CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (12): 5754-5762.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200360
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xiaohui( ),XU Qiang,ZHENG Huaxing,SUN Changyu,CHEN Guangjin(
),XU Qiang,ZHENG Huaxing,SUN Changyu,CHEN Guangjin( )
)
Received:2020-04-07
Revised:2020-06-22
Online:2020-12-05
Published:2020-12-05
Contact:
CHEN Guangjin
通讯作者:
陈光进
作者简介:王晓辉(1987—),男,博士,讲师,基金资助:CLC Number:
WANG Xiaohui,XU Qiang,ZHENG Huaxing,SUN Changyu,CHEN Guangjin. Energy efficiency analysis of natural gas hydrates production method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5754-5762.
王晓辉,许强,郑华星,孙长宇,陈光进. 天然气水合物置换开采的能源效率研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5754-5762.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 组分 | 组成/% |
|---|---|
| N2 | 75.60 |
| O2 | 20.34 |
| H2O | 3.12 |
| CO2 | 0.03 |
| Ar | 0.91 |
| Ne | 0.0018 |
| He | 0.00052 |
Table 1 The standard compositions of air
| 组分 | 组成/% |
|---|---|
| N2 | 75.60 |
| O2 | 20.34 |
| H2O | 3.12 |
| CO2 | 0.03 |
| Ar | 0.91 |
| Ne | 0.0018 |
| He | 0.00052 |
| 条件 | 焓,H/(kJ/mol) | 熵, S/(J/(mol·K)) |
|---|---|---|
| 基态(0℃, 0.1 MPa) | 8.8 | 44 |
| 运输条件(-20℃, 2 MPa) | 6.797 | 36.653 |
| 注入条件(20℃, 15 MPa) | 10.406 | 47.64 |
| 回注条件(20℃, 0.1 MPa) | 22.076 | 119.93 |
Table 2 The enthalpy and entropy of CO2 under different conditions
| 条件 | 焓,H/(kJ/mol) | 熵, S/(J/(mol·K)) |
|---|---|---|
| 基态(0℃, 0.1 MPa) | 8.8 | 44 |
| 运输条件(-20℃, 2 MPa) | 6.797 | 36.653 |
| 注入条件(20℃, 15 MPa) | 10.406 | 47.64 |
| 回注条件(20℃, 0.1 MPa) | 22.076 | 119.93 |
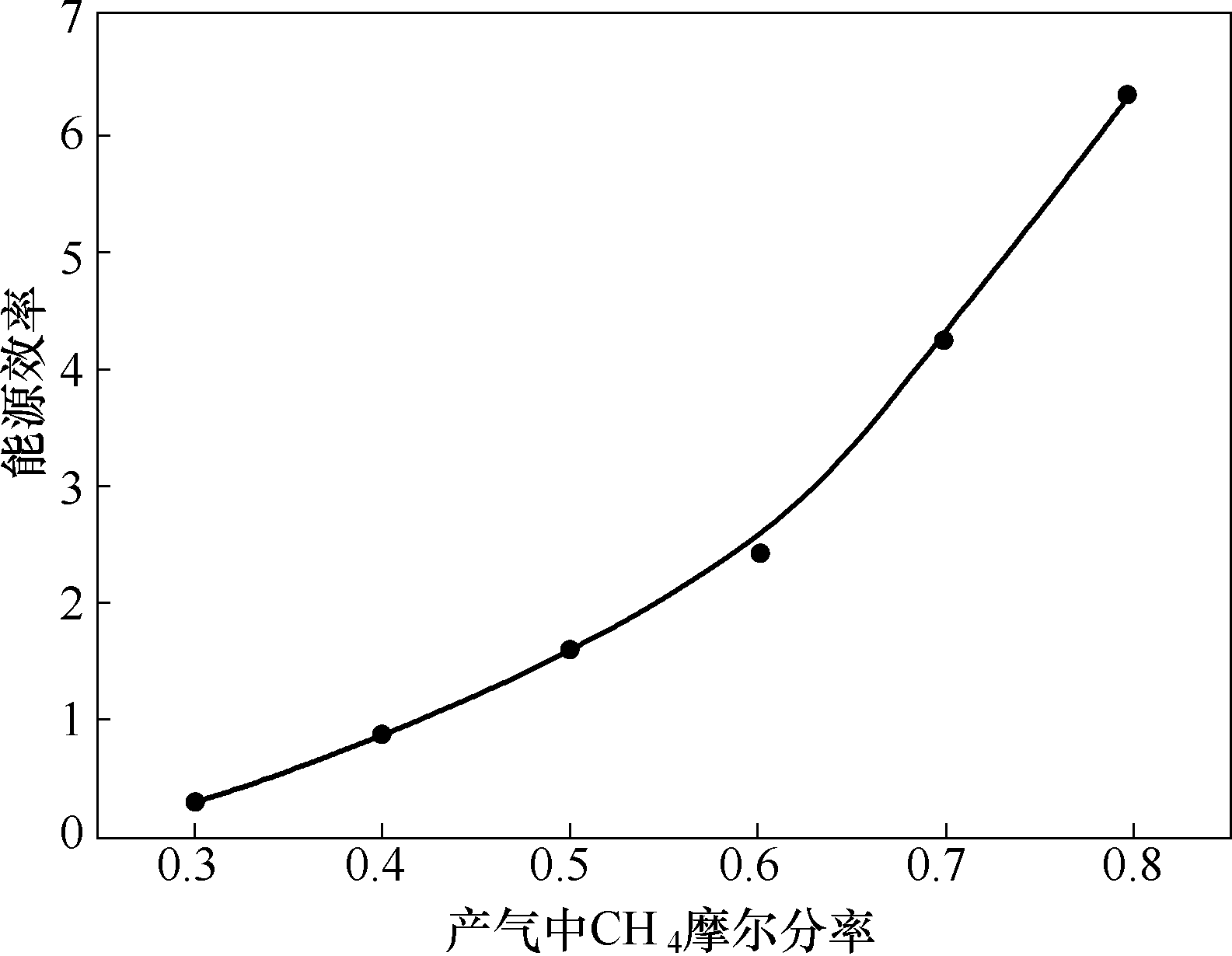
Fig.7 The relationship between energy efficiency ratio and CH4 mole fraction in produced gas for the production of natural gas hydrates by CO2 replacement
| 1 | 陈光进, 孙长宇, 马庆兰. 气体水合物科学与技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| Chen G J, Sun C Y, Ma Q L. Gas Hydrate Science and Technology [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. | |
| 2 | Chong Z R, Yang S H B, Babu P, et al. Review of natural gas hydrates as an energy resource: prospects and challenges [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1633-1652. |
| 3 | Boswell R, Collett T S. Current perspectives on gas hydrate resources[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 4(4): 1206-1215. |
| 4 | 周守为, 陈伟, 李清平, 等. 深水浅层非成岩天然气水合物固态流化试采技术研究及进展[J].中国海上油气, 2017, 29(4): 1-8. |
| Zhou S W, Chen W, Li Q P, et al. Research on the solid fluidization well testing and production for shallow non-diagenetic natural gas hydrate in deep water area[J]. China Offshore Oil Gas, 2017, 29(4): 1-8. | |
| 5 | 赵金洲, 李海涛, 张烈辉, 等. 海洋天然气水合物固态流化开采大型物理模拟实验[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(10): 76-83. |
| Zhao J Z, Li H T, Zhang L H, et al. Large-scale physical simulation experiment of solid fluidization exploitation of marine gas hydrate[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(10): 76-83. | |
