CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (7): 3757-3767.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201841
• Biochemical engineering and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
DUAN Lingxuan( ),YAO Guangxiao,JIANG Liang,WANG Shizhen(
),YAO Guangxiao,JIANG Liang,WANG Shizhen( )
)
Received:2020-12-16
Revised:2021-01-27
Online:2021-07-05
Published:2021-07-05
Contact:
WANG Shizhen
通讯作者:
王世珍
作者简介:段凌暄(1998—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
DUAN Lingxuan, YAO Guangxiao, JIANG Liang, WANG Shizhen. Genome mining of organic solvent tolerant amino acid dehydrogenase for biosynthesis of unnatural amino acids in non-aqueous system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3757-3767.
段凌暄, 姚光晓, 江亮, 王世珍. 耐有机溶剂氨基酸脱氢酶基因挖掘与非天然氨基酸的非水相合成[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3757-3767.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 分类 | 菌株名称 | 分类 | 菌株名称 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 嗜热 | Geobacillus kaustophilus | 嗜盐 | Halobacterium salinarum |
| Natranaerobius thermophilus | Haloferax volcanii | ||
| Methanococcus jannaschii | Haloferax lucentense | ||
| Thermotoga maritima | Haloarcula japonica | ||
| Geobacillus stearothermophilus 10 | Halogranum rubrum | ||
| Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans | Halogeometyicum borinquense | ||
| 嗜热嗜碱 | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | 嗜盐嗜碱 | Euhalothece natronophila |
| Halothermothrix orenii | Ferroplasma acidiphilum |
Table 1 Screening of amino acid dehydrogenases from extremophiles
| 分类 | 菌株名称 | 分类 | 菌株名称 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 嗜热 | Geobacillus kaustophilus | 嗜盐 | Halobacterium salinarum |
| Natranaerobius thermophilus | Haloferax volcanii | ||
| Methanococcus jannaschii | Haloferax lucentense | ||
| Thermotoga maritima | Haloarcula japonica | ||
| Geobacillus stearothermophilus 10 | Halogranum rubrum | ||
| Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans | Halogeometyicum borinquense | ||
| 嗜热嗜碱 | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | 嗜盐嗜碱 | Euhalothece natronophila |
| Halothermothrix orenii | Ferroplasma acidiphilum |
| Number | Average value | ΔHm/(kcal/mol) | ΔCp/(kcal/(mol·K)) | Tm/℃ | ΔGr/(kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KJE28589.1 | -144.7 | -4.02 | 67.1 | -7 |
| 2 | WP-010871127.1 | -127.1 | -3.65 | 65 | -6 |
| 3 | WP-091347685.1 | -138 | -3.6 | 71.2 | -6.8 |
| 4 | WP-004590695.1 | -154 | -4.36 | 65.9 | -7.4 |
| 5 | ALA71326.1 | -118.5 | -3.49 | 63.4 | -5.6 |
| 6 | PSR36482.1 | -128 | -3.42 | 69.6 | -6.3 |
| 7 | WP-012635747.1 | -95.9 | -2.71 | 66 | -4.6 |
| 8 | NT2349 | -113.3 | -3.34 | 63.5 | -5.3 |
Table 2 Comparison of thermodynamic parameters of amino acid dehydrogenases from extremophiles
| Number | Average value | ΔHm/(kcal/mol) | ΔCp/(kcal/(mol·K)) | Tm/℃ | ΔGr/(kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KJE28589.1 | -144.7 | -4.02 | 67.1 | -7 |
| 2 | WP-010871127.1 | -127.1 | -3.65 | 65 | -6 |
| 3 | WP-091347685.1 | -138 | -3.6 | 71.2 | -6.8 |
| 4 | WP-004590695.1 | -154 | -4.36 | 65.9 | -7.4 |
| 5 | ALA71326.1 | -118.5 | -3.49 | 63.4 | -5.6 |
| 6 | PSR36482.1 | -128 | -3.42 | 69.6 | -6.3 |
| 7 | WP-012635747.1 | -95.9 | -2.71 | 66 | -4.6 |
