CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (8): 2970-2982.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240221
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoyuan ZHENG( ), Yanlin CAI, Zhi YING, Bo WANG, Binlin DOU
), Yanlin CAI, Zhi YING, Bo WANG, Binlin DOU
Received:2024-02-29
Revised:2024-04-16
Online:2024-08-21
Published:2024-08-25
Contact:
Xiaoyuan ZHENG
通讯作者:
郑晓园
作者简介:郑晓园(1986—),男,博士,副教授,xyzheng@usst.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiaoyuan ZHENG, Yanlin CAI, Zhi YING, Bo WANG, Binlin DOU. Phosphorus transformation during subcritical hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2970-2982.
郑晓园, 蔡炎嶙, 应芝, 王波, 豆斌林. 污水污泥磷形态亚临界水热转化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2970-2982.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
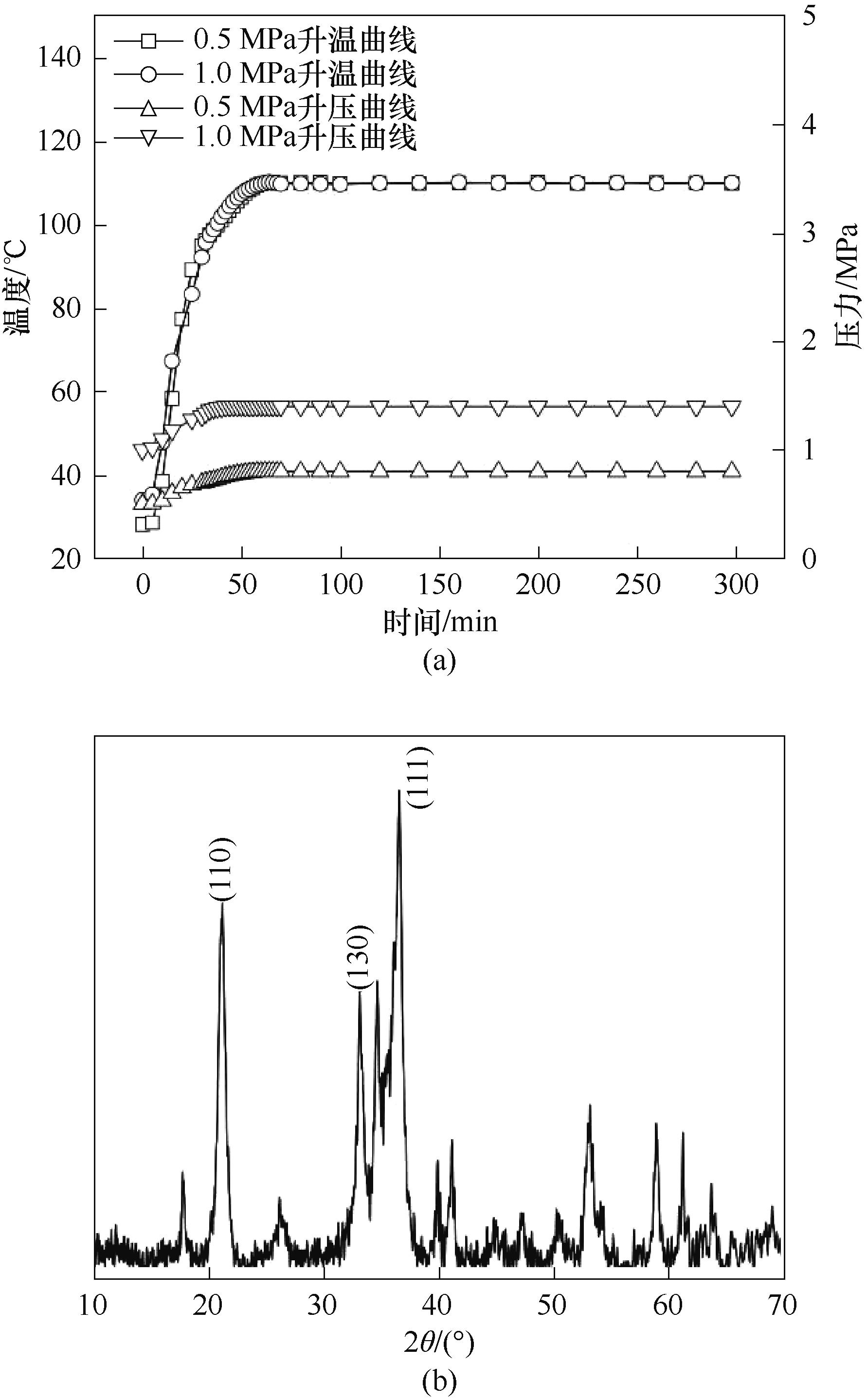
Fig.1 Changes of temperature and pressure in the decoupling temperature-pressure hydrothermal process and X-ray diffraction pattern of self-made goethite
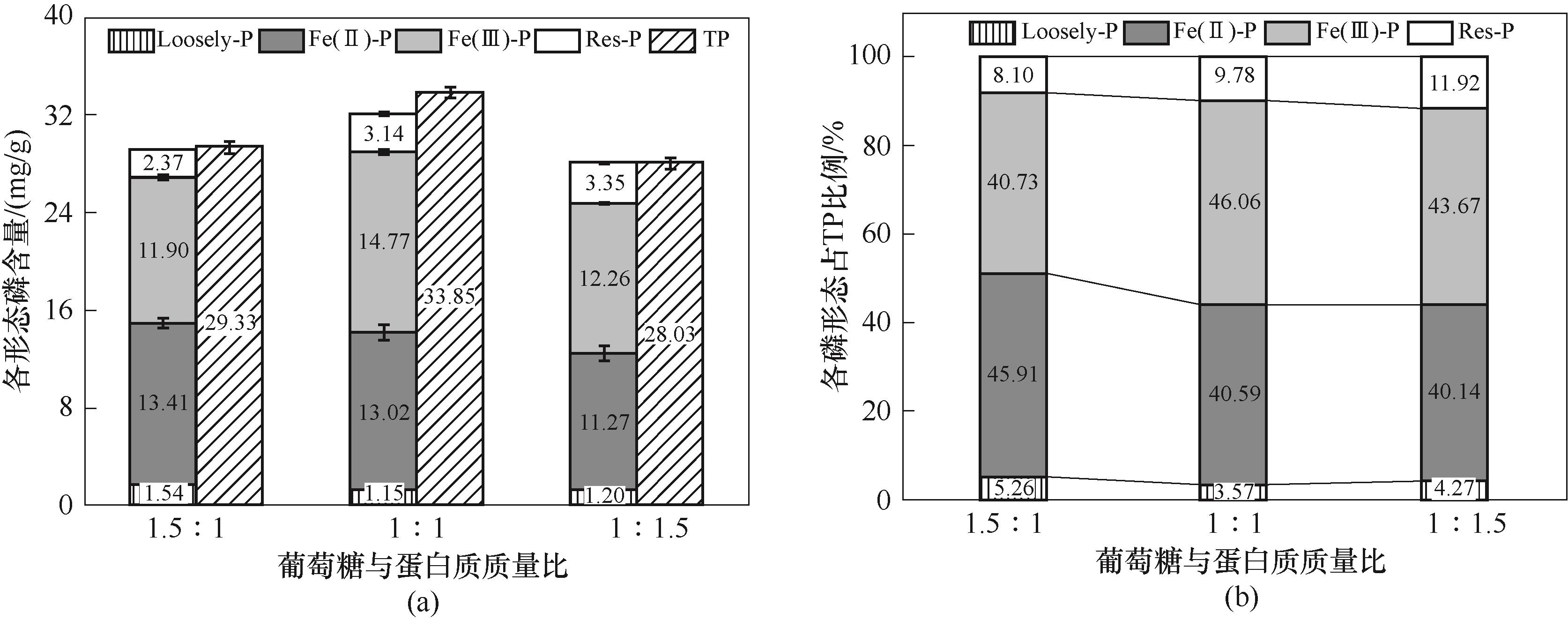
Fig.4 Effect of mass ratio of glucose to protein on the content of each phosphorus fraction and the proportion of each phosphorus fraction in TP in hydrochar samples
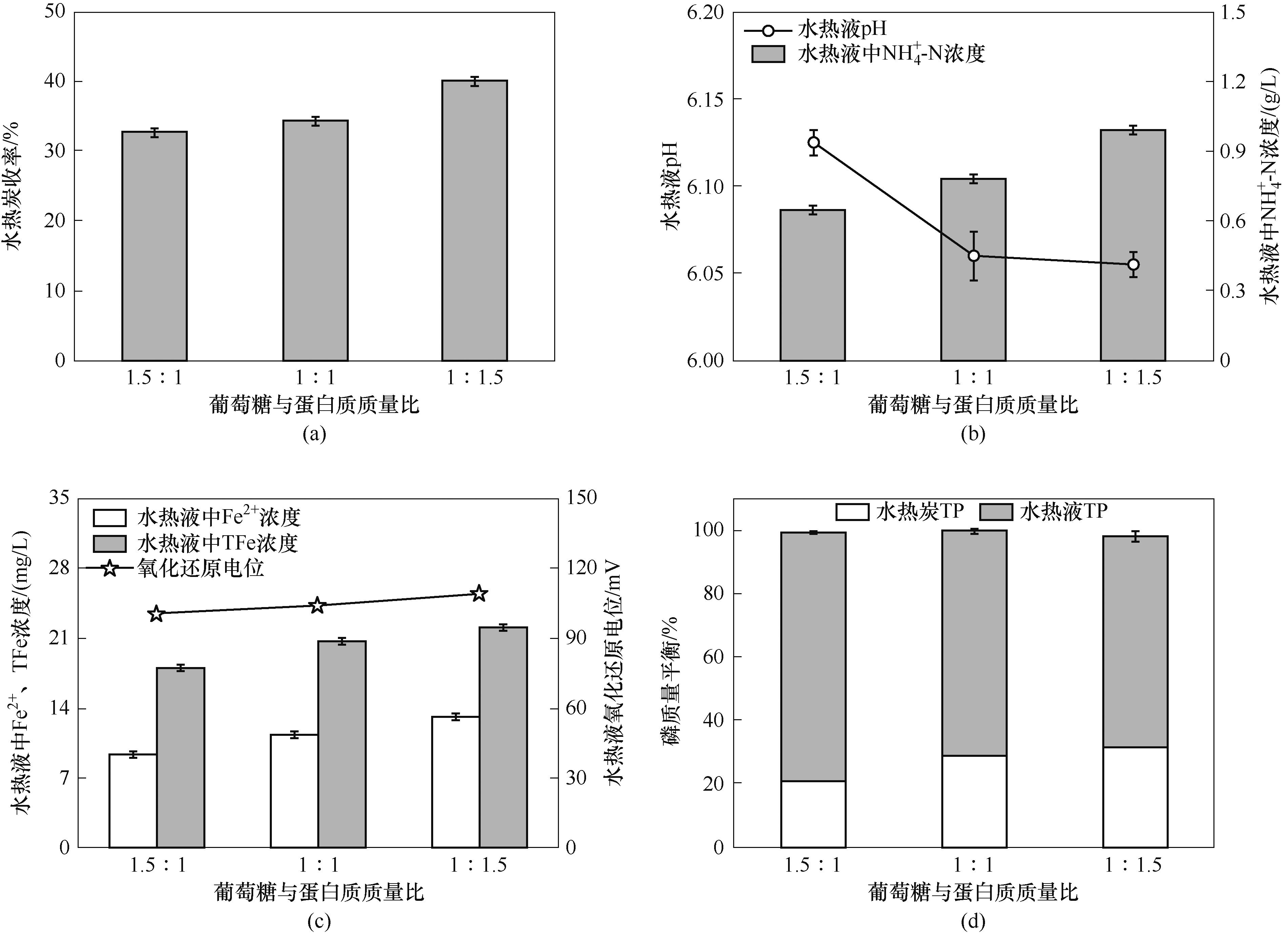
Fig.3 Effect of mass ratio of glucose to protein on hydrochar yield, pH and NH4+-N concentration of process water, Fe2+and TFe concentration and ORP of process water, and mass balance of phosphorus
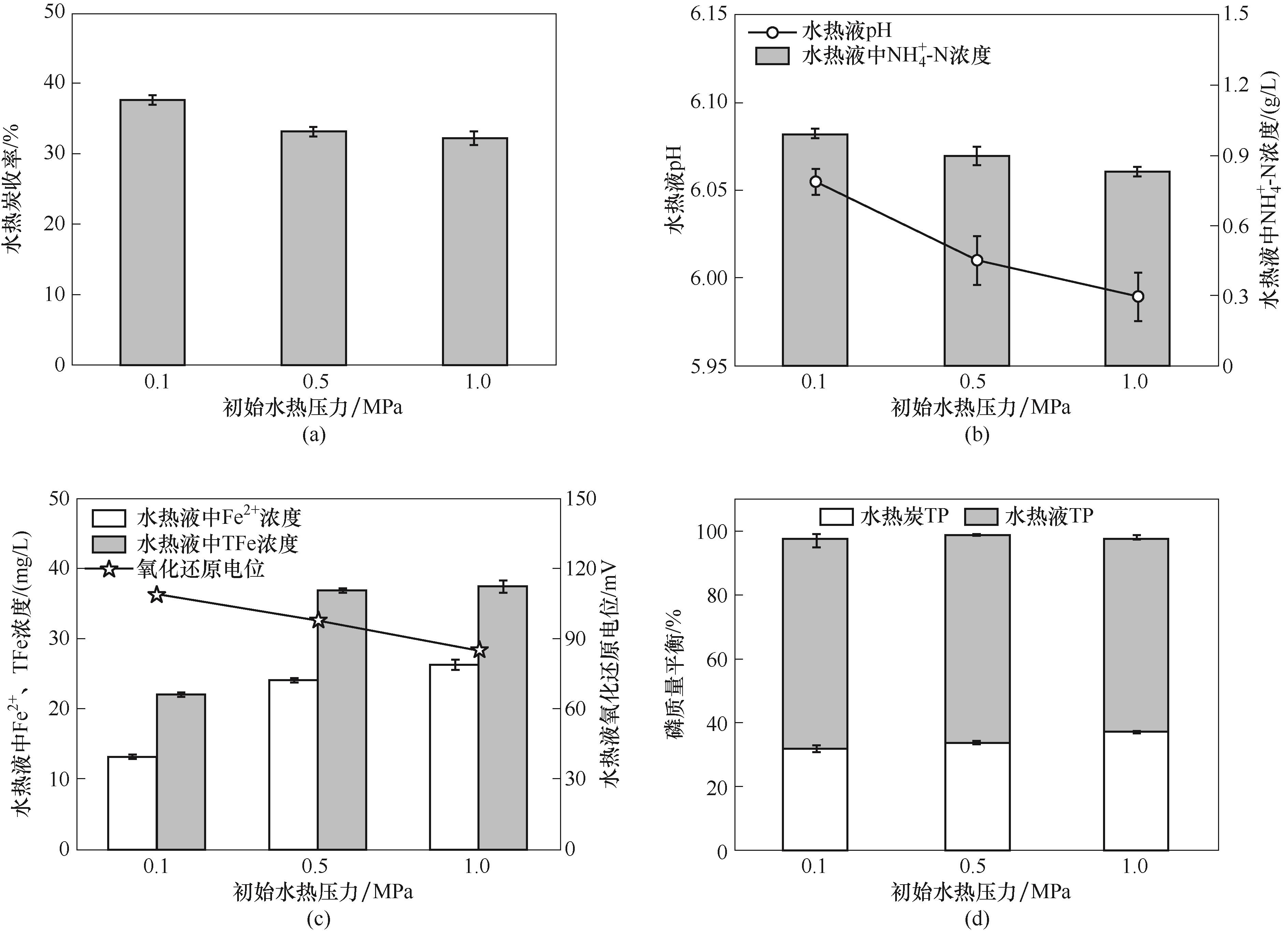
Fig.6 Effect of initial pressure on hydrochar yield, pH and NH4+-N concentration of process water, Fe2+ and TFe concentration and ORP of process water, and mass balance of phosphorus at the mass ratio of glucose to protein = 1∶1.5
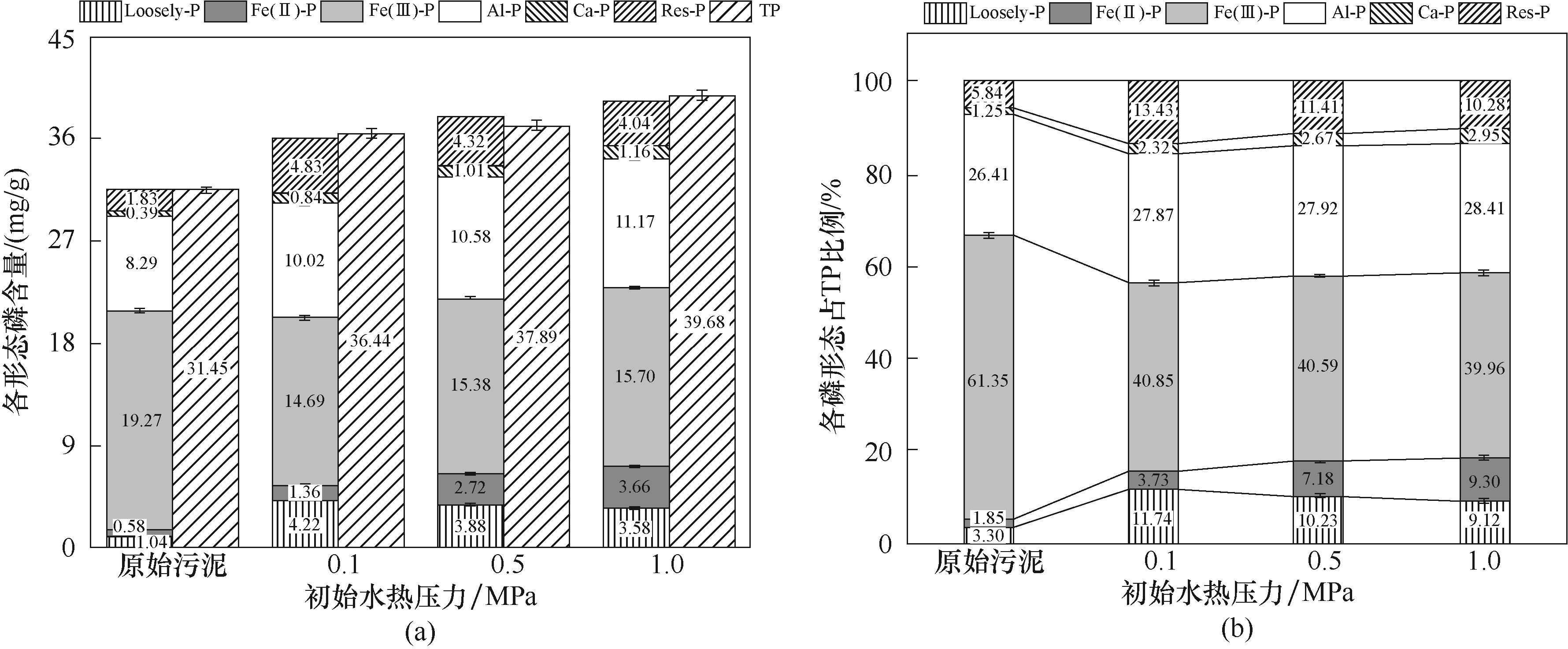
