CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 2197-2206.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230042
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chengze WANG( ), Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI(
), Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI( )
)
Received:2023-01-17
Revised:2023-03-30
Online:2023-06-29
Published:2023-05-05
Contact:
Jinxiang LI
王承泽( ), 顾凯丽, 张晋华, 石建轩, 刘艺娓, 李锦祥(
), 顾凯丽, 张晋华, 石建轩, 刘艺娓, 李锦祥( )
)
通讯作者:
李锦祥
作者简介:王承泽(1999—),男,硕士研究生,1329983815@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chengze WANG, Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI. Sulfidation couples with aging to enhance the reactivity of zerovalent iron toward Cr(Ⅵ) in water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206.
王承泽, 顾凯丽, 张晋华, 石建轩, 刘艺娓, 李锦祥. 硫化协同老化零价铁增效去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)的作用机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
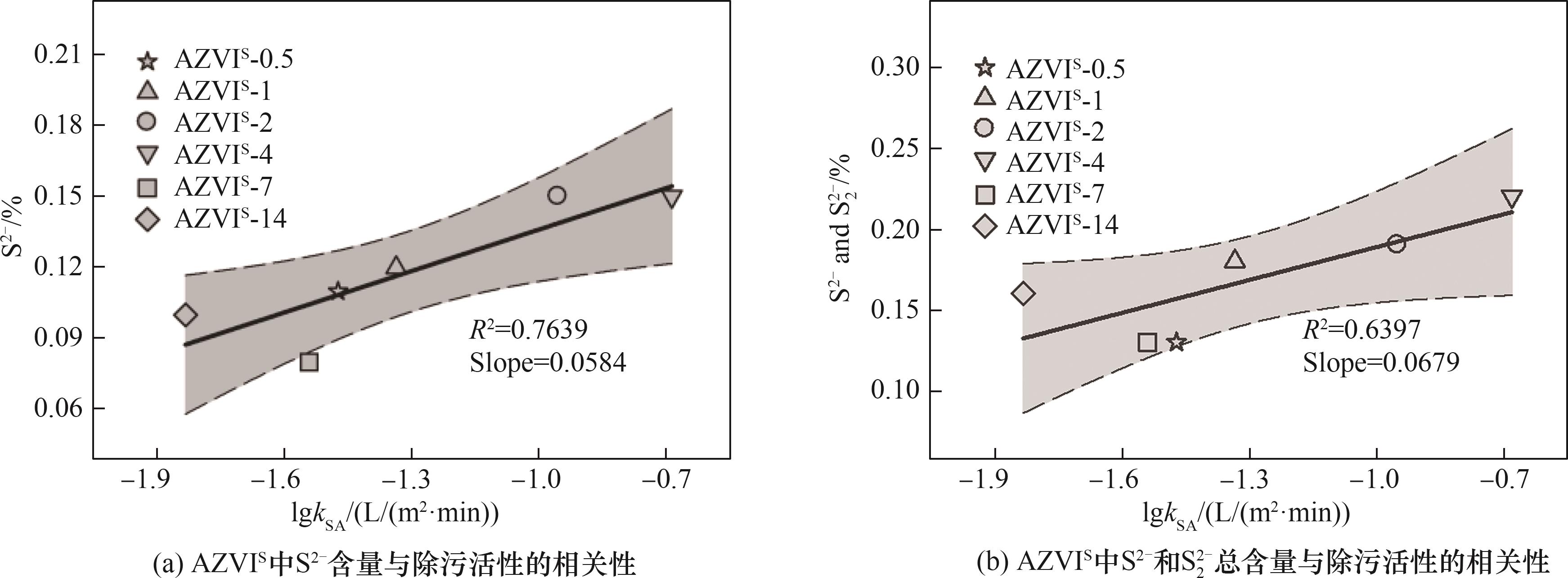
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of the normalization constant of the specific surface area of AZVIS for the removal of Cr(Ⅵ) and its S content at a depth of 20 nm
| 1 | 王兴润, 张艳霞, 王琪, 等. 铬污染建筑废物不同清洗剂的作用效果比较[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(10): 3255-3261. |
| Wang X R, Zhang Y X, Wang Q, et al. Comparison of different washing agents for disposal of chromium-contaminated construction waste[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(10): 3255-3261. | |
| 2 | 朱文会, 李志涛, 王夏晖, 等. 不同异位修复工艺对高浓度铬渣污染土壤中Cr的去除特性[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6): 2730-2736. |
| Zhu W H, Li Z T, Wang X H, et al. Characteristics of chromium removing using different ex-situ remediations in soil seriously contaminated by chromite ore processing residue[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(6): 2730-2736. | |
| 3 | 程治良, 全学军, 代黎, 等. 水力喷射空气旋流器用于含Cr(Ⅵ)废水处理[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(4): 1403-1410. |
| Cheng Z L, Quan X J, Dai L, et al. Treatment of Cr(Ⅵ)-containing wastewater in a water-sparged aerocyclone[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(4): 1403-1410. | |
| 4 | Zafar A M, Javed M A, Hassan A A, et al. Groundwater remediation using zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI)[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2021, 15: 100694. |
| 5 | Vollprecht D, Krois L M, Sedlazeck K P, et al. Removal of critical metals from waste water by zero-valent iron[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 208: 1409-1420. |
| 6 | Guan X H, Sun Y K, Qin H J, et al. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994—2014)[J]. Water Research, 2015, 75: 224-248. |
| 7 | Xie Y, Cwiertny D M. Influence of anionic cosolutes and pH on nanoscale zerovalent iron longevity: time scales and mechanisms of reactivity loss toward 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrachloroethane and Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(15): 8365-8373. |
| 8 | Sun Y K, Li J X, Huang T L, et al. The influences of iron characteristics, operating conditions and solution chemistry on contaminants removal by zero-valent iron: a review[J]. Water Research, 2016, 100: 277-295. |
| 9 | 曹贝, 李锦祥, 关小红. 弱磁场强化零价铁对水中U(Ⅵ)去除效能[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(8): 3282-3290. |