| 8 | NT2349 | -113.3 | -3.34 | 63.5 | -5.3 |

Fig.2 Structure of NT2349 and surface charged residues distribution(a) NT2349 three-dimensional structure; (b) acidic and basic amino acid residue distribution (red represents acidic amino acids, blue represents basic amino acids); (c) the surface charge distribution of NT2349 (red represents negative charge, blue represents positive charge)
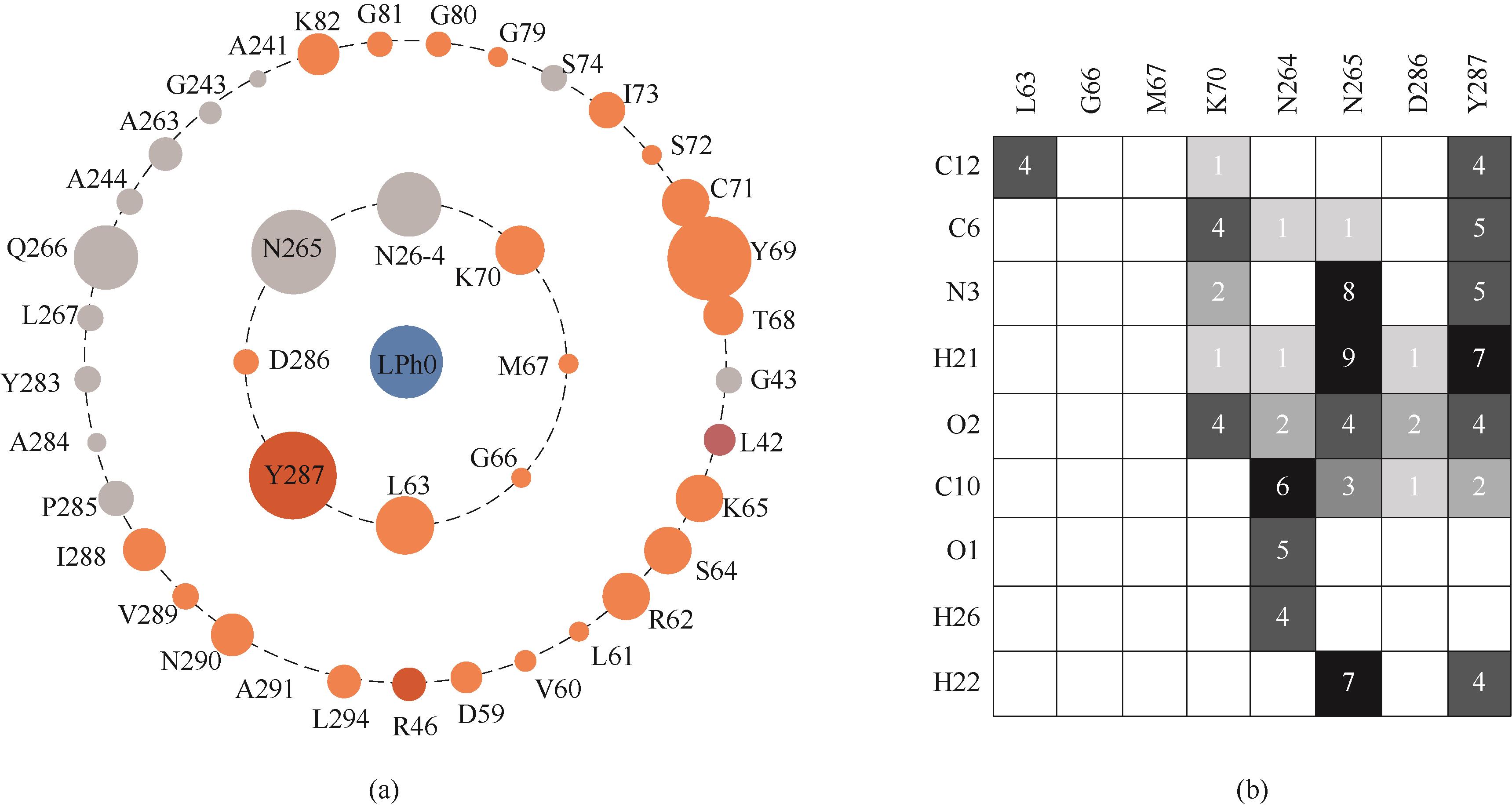
Fig.3 Interactions of secondary structure of NT2349 with L-phenylalanine(a) key residues interact with L-phenylalanine; (b) interaction Heatmap of active site with L-phenylalanine
| 1 | Liszka M J, Clark M E, Schneider E, et al. Nature versus nurture: developing enzymes that function under extreme conditions[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 2012, 3: 77-102. |
| 2 | Chen F F, Zheng G W, Liu L, et al. Reshaping the active pocket of amine dehydrogenases for asymmetric synthesis of bulky aliphatic amines[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(3): 2622-2628. |
| 3 | Dhake K P, Thakare D D, Bhanage B M. Lipase: a potential biocatalyst for the synthesis of valuable flavour and fragrance ester compounds[J]. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 2013, 28(2): 71-83. |
| 4 | DasSarma S, DasSarma P. Halophiles and their enzymes: negativity put to good use[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2015, 25: 120-126. |
| 5 | Chen S, Engel P. An engineered mutant, L307V of phenylalanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus: high activity and stability in organic-aqueous solvent mixtures and utility for synthesis of non-natural L-amino acids [J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2007, 131(2): 116. |
| 6 | Munawar N, Engel P C. Overexpression in a non-native halophilic host and biotechnological potential of NAD+-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium salinarum strain NRC-36014[J]. Extremophiles, 2012, 16(3): 463-476. |
| 7 | Alsafadi D, Paradisi F. Effect of organic solvents on the activity and stability of halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2) from Haloferax volcanii[J]. Extremophiles, 2013, 17(1): 115-122. |
| 8 | Munawar N, Engel P C. Prospects for robust biocatalysis: engineering of novel specificity in a halophilic amino acid dehydrogenase[J]. Extremophiles, 2013, 17(1): 43-51. |
| 9 | Timpson L M, Alsafadi D, Mac Donnchadha C, et al. Characterization of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH12) from Haloarcula marismortui, an extreme halophile from the Dead Sea[J]. Extremophiles, 2012, 16(1): 57-66. |
| 10 | Hartmann E M, Durighello E, Pible O, et al. Proteomics meets blue biotechnology: a wealth of novelties and opportunities[J]. Marine Genomics, 2014, 17: 35-42. |
| 11 | Nguyen V, Wilson C, Hoemberger M, et al. Evolutionary drivers of thermoadaptation in enzyme catalysis[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6322): 289-294. |
| 12 | Broom A, Trainor K, MacKenzie D W, et al. Using natural sequences and modularity to design common and novel protein topologies[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 38: 26-36. |