Fig.10 Effect of initial pressure on the content of each phosphorus fraction and the proportion of each phosphorus fraction in TP in hydrochar samples
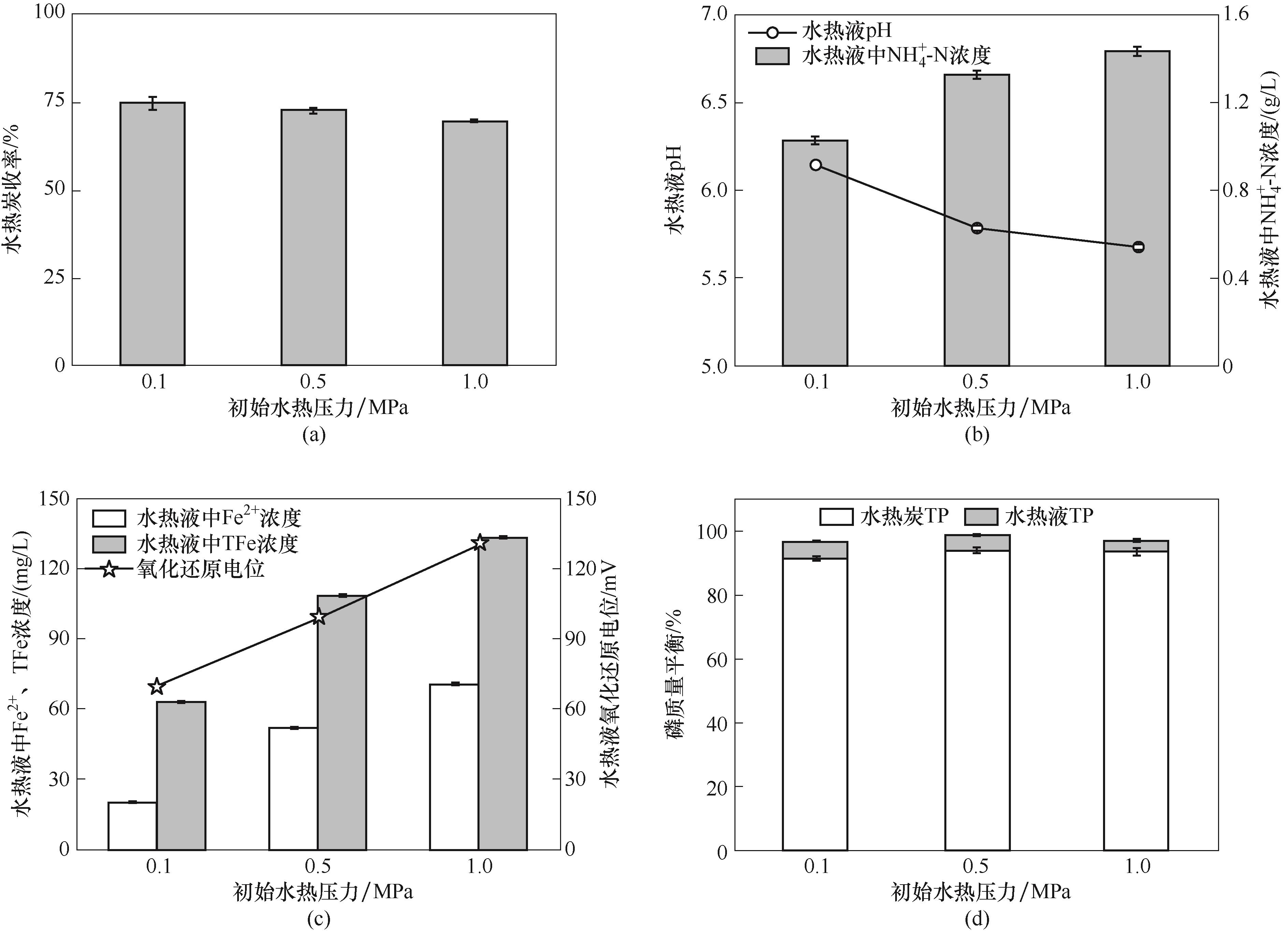
Fig.9 Effect of initial pressure on hydrochar yield, pH of and NH4+-N concentration of process water, Fe2+ and TFe concentration and ORP of process water, and mass balance of phosphorus
| 1 | Cordell D, Drangert J O, White S. The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19(2): 292-305. |
| 2 | Cooper J, Lombardi R, Boardman D, et al. The future distribution and production of global phosphate rock reserves[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2011, 57: 78-86. |
| 3 | Li K, Zhang D Q, Niu X J, et al. Insights into CO2 adsorption on KOH-activated biochars derived from the mixed sewage sludge and pine sawdust[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 826: 154133. |
| 4 | Zheng X Y, Ye Y T, Jiang Z W, et al. Enhanced transformation of phosphorus (P) in sewage sludge to hydroxyapatite via hydrothermal carbonization and calcium-based additive[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 738: 139786. |
| 5 | 王超, 刘清伟, 职音, 等. 中国市政污泥中磷的含量与形态分布[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1922-1930. |
| Wang C, Liu Q W, Zhi Y, et al. Contents and forms of phosphorous in the municipal sewage sludge of China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(4): 1922-1930. | |
| 6 | Wilfert P, Dugulan A I, Goubitz K, et al. Vivianite as the main phosphate mineral in digested sewage sludge and its role for phosphate recovery[J]. Water Research, 2018, 144: 312-321. |
