CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (10): 4603-4612.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220502
• Biochemical engineering and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haibo LIU( ), Nan WANG, Hongzhou LIU, Tiezhu CHEN, Jianchang LI(
), Nan WANG, Hongzhou LIU, Tiezhu CHEN, Jianchang LI( )
)
Received:2022-04-06
Revised:2022-09-04
Online:2022-11-02
Published:2022-10-05
Contact:
Jianchang LI
通讯作者:
李建昌
作者简介:刘海波(1997—),男,硕士研究生,2411367039@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Haibo LIU, Nan WANG, Hongzhou LIU, Tiezhu CHEN, Jianchang LI. Effects of voltage perturbation on the activities of microorganisms and key enzymes in EAD metabolic flux[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4603-4612.
刘海波, 王楠, 刘洪周, 陈铁柱, 李建昌. 电压扰动对EAD代谢通量中微生物与关键酶活性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4603-4612.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
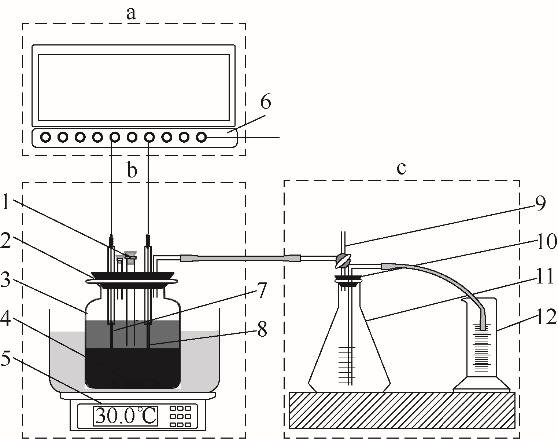
Fig.1 EAD experimental setupa—electrolytic current and voltage recording unit; b—EAD reaction unit; c—drainage gas gathering unit; 1—pH determination, feeding and sampling port; 2—intake port; 3—fermentation tank; 4—stirner; 5—thermostatic magnetic stirrer; 6—broadscreen paperless recorder; 7—graphite electrode; 8—platinum electrode; 9—glass tee; 10—sealing cover; 11—collector; 12—gauge tube
| No. | 反应式 | No. | 反应式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Glu+PEP  G6P + Pyr G6P + Pyr | R20 | HPr + 2 H2O  Ace + CO2 +3 H2 Ace + CO2 +3 H2 |
| R2 | NADH + Pyr  Lac + NAD Lac + NAD | R21 | But + 2 H2O  2 Ace + 2 H2 + H+ 2 Ace + 2 H2 + H+ |
| R3 | Pyr + NADH  NAD + For +AcCoA NAD + For +AcCoA | R22 | HPr  HPr (ext) HPr (ext) |
| R4 | 2 Fd + Pyr + CoA  CO2 + AcCoA + 2 FdH CO2 + AcCoA + 2 FdH | R23 | Eth+ HPr  Val (ext) + H2O Val (ext) + H2O |
| R5 | 2 Fd + NADH  2 FdH + NAD 2 FdH + NAD | R24 | For  For (ext) For (ext) |
| R6 | NADPH + NAD  NADH + NADP NADH + NADP | R25 | CO2 CO2 (ext) CO2 (ext) |
| R7 | 2 NADH  H2 + 2 NAD H2 + 2 NAD | R26 | CO2 + 4 H2 CH4 + 2 H2O CH4 + 2 H2O |
| R8 | 2 FdH  H2 + 2 Fd H2 + 2 Fd | R27 | H2 H2 (ext) H2 (ext) |
| R9 | Lac  Lac (ext) Lac (ext) | R28 | 2 AcCoA + H2 PrOH(ext) +2 CoA + CO2 PrOH(ext) +2 CoA + CO2 |
| R10 | Lac + NADH  HPr + NAD HPr + NAD | R29 | Ace  CO2 + CH4 CO2 + CH4 |
| R11 | For  CO2 + H2 CO2 + H2 | R30 | Ace  Ace (ext) Ace (ext) |
| R12 | AcCoA + ADP + iP  ATP + Ace + CoA ATP + Ace + CoA | R31 | Eth  Eth (ext) Eth (ext) |
| R13 | AcCoA + 2 NADH  Eth + CoA + 2 NAD Eth + CoA + 2 NAD | R32 | But + Eth  Hex (ext) + H2O Hex (ext) + H2O |
| R14 | 2 AcCoA + NADH  CoA + H2O + CroCoA + NAD CoA + H2O + CroCoA + NAD | R33 | But  But (ext) But (ext) |
| R15 | CroCoA + 2 Fd + NADH  ButCoA + 2 FdH + NAD ButCoA + 2 FdH + NAD | R34 | But + 2 NADH  BuOH(ext) + CoA + 2 NAD BuOH(ext) + CoA + 2 NAD |
| R16 | CroCoA + NADH  ButCoA + NAD ButCoA + NAD | R35 | Pyr  Pyr (ext) Pyr (ext) |
| R17 | ButCoA + ADP + iP  But + ATP + CoA But + ATP + CoA | R36 | CH4  CH4 (ext) CH4 (ext) |
| R18 | 2 CO2 + 4 H2 Ace +2 H2O Ace +2 H2O | R37 | 2 H+ + 2 e- H2 H2 |
| R19 | Eth + 2H2O  4 H+ + Ace 4 H+ + Ace |
Table 1 Reaction formula of EAD methanogenesis metabolic pathway
| No. | 反应式 | No. | 反应式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Glu+PEP  G6P + Pyr G6P + Pyr | R20 | HPr + 2 H2O  Ace + CO2 +3 H2 Ace + CO2 +3 H2 |
| R2 | NADH + Pyr  Lac + NAD Lac + NAD | R21 | But + 2 H2O  2 Ace + 2 H2 + H+ 2 Ace + 2 H2 + H+ |
| R3 | Pyr + NADH  NAD + For +AcCoA NAD + For +AcCoA | R22 | HPr  HPr (ext) HPr (ext) |
