress on regulation of meso-scale structures for microfluidic emulsion-template synthesis of functional microparticles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2306-2317.

图1 乳液液滴跨界面运动过程中的介尺度结构调控。(a)乳液液滴跨界面运动过程的示意图[21];(b)微通道中水相液滴W1由连续油相O1至连续水相W2的跨界面运动过程,以及其液滴界面上两亲分子聚集态介尺度结构的示意图[21]
Fig.1 Regulation of meso-scale structures of emulsion droplets during their trans-interfacial transfer process. (a) Schematic illustration of the trans-interfacial transfer process of an emulsion droplet[21]. (b) Schematic illustration of the trans-interfacial transfer of aqueous droplets (W1) from continuous oil phase (O1) to continuous water phase (W2), and the aggregation meso-scale structures of amphiphilic molecules at the droplet interface[21]
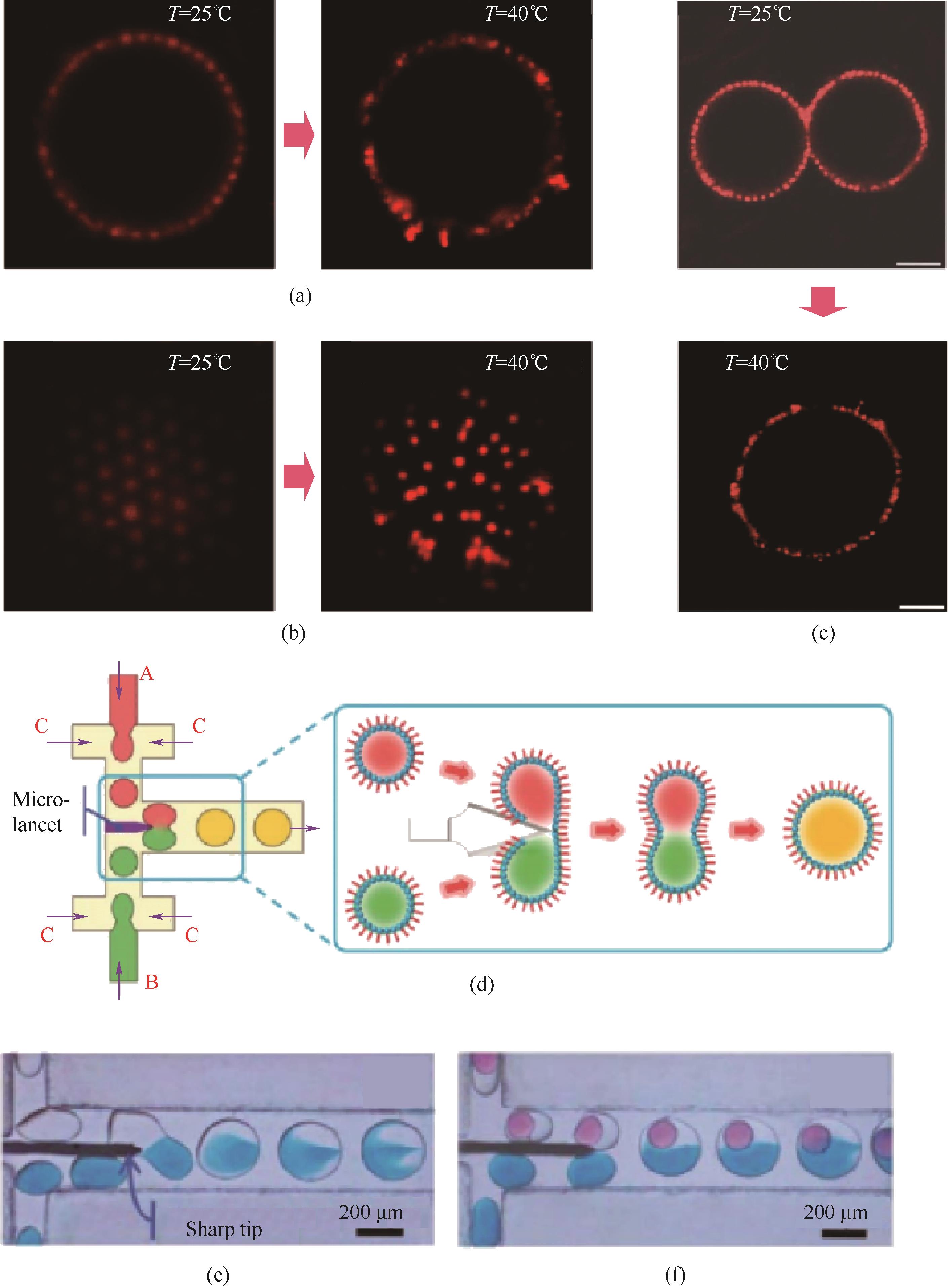
图2 乳液液滴融合过程中的介尺度结构调控。不同温度下液滴的赤道位置(a)和顶部位置(b)界面上荧光PNIPAM纳米颗粒的排布结构[17];(c)温控触发融合过程中液滴界面上荧光PNIPAM纳米颗粒的排布结构变化[17];(d)T型微通道中经金属微针介导的液滴融合过程示意图[18];T型微通道中经金属微针介导的单乳液滴对的融合过程(e)以及单乳液滴和双重乳液液滴融合过程(f)的高速摄像图[18]
Fig.2 Regulation of meso-scale structures of emulsion droplets during their coalescence process. Packing structures of fluorescent PNIPAM nanoparticles on the equator (a) and the top (b) of a droplet at different temperatures[17]. (c) Packing structural change of fluorescent PNIPAM nanoparticles at droplet interface during the temperature-triggered coalescence process[17]. (d) Schematic illustration showing the metal-microneedle-induced coalescence of emulsion droplets in T-junction microchannels[18]. High-speed snapshots showing the metal-microneedle-induced coalescence between two single emulsion droplets (e), and between one single emulsion droplet and one double emulsion droplet (f)[18]