| 7 | Frederichs T, Dobeneck von T, Bleil U, et al. Towards the identification of siderite, rhodochrosite, and vivianite in sediments by their low-temperature magnetic properties[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2003, 28(16/17/18/19): 669-679. |
| 8 | 钟旭群, 庄故章. 蓝铁矿特征及其对铁矿选矿的意义[J]. 有色金属, 2011, 63(2): 199-203. |
| Zhong X Q, Zhuang G Z. The mineralogical features of vivianite and its significance on iron ore process[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 63(2): 199-203. | |
| 9 | Prot T, Nguyen V H, Wilfert P, et al. Magnetic separation and characterization of vivianite from digested sewage sludge[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 224: 564-579. |
| 10 | 康素琴, 郑亚卿, 杨睿, 等. 基于酸浸焚烧污泥灰中的磷释放及蓝铁矿生成[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(1): 225-233. |
| Kang S Q, Zheng Y Q, Yang R, et al. Phosphorus release and formation of vivianite from acid leaching incineration sludge ash[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(1): 225-233. | |
| 11 | Wang S, Wu Y, An J K, et al. Geobacter autogenically secretes fulvic acid to facilitate the dissimilated iron reduction and vivianite recovery[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(17): 10850-10858. |
| 12 | Wang Q, Zhang C Q, Patel D, et al. Coevolution of iron, phosphorus, and sulfur speciation during anaerobic digestion with hydrothermal pretreatment of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(13): 8362-8372. |
| 13 | 陈伟, 郑晓园, 纪莎莎, 等. 污水污泥水热炭化处理研究进展[J]. 热能动力工程, 2020, 35(2): 1-8, 25. |
| Chen W, Zheng X Y, Ji S S, et al. Research progress on hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2020, 35(2): 1-8, 25. | |
| 14 | Wang F, Guo C N, Liu X Y, et al. Revealing carbon-iron interaction characteristics in sludge-derived hydrochars under different hydrothermal conditions[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 300: 134572. |