| R4 | 2 Fd + Pyr + CoA  CO2 + AcCoA + 2 FdH CO2 + AcCoA + 2 FdH | R23 | Eth+ HPr  Val (ext) + H2O Val (ext) + H2O |
| R5 | 2 Fd + NADH  2 FdH + NAD 2 FdH + NAD | R24 | For  For (ext) For (ext) |
| R6 | NADPH + NAD  NADH + NADP NADH + NADP | R25 | CO2 CO2 (ext) CO2 (ext) |
| R7 | 2 NADH  H2 + 2 NAD H2 + 2 NAD | R26 | CO2 + 4 H2 CH4 + 2 H2O CH4 + 2 H2O |
| R8 | 2 FdH  H2 + 2 Fd H2 + 2 Fd | R27 | H2 H2 (ext) H2 (ext) |
| R9 | Lac  Lac (ext) Lac (ext) | R28 | 2 AcCoA + H2 PrOH(ext) +2 CoA + CO2 PrOH(ext) +2 CoA + CO2 |
| R10 | Lac + NADH  HPr + NAD HPr + NAD | R29 | Ace  CO2 + CH4 CO2 + CH4 |
| R11 | For  CO2 + H2 CO2 + H2 | R30 | Ace  Ace (ext) Ace (ext) |
| R12 | AcCoA + ADP + iP  ATP + Ace + CoA ATP + Ace + CoA | R31 | Eth  Eth (ext) Eth (ext) |
| R13 | AcCoA + 2 NADH  Eth + CoA + 2 NAD Eth + CoA + 2 NAD | R32 | But + Eth  Hex (ext) + H2O Hex (ext) + H2O |
| R14 | 2 AcCoA + NADH  CoA + H2O + CroCoA + NAD CoA + H2O + CroCoA + NAD | R33 | But  But (ext) But (ext) |
| R15 | CroCoA + 2 Fd + NADH  ButCoA + 2 FdH + NAD ButCoA + 2 FdH + NAD | R34 | But + 2 NADH  BuOH(ext) + CoA + 2 NAD BuOH(ext) + CoA + 2 NAD |
| R16 | CroCoA + NADH  ButCoA + NAD ButCoA + NAD | R35 | Pyr  Pyr (ext) Pyr (ext) |
| R17 | ButCoA + ADP + iP  But + ATP + CoA But + ATP + CoA | R36 | CH4  CH4 (ext) CH4 (ext) |
| R18 | 2 CO2 + 4 H2 Ace +2 H2O Ace +2 H2O | R37 | 2 H+ + 2 e- H2 H2 |
| R19 | Eth + 2H2O  4 H+ + Ace 4 H+ + Ace |
| 代谢物 | 含量/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组(1.0 V) | 0.6 V扰动 | 1.4 V扰动 | |
| 葡萄糖 | 1.1274 ± 0.0154 | 1.1274 ± 0.0055 | 1.1274 ± 0.0175 |
| 甲酸 | 0.0026± 0.0000 | 0.0091 ± 0.0021 | 0.0095± 0.0026 |
| 乙酸 | 0.7511 ± 0.1440 | 0.5563 ± 0.0770 | 0.7114 ± 0.1202 |
| 丙酸 | 0.1061 ± 0.0096 | 0.0915 ± 0.0049 | 0.1062 ± 0.0023 |
| 丁酸 | 0.4180± 0.0335 | 0.4487 ± 0.0391 | 0.4054 ± 0.0201 |
| 乳酸 | 0.0107 ± 0.0046 | 0.0086 ± 0.0035 | 0.0129 ± 0.0056 |
| 丙酮酸 | 0.0157 ± 0.0037 | 0.0355± 0.0074 | 0.0265 ± 0.0171 |
| 戊酸 | 0.0230 ± 0.0107 | 0.0114 ± 0.0046 | 1.2740 ± 0.0093 |
| 己酸 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| 乙醇 | 0.0173 ± 0.0014 | 0.0099 ± 0.0019 | 0.0161 ± 0.0067 |
| 丙醇 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| 丁醇 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| CO2 | 0.2258 ± 0.0229 | 0.2398 ± 0.0376 | 0.2398 ± 0.0071 |
| CH4 | 0.2974 ± 0.0127 | 0.5222 ± 0.0515 | 0.3951 ± 0.0293 |
| H2 | 0.0281 ± 0.0231 | 0.0242 ± 0.0137 | 0.0039 ± 0.0024 |
Table 2 Contents of metabolites related to voltage disturbance
| 代谢物 | 含量/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组(1.0 V) | 0.6 V扰动 | 1.4 V扰动 | |
| 葡萄糖 | 1.1274 ± 0.0154 | 1.1274 ± 0.0055 | 1.1274 ± 0.0175 |
| 甲酸 | 0.0026± 0.0000 | 0.0091 ± 0.0021 | 0.0095± 0.0026 |
| 乙酸 | 0.7511 ± 0.1440 | 0.5563 ± 0.0770 | 0.7114 ± 0.1202 |
| 丙酸 | 0.1061 ± 0.0096 | 0.0915 ± 0.0049 | 0.1062 ± 0.0023 |
| 丁酸 | 0.4180± 0.0335 | 0.4487 ± 0.0391 | 0.4054 ± 0.0201 |
| 乳酸 | 0.0107 ± 0.0046 | 0.0086 ± 0.0035 | 0.0129 ± 0.0056 |
| 丙酮酸 | 0.0157 ± 0.0037 | 0.0355± 0.0074 | 0.0265 ± 0.0171 |
| 戊酸 | 0.0230 ± 0.0107 | 0.0114 ± 0.0046 | 1.2740 ± 0.0093 |
| 己酸 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| 乙醇 | 0.0173 ± 0.0014 | 0.0099 ± 0.0019 | 0.0161 ± 0.0067 |
| 丙醇 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| 丁醇 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| CO2 | 0.2258 ± 0.0229 | 0.2398 ± 0.0376 | 0.2398 ± 0.0071 |
| CH4 | 0.2974 ± 0.0127 | 0.5222 ± 0.0515 | 0.3951 ± 0.0293 |
| H2 | 0.0281 ± 0.0231 | 0.0242 ± 0.0137 | 0.0039 ± 0.0024 |
