化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3588-3599.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240634
颜诗宇1( ), 高姣姣1, 杨太顺1, 谢尚志1, 杨艳娟1, 徐晶1,2(
), 高姣姣1, 杨太顺1, 谢尚志1, 杨艳娟1, 徐晶1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-07
修回日期:2024-07-08
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
徐晶
作者简介:颜诗宇(1998—),女,硕士研究生,1090336837@qq.com
基金资助:
Shiyu YAN1( ), Jiaojiao GAO1, Taishun YANG1, Shangzhi XIE1, Yanjuan YANG1, Jing XU1,2(
), Jiaojiao GAO1, Taishun YANG1, Shangzhi XIE1, Yanjuan YANG1, Jing XU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-06-07
Revised:2024-07-08
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Jing XU
摘要:
聚乙烯氢解可以产生多种碳氢化合物,产品分布非常宽,产物选择性调控具有一定挑战性。通过调控钌负载量制备了不同钌粒径的Ru/CeO2催化剂,利用TEM、in situ DRIFTS和模型计算等多种技术,发现聚乙烯催化氢解的产物分布与钌金属配位环境密切相关。表征和模型计算表明,不同尺寸的钌纳米颗粒具有不同的几何结构和配位环境。钌平均粒径为0.85 nm时,低配位的边/角位点占主导,其C2~C40选择性达到92%。钌平均粒径达到2.75 nm时,高配位的平台位点占主导,C2~C40选择性仅为8%,甲烷选择性高达92%。结合截断六角双锥模型和CO-DRIFTS实验,推断Ru/CeO2催化剂上产物的选择性可能与聚乙烯氢解中间体和钌纳米颗粒表面的相互作用有关,提出了Ru/CeO2催化剂上聚乙烯氢解两种反应路径与配位环境的关系。
中图分类号:
颜诗宇, 高姣姣, 杨太顺, 谢尚志, 杨艳娟, 徐晶. 钌基催化剂配位环境对聚乙烯氢解性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3588-3599.
Shiyu YAN, Jiaojiao GAO, Taishun YANG, Shangzhi XIE, Yanjuan YANG, Jing XU. Effect of coordination environment of ruthenium-based catalysts on their performance for polyethylene hydrogenolysis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3588-3599.
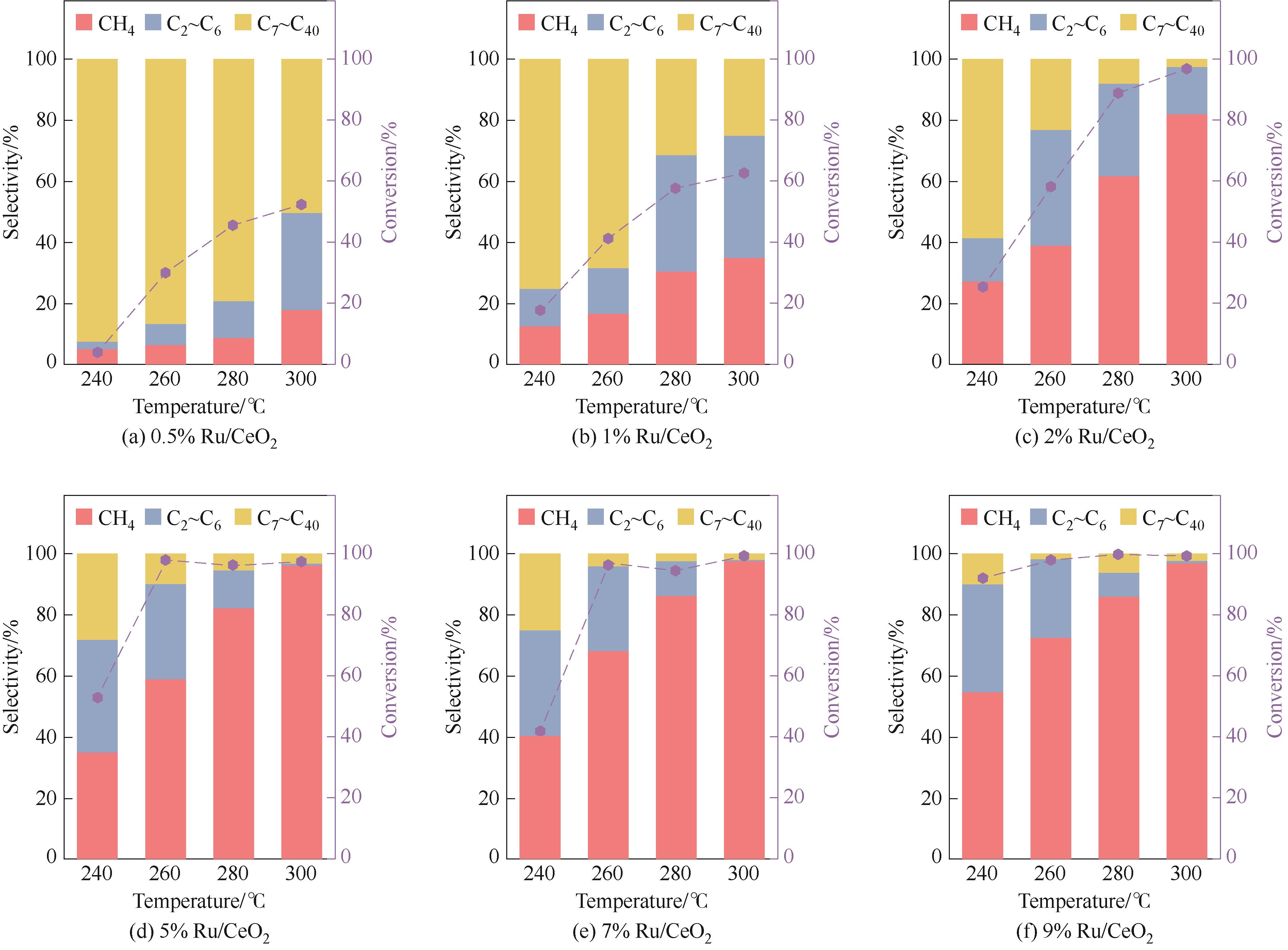
图1 不同钌负载量的Ru/CeO2催化剂的性能评价(反应条件:1 g PE,50 mg Ru/CeO2,3.5 MPa H2,500 r/min,4 h)
Fig.1 Performance evaluation of Ru/CeO2 catalysts with different Ru loadings(reaction conditions: 1 g PE, 50 mg Ru/CeO2, 3.5 MPa H2, 500 r/min, 4 h)
| 催化剂 | 产率/% | 转化率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2~C6 | C7~C40 | ||
| CeO2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 1.4 |
表1 纯CeO2载体的性能评价
Table 1 Performance evaluation of CeO2 support
| 催化剂 | 产率/% | 转化率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2~C6 | C7~C40 | ||
| CeO2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 1.4 |

图2 相同钌投入量的Ru/CeO2催化剂的性能评价[反应条件:1 g PE,Ru/CeO2 (1 mg Ru),3.5 MPa H2,500 r/min,4 h]