| 15 | Xiao Y, Ding L, Yang Y, et al. Iron valence state evolution and hydrochar properties under hydrothermal carbonization of dyeing sludge[J]. Waste Management, 2022, 152: 94-101. |
| 16 | Wang Q, Zhang C Q, Liu P, et al. Effect of interstage hydrothermal treatment on anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: speciation evolution of phosphorus, iron, and sulfur[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8: 16515-16525. |
| 17 | Ogorodova L, Vigasina M, Mel'chakova L, et al. Enthalpy of formation of natural hydrous iron phosphate: vivianite[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2017, 110: 193-200. |
| 18 | Yu S J, Zhao P, Yang X X, et al. Low-temperature hydrothermal carbonization of pectin enabled by high pressure[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2022, 166: 105627. |
| 19 | 于士杰, 赵鹏, 刘茂清, 等. 温度-压力解耦对木质素水热过程中结构变化及解聚产物的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2023, 51(8): 1106-1113, 1026. |
| Yu S J, Zhao P, Liu M Q, et al. Effects of decoupled temperature and pressure on the hydrothermal process of lignin[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2023, 51(8): 1106-1113, 1026. | |
| 20 | Zhuang X Z, Liu J G, Zhang Q, et al. A review on the utilization of industrial biowaste via hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 154: 111877. |
| 21 | Lu K X, Ping Q, Li Y M. Understanding the abiotic interaction between phosphate and macromolecular organic compounds in waste activated sludge during anaerobic treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 782: 146864. |
| 22 | Zhang X, Zhao B W, Li R, et al. Study on the feasibility of carbon source recovery by upflow anaerobic sludge blanket in simulated municipal wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 878: 163157. |