| Cao B, Li J X, Guan X H. Enhancing reactivity of zerovalent iron toward U(Ⅵ) by weak magnetic field[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(8): 3282-3290. | |
| 10 | Su Y M, Adeleye A S, Keller A A, et al. Magnetic sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron (S-nZVI) for dissolved metal ion removal[J]. Water Research, 2015, 74: 47-57. |
| 11 | Liu T X, Li X M, Waite T D. Depassivation of aged Fe0 by divalent cations: correlation between contaminant degradation and surface complexation constants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(24): 14564-14571. |
| 12 | Liu T X, Li X M, Waite T D. Depassivation of aged Fe0 by ferrous ions: implications to contaminant degradation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(23): 13712-13720. |
| 13 | Liu T X, Li X M, Waite T D. Depassivation of aged Fe0 by inorganic salts: implications to contaminant degradation in seawater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(13): 7350-7356. |
| 14 | Lipczynska-Kochany E, Harms S, Milburn R, et al. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride in the presence of iron and sulphur containing compounds[J]. Chemosphere, 1994, 29(7): 1477-1489. |
| 15 | Kim E J, Kim J H, Azad A M, et al. Facile synthesis and characterization of Fe/FeS nanoparticles for environmental applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2011, 3(5): 1457-1462. |
| 16 | Li J X, Zhang X Y, Liu M C, et al. Enhanced reactivity and electron selectivity of sulfidated zerovalent iron toward chromate under aerobic conditions[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(5): 2988-2997. |
| 17 | Li D, Mao Z, Zhong Y, et al. Reductive transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A by sulfidated nano zerovalent iron[J]. Water Research, 2016, 103: 1-9. |
| 18 | Wang B, Dong H R, Li L, et al. Influence of different co-contaminants on trichloroethylene removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122773. |
| 19 | Dong H R, Zhang C, Deng J M, et al. Factors influencing degradation of trichloroethylene by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution[J]. Water Research, 2018, 135: 1-10. |
| 20 | Xu J, Cao Z, Zhou H, et al. Sulfur dose and sulfidation time affect reactivity and selectivity of post-sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(22): 13344-13352. |
| 21 | Semerád J, Filip J, Ševců A, et al. Environmental fate of sulfidated nZVI particles: the interplay of nanoparticle corrosion and toxicity during aging[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2020, 7(6): 1794-1806. |
| 22 | Fan D M, Johnson G O, Tratnyek P G, et al. Sulfidation of nano zerovalent iron (nZVI) for improved selectivity during in-situ chemical reduction (ISCR)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(17): 9558-9565. |
| 23 | Cao Z, Li H, Xu X H, et al. Correlating surface chemistry and hydrophobicity of sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron with its reactivity and selectivity for denitration and dechlorination[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 394: 124876. |
| 24 | Liang L P, Guan X H, Shi Z, et al. Coupled effects of aging and weak magnetic fields on sequestration of selenite by zero-valent iron[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(11): 6326-6334. |
| 25 | Xu H Y, Sun Y K, Li J X, et al. Aging of zerovalent iron in synthetic groundwater: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy depth profiling characterization and depassivation with uniform magnetic field[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(15): 8214-8222. |
