CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (7): 3869-3879.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201825
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Xian1( ),XU Wenhao1,SHEN Liang1,2(
),XU Wenhao1,SHEN Liang1,2( ),WANG Yuanpeng1,2,LU Yinghua1,2
),WANG Yuanpeng1,2,LU Yinghua1,2
Received:2020-12-15
Revised:2021-04-04
Online:2021-07-05
Published:2021-07-05
Contact:
SHEN Liang
肖弦1( ),徐文昊1,沈亮1,2(
),徐文昊1,沈亮1,2( ),王远鹏1,2,卢英华1,2
),王远鹏1,2,卢英华1,2
通讯作者:
沈亮
作者简介:肖弦(1997—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
XIAO Xian, XU Wenhao, SHEN Liang, WANG Yuanpeng, LU Yinghua. Preparation and electrochemical properties of new porous carbon materials by synthesizing graphene oxide and waste activated sludge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3869-3879.
肖弦, 徐文昊, 沈亮, 王远鹏, 卢英华. 氧化石墨烯与剩余活性污泥聚合制备多孔碳材料及其电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3869-3879.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
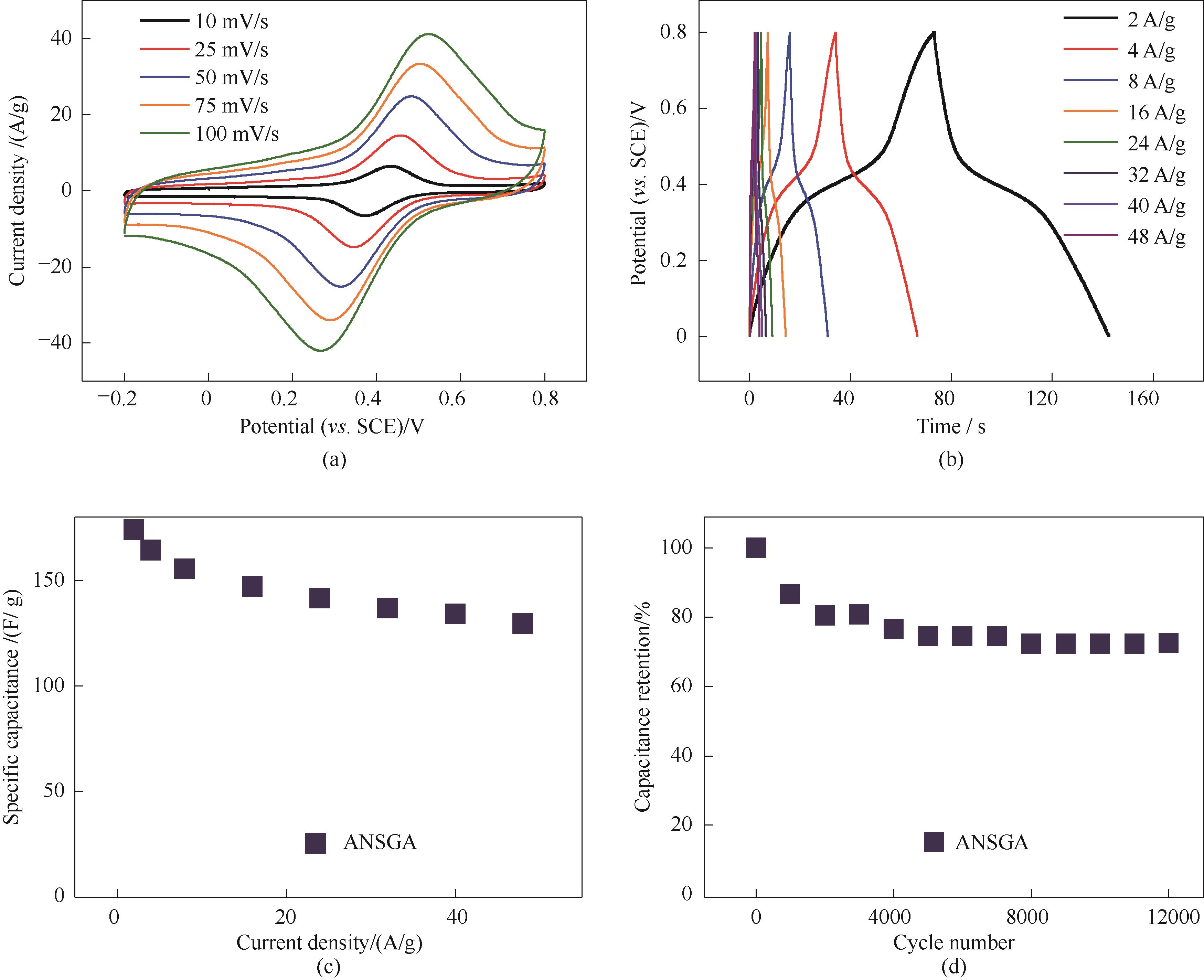
Fig.7 Electrochemical performance of ANSGA: CV curves (a), GCD curves (b), specific capacitance at different current densities (c), and cyclic stability test at a current density of 21 A/g (d)
| 主要材料 | 比电容/(F/g) | 电容保留率/% | 掺氮量/%(质量) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO/ammonia water | 233.3(0.5 A/g) | 64.3(20 A/g) | 4.4 | [ |
| GO/NH3 | 175(2 A/g) | 53.8(6 A/g) | 3.97 | [ |
| GO/uric acid | 196(2 A/g) | 79.1(3 A/g) | 5.63 | [ |
| GO/MnCo2O4/DMF | 95.1(2 A/g) | 65.2(4 A/g) | 4.14 | [ |
| GO/CuO/NH4NO3 | 197(5 A/g) | 57.9(5 A/g) | 4.54 | [ |
| GO/Fe3O4/Mn2O3/N2H4 | 90.58(0.5 A/g) | 80.7(2.5 A/g) | — | [ |
| GO/FeCl3/E.coli | 224(2 A/g) | 51.3(5 A/g) | 5.58 | [ |
| ANSGA(GO/activated sludge) | 174(2 A/g) | 74.7(48 A/g) | 5.61 | 本文 |
Table 1 Comparison of specific capapcitance, capacitance retention and N-doped content of graphene-based carbon material
| 主要材料 | 比电容/(F/g) | 电容保留率/% | 掺氮量/%(质量) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO/ammonia water | 233.3(0.5 A/g) | 64.3(20 A/g) | 4.4 | [ |
| GO/NH3 | 175(2 A/g) | 53.8(6 A/g) | 3.97 | [ |
| GO/uric acid | 196(2 A/g) | 79.1(3 A/g) | 5.63 | [ |
| GO/MnCo2O4/DMF | 95.1(2 A/g) | 65.2(4 A/g) | 4.14 | [ |
| GO/CuO/NH4NO3 | 197(5 A/g) | 57.9(5 A/g) | 4.54 | [ |
| GO/Fe3O4/Mn2O3/N2H4 | 90.58(0.5 A/g) | 80.7(2.5 A/g) | — | [ |
| GO/FeCl3/E.coli | 224(2 A/g) | 51.3(5 A/g) | 5.58 | [ |
| ANSGA(GO/activated sludge) | 174(2 A/g) | 74.7(48 A/g) | 5.61 | 本文 |
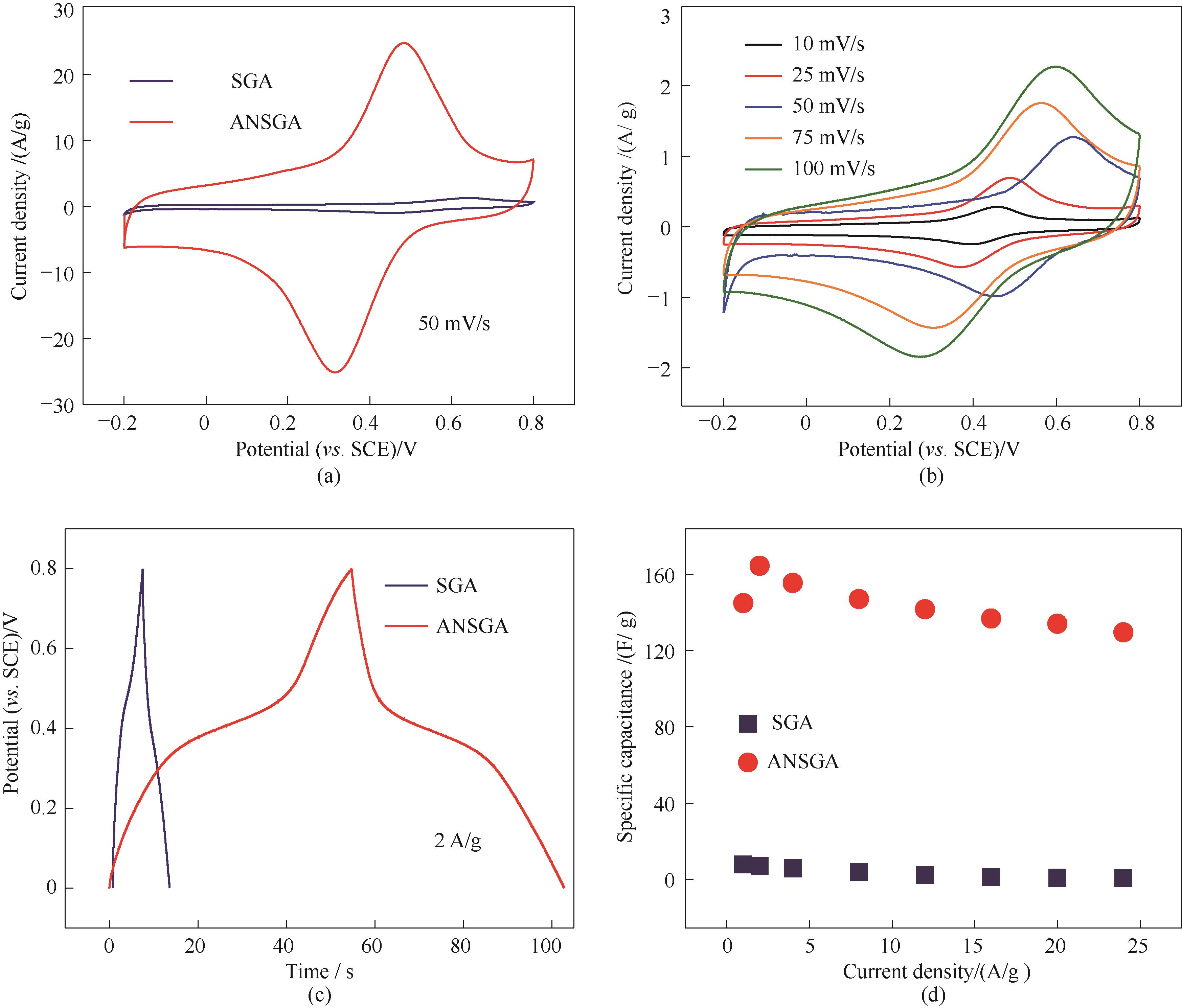