| Sample ID | Observed species | Shannon | Chao1 | ACE | Goods coverage | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 798.5 | 4.88 | 885.14 | 909.99 | 0.997 | 0.86 |
| 0.6 V | 1605.5 | 5.33 | 1776.61 | 1822.77 | 0.994 | 0.84 |
| 1.0 V | 1218 | 5.11 | 1363.39 | 1399.28 | 0.995 | 0.85 |
| 1.4 V | 1263.66 | 5.20 | 1416.81 | 1454.71 | 0.995 | 0.87 |
Table 3 Analysis of Alpha Diversity index of anodic film microorganisms
| Sample ID | Observed species | Shannon | Chao1 | ACE | Goods coverage | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 798.5 | 4.88 | 885.14 | 909.99 | 0.997 | 0.86 |
| 0.6 V | 1605.5 | 5.33 | 1776.61 | 1822.77 | 0.994 | 0.84 |
| 1.0 V | 1218 | 5.11 | 1363.39 | 1399.28 | 0.995 | 0.85 |
| 1.4 V | 1263.66 | 5.20 | 1416.81 | 1454.71 | 0.995 | 0.87 |
| 1 | Nookwam K, Cheirsilp B, Maneechote W, et al. Microbial fuel cells with photosynthetic-cathodic chamber in vertical cascade for integrated bioelectricity, biodiesel feedstock production and wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 346: 126559. |
| 2 | Lim S S, Fontmorin J M, Ikhmal Salehmin M N, et al. Enhancing hydrogen production through anode fed-batch mode and controlled cell voltage in a microbial electrolysis cell fully catalysed by microorganisms[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 288(Pt 2): 132548. |
| 3 | Liu H, Grot S, Logan B E. Electrochemically assisted microbial production of hydrogen from acetate[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(11): 4317-4320. |
| 4 | Yu Z S, Leng X Y, Zhao S, et al. A review on the applications of microbial electrolysis cells in anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 255: 340-348. |
| 5 | Hasany M, Mardanpour M M, Yaghmaei S. Biocatalysts in microbial electrolysis cells: a review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(3): 1477-1493. |
| 6 | Logan B E, Call D, Cheng S A, et al. Microbial electrolysis cells for high yield hydrogen gas production from organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(23): 8630-8640. |
| 7 | Bakonyi P, Kumar G, Koók L, et al. Microbial electrohydrogenesis linked to dark fermentation as integrated application for enhanced biohydrogen production: a review on process characteristics, experiences and lessons[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 251: 381-389. |
| 8 | Wang X T, Zhang Y F, Wang B, et al. Enhancement of methane production from waste activated sludge using hybrid microbial electrolysis cells-anaerobic digestion (MEC-AD) process — a review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 346: 126641. |
| 9 | Raphael R, Luc E, Emma R, et al. Microbial electrolysis cell (MEC): strengths, weaknesses and research needs from electrochemical engineering standpoint[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 257: 113938. |
| 10 | Yang G Q, Huang L Y, Yu Z, et al. Anode potentials regulate Geobacter biofilms: new insights from the composition and spatial structure of extracellular polymeric substances[J]. Water Research, 2019, 159: 294-301. |
| 11 | Lee H S, Vermaas W F J, Rittmann B E. Biological hydrogen production: prospects and challenges[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2010, 28(5): 262-271. |
| 12 | Cai G Q, Jin B, Monis P, et al. Metabolic flux network and analysis of fermentative hydrogen production[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2011, 29(4): 375-387. |