| 13 | Wang H Y, Qu G, Li J K, et al. Data mining of amine dehydrogenases for the synthesis of enantiopure amino alcohols[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(17): 5945-5952. |
| 14 | Dalmaso G Z, Ferreira D, Vermelho A B. Marine extremophiles: a source of hydrolases for biotechnological applications[J]. Marine Drugs, 2015, 13(4): 1925-1965. |
| 15 | Trincone A. Biocatalytic processes using marine biocatalysts: ten cases in point[J]. Current Organic Chemistry, 2013, 17(10): 1058-1066. |
| 16 | Mutti F G, Knaus T, Scrutton N S, et al. Conversion of alcohols to enantiopure amines through dual-enzyme hydrogen-borrowing cascades[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6255): 1525-1529. |
| 17 | Ducrot L, Bennett M, Grogan G, et al. NAD(P)H-dependent enzymes for reductive amination: active site description and carbonyl-containing compound spectrum[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2021, 363(2): 328-351. |
| 18 | Liu Z N, Lei D W, Qiao B, et al. Integrative biosynthetic gene cluster mining to optimize a metabolic pathway to efficiently produce L-homophenylalanine in Escherichia coli[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(11): 2943-2954. |
| 19 | 陈曦, 高秀珍, 朱敦明. 氨基酸脱氢酶的催化机理、分子改造及合成应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2017, 57(8): 1249-1261. |
| Chen X, Gao X Z, Zhu D M. Catalysis, engineering and application of amino acid dehydrogenases[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2017, 57(8): 1249-1261. | |
| 20 | Vallenet D, Calteau A, Cruveiller S, et al. MicroScope in 2017: an expanding and evolving integrated resource for community expertise of microbial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(D1): D517-D528. |
| 21 | Schaeffer D, Grishin N V. Identification of protein homologs and domain boundaries by iterative sequence alignment [J]. Computational Methods in Protein Evolution, 2019, 1851: 277-286. |
| 22 | Yang J Y, Zhang Y. I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(W1): W174-W181. |
| 23 | Studer G, Rempfer C, Waterhouse A M, et al. QMEANDisCo—distance constraints applied on model quality estimation[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(6): 1765-1771. |
| 24 | Kikani B A, Singh S P. The stability and thermodynamic parameters of a very thermostable and calcium-independent α-amylase from a newly isolated bacterium, Anoxybacillus beppuensis TSSC-1[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2012, 47(12): 1791-1798. |
| 25 | Lin P, Zhang Y H, Yao G X, et al. Immobilization of formate dehydrogenase on polyethylenimine-grafted graphene oxide with kinetics and stability study[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2020, 20(3/4): 104-111. |
| 26 | 石云云, 李信志, 张桂敏. 微生物嗜盐酶的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2017, 57(8): 1180-1188. |
| Shi Y Y, Li X Z, Zhang G M. Advances in microbial halophilic enzymes[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2017, 57(8): 1180-1188. | |
| 27 | Kayikci M, Venkatakrishnan A J, Scott-Brown J, et al. Visualization and analysis of non-covalent contacts using the Protein Contacts Atlas[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2018, 25(2): 185-194. |