Fig.8 Electrochemical performance of SGA and ANSGA: CV curves at a scan rate of 50 mV/s (a), CV curves of SGA (b), GCD curves at a current density of 2 A/g (c), and specific capacitance at different current densities (d)
| 1 | Yuan S J, Dai X H. Sewage sludge-based functional nanomaterials: development and applications[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2017, 4(1): 17-26. |
| 2 | Feng H B, Zheng M T, Dong H W, et al. Three-dimensional honeycomb-like hierarchically structured carbon for high-performance supercapacitors derived from high-ash-content sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(29): 15225-15234. |
| 3 | Lee C, Wei X, Kysar J W, et al. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5887): 385-388. |
| 4 | Zhang Y, Tan Y W, Stormer H L, et al. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry's phase in graphene[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7065): 201-204. |
| 5 | Chae H K, Siberio-Pérez D Y, Kim J, et al. A route to high surface area, porosity and inclusion of large molecules in crystals[J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6974): 523-527. |
| 6 | Ma Y F, Chen Y S. Three-dimensional graphene networks: synthesis, properties and applications[J]. National Science Review, 2015, 2(1): 40-53. |
| 7 | Wang Y, Wei Z D, Nie Y, et al. Generation of three dimensional pore-controlled nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogels for high-performance supercapacitors by employing formamide as the modulator[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(4): 1442-1445. |
| 8 | Ruiz O N, Fernando K A, Wang B, et al. Graphene oxide: a nonspecific enhancer of cellular growth[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(10): 8100-8107. |
| 9 | Chen J, Deng F, Hu Y Y, et al. Antibacterial activity of graphene-modified anode on Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilm in microbial fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 290: 80-86. |
| 10 | Yoshida N, Miyata Y, Mugita A, et al. Electricity recovery from municipal sewage wastewater using a hydrogel complex composed of microbially reduced graphene oxide and sludge[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(9): E742. |
| 11 | Xu W H, Jin Z H, Pang X, et al. Interaction between biocompatible graphene oxide and live shewanella in the self-assembled hydrogel: the role of physicochemical properties[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(7): 4263-4272. |
| 12 | 周群英, 王士芬. 环境工程微生物学[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2018. |