| 13 | Schmidt-Rohr K. Oxygen is the high-energy molecule powering complex multicellular life: fundamental corrections to traditional bioenergetics[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(5): 2221-2233. |
| 14 | Iyer P P, Lawrence S H, Luther K B, et al. Crystal structure of phosphotransacetylase from the methanogenic archaeon methanosarcina thermophila[J]. Structure, 2004, 12(4): 559-567. |
| 15 | Zhang M, Zhang Y, Li Z W, et al. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste/excess sludge: substrates - products transformation and role of NADH as an indicator[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 232: 197-206. |
| 16 | Sun H L, Li J C, Yang M H, et al. Influence of initial pH on anodic biofilm formation in single-chambered microbial electrolysis cells[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2019, 28(3): 1377-1384. |
| 17 | Förster J, Famili I, Fu P, et al. Genome-scale reconstruction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic network[J]. Genome Research, 2003, 13(2): 244-253. |
| 18 | Gonzalez-Garcia R A, Aispuro-Castro R, Salgado-Manjarrez E, et al. Metabolic pathway and flux analysis of H2 production by an anaerobic mixed culture [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(7): 4069-4082. |
| 19 | Li F, Li Y X, Cao Y X, et al. Modular engineering to increase intracellular NAD(H/+) promotes rate of extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3637. |
| 20 | Rafieenia R, Chaganti S R. Flux balance analysis of different carbon source fermentation with hydrogen producing Clostridium butyricum using cell net analyzer[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 175: 613-618. |
| 21 | Sheng W, Yang L, Wang J P, et al. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of gentamycin residues in animal-derived foods[J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2013, 50(1): 204-209. |
| 22 | Choi J H, Lim Y T, Oh B K. Development of colorimetric enzyme-ball for signal amplification of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay[J]. Science of Advanced Materials, 2014, 6(11): 2572- 2576. |
| 23 | Marsili E, Rollefson J B, Baron D B, et al. Microbial biofilm voltammetry: direct electrochemical characterization of catalytic electrode-attached biofilms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(23): 7329-7337. |
| 24 | Westermann P, Jorgensen B, Lange L, et al. Maximizing renewable hydrogen production from biomass in a bio/catalytic refinery[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(17): 4135-4141. |
| 25 | Cheng H H, Whang L M, Lin C A, et al. Metabolic flux network analysis of fermentative hydrogen production: using Clostridium tyrobutyricum as an example[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 141: 233-239. |
| 26 | Wang K, Sheng Y X, Cao H B, et al. Impact of applied current on sulfate-rich wastewater treatment and microbial biodiversity in the cathode chamber of microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 307: 150-158. |
| 27 | Eryildiz B, Lukitawesa, Taherzadeh M J. Effect of pH, substrate loading, oxygen, and methanogens inhibitors on volatile fatty acid (VFA) production from citrus waste by anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 302: 122800. |
| 28 | Zhu Y, Yang S T. Effect of pH on metabolic pathway shift in fermentation of xylose by Clostridium tyrobutyricum [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2004, 110(2): 143-157. |