Fig.2 Performance evaluation of Ru/CeO2 catalysts with the same Ru amount[reaction conditions: 1 g PE, Ru/CeO2 (1 mg Ru), 3.5 MPa H2, 500 r/min, 4 h]
| 催化剂 | 钌含量① /% | 比表面积②/(m2/g) | 孔容③ /(cm3/g) | 平均孔径④/nm | 钌平均粒径⑤/nm | 钌金属分散度⑥/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | — | 16.4 | 0.045 | 6.66 | — | — |
| 0.5% Ru/CeO2 | 0.38 | 17.9 | 0.051 | 7.25 | 0.85 | 100 |
| 2% Ru/CeO2 | 1.83 | 18.8 | 0.049 | 7.12 | 1.55 | 85 |
| 9% Ru/CeO2 | 8.58 | 13.0 | 0.028 | 8.41 | 2.75 | 48 |
表2 催化剂的结构参数
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of the catalysts
| 催化剂 | 钌含量① /% | 比表面积②/(m2/g) | 孔容③ /(cm3/g) | 平均孔径④/nm | 钌平均粒径⑤/nm | 钌金属分散度⑥/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | — | 16.4 | 0.045 | 6.66 | — | — |
| 0.5% Ru/CeO2 | 0.38 | 17.9 | 0.051 | 7.25 | 0.85 | 100 |
| 2% Ru/CeO2 | 1.83 | 18.8 | 0.049 | 7.12 | 1.55 | 85 |
| 9% Ru/CeO2 | 8.58 | 13.0 | 0.028 | 8.41 | 2.75 | 48 |
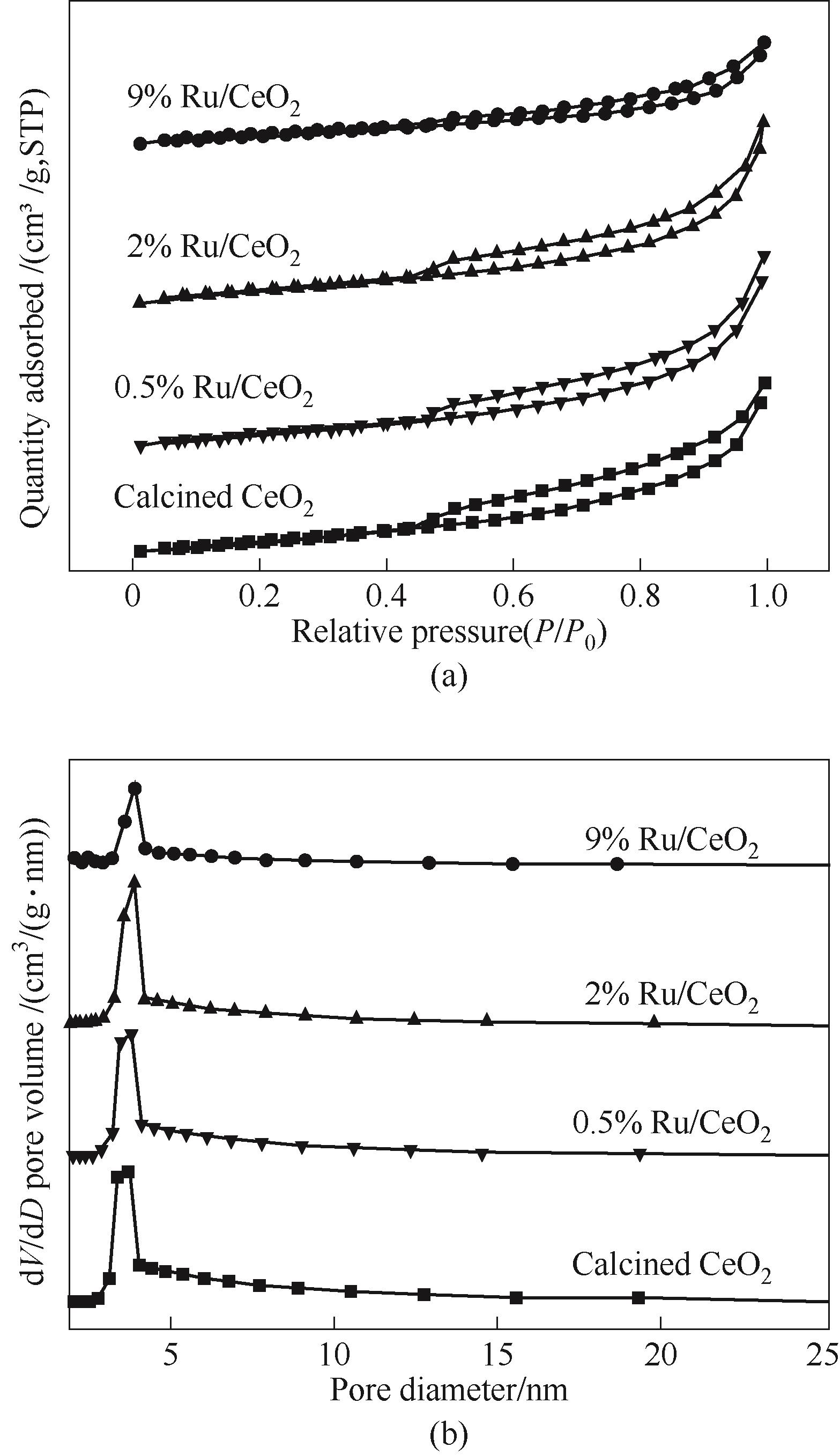
图3 CeO2和还原后的Ru/CeO2催化剂的氮气脱附曲线(a)和孔径分布(b)
Fig.3 Nitrogen desorption curves (a) and pore size distribution (b) of CeO2 and Ru/CeO2 catalysts after reduction
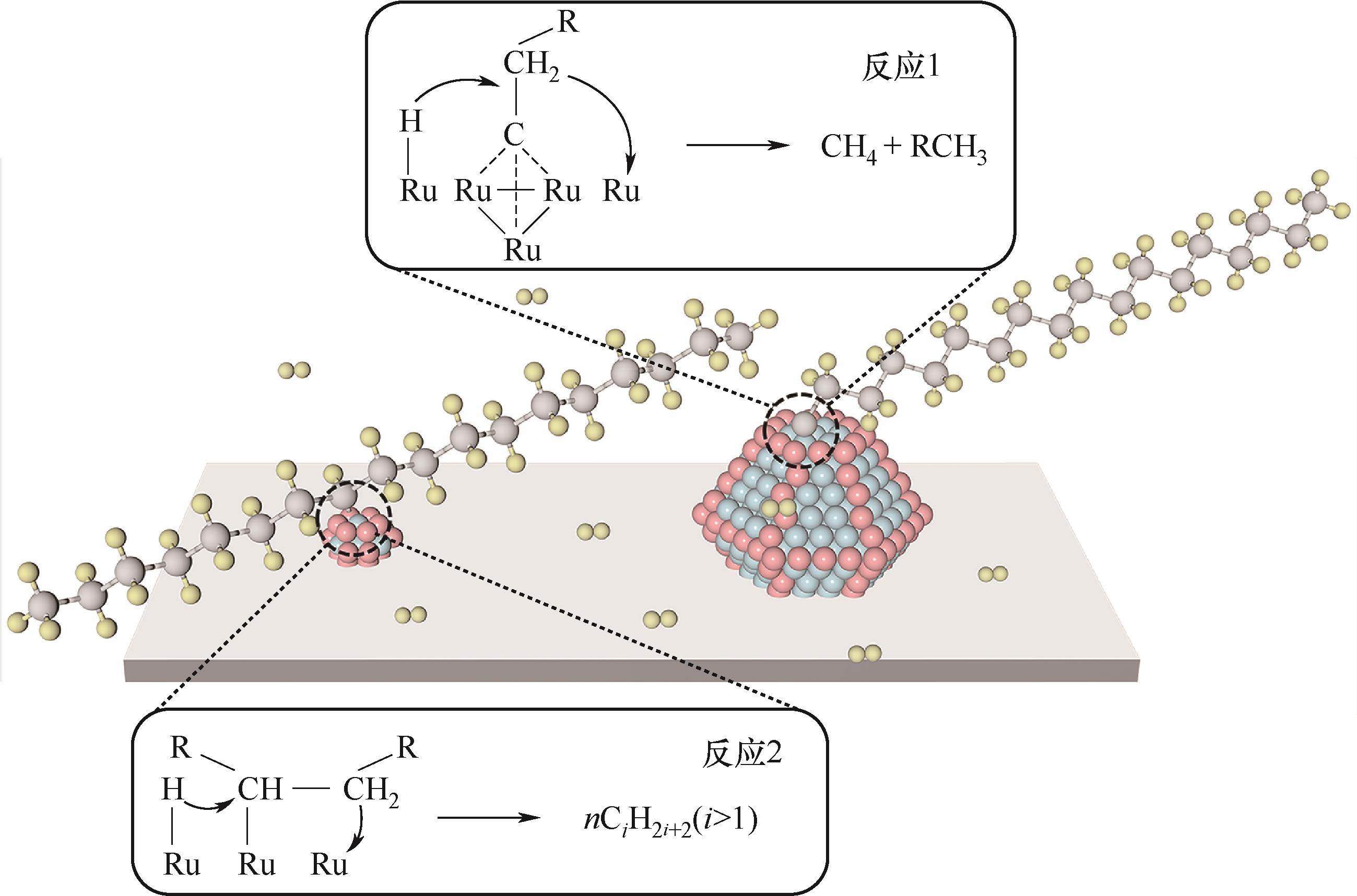
图11 Ru/CeO2催化PE氢解的两种可能反应机制(参考文献[45])
Fig.11 Two possible mechanisms with which hydrogenolysis on the surface of Ru/CeO2 could proceed (based on the works of Ref.[45])
| 1 | van Fan Y, Jiang P, Tan R R, et al. Forecasting plastic waste generation and interventions for environmental hazard mitigation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127330. |
| 2 | Ali W, Ali H, Souissi S, et al. Are bioplastics an ecofriendly alternative to fossil fuel plastics?[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2023, 21(4): 1991-2002. |
| 3 | Kunwar B, Cheng H N, Chandrashekaran S R, et al. Plastics to fuel: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 54: 421-428. |
| 4 | Bunescu A, Lee S, Li Q, et al. Catalytic hydroxylation of polyethylenes[J]. ACS Central Science, 2017, 3(8): 895-903. |
| 5 | Schwab S T, Baur M, Nelson T F, et al. Synthesis and deconstruction of polyethylene-type materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(5): 2327-2351. |