| 28 | Xu L S, Wang Z Y, Mao P T, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of S-phenyl-L-cysteine from keratin hydrolysis industries wastewater with tryptophan synthase[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 133: 635-637. |
| 29 | Dumorné K, Córdova D C, Astorga-Eló M, et al. Extremozymes: a potential source for industrial applications[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 27(4): 649-659. |
| 30 | Raddadi N, Cherif A, Daffonchio D, et al. Biotechnological applications of extremophiles, extremozymes and extremolytes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(19): 7907-7913. |
| 31 | Jin M, Gai Y, Guo X, et al. Properties and applications of extremozymes from deep-sea extremophilic microorganisms: a mini review[J]. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17(12): 656. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [3] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [4] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [5] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [6] | Lanhe ZHANG, Qingyi LAI, Tiezheng WANG, Xiaozhuo GUAN, Mingshuang ZHANG, Xin CHENG, Xiaohui XU, Yanping JIA. Effect of H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge properties in SBR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [7] | Lufan JIA, Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG. Aqueous two-phase system based adherent droplet microfluidics for enhanced enzymatic reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [8] | Yang HU, Yan SUN. Self-propulsion of enzyme and enzyme-induced micro-/nanomotor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 116-132. |
| [9] | Xin LIU, Jun GE, Chun LI. Light-driven microbial hybrid systems improve level of biomanufacturing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 330-341. |
| [10] | Zhuotao TAN, Siyu QI, Mengjiao XU, Jie DAI, Chenjie ZHU, Hanjie YING. Application of the redox cascade systems with coenzyme self-cycling in biocatalytic processes: opportunities and challenges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 45-59. |
| [11] | Shaojie AN, Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI. Construction of pH sensitive artificial glutathione peroxidase based on the formation and dissociation of molecular machine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678. |
| [12] | Mai ZHANG, Yao TIAN, Zhiqi GUO, Ye WANG, Guangjin DOU, Hao SONG. Design and optimization of photocatalysis-biological hybrid system for green synthesis of fuels and chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2774-2789. |
| [13] | Jiachen SUN, Wentao SUN, Hui SUN, Bo LYU, Chun LI. Licorice flavone synthase Ⅱ catalyzes liquiritigenin to specifically synthesize 7,4′-dihydroxyflavone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3202-3211. |
| [14] | Xinzhe ZHANG, Wentao SUN, Bo LYU, Chun LI. Oxidative modification of plant natural products and microbial manufacturing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2790-2805. |
| [15] | Yinlong XU, Wenchieh CHENG, Lin WANG, Zhongfei XUE, Yixin XIE. Implication and enhancement mechanism of chitosan-assisted enzyme- induced carbonate precipitation for copper wastewater treatment [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2222-2232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||