| Zhou Q Y, Wang S F. Microbiology of Environmental Engineering[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2018. | |
| 13 | Shen L, Hu H Y, Ji H F, et al. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from excess activated sludge as a promising substitute of pure culture[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 189: 236-242. |
| 14 | Shen L, Yuan X, Shen W H, et al. Positive impact of biofilm on reducing the permeation of ampicillin through membrane for membrane bioreactor[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 97: 34-39. |
| 15 | Shen L, Jin Z H, Wang D, et al. Enhance wastewater biological treatment through the bacteria induced graphene oxide hydrogel[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 190: 201-210. |
| 16 | Shen L, Jin Z H, Xu W H, et al. Enhanced treatment of anionic and cationic dyes in wastewater through live bacteria encapsulation using graphene hydrogel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(19): 7817-7824. |
| 17 | Salas E C, Sun Z, Lüttge A, et al. Reduction of graphene oxide via bacterial respiration[J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(8): 4852-4856. |
| 18 | Dreyer D R, Park S, Bielawski C W, et al. The chemistry of graphene oxide[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(1): 228-240. |
| 19 | Wang D, Jin Z H, Pang X, et al. Fabrication and functionalization of biological graphene aerogel by reusing microorganism in activated sludge and ionic dyes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 124823. |
| 20 | Wei Y, Hu X Y, Jiang Q R, et al. Influence of graphene oxide with different oxidation levels on the properties of epoxy composites [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 161: 74-84. |
| 21 | Sui Z Y, Meng Q H, Li J T, et al. High surface area porous carbons produced by steam activation of graphene aerogels[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(25): 9891-9898. |
| 22 | Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, et al. Water-enhanced oxidation of graphite to graphene oxide with controlled species of oxygenated groups[J]. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(3): 1874-1881. |
| 23 | Zhao J, Li Y J, Wang G L, et al. Enabling high-volumetric-energy-density supercapacitors: designing open, low-tortuosity heteroatom-doped porous carbon-tube bundle electrodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(44): 23085-23093. |
| 24 | Wu J F, Zhang Q N, Wang J J, et al. A self-assembly route to porous polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide composite materials with molecular-level uniformity for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(5): 1280-1286. |