| 6 | Faraca G, Astrup T. Plastic waste from recycling centres: characterisation and evaluation of plastic recyclability[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 95: 388-398. |
| 7 | Zhang F, Zeng M H, Yappert R D, et al. Polyethylene upcycling to long-chain alkylaromatics by tandem hydrogenolysis/aromatization[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6515): 437-441. |
| 8 | Celik G, Kennedy R M, Hackler R A, et al. Upcycling single-use polyethylene into high-quality liquid products[J]. ACS Central Science, 2019, 5(11): 1795-1803. |
| 9 | Yuan X Z, Cho M K, Lee J G, et al. Upcycling of waste polyethylene terephthalate plastic bottles into porous carbon for CF4 adsorption[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 114868. |
| 10 | Lee W T, van Muyden A, Bobbink F D, et al. Mechanistic classification and benchmarking of polyolefin depolymerization over silica-alumina-based catalysts[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4850. |
| 11 | Rorrer J E, Troyano-Valls C, Beckham G T, et al. Hydrogenolysis of polypropylene and mixed polyolefin plastic waste over Ru/C to produce liquid alkanes[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(35): 11661-11666. |
| 12 | Rorrer J E, Beckham G T, Román-Leshkov Y. Conversion of polyolefin waste to liquid alkanes with Ru-based catalysts under mild conditions[J]. JACS Au, 2020, 1(1): 8-12. |
| 13 | Fihri A, Bouhrara M, Patil U, et al. Fibrous nano-silica supported ruthenium (KCC-1/Ru): a sustainable catalyst for the hydrogenolysis of alkanes with good catalytic activity and lifetime[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2012, 2(7): 1425-1431. |
| 14 | Lee W T, Bobbink F D, van Muyden A P, et al. Catalytic hydrocracking of synthetic polymers into grid-compatible gas streams[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2021, 2(2): 100332. |
| 15 | Chen L X, Zhu Y F, Meyer L C, et al. Effect of reaction conditions on the hydrogenolysis of polypropylene and polyethylene into gas and liquid alkanes[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 7(4): 844-854. |
