CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (9): 3940-3949.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220362
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guojun XI( ), Zihan LIU, Guangping LEI(
), Zihan LIU, Guangping LEI( )
)
Received:2022-03-11
Revised:2022-08-12
Online:2022-10-09
Published:2022-09-05
Contact:
Guangping LEI
通讯作者:
雷广平
作者简介:席国君(1997—),男,硕士研究生,15035720803@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Guojun XI, Zihan LIU, Guangping LEI. Enhanced adsorption and separation of low concentration coalbed methane based on synergistic effect between FeTPPs and CuBTC[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3940-3949.
席国君, 刘子涵, 雷广平. FeTPPs-CuBTC协同强化低浓度煤层气吸附分离[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3940-3949.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 元素 | 含量/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| Cu | 26.229 |
| Fe | 0.339 |
Table 1 Cu and Fe contents in FeTPPs@CuBTC samples
| 元素 | 含量/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| Cu | 26.229 |
| Fe | 0.339 |
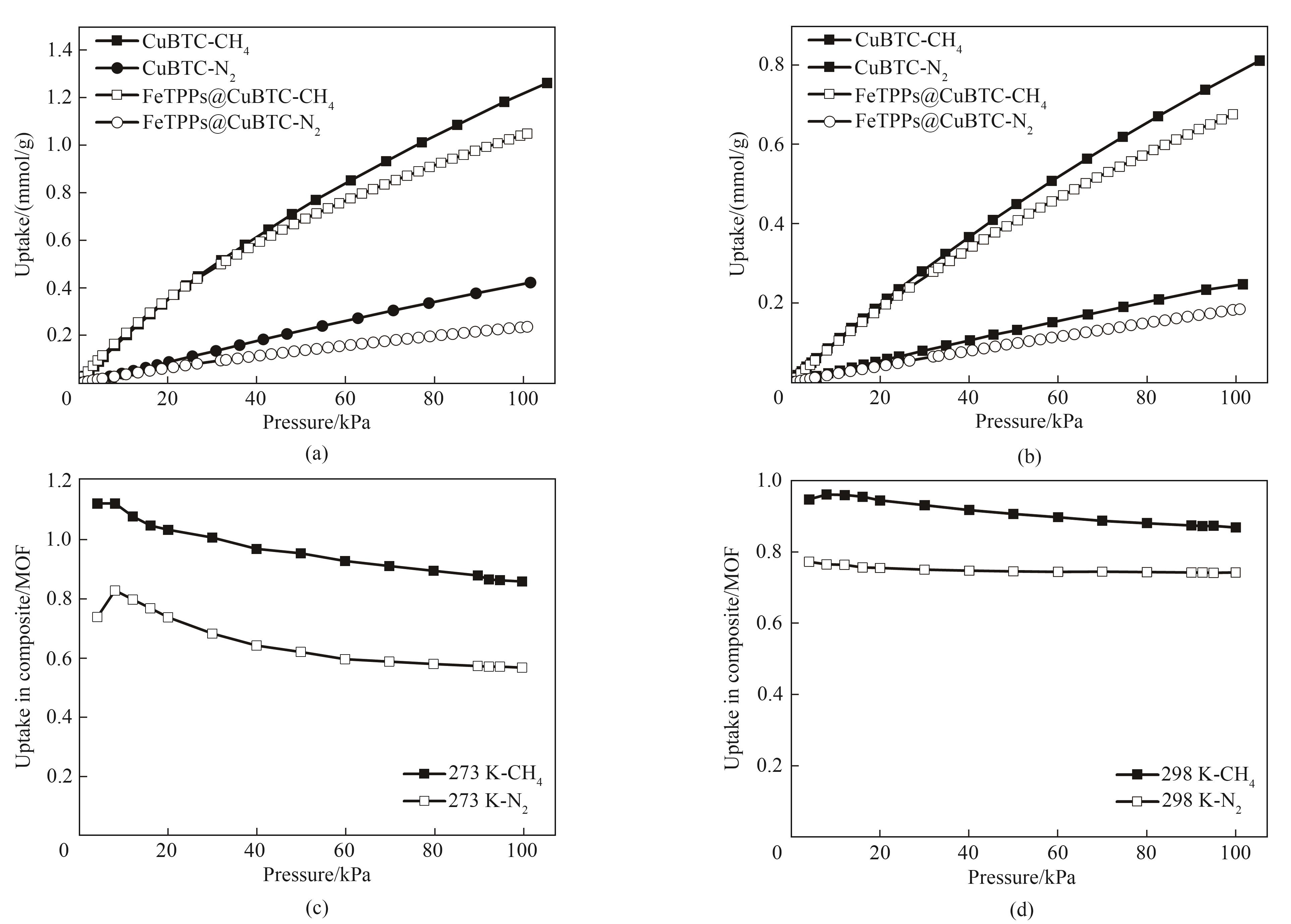
Fig.7 Isothermal adsorption curves of CH4 and N2 at 0℃ (a) and 25℃ (b) for CuBTC and FeTPPs@CuBTC; The change degree of CH4 and N2 adsorption capacity of FeTPPs@CuBTC compared with CuBTC at 0℃ (c)和25℃ (d)
| 样品 | 气体 | q1/(mmol/g) | q2/(mmol/g) | a1/kPa-1 | a2/kPa-1 | k1 | k2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuBTC | CH4 | 0.035 | 3.21 | 0.095 | 0.003 | 0.801 | 1.024 | 0.99999 |
| N2 | 0.03 | 0.805 | 0.051 | 9.89×10-4 | 1.099 | 1.288 | 0.9999 | |
| FeTPPs@CuBTC | CH4 | 0.4 | 0.369 | 1.19×10-5 | 0.006 | 2.000 | 1.02 | 0.99997 |
| N2 | 0.05 | 2.769 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 1.304 | 0.959 | 1 |
Table 2 Fitted parameters of CH4 and N2 at 25 ℃ for CuBTC and FeTPPs@CuBTC
| 样品 | 气体 | q1/(mmol/g) | q2/(mmol/g) | a1/kPa-1 | a2/kPa-1 | k1 | k2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuBTC | CH4 | 0.035 | 3.21 | 0.095 | 0.003 | 0.801 | 1.024 | 0.99999 |
| N2 | 0.03 | 0.805 | 0.051 | 9.89×10-4 | 1.099 | 1.288 | 0.9999 | |
| FeTPPs@CuBTC | CH4 | 0.4 | 0.369 | 1.19×10-5 | 0.006 | 2.000 | 1.02 | 0.99997 |
| N2 | 0.05 | 2.769 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 1.304 | 0.959 | 1 |

Fig.10 Comparison between FeTPPs@CuBTC and some adsorbents reported in literatures[12,20-21,24,35-39] in CH4 adsorption capacity and CH4/N2 adsorption selectivity (CH4∶N2=50∶50, 25℃)
| 1 | 门相勇, 韩征, 宫厚健, 等. 新形势下中国煤层气勘探开发面临的挑战与机遇[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(9): 10-16. |
| Men X Y, Han Z, Gong H J, et al. Challenges and opportunities of CBM exploration and development in China under new situations[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(9): 10-16. | |
| 2 | Liang W G, Yan J W, Zhang B N, et al. Review on coal bed methane recovery theory and technology: recent progress and perspectives[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(6): 4633-4643. |
| 3 | 刘见中, 孙海涛, 雷毅, 等. 煤矿区煤层气开发利用新技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(1): 258-267. |
| Liu J Z, Sun H T, Lei Y, et al. Current situation and development trend of coalbed methane development and utilization technology in coal mine area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 258-267. | |