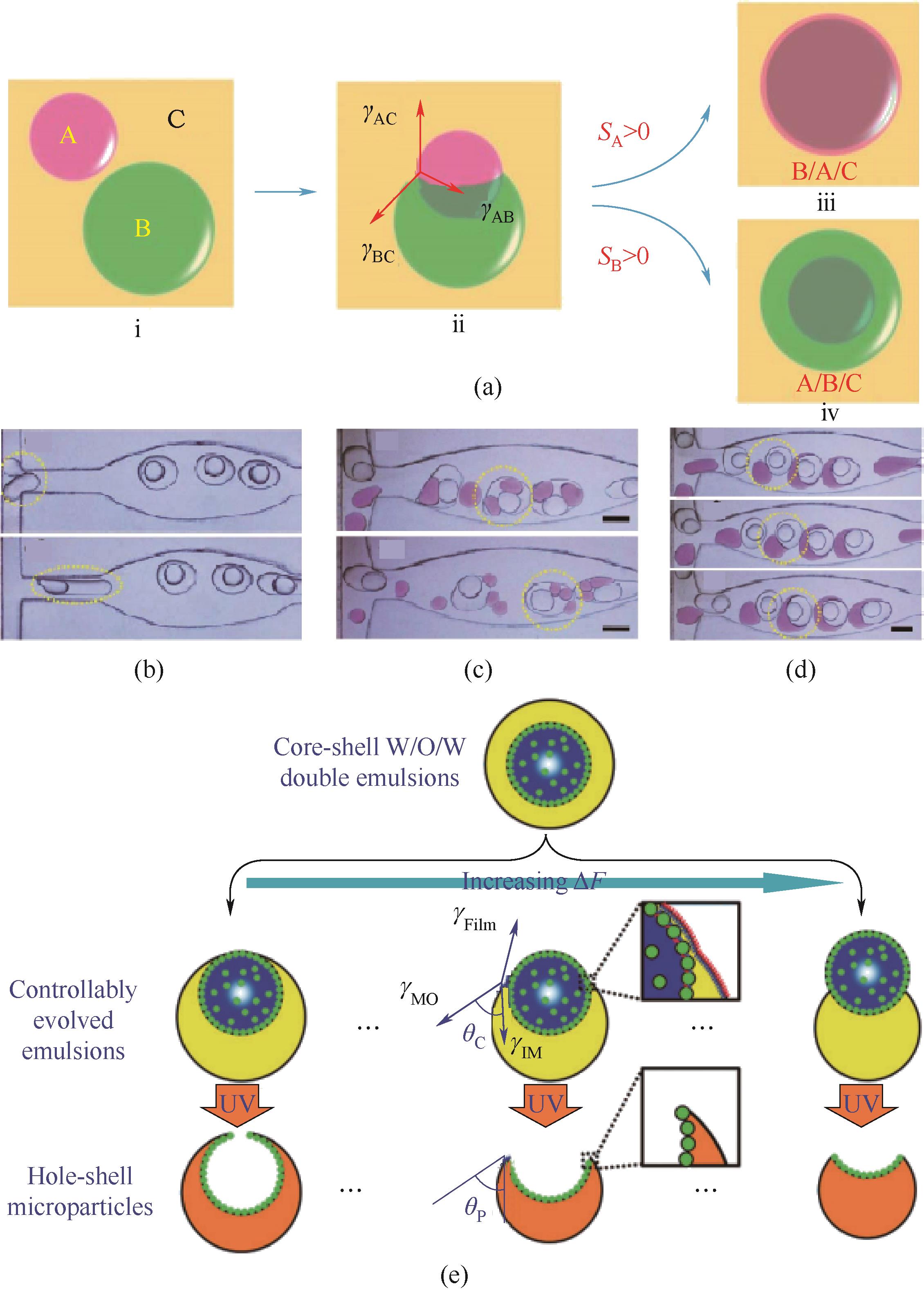
图3 乳液液滴在浸润吞并过程和反浸润演化过程中的介尺度结构调控。(a)液滴经选择性浸润吞并形成双重乳液液滴的示意图[20];微通道中液滴经浸润吞并形成单核双重乳液液滴(b)、多核双重乳液液滴(c)以及三重乳液液滴(d)的高速摄像图[20];(e)球形核壳型双重乳液液滴经反浸润演化形成非球形橡子型乳液液滴的示意图[22]
Fig.3 Regulation of meso-scale structures of emulsion droplets during their wetting-induced engulfment and dewetting-induced evolution processes. (a) Schematic illustration showing the formation of double emulsion droplets from selective wetting-induced engulfment between single emulsion droplets[20]. High-speed snapshots showing the formation process of single-core double emulsion droplets (b), multi-core double emulsion droplets (c), and triple emulsion droplets (d) via wetting-induced engulfment[20]. (e) Schematic illustration showing the dewetting-induced evolution from spherical core-shell double emulsion droplets to non-spherical acorn-like emulsion droplet[22]

图4 界面传质与自组装对微颗粒材料介尺度结构的调控。经可控跨界面传质和自组装过程由W/W型乳液液滴模板制备实心(a)和中空(b)PAH/PSS聚电解质微颗粒的示意图[23];(c)经可控跨界面传质和自组装过程由W/W型乳液液滴模板制备实心金纳米颗粒/PSS微颗粒的示意图[37];(d)实心金纳米颗粒/PSS微颗粒的扫描电镜图[37];(e)实心金纳米颗粒/PSS微颗粒制备过程的光学显微镜图[37]
Fig.4 Regulation of the meso-scale structures of microparticles via trans-interfacial mass transfer and self-assembly. Schematic illustrations showing the synthesis of solid (a) and hollow (b) PAH/PSS polyelectrolyte microparticles from W/W emulsion templates via controllable trans-interfacial mass transfer and self-assembly[23]. (c) Schematic illustrations