| 16 | Nakaji Y, Tamura M, Miyaoka S, et al. Low-temperature catalytic upgrading of waste polyolefinic plastics into liquid fuels and waxes[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 285: 119805. |
| 17 | Wang C, Xie T J, Kots P A, et al. Polyethylene hydrogenolysis at mild conditions over ruthenium on tungstated zirconia[J]. JACS Au, 2021, 1(9): 1422-1434. |
| 18 | Kim T, Nguyen-Phu H, Kwon T, et al. Investigating the impact of TiO2 crystalline phases on catalytic properties of Ru/TiO2 for hydrogenolysis of polyethylene plastic waste[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 331: 121876. |
| 19 | Jaydev S D, Martín A J, Pérez-Ramírez J. Direct conversion of polypropylene into liquid hydrocarbons on carbon-supported platinum catalysts[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(23): 5179-5185. |
| 20 | Pinzón M, Romero A, de Lucas Consuegra A, et al. Hydrogen production by ammonia decomposition over ruthenium supported on SiC catalyst[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2021, 94: 326-335. |
| 21 | Sakpal T, Lefferts L. Structure-dependent activity of CeO2 supported Ru catalysts for CO2 methanation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 367: 171-180. |
| 22 | Guo Y, Mei S, Yuan K, et al. Low-temperature CO2 methanation over CeO2-supported Ru single atoms, nanoclusters, and nanoparticles competitively tuned by strong metal–support interactions and H-spillover effect[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(7): 6203-6215. |
| 23 | Mi R L, Li D, Hu Z, et al. Morphology effects of CeO2 nanomaterials on the catalytic combustion of toluene: a combined kinetics and diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy study[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(13): 7876-7889. |
| 24 | Wang C F, Sun H M, Liu X Q, et al. Low-temperature CO2 methanation over Ru/CeO2: investigation into Ru loadings[J]. Fuel, 2023, 345: 128238. |
| 25 | Bezkrovnyi O, Vorokhta M, Pawlyta M, et al. In situ observation of highly oxidized Ru species in Ru/CeO2 catalyst under propane oxidation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(31): 16675-16684. |