| 26 | Ling J F, Qiao J L, Song Y D, et al. Influence of coexisting ions on the electron efficiency of sulfidated zerovalent iron toward Se(Ⅵ) removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 378: 122124. |
| 27 | Li J X, Zhang X Y, Sun Y K, et al. Advances in sulfidation of zerovalent iron for water decontamination[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(23): 13533-13544. |
| 28 | Mangayayam M C, Perez J P H, Dideriksen K, et al. Structural transformation of sulfidized zerovalent iron and its impact on long-term reactivity[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019, 6(11): 3422-3430. |
| 29 | Gu Y W, Gong L, Qi J L, et al. Sulfidation mitigates the passivation of zero valent iron at alkaline pHs: experimental evidences and mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2019, 159: 233-241. |
| 30 | Gu Y W, Wang B B, He F, et al. Mechanochemically sulfidated microscale zero valent iron: pathways, kinetics, mechanism, and efficiency of trichloroethylene dechlorination[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(21): 12653-12662. |
| 31 | Xu J, Wang Y, Weng C, et al. Reactivity, selectivity, and long-term performance of sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron with different properties[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(10): 5936-5945. |
| [1] | Zhenghao JIN, Lijie FENG, Shuhong LI. Energy and exergy analysis of a solution cross-type absorption-resorption heat pump using NH3/H2O as working fluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [2] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [5] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [6] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [7] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [8] | Jipeng ZHOU, Wenjun HE, Tao LI. Reaction engineering calculation of deactivation kinetics for ethylene catalytic oxidation over irregular-shaped catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [9] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [10] | Zheng ZHANG, Yongping HE, Haidong SUN, Rongzi ZHANG, Zhengping SUN, Jinlan CHEN, Yixuan ZHENG, Xiao DU, Xiaogang HAO. Electrochemically switched ion exchange device with serpentine flow field for selective extraction of lithium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| [11] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [12] | Ruiqi LIU, Xitong ZHOU, Yue ZHANG, Ying HE, Jing GAO, Li MA. The construction and application of biosensor based on gold nanoparticles loaded SiO2-nanoflowers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| [13] | Jieyuan ZHENG, Xianwei ZHANG, Jintao WAN, Hong FAN. Synthesis and curing kinetic analysis of eugenol-based siloxane epoxy resin [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 924-932. |
| [14] | Weijiang CHENG, Heqi WANG, Xiang GAO, Na LI, Sainan MA. Research progress on film-forming electrolyte additives for Si-based lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. |
| [15] | Yue SONG, Qicheng ZHANG, Wenchao PENG, Yang LI, Fengbao ZHANG, Xiaobin FAN. Synthesis of MoS2-based single atom catalyst and its application in electrocatalysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 535-545. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||