| 23 | Shen Y T, Qiu S, Chen Z P, et al. Free ammonia is the primary stress factor rather than total ammonium to Chlorella sorokiniana in simulated sludge fermentation liquor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125490. |
| 24 | Piaskowski K. Orthophosphate removal from aqueous solutions using drinking-water treatment sludge[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2013, 68(8): 1757-1762. |
| 25 | Yu B H, Luo J H, Xie H H, et al. Species, fractions, and characterization of phosphorus in sewage sludge: a critical review from the perspective of recovery[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 786: 147437. |
| 26 | Guo Q Q, Wang Y N, Zhao L Q, et al. Bioavailability transition path of phosphorus species during the sewage sludge incineration process[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 247: 118167. |
| 27 | Deng S Y, Liu J Q, Yang X F, et al. Release of phosphorus through pretreatment of waste activated sludge differs essentially from that of carbon and nitrogen resources: comparative analysis across four wastewater treatment facilities[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 396: 130423. |
| 28 | Gu S, Qian Y G, Jiao Y, et al. An innovative approach for sequential extraction of phosphorus in sediments: ferrous iron P as an independent P fraction[J]. Water Research, 2016, 103: 352-361. |
| 29 | Wang Q, Kim T H, Reitzel K, et al. Quantitative determination of vivianite in sewage sludge by a phosphate extraction protocol validated by PXRD, SEM-EDS, and 31P NMR spectroscopy towards efficient vivianite recovery[J]. Water Research, 2021, 202: 117411. |