showing the synthesis of solid Au-nanoparticle/PSS microparticles from W/W emulsion templates via controllable trans-interfacial mass transfer and self-assembly[37]. (d) SEM image of the solid nanoparticle/PSS microparticle[37]. (e) Optical microscopic snapshots showing the fabrication process of Au-nanoparticle/PSS microparticle[37]

图5 界面传质与反应对中空微颗粒材料的介尺度结构调控。(a)经跨界面传质和交联反应由W/O型乳液液滴模板制备中空壳聚糖微颗粒的示意图[25];(b)~(d)经界面传质和反应调控制得的不同结构中空壳聚糖微颗粒的激光共聚焦图[25]
Fig.5 Regulation of the meso-scale structures of hollow microparticles via trans-interfacial mass transfer and reaction. (a) Schematic illustrations showing the synthesis of hollow chitosan microparticles from W/O emulsion templates via trans-interfacial mass transfer and crosslinking reaction[25]. (b) — (d) Confocal laser scanning microscope images of hollow chitosan microparticles with different structures from regulation of trans-interfacial mass transfer and reaction[25]
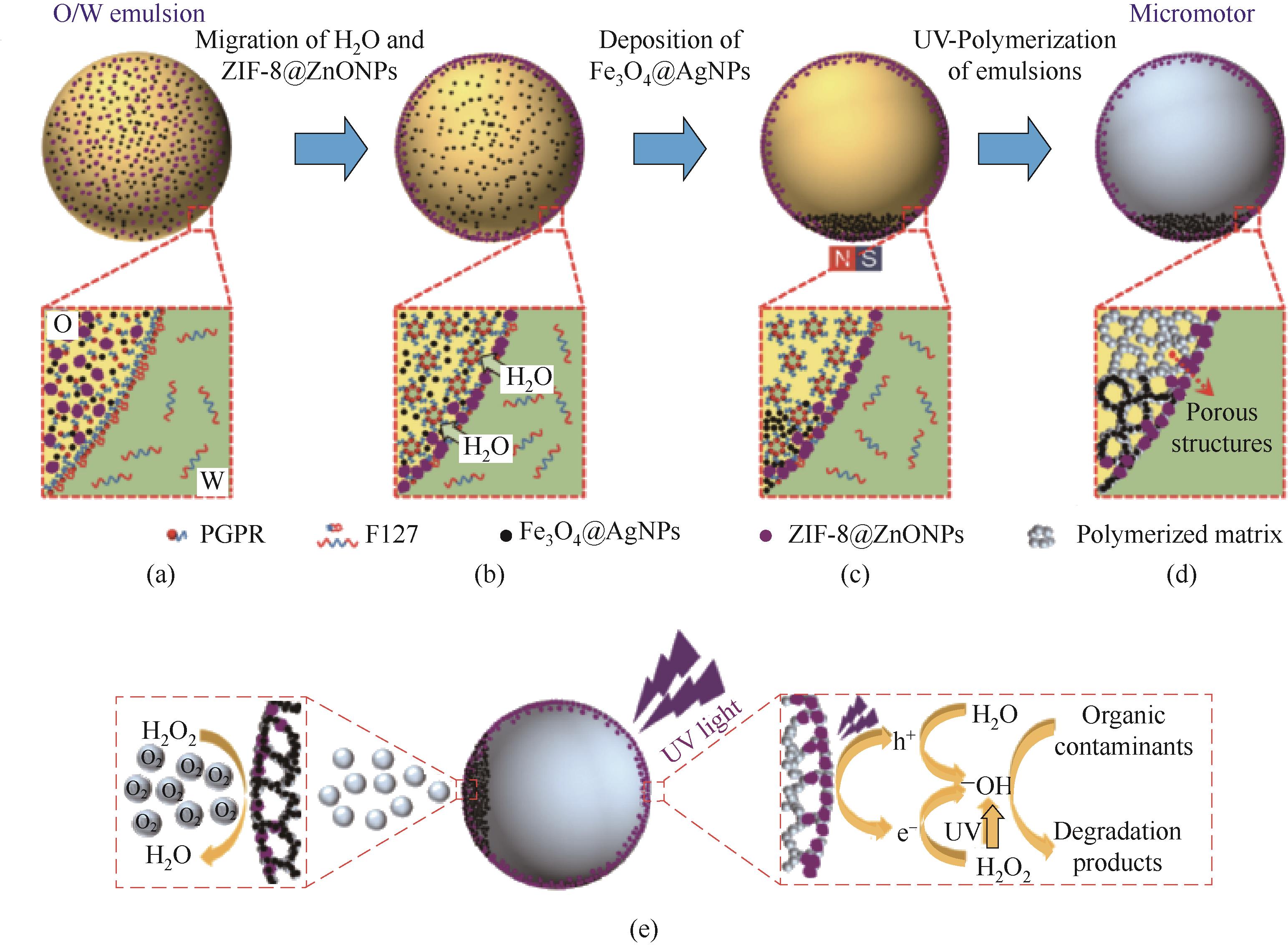
图6 界面传质与反应对多孔微颗粒材料的介尺度结构调控。(a)~(d)基于跨界面传质过程在乳液液滴内形成纳米级水滴作为致孔模板以构建具有多孔结构的气泡驱动型微颗粒的示意图[41];(e)气泡驱动型多孔微颗粒基于气泡驱动运动的传质强化和ZIF-8@ZnO的光催化降解耦合以有效降解水中有机污染物的示意图[41]
Fig.6 Regulation of the meso-scale structures of porous microparticles via trans-interfacial mass transfer and reaction. (a) — (d) Schematic illustrations showing the synthesis of bubble-propelled porous microparticles via creation of water nanodroplets in emulsion droplets as pore-forming templates induced by trans-interfacial mass transfer[41]. (e) Schematic illustrations showing the bubble-propelled porous microparticles for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water based on coupling mass-transfer intensification of bubble-propelled motion and photo-catalytic degradation of ZIF-8@ZnO[41]

