CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (4): 2317-2327.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201182
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Rui( ),SHAO Qi,ZHANG Huayu,JIN Zelong,ZHANG Xiaoliang(
),SHAO Qi,ZHANG Huayu,JIN Zelong,ZHANG Xiaoliang( )
)
Received:2020-08-19
Revised:2020-09-18
Online:2021-04-05
Published:2021-04-05
Contact:
ZHANG Xiaoliang
通讯作者:
张小亮
作者简介:张锐(1996—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Rui, SHAO Qi, ZHANG Huayu, JIN Zelong, ZHANG Xiaoliang. Fabrication of boron-doped hybrid silica membranes for pervaporation desalination[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2317-2327.
张锐, 邵琦, 张华宇, 金泽龙, 张小亮. 硼掺杂二氧化硅杂化膜的制备及渗透汽化脱盐性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2317-2327.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.10 Arrhenius plots of temperature dependent water permeation flux [(a), (b)] and permeance [(c), (d)] of B-BTESE- SiO2 hybrid membranes towards pure water and 3.5%(mass) NaCl solutions
| Membrane | Ej/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | (Ej-Ep)/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | |
| BTESE | 16.57±2.18 | 18.23±1.85 | -26.64±2.10 | -24.99±1.86 | 43.21 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.05 | 13.80±1.57 | 17.40±1.74 | -29.42±1.58 | -25.82±1.77 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.13 | 12.83±1.61 | 17.04±1.90 | -30.39±1.38 | -26.18±1.41 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.25 | 10.71±1.54 | 14.27±1.40 | -32.50±1.38 | -28.95±1.41 | 43.21 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.50 | 19.44±0.64 | 19.00±1.10 | -23.73±0.35 | -24.22±1.39 | 43.17 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-1.00 | 19.98±2.80 | 20.02±1.80 | -23.24±2.75 | -23.20±1.74 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
Table 1 Activation energy of B-BTESE-SiO2 hybrid membranes for PV desalination processes
| Membrane | Ej/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | (Ej-Ep)/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | pure H2O | 3.5%(质量) NaCl | |
| BTESE | 16.57±2.18 | 18.23±1.85 | -26.64±2.10 | -24.99±1.86 | 43.21 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.05 | 13.80±1.57 | 17.40±1.74 | -29.42±1.58 | -25.82±1.77 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.13 | 12.83±1.61 | 17.04±1.90 | -30.39±1.38 | -26.18±1.41 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.25 | 10.71±1.54 | 14.27±1.40 | -32.50±1.38 | -28.95±1.41 | 43.21 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-0.50 | 19.44±0.64 | 19.00±1.10 | -23.73±0.35 | -24.22±1.39 | 43.17 | 43.22 |
| B-BTESE-1.00 | 19.98±2.80 | 20.02±1.80 | -23.24±2.75 | -23.20±1.74 | 43.22 | 43.22 |
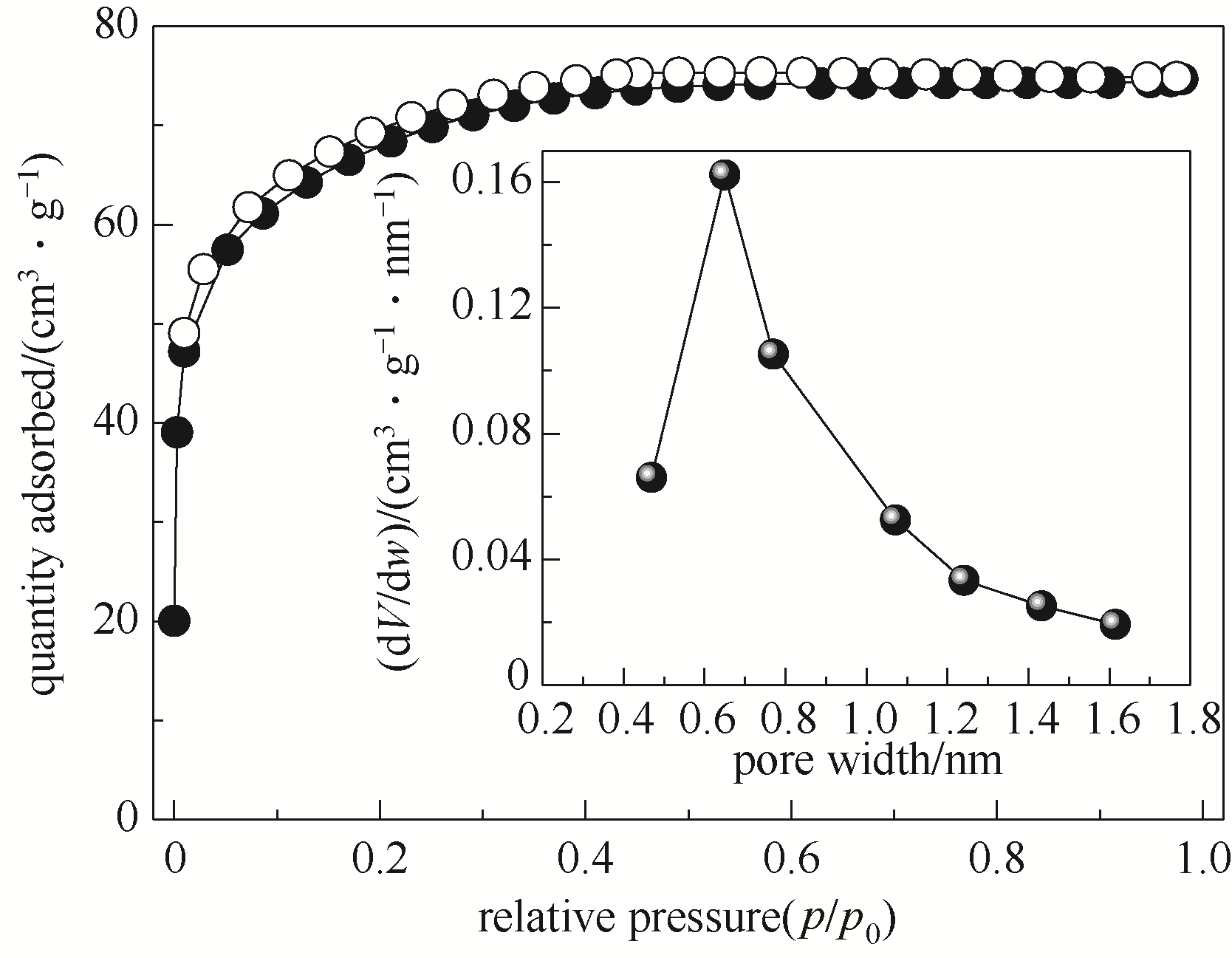
Fig.11 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms (close symbols for adsorption, open symbols for desorption) and pore size distribution (inset) of B-BTESE-0.25 gel powder
| Membrane | c(NaCl)/%(mass) | T/℃ | J/(kg·m-2·h-1) | P/(mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Rej/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/SiO2 | 0.2 | 60 | 20.6 | 16×10-6 | 99 | [ |
| BTESEthy-SiO2 | 0.2 | 70 | 14.2 | 7×10-6 | 99.6 | [ |
| PVA/SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 12.3 | 9.7×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| ES40-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 17.8 | 14.1×10-6 | 99 | [ |
| Co-TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 11.3 | 9.7×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| Ni/TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 25 | 2.5 | 23.9×10-6 | 97 | [ |