| 30 | 郑晓园, 蒋正伟, 陈伟, 等. 污水污泥水热炭化过程中磷的迁移转化特性[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(5): 2017-2025. |
| Zheng X Y, Jiang Z W, Chen W, et al. Migration and transformation of phosphorus in sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization process[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(5): 2017-2025. | |
| 31 | Zhuang X Z, Huang Y Q, Song Y P, et al. The transformation pathways of nitrogen in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 463-470. |
| 32 | Wang T F, Zhai Y B, Zhu Y, et al. Influence of temperature on nitrogen fate during hydrothermal carbonization of food waste[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 182-189. |
| 33 | Zhang Q Z, Cao Y, He M J, et al. Improved energy recovery from yard waste by water-starved hydrothermal treatment: effects of process water and pressure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 394: 130211. |
| 34 | Zheng X Y, Shen M X, Ying Z, et al. Correlating phosphorus transformation with process water during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge via experimental study and mathematical modelling[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 807: 150750. |
| 35 | Wang S N, Cao J S, Zhang J L, et al. Recovery of phosphorus from wastewater containing humic substances through vivianite crystallization: interaction and mechanism analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 331: 117324. |
| 36 | 郝晓地, 周健, 王崇臣. 探究污泥厌氧消化系统中蓝铁矿生成的干扰因子[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(23): 1-7. |
| Hao X D, Zhou J, Wang C C. Determination of interference factors of vivianite formation in anaerobic digestion of excess sludge[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2018, 34(23): 1-7. | |