图7 界面传质与反应对分级式多孔微颗粒材料的介尺度结构调控。(a)基于跨界面传质和反应过程由W/O/W型双重乳液液滴模板制备分级式多孔微颗粒示意图[39];具有分级式多孔结构的气泡驱动型功能微颗粒[40] (b)以及结合MIL-88A纳米颗粒的分级式多孔微颗粒(c)的扫描电镜图[42]
Fig.7 Regulation of the meso-scale structures of hierarchical porous microparticles via trans-interfacial mass transfer and reaction. (a) Schematic illustrations showing the synthesis of hierarchical porous microparticles from W/O/W double emulsions via trans-interfacial mass transfer and reaction[39]. SEM images of bubble-propelled hierarchical porous microparticles[40] (b), and hierarchical porous microparticles integrated with MIL-88A nanoparticles (c)[42]
| 31 | Geng Y H, Ling S D, Huang J P, et al. Multiphase microfluidics: fundamentals, fabrication, and functions[J]. Small, 2020, 16(6): 1906357. |
| 32 | Chong Z Z, Tan S H, Gañán-Calvo A M, et al. Active droplet generation in microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(1): 35-58. |
| 33 | He F, Wang W, He X H, et al. Controllable multicompartmental capsules with distinct cores and shells for synergistic release[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(13): 8743-8754. |
| 34 | Aronson M P, Princen H M. Contact angles associated with thin liquid films in emulsions[J]. Nature, 1980, 286(5771): 370-372. |
| 35 | Poulin P, Bibette J. Adhesion of water droplets in organic solvent[J]. Langmuir, 1998, 14(22): 6341-6343. |