| 25 | Smith K M, Fowler G D, Pullket S, et al. Sewage sludge-based adsorbents: a review of their production, properties and use in water treatment applications[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(10): 2569-2594. |
| 26 | Zhou Q Y, Jiang X, Li X, et al. Preparation of high-yield N-doped biochar from nitrogen-containing phosphate and its effective adsorption for toluene[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(53): 30171-30179. |
| 27 | 魏风, 毕宏晖, 焦帅, 等. 超级电容器用相互连接的类石墨烯纳米片[J]. 物理化学学报, 2020, 36(2): 142-149. |
| Wei F, Bi H H, Jiao S, et al. Interconnected graphene-like nanosheets for supercapacitors[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2020, 36(2): 142-149. | |
| 28 | Wei F, Zhang H F, He X J, et al. Synthesis of porous carbons from coal tar pitch for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2019, 34(2): 132-139. |
| 29 | Tajik S, Dubal D P, Gomez-Romero P, et al. Nanostructured mixed transition metal oxides for high performance asymmetric supercapacitors: facile synthetic strategy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(17): 12384-12395. |
| 30 | Gao F, Qin S H, Zang Y H, et al. Highly efficient formation of Mn3O4-graphene oxide hybrid aerogels for use as the cathode material of high performance lithium ion batteries[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2020, 35(2): 121-130. |
| 31 | Du X S, Zhou C F, Liu H Y, et al. Facile chemical synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene sheets and their electrochemical capacitance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 241: 460-466. |
| 32 | Li D L, Yu C Z, Wang M S, et al. Synthesis of nitrogen doped graphene from graphene oxide within an ammonia flame for high performance supercapacitors[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(98): 55394-55399. |
| 33 | Wang X Q, Ding Y J, Chen F, et al. Hierarchical porous N-doped graphene monoliths for flexible solid-state supercapacitors with excellent cycle stability[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(9): 5024-5032. |
| 34 | Pettong T, Iamprasertkun P, Krittayavathananon A, et al. High-performance asymmetric supercapacitors of MnCo2O4 nanofibers and N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogel[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(49): 34045-34053. |
| 35 | Li Y J, Ye K, Cheng K, et al. Anchoring CuO nanoparticles on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as electrode material for supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 727: 154-162. |