| 29 | Sikora A, Detman A, Mielecki D, et al. Searching for Metabolic Pathways of Anaerobic Digestion: a Useful List of the Key Enzymes[M]. London: IntechOpen Press, 2018. |
| 30 | Jo J H, Kim W. Carbon material distribution and flux analysis under varying glucose concentrations in hydrogen-producing Clostridium tyrobutyricum JM1[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 228: 103-111. |
| 31 | Ney B, Ahmed F H, Carere C R, et al. The methanogenic redox cofactor F420 is widely synthesized by aerobic soil bacteria[J]. The ISME Journal, 2017, 11(1): 125-137. |
| 32 | Welte C, Deppenmeier U. Bioenergetics and anaerobic respiratory chains of aceticlastic methanogens[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2014, 1837(7): 1130-1147. |
| [1] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [2] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [3] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [4] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [5] | Lanhe ZHANG, Qingyi LAI, Tiezheng WANG, Xiaozhuo GUAN, Mingshuang ZHANG, Xin CHENG, Xiaohui XU, Yanping JIA. Effect of H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge properties in SBR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [6] | Lufan JIA, Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG. Aqueous two-phase system based adherent droplet microfluidics for enhanced enzymatic reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [7] | Zhuotao TAN, Siyu QI, Mengjiao XU, Jie DAI, Chenjie ZHU, Hanjie YING. Application of the redox cascade systems with coenzyme self-cycling in biocatalytic processes: opportunities and challenges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 45-59. |
| [8] | Yang HU, Yan SUN. Self-propulsion of enzyme and enzyme-induced micro-/nanomotor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 116-132. |
| [9] | Shaojie AN, Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI. Construction of pH sensitive artificial glutathione peroxidase based on the formation and dissociation of molecular machine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678. |
| [10] | Mai ZHANG, Yao TIAN, Zhiqi GUO, Ye WANG, Guangjin DOU, Hao SONG. Design and optimization of photocatalysis-biological hybrid system for green synthesis of fuels and chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2774-2789. |
| [11] | Xinzhe ZHANG, Wentao SUN, Bo LYU, Chun LI. Oxidative modification of plant natural products and microbial manufacturing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2790-2805. |
| [12] | Yinlong XU, Wenchieh CHENG, Lin WANG, Zhongfei XUE, Yixin XIE. Implication and enhancement mechanism of chitosan-assisted enzyme- induced carbonate precipitation for copper wastewater treatment [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2222-2232. |
| [13] | Haihang TONG, Dezhi SHI, Jiayu LIU, Huayi CAI, Dan LUO, Fei CHEN. Research progress on dark fermentative bio-hydrogen production from lignocellulose assisted by metal nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1417-1435. |
| [14] | Ming HUANG, Liang ZHU, Zixia DING, Yiting MAO, Zhongqing MA. Synergistic interactions of biomass three-component and low-density polyethylene during co-catalytic fast pyrolysis for the production of light aromatics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 699-711. |
| [15] | Xinhui WANG, Ying WANG, Mingdong YAO, Wenhai XIAO. Research progress of vitamin A biosynthesis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4311-4323. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||