| 4 | 贾晓霞, 王丽, 元宁, 等. 二价铬/钼/镍空配位MOFs的CH4/N2吸附分离研究[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(9): 3896-3904. |
| Jia X X, Wang L, Yuan N, et al. CH4/N2 adsorption separation research of MOFs with divalent Cr/Mo/Ni unsaturated metal sites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(9): 3896-3904. | |
| 5 | Águeda Maté V I, Delgado Dobladez J A, Álvarez-Torrellas S, et al. Modeling and simulation of the efficient separation of methane/nitrogen mixtures with [Ni3(HCOO)6] MOF by PSA[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 1007-1018. |
| 6 | Liang D, Hu Y F, Bao Q, et al. A suitable zeolite Rho for separating CO2/CH4 in pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2021, 127: 108547. |
| 7 | Feng W R, Wu H, Jin J S, et al. Transformation of Al-CDC from 3D crystals to 2D nanosheets in macroporous polyacrylates with enhanced CH4/N2 separation efficiency and stability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132285. |
| 8 | Ali Abd A, Roslee Othman M. Biogas upgrading to fuel grade methane using pressure swing adsorption: parametric sensitivity analysis on an industrial scale[J]. Fuel, 2022, 308: 121986. |
| 9 | Shang H, Li Y P, Liu J Q. CH4/N2 separation on methane molecules grade diameter channel molecular sieves with a CHA-type structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 27(5): 1044-1049. |
| 10 | Krishna R. Methodologies for evaluation of metal-organic frameworks in separation applications[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(64): 52269-52295. |
| 11 | Yuan S, Qin J S, Li J L, et al. Retrosynthesis of multi-component metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 808. |
| 12 | Wang X Q, Li L B, Yang J F, et al. CO2/CH4 and CH4/N2 separation on isomeric metal organic frameworks[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 1687-1694. |
| 13 | Ullah S, Bustam M A, Assiri M A, et al. Synthesis, and characterization of metal-organic frameworks-177 for static and dynamic adsorption behavior of CO2 and CH4 [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 288: 109569. |
| 14 | Saha D, Bao Z B, Jia F, et al. Adsorption of CO2, CH4, N2O, and N2 on MOF-5, MOF-177, and zeolite 5A[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(5): 1820-1826. |
| 15 | Liu H, Li B R, Zhao Y Y, et al. Investigation on a Zr-based metal-organic framework (MOF-801) for the high-performance separation of light alkanes[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(96): 13008-13011. |
| 16 | Li J M, Yang J F, Li L B, et al. Separation of CO2/CH4 and CH4/N2 mixtures using MOF-5 and Cu3(BTC)2 [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2014, 23(4): 453-460. |
| 17 | Pan R, Guo Y N, Tang Y N, et al. Dicationic liquid containing alkenyl modified CuBTC improves the performance of the composites: increasing the CO2 adsorption effect[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132127. |
| 18 | Kloutse F A, Gauthier W, Hourri A, et al. Study of competitive adsorption of the N2O-CO2-CH4-N2 quaternary mixture on CuBTC[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 235: 116211. |