| 6 | Sun J, Ning F, Liu T, et al. Gas production from a silty hydrate reservoir in the South China Sea using hydraulic fracturing: a numerical simulation[J]. Energy Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: 1106-1122. |
| 7 | Wang B, Dong H S, Fan Z, et al. Numerical analysis of microwave stimulation for enhancing energy recovery from depressurized methane hydrate sediments[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 262: 114559. |
| 8 | Sun Y F, Wang Y F, Zhong J R, et al. Gas hydrate exploitation using CO2/H2 mixture gas by semi-continuous injection-production mode[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 240: 215-225. |
| 9 | Yang X, Sun C Y, Su K H, et al. A three-dimensional study on the formation and dissociation of methane hydrate in porous sediment by depressurization[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2012, 56(2): 1-7. |
| 10 | 李佳, 梁贞菊, 王照亮, 等. 不同分子模型对甲烷水合物分解微观特性表征[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 955-964. |
| Li J, Liang Z J, Wang Z L, et al. Characterization of microscopic nature of methane hydrate decomposition by different molecular models[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 955-964. | |
| 11 | 李淑霞, 李杰, 靳玉蓉. 不同饱和度的天然气水合物降压分解实验[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(4): 1411-1415. |
| Li S X, Li J, Jin Y R. Depressurizing dissociation of natural gas hydrate with different saturation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(4): 1411-1415. | |
| 12 | Sun X, Luo T T, Wang L, et al. Numerical simulation of gas recovery from a low-permeability hydrate reservoir by depressurization[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250: 7-18. |
| 13 | 周雪冰, 刘婵娟, 罗金琼, 等. 甲烷水合物分解过程的微尺度测量[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1042-1047. |
| Zhou X B, Liu C J, Luo J Q, et al. Microscopic measurements on methane hydrate dissociation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 1042-1047. | |
| 14 | Grover T, Holditch S A, Moridis G. Analysis of reservoir performance of messoyakha gas hydrate field[C]//Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. 2008. |
| 15 | Falser S, Uchida S, Palmer A C, et al. Increased gas production from hydrates by combining depressurization with heating of the wellbore[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(10): 6259-6267. |
| 16 | 阮徐可, 李小森, 徐纯刚, 等. 天然气水合物降压联合井壁加热开采的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(4): 1544-1550. |
| Ruan X K, Li X S, Xu C G, et al. Numerical simulation of gas production from hydrate by depressurization combined with well-wall heating[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(4): 1544-1550. | |
| 17 | Li S X, Zheng R Y, Xu X H, et al. Energy efficiency analysis of hydrate dissociation by thermal stimulation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2016, 30: 148-155. |