| 26 | Liao W Q, Yue M N, Chen J Y, et al. Decoupling the interfacial catalysis of CeO2-supported Rh catalysts tuned by CeO2 morphology and Rh particle size in CO2 hydrogenation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(8): 5767-5779. |
| 27 | Wang J, Wei Z Z, Mao S J, et al. Highly uniform Ru nanoparticles over N-doped carbon: pH and temperature-universal hydrogen release from water reduction[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(4): 800-806. |
| 28 | Zhang Q, Kusada K, Wu D S, et al. Selective control of FCC and hcp crystal structures in Au-Ru solid-solution alloy nanoparticles[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 510. |
| 29 | Ye M X, Li Y R, Yang Z R, et al. Ruthenium/TiO2-catalyzed hydrogenolysis of polyethylene terephthalate: reaction pathways dominated by coordination environment[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(19): e202301024. |
| 30 | Mahmood J, Li F, Jung S M, et al. An efficient and pH-universal ruthenium-based catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(5): 441-446. |
| 31 | Van Hardeveld R, Hartog F. The statistics of surface atoms and surface sites on metal crystals[J]. Surface Science, 1969, 15(2): 189-230. |
| 32 | Kim T W, Kim D, Jo Y, et al. Potassium as the best alkali metal promoter in boosting the hydrogenation activity of Ru/MgO for aromatic LOHC molecules by facilitated heterolytic H2 adsorption[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 419: 112-124. |
| 33 | Kim T W, Chun H J, Jo Y, et al. Electronic vs. geometric effects of Al2O3-supported Ru species on the adsorption of H2 and substrate for aromatic LOHC hydrogenation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 428: 115178. |
| 34 | Matsubu J C, Yang V N, Christopher P. Isolated metal active site concentration and stability control catalytic CO2 reduction selectivity[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(8): 3076-3084. |
| 35 | Lyu S S, Cheng Q P, Liu Y H, et al. Dopamine sacrificial coating strategy driving formation of highly active surface-exposed Ru sites on Ru/TiO2 catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 278: 119261. |