| 36 | Li Z L, Wang W, Li M, et al. Facile fabrication of bubble-propelled micromotors carrying nanocatalysts for water remediation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(13): 4562-4570. |
| 37 | Fu G B, Xie R, Qin J W, et al. Facile fabrication of photocatalyst-immobilized gel beads with interconnected macropores for the efficient removal of pollutants in water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(24): 8762-8775. |
| 38 | Zhang M J, Chen T, Zhang P, et al. Magnetic hierarchical porous SiO2 microparticles from droplet microfluidics for water decontamination[J]. Soft Matter., 2020, 16(10): 2581-2593. |
| 39 | Zhang M J, Wang W, Yang X L, et al. Uniform microparticles with controllable highly interconnected hierarchical porous structures[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(25): 13758-13767. |
| 40 | Su Y Y, Zhang M J, Wang W, et al. Bubble-propelled hierarchical porous micromotors from evolved double emulsions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(4): 1590-1600. |
| 41 | Chen L, Zhang M J, Zhang S Y, et al. Simple and continuous fabrication of self-propelled micromotors with photocatalytic metal-organic frameworks for enhanced synergistic environmental remediation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(31): 35120-35131. |
| 42 |
Zhang P, Li Y H, Chen L, et al. Hierarchical porous metal-organic frameworks/polymer microparticles for enhanced catalytic degradation of organic contaminants[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2022, DOI: 10.1007/s11705-022-2152-4 .