| 37 | Shi Y, Chen Z, Cao Y, et al. Migration and transformation mechanism of phosphorus in waste activated sludge during anaerobic fermentation and hydrothermal conversion[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123649. |
| 38 | Qian T T, Yang Q, Jun D C F, et al. Transformation of phosphorus in sewage sludge biochar mediated by a phosphate-solubilizing microorganism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 1573-1580. |
| [1] | Xusheng LIU, Zeyang LI, Yusen YANG, Min WEI. Research progress on electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction to gaseous products [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2385-2408. |
| [2] | Chenggong CHANG, Haonan SONG, Feixia LEI, Zichen DI, Fangqin CHENG. Study on the carbon reduction potential of blast furnace injection process using reformed coke oven gas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2344-2352. |
| [3] | Kaibo ZHANG, Jiaxin SHEN, Yuxia LI, Peng TAN, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN. Controllable construction of Cu(Ⅰ) in Y zeolite for adsorptive separation of ethylene/ethane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1607-1615. |
| [4] | Mingze SUN, Helai HUANG, Zhiqiang NIU. Pt-based oxygen reduction reaction catalysts: from single crystal electrode to nanostructured extended surface [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1256-1269. |
| [5] | Tiantian LYU, Min YUAN, Jiang WANG, Meizhen GAO, Jiahui YANG, Hong XU, Jinxiang DONG, Qi SHI. Preparation of ZTIF based hydrophobic micro-mesoporous carbon and their adsorption and separation performance of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1642-1654. |