| 18 | Yuan Q, Sun C Y, Wang X H, et al. Experimental study of gas production from hydrate dissociation with continuous injection mode using a three-dimensional quiescent reactor[J]. Fuel, 2013, 106(4): 417-424. |
| 19 | Feng J C, Wang Y, Li X S, et al. Production performance of gas hydrate accumulation at the GMGS2-Site 16 of the Pearl River Mouth Basin in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2015, 27: 306-320. |
| 20 | Feng J C, Wang Y, Li X S, et al. Investigation into optimization condition of thermal stimulation for hydrate dissociation in the sandy reservoir[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 154: 995-1003. |
| 21 | Feng J C, Wang Y, Li X S. Energy and entropy analyses of hydrate dissociation in different scales of hydrate simulator[J]. Energy, 2016, 102: 176-186. |
| 22 | Li S, Zheng R, Xu X, et al. Energy efficiency analysis of hydrate dissociation by thermal stimulation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 30: 148-155. |
| 23 | Sun Y F, Zhong J R, Li W Z, et al. Methane recovery from hydrate-bearing sediments by the combination of ethylene glycol injection and depressurization[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(7): 7585-7594. |
| 24 | Zhao J F, Xu K, Song Y C, et al. A review on replacement of CH4 in natural gas hydrates by use of CO2[J]. Energies, 2012, 5(2): 399-419. |
| 25 | Wang M, Wang X, Deng C, et al. Process modeling and energy efficiency analysis of natural gas hydrate production by CH4-CO2/H2 replacement coupling steam methane reforming[J]. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 2019, 47: 131-136. |
| 26 | 王晓辉. 注气开采天然气水合物实验模拟与能效分析[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2017. |
| Wang X H. Experimental simulation and energy efficiency analysis of gas hydrates production by gas injection method[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. | |
| 27 | Teng Y F, Zhang D X. Long-term viability of carbon sequestration in deep-sea sediments[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4: eaao6588. |
| 28 | 刘玉亮. LNG公路槽车运输经济性研究评价[J]. 时代金融, 2013, 27: 293. |
| Liu Y L. Study on the economy of LNG transportation by tank car[J]. Times Finance, 2013, 27: 293. | |
| 29 | Mallon W, Buit L, Wingerden J V, et al. Costs of CO2 transportation infrastructures [J]. Energy Procedia, 2013, 37: 2969-2980. |
| 30 | Yuan Q, Sun C Y, Yang X, et al. Recovery of methane from hydrate reservoir with gaseous carbon dioxide using a three-dimensional middle-size reactor[J]. Energy, 2012, 40(1): 47-58. |
| 31 | Yuan Q, Sun C Y, Liu B, et al. Methane recovery from natural gas hydrate in porous sediment using pressurized liquid CO2[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2013, 67: 257-264. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||