| 36 | Kellner C S, Bell A T. Effects of dispersion on the activity and selectivity of alumina-supported ruthenium catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1982, 75(2): 251-261. |
| 37 | Abdel-Mageed A M, Widmann D, Olesen S E, et al. Selective CO methanation on Ru/TiO2 catalysts: role and influence of metal-support interactions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(11): 6753-6763. |
| 38 | Chen S L, Abdel-Mageed A M, Li D, et al. Morphology-engineered highly active and stable Ru/TiO2 catalysts for selective CO methanation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(31): 10732-10736. |
| 39 | Yu H L, Wei Y, Lin T J, et al. Identifying the performance descriptor in direct syngas conversion to long-chain α-olefins over ruthenium-based catalysts promoted by alkali metals[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(6): 3949-3959. |
| 40 | Kale M J, Christopher P. Utilizing quantitative in situ FTIR spectroscopy to identify well-coordinated Pt atoms as the active site for CO oxidation on Al2O3-supported Pt catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(8): 5599-5609. |
| 41 | Jia C H, Xie S Q, Zhang W L, et al. Deconstruction of high-density polyethylene into liquid hydrocarbon fuels and lubricants by hydrogenolysis over Ru catalyst[J]. Chem Catalysis, 2021, 1(2): 437-455. |
| 42 | Flaherty D W, Iglesia E. Transition-state enthalpy and entropy effects on reactivity and selectivity in hydrogenolysis of n-alkanes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(49): 18586-18599. |
| 43 | Flaherty D W, Hibbitts D D, Iglesia E. Metal-catalyzed C—C bond cleavage in alkanes: effects of methyl substitution on transition-state structures and stability[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(27): 9664-9676. |
| 44 | Xie T J, Wittreich G R, Vlachos D G. Multiscale modeling of hydrogenolysis of ethane and propane on Ru(0001): implications for plastics recycling[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 316: 121597. |
| 45 | Nakagawa Y, Oya S I, Kanno D, et al. Regioselectivity and reaction mechanism of Ru-catalyzed hydrogenolysis of squalane and model alkanes[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(1): 189-198. |