| 36 | Chong B, Azman N, Mohd Abdah M, et al. Supercapacitive performance of N-doped graphene/Mn3O4/Fe3O4 as an electrode material[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(6): 1040. |
| 37 | Sun H M, Cao L Y, Lu L H. Bacteria promoted hierarchical carbon materials for high-performance supercapacitor[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(3): 6206-6213. |
| 38 | Wang Z C, Wang Y, Shu X, et al. Hierarchical three-dimensional MnO2/carbon@TiO2 nanotube arrays for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(68): 63642-63651. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [3] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [4] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [5] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [6] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [7] | Nan HU, Demin TAO, Zhaolan YANG, Xuebing WANG, Xiangxu ZHANG, Yulong LIU, Dexin DING. Remediation of percolate water from uranium tailings reservoir by coupling iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and sulfate reducing bacteria [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2655-2667. |
| [8] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [9] | Chengze WANG, Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI. Sulfidation couples with aging to enhance the reactivity of zerovalent iron toward Cr(Ⅵ) in water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206. |
| [10] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [11] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [12] | Zheng ZHANG, Yongping HE, Haidong SUN, Rongzi ZHANG, Zhengping SUN, Jinlan CHEN, Yixuan ZHENG, Xiao DU, Xiaogang HAO. Electrochemically switched ion exchange device with serpentine flow field for selective extraction of lithium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| [13] | Ruiqi LIU, Xitong ZHOU, Yue ZHANG, Ying HE, Jing GAO, Li MA. The construction and application of biosensor based on gold nanoparticles loaded SiO2-nanoflowers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| [14] | Yue SONG, Qicheng ZHANG, Wenchao PENG, Yang LI, Fengbao ZHANG, Xiaobin FAN. Synthesis of MoS2-based single atom catalyst and its application in electrocatalysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 535-545. |
| [15] | Weijiang CHENG, Heqi WANG, Xiang GAO, Na LI, Sainan MA. Research progress on film-forming electrolyte additives for Si-based lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||