| La25Y75-BTESE-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 15.6 | 12.4×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| P123/TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 8 | 6.9×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| CTAB/SiO2 | 4 | 25 | 2.6 | 12.9×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| P123/TEOS-TEVS-SiO2 | 15 | 60 | 9.2 | 8.7×10-6 | 98.6 | [ |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 0.3 | 60 | 24.5 | 19×10-6 | 100 | 本工作 |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 16.5 | 13.1×10-6 | 100 | 本工作 |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 15 | 60 | 9.6 | 8.4×10-6 | 99.9 | 本工作 |
Table 2 Comparison of PV desalination performance of SiO2 membranes
| Membrane | c(NaCl)/%(mass) | T/℃ | J/(kg·m-2·h-1) | P/(mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Rej/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/SiO2 | 0.2 | 60 | 20.6 | 16×10-6 | 99 | [ |
| BTESEthy-SiO2 | 0.2 | 70 | 14.2 | 7×10-6 | 99.6 | [ |
| PVA/SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 12.3 | 9.7×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| ES40-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 17.8 | 14.1×10-6 | 99 | [ |
| Co-TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 11.3 | 9.7×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| Ni/TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 25 | 2.5 | 23.9×10-6 | 97 | [ |
| La25Y75-BTESE-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 15.6 | 12.4×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| P123/TEOS-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 8 | 6.9×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| CTAB/SiO2 | 4 | 25 | 2.6 | 12.9×10-6 | 99.9 | [ |
| P123/TEOS-TEVS-SiO2 | 15 | 60 | 9.2 | 8.7×10-6 | 98.6 | [ |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 0.3 | 60 | 24.5 | 19×10-6 | 100 | 本工作 |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 3.5 | 60 | 16.5 | 13.1×10-6 | 100 | 本工作 |
| B-BTESE-SiO2 | 15 | 60 | 9.6 | 8.4×10-6 | 99.9 | 本工作 |
| 1 | Werber J R, Osuji C O, Elimelech M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1: 16018. |
| 2 | Lin S H. Energy efficiency of desalination: fundamental insights from intuitive interpretation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(1): 76-84. |
| 3 | Yang Z, Ma X H, Tang C Y. Recent development of novel membranes for desalination[J]. Desalination, 2018, 434: 37-59. |
| 4 | 高从堦, 周勇, 刘立芬. 反渗透海水淡化技术现状和展望[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2016, 35(1): 1-14. |
| Gao C J, Zhou Y, Liu L F. Recent development and prospect of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016, 35(1): 1-14. | |
| 5 | 葛亮, 伍斌, 王鑫, 等. MOFs分离膜在水系分离中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 3748-3763. |
| Ge L, Wu B, Wang X, et al. Application in water system separation of MOFs separation membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 3748-3763. | |
| 6 | Wang Q Z, Li N, Bolto B, et al. Desalination by pervaporation: a review[J]. Desalination, 2016, 387: 46-60. |
| 7 | Selim A, Toth A J, Haaz E, et al. Preparation and characterization of PVA/GA/Laponite membranes to enhance pervaporation desalination performance[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 221: 201-210. |
| 8 | Cao Z S, Zeng S X, Xu Z, et al. Ultrathin ZSM-5 zeolite nanosheet laminated membrane for high-flux desalination of concentrated brines[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(11): eaau8634. |