| [6] | Xudong JIA, Bolong YANG, Qian CHENG, Xueli LI, Zhonghua XIANG. Preparation of high-efficiency iron-cobalt bimetallic site oxygen reduction electrocatalysts by step-by-step metal loading method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1578-1593. |
| [7] | Baofeng WANG, Shugao WANG, Fangqin CHENG. Progress in preparation and CO2 adsorption properties of solid waste-based sulfur-doped porous carbon materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 395-411. |
| [8] | Runmiao GAO, Mengjie SONG, Enyuan GAO, Long ZHANG, Xuan ZHANG, Keke SHAO, Zekang ZHEN, Zhengyong JIANG. Review on greenhouse gas reduction related to refrigerants in cold chain [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 1-7. |
| [9] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [10] | Song HE, Qiaomai LIU, Guangshuo XIE, Simin WANG, Juan XIAO. Two-phase flow simulation and surrogate-assisted optimization of gas film drag reduction in high-concentration coal-water slurry pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [11] | Xiaoxiong FAN, Lifang HAO, Chuigang FAN, Songgeng LI. Study on the catalytic denitrification performance of low-temperature NH3-SCR over LaMnO3/biochar catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [12] | Chen HAN, Youmin SITU, Bin ZHU, Jianliang XU, Xiaolei GUO, Haifeng LIU. Study of reaction and flow characteristics in multi-nozzle pulverized coal gasifier with co-processing of wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [13] | Manzheng ZHANG, Meng XIAO, Peiwei YAN, Zheng MIAO, Jinliang XU, Xianbing JI. Working fluid screening and thermodynamic optimization of hazardous waste incineration coupled organic Rankine cycle system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [14] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [15] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||