| 19 | Kloutse F A, Hourri A, Natarajan S, et al. Hydrogen separation by adsorption: experiments and modelling of H2-N2-CO2 and H2-CH4-CO2 mixtures adsorption on CuBTC and MOF-5[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 271: 175-185. |
| 20 | Nozari V, Zeeshan M, Keskin S, et al. Effect of methylation of ionic liquids on the gas separation performance of ionic liquid/metal-organic framework composites[J]. Crystengcomm, 2018, 20(44): 7137-7143. |
| 21 | Wu Y Q, Yuan D H, Zeng S, et al. Significant enhancement in CH4/N2 separation with amine-modified zeolite Y[J]. Fuel, 2021, 301: 121077. |
| 22 | Chen Y W, Wu H X, Yuan Y N, et al. Highly rapid mechanochemical synthesis of a pillar-layer metal-organic framework for efficient CH4/N2 separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 385: 123836. |
| 23 | Sezginel K B, Keskin S, Uzun A. Tuning the gas separation performance of CuBTC by ionic liquid incorporation[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(4): 1139-1147. |
| 24 | Chang M, Zhao Y J, Yang Q Y, et al. Microporous metal-organic frameworks with hydrophilic and hydrophobic pores for efficient separation of CH4/N2 mixture[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(11): 14511-14516. |
| 25 | Pirngruber G D, Hamon L, Bourrelly S, et al. A method for screening the potential of MOFs as CO2 adsorbents in pressure swing adsorption processes[J]. ChemSusChem, 2012, 5(4): 762-776. |
| 26 | Kondo A, Noguchi H, Ohnishi S, et al. Novel expansion/shrinkage modulation of 2D layered MOF triggered by clathrate formation with CO2 molecules[J]. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(11): 2581-2584. |
| 27 | Ribeiro R P P L, Mota J P B. Surface area and porosity of Co3(ndc)3(dabco) metal-organic framework and its methane storage capacity: a combined experimental and simulation study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(4): 2411-2423. |
| 28 | Tu T N, Nguyen H T D, Tran N T. Tailoring the pore size and shape of the one-dimensional channels in iron-based MOFs for enhancing the methane storage capacity[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2019, 6(9): 2441-2447. |
| 29 | Ye Y X, Lin R B, Cui H, et al. A microporous metal-organic framework with naphthalene diimide groups for high methane storage[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2020, 49(12): 3658-3661. |
| 30 | Larsen R W, Wojtas L, Perman J, et al. Mimicking heme enzymes in the solid state: metal-organic materials with selectively encapsulated heme[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(27): 10356-10359. |
| 31 | Luo F Q, Lin Y L, Zheng L Y, et al. Encapsulation of hemin in metal-organic frameworks for catalyzing the chemiluminescence reaction of the H2O2-luminol system and detecting glucose in the neutral condition[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(21): 11322-11329. |
| 32 | Yan T T, Guo J H, Liu Z Q, et al. Metalloporphyrin encapsulation for enhanced conversion of CO2 to C2H4 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(22): 25937-25945. |
| 33 | 叶振华. 化工吸附分离过程[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 1992. |
| Ye Z H. Chemical Adsorption Separation Process [M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 1992. | |