| [1] | 王冉, 王焕, 熊晓云, 关慧敏, 郑云锋, 陈彩琳, 秦玉才, 宋丽娟. FCC催化剂传质强化活性位利用效率的可视化分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3198-3209. |
| [2] | 胡德政, 王榕, 王世栋, 杨文菲, 张宏伟, 袁珮. 兼具加氢和脱硫活性的富含Ni δ+非晶态NiP@γ-Al2O3催化剂的构筑及其用于石油树脂加氢的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3152-3162. |
| [3] | 王树振, 王玉婷, 马梦茜, 张巍, 向江南, 鲁海莹, 王琰, 范彬彬, 郑家军, 代卫炯, 李瑞丰. 两步晶化合成ZSM-22分子筛及其临氢异构反应性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3176-3187. |
| [4] | 刘亚超, 谭晓杰, 李旭东, 王瑞, 王慧, 韩璇, 赵青山. DES合成高活性CoCO3纳米片及析氧反应性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3320-3328. |
| [5] | 张梦婷, 王书林, 桑熙, 元兴昊, 徐刚. 人工Cu-TM1459金属酶催化不对称迈克尔加成反应[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3255-3265. |
| [6] | 刘旭升, 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 电催化二氧化碳还原制备气态产物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2385-2408. |
| [7] | 罗莉, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 氧化铝结构与表面性质调控及其催化甲醇脱水制二甲醚性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2522-2532. |
| [8] | 李沛奇, 陈雪娇, 武博翔, 蒋榕培, 杨超, 刘朝晖. 高参数石油基和煤基火箭煤油射线法密度测量实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2422-2432. |
| [9] | 王寅, 初鹏飞, 刘虎, 吕静, 黄守莹, 王胜平, 马新宾. 不同pH铝溶胶对二甲醚羰基化成型丝光沸石催化剂性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2533-2543. |
| [10] | 杨露, 刘聪聪, 孟彤彤, 张博远, 杨腾飞, 邓文安, 王晓斌. 分散型催化剂在煤/重油共炼体系中的加氢抑焦作用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2556-2564. |
| [11] | 王天闻, 闫肃, 赵梦园, 杨天让, 刘建国. 固体氧化物电池空气电极铬中毒机理及抗铬性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2091-2108. |
| [12] | 丁禹, 杨昌泽, 李军, 孙会东, 商辉. 原子尺度钼系加氢脱硫催化剂的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1735-1749. |
| [13] | 赵亭亭, 鄢立祥, 唐福利, 肖敏之, 谭烨, 宋刘斌, 肖忠良, 李灵均. 光辅助锂-二氧化碳电池催化剂的设计策略与反应机理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1750-1764. |
| [14] | 莫锦洪, 韩雪, 朱毅翔, 李菁, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. Pt-Ga/CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3脱氢裂解双功能催化剂用于正丁烷催化制烯烃研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1855-1869. |
| [15] | 黄志鸿, 周利, 柴士阳, 吉旭. 耦合加氢装置优化的多周期氢网络集成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1951-1965. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号