DOI |
| 1 | Wang W, Zhang M J, Chu L Y. Functional polymeric microparticles engineered from controllable microfluidic emulsions[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2014, 47(2): 373-384. |
| 2 | 苏瑶瑶, 李平凡, 汪伟, 等. 微流控液滴模板法可控构建功能微颗粒材料[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 42-60. |
| Su Y Y, Li P F, Wang W, et al. Controllable fabrication of functional microparticle materials from microfluidic droplet templates[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 42-60. | |
| 3 | Zhang M J, Zhang P, Qiu L D, et al. Controllable microfluidic fabrication of microstructured functional materials[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2020, 14(6): 061501. |
| 4 | Liu W Y, Wang W, Ju X J, et al. Functional microparticles from multiscale regulation of multiphase emulsions for mass-transfer intensification[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 231: 116242. |
| 5 | Abbaspourrad A, Carroll N J, Kim S H, et al. Surface functionalized hydrophobic porous particles toward water treatment application[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(23): 3215-3221. |
| 6 | Zhang M J, Wang W, Xie R, et al. Controllable microfluidic strategies for fabricating microparticles using emulsions as templates[J]. Particuology, 2016, 24: 18-31. |
| 7 | 汪伟, 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 等. 微流控法制备新型微颗粒功能材料研究新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2555-2562. |
| Wang W, Xie R, Ju X J, et al. Recent progress of microfluidic fabrication of novel functional microparticles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2555-2562. | |
| 8 | 蔡泉威, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 等. 微流控技术可控制备异形微颗粒功能材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 3738-3747. |
| Cai Q W, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Recent progress in controllable preparation of anisotropic microparticle functional materials based on microfluidics[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 3738-3747. | |
| 9 | Tang M J, Wang W, Li Z L, et al. Controllable microfluidic fabrication of magnetic hybrid microswimmers with hollow helical structures[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(29): 9430-9438. |
| 10 | Cai Q W, Ju X J, Chen C, et al. Fabrication and flow characteristics of monodisperse bullet-shaped microparticles with controllable structures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 370: 925-937. |
| 11 | 褚良银, 汪伟, 巨晓洁, 等. 微流控法构建微尺度相界面及制备新型功能材料研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(9): 2229-2234. |
| Chu L Y, Wang W, Ju X J, et al. Progress of construction of micro-scale phase interfaces and preparation of novel functional materials with microfluidics[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(9): 2229-2234. | |
| 12 | Li W, Zhang L Y, Ge X H, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of microparticles for biomedical applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(15): 5646-5683. |
| 13 | He F, Zhang M J, Wang W, et al. Designable polymeric microparticles from droplet microfluidics for controlled drug release[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(6): 1800687. |
| 14 | Chen L, Yang C, Xiao Y, et al. Millifluidics, microfluidics, and nanofluidics: manipulating fluids at varying length scales[J]. Materials Today Nano, 2021, 16: 100136. |
| 15 | 何晓恒, 褚良银. 微流控模板法制备功能化非球形微颗粒研究新进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(9): 4109-4118. |
| He X H, Chu L Y. Recent progress of fabrication of functional non-spherical microparticles from microfluidic templates[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(9): 4109-4118. | |
| 16 | Sun Z, Yan X X, Xiao Y, et al. Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal surfactants: role of solid particles[J]. Particuology, 2022, 64: 153-163. |
| 17 | Sun J, Wang W, He F, et al. On-chip thermo-triggered coalescence of controllable Pickering emulsion droplet pairs[J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6: 64182-64192. |
| 18 | Deng N N, Sun S X, Wang W, et al. A novel surgery-like strategy for droplet coalescence in microchannels[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13(18): 3653-3657. |