| 9 | Cho C H, Oh K Y, Kim S K, et al. Pervaporative seawater desalination using NaA zeolite membrane: mechanisms of high water flux and high salt rejection[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 371(1/2): 226-238. |
| 10 | Zhang H Y, Wen J L, Shao Q, et al. Fabrication of La/Y-codoped microporous organosilica membranes for high-performance pervaporation desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 584: 353-363. |
| 11 | Qian X W, Li N, Wang Q Z, et al. Chitosan/graphene oxide mixed matrix membrane with enhanced water permeability for high-salinity water desalination by pervaporation[J]. Desalination, 2018, 438: 83-96. |
| 12 | Liu G Z, Shen J, Liu Q, et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional MXene membrane for pervaporation desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 548: 548-558. |
| 13 | Kanezashi M, Yada K, Yoshioka T, et al. Design of silica networks for development of highly permeable hydrogen separation membranes with hydrothermal stability[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(2): 414-415. |
| 14 | Elma M, Yacou C, Wang D K, et al. Microporous silica based membranes for desalination[J]. Water, 2012, 4(3): 629-649. |
| 15 | Wijaya S, Duke M C, Diniz da Costa J C. Carbonised template silica membranes for desalination[J]. Desalination, 2009, 236(1/2/3): 291-298. |
| 16 | Yamamoto K, Muragishi H, Mizumo T, et al. Diethylenedioxane-bridged microporous organosilica membrane for gas and water separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 207: 370-376. |
| 17 | Xu R, Ibrahim S M, Kanezashi M, et al. New insights into the microstructure-separation properties of organosilica membranes with ethane, ethylene, and acetylene bridges[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(12): 9357-9364. |
| 18 | Qureshi H F, Besselink R, Elshof J E, et al. Doped microporous hybrid silica membranes for gas separation[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2015, 75(1): 180-188. |
| 19 | Zheng F T, Yamamoto K, Kanezashi M, et al. Preparation of bridged silica RO membranes from copolymerization of bis(triethoxysilyl)ethene/(hydroxymethyl)triethoxysilane. Effects of ethenylene-bridge enhancing water permeability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 546: 173-178. |
| 20 | Castricum H L, Kreiter R, van Veen H M, et al. High-performance hybrid pervaporation membranes with superior hydrothermal and acid stability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 324(1/2): 111-118. |
| 21 | Song H T, Wei Y B, Qi H. Tailoring pore structures to improve the permselectivity of organosilica membranes by tuning calcination parameters[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(47): 24657-24666. |
| 22 | Niimi T, Nagasawa H, Kanezashi M, et al. Preparation of BTESE-derived organosilica membranes for catalytic membrane reactors of methylcyclohexane dehydrogenation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 455: 375-383. |
| 23 | Qi H, Han J, Xu N P. Effect of calcination temperature on carbon dioxide separation properties of a novel microporous hybrid silica membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 382(1/2): 231-237. |
| 24 | Zhang Q H, Gu J L, Chen G Q, et al. Durable flame retardant finish for silk fabric using boron hybrid silica sol[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 387: 446-453. |
| 25 |
Sorarù G D, Dallabona N, Gervais C, et al. Organically modified SiO2-B2O3 gels displaying a high content of borosiloxane ( B—O—Si B—O—Si ) bonds[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1999, 11(4): 910-919. ) bonds[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1999, 11(4): 910-919.