| 19 | Deng N N, Sun J, Wang W, et al. Wetting-induced coalescence of nanoliter drops as microreactors in microfluidics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(6): 3817-3821. |
| 20 | Deng N N, Wang W, Ju X J, et al. Wetting-induced formation of controllable monodisperse multiple emulsions in microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13(20): 4047-4052. |
| 21 | Deng N N, Wang W, Ju X J, et al. Spontaneous transfer of droplets across microfluidic laminar interfaces[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(22): 4326-4332. |
| 22 | Wang W, Zhang M J, Xie R, et al. Hole-shell microparticles from controllably evolved double emulsions[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2013, 125(31): 8242-8245. |
| 23 | Ma Q M, Song Y, Kim J W, et al. Affinity partitioning-induced self-assembly in aqueous two-phase systems: templating for polyelectrolyte microcapsules[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2016, 5(6): 666-670. |
| 24 | Ma Q M, Yuan H, Song Y, et al. Partitioning-dependent conversion of polyelectrolyte assemblies in an aqueous two-phase system[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14(9): 1552-1558. |
| 25 | Mu X T, Li Y, Ju X J, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of structure-controlled chitosan microcapsules via interfacial cross-linking of droplet templates[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(51): 57514-57525. |
| 26 | Mu X T, Ju X J, Zhang L, et al. Chitosan microcapsule membranes with nanoscale thickness for controlled release of drugs[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 590: 117275. |
| 27 | Peng H Y, Wang W, Xie R, et al. Mesoscale regulation of droplet templates to tailor microparticle structures and functions[J]. Particuology, 2020, 48: 74-87. |
| 28 | 汪伟, 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 等. 液滴模板法制备颗粒材料过程中介尺度结构调控的研究进展[J]. 化学进展, 2018, 30(1): 44-50. |
| Wang W, Xie R, Ju X J, et al. Progress on control of meso-scale structures for droplet-template syntheses of particle materials[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2018, 30(1): 44-50. | |
| 29 | 李洪钟. 聚焦结构、界面与多尺度问题, 开辟化学工程的新里程[J]. 过程工程学报, 2006, 6(6): 991-996. |
| Li H Z. Focus attention on structure, interface and multi-scale issues to open up new mileage of chemical engineering[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006, 6(6): 991-996. | |
| 30 | Chao Y C, Mak S Y, Shum H C. The transformation dynamics towards equilibrium in non-equilibrium W/W/O double emulsions[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 109(18): 181601. |
| [1] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [2] | 汤晓玲, 王嘉瑞, 朱玄烨, 郑仁朝. 基于Pickering乳液的卤醇脱卤酶催化合成手性环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [3] | 徐文超, 孙志高, 李翠敏, 李娟, 黄海峰. 静态条件下表面活性剂E-1310对HCFC-141b水合物生成的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2179-2185. |
| [4] | 邓璐, 巨晓洁, 张文杰, 谢锐, 汪伟, 刘壮, 潘大伟, 褚良银. 微流控法可控制备放射性壳聚糖栓塞微球[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1781-1794. |
| [5] | 贾露凡, 王艺颖, 董钰漫, 李沁园, 谢鑫, 苑昊, 孟涛. 微流控双水相贴壁液滴流动强化酶促反应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [6] | 陈余, 郑晓妍, 赵辉, 王二强, 李杰, 李春山. Pickering乳液催化非均相羟醛缩合反应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 449-458. |
| [7] | 黄心童, 耿宇昊, 刘恒源, 陈卓, 徐建鸿. 微流控制备新型功能纳米粒子研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 355-364. |
| [8] | 廖艺, 牛亚宾, 潘艳秋, 俞路. 复配表面活性剂对油水界面行为和性质影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4003-4014. |
| [9] | 李承威, 骆华勇, 张铭轩, 廖鹏, 方茜, 荣宏伟, 王竞茵. 氢氧化镧交联壳聚糖微球的微流控制备及其除磷性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3929-3939. |
| [10] | 徐珂, 史国强, 薛冬峰. 无机杂化钙钛矿团簇材料:介尺度钙钛矿材料发光性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2748-2756. |
| [11] | 王利民, 郭舒宇, 向星, 付少童. 湍流系统的能量最小多尺度模型研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2415-2426. |
| [12] | 唐天琪, 何玉荣. 磁场对湿颗粒流化床系统中介尺度结构影响机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2636-2648. |
| [13] | 陈泉, 郑泽希, 李然, 孙其诚, 杨晖. 散斑能见度光谱法测量筒仓内颗粒流的颗粒温度[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2603-2611. |
| [14] | 牛犁, 刘梦溪, 王海北. 密相流化床中介尺度流动结构的流体力学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2622-2635. |
| [15] | 刘怡琳, 李钰, 余亚雄, 黄哲庆, 周强. 基于重置温度方法的双参数介尺度气固传热模型构建[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2612-2621. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号