|
| 26 | Ivanova Y, Vueva Y, Fernandes M H F V. Si—O—C—B amorphous materials from organic-inorganic hybrid precursors[J]. Journal of the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, 2006, 41(4): 417-422. |
| 27 | Elma M, Wang D K, Yacou C, et al. High performance interlayer-free mesoporous cobalt oxide silica membranes for desalination applications[J]. Desalination, 2015, 365: 308-315. |
| 28 | Wu D H, Gao A R, Zhao H T, et al. Pervaporative desalination of high-salinity water[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2018, 136: 154-164. |
| 29 | Halakoo E, Feng X S. Layer-by-layer assembly of polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide membranes for desalination of high-salinity water via pervaporation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 234: 116077. |
| 30 | Chaudhri S G, Chaudhari J C, Singh P S. Fabrication of efficient pervaporation desalination membrane by reinforcement of poly(vinyl alcohol)-silica film on porous polysulfone hollow fiber[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(3): 45718. |
| 31 | Xu R, Lin P, Zhang Q, et al. Development of ethenylene-bridged organosilica membranes for desalination applications[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(7): 2183-2190. |
| 32 | Reino Olegário da Silva D A, Bosmuler Zuge L C, de Paula Scheer A. Preparation and characterization of a novel green silica/PVA membrane for water desalination by pervaporation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 247: 116852. |
| 33 | Wang S N, Wang D K, Motuzas J, et al. Rapid thermal treatment of interlayer-free ethyl silicate 40 derived membranes for desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 516: 94-103. |
| 34 | Darmawan A, Karlina L, Astuti Y, et al. Structural evolution of nickel oxide silica sol-gel for the preparation of interlayer-free membranes[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016, 447: 9-15. |
| 35 | Elma M, Wang D K, Yacou C, et al. Interlayer-free P123 carbonised template silica membranes for desalination with reduced salt concentration polarisation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 475: 376-383. |
| 36 | Singh P S, Chaudhri S G, Kansara A M, et al. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-silica membrane for seawater desalination through pervaporation[J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2015, 38(2): 565-572. |
| 37 | Yang H, Elma M, Wang D K, et al. Interlayer-free hybrid carbon-silica membranes for processing brackish to brine salt solutions by pervaporation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 523: 197-204. |
| [1] | Yanpeng WU, Xiaoyu LI, Qiaoyang ZHONG. Experimental analysis on filtration performance of electrospun nanofibers with amphiphobic membrane of oily fine particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 259-264. |
| [2] | Meisi CHEN, Weida CHEN, Xinyao LI, Shangyu LI, Youting WU, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Advances in silicon-based ionic liquid microparticle enhanced gas capture and conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [3] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [4] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [5] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [7] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [8] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [9] | Xueyan WEI, Yong QIAN. Experimental study on the low to medium temperature oxidation characteristics and kinetics of micro-size iron powder [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [10] | Lei WANG, Lei WANG, Yunlong BAI, Liuliu HE. Preparation of SA lithium ion sieve membrane and its adsorptive properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [11] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [12] | Yongyao SUN, Qiuying GAO, Wenguang ZENG, Jiaming WANG, Yifei CHEN, Yongzhe ZHOU, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Design and optimization of membrane-based integration process for advanced utilization of associated gases in N2-EOR oilfields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [13] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [14] | Xiaoxuan WANG, Xiaohong HU, Yunan LU, Shiyong WANG, Fengxian FAN. Numerical simulation of flow characteristics in a rotating membrane filter [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1489-1498. |
| [15] | Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||