| 34 | Zhou X, Huang W Y, Miao J P, et al. Enhanced separation performance of a novel composite material GrO@MIL-101 for CO2/CH4 binary mixture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 266: 339-344. |
| 35 | Hu J L, Sun T J, Liu X W, et al. Separation of CH4/N2 mixtures in metal-organic frameworks with 1D micro-channels[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(68): 64039-64046. |
| 36 | Liu J Q, Shang H, Yang J F, et al. Novel zeolite/carbon monolith adsorbents for efficient CH4/N2 separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 130163. |
| 37 | Li L B, Yang J F, Li J M, et al. Separation of CO2/CH4 and CH4/N2 mixtures by M/DOBDC: a detailed dynamic comparison with MIL-100(Cr) and activated carbon[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014, 198: 236-246. |
| 38 | Wu Y Q, Yuan D H, He D W, et al. Decorated traditional zeolites with subunits of metal-organic frameworks for CH4/N2 separation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(30): 10241-10244. |
| 39 | Nguyen P T K, Nguyen H T D, Pham H Q, et al. Synthesis and selective CO2 capture properties of a series of hexatopic linker-based metal-organic frameworks[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(20): 10065-10072. |
| [1] | Yaxin ZHAO, Xueqin ZHANG, Rongzhu WANG, Guo SUN, Shanjing YAO, Dongqiang LIN. Removal of monoclonal antibody aggregates with ion exchange chromatography by flow-through mode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [2] | Shuang LIU, Linzhou ZHANG, Zhiming XU, Suoqi ZHAO. Study on molecular level composition correlation of viscosity of residual oil and its components [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3226-3241. |
| [3] | Lei XING, Chunyu MIAO, Minghu JIANG, Lixin ZHAO, Xinya LI. Optimal design and performance analysis of downhole micro gas-liquid hydrocyclone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [4] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [5] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [6] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [7] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [8] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [9] | Yuanliang ZHANG, Xinqi LUAN, Weige SU, Changhao LI, Zhongxing ZHAO, Liqin ZHOU, Jianmin CHEN, Yan HUANG, Zhenxia ZHAO. Study on selective extraction of nicotine by ionic liquids composite extractant and DFT calculation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2947-2956. |
| [10] | Jinming GAO, Yujiao GUO, Chenglin E, Chunxi LU. Study on the separation characteristics of a downstream gas-liquid vortex separator in a closed hood [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2957-2966. |
| [11] | Zhaolun WEN, Peirui LI, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiao DU, Qiwang HOU, Yegang LIU, Xiaogang HAO, Guoqing GUAN. Design and optimization of cryogenic air separation process with dividing wall column based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [12] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [13] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [14] | Xingchi ZHU, Zhiyuan GUO, Zhiyong JI, Jing WANG, Panpan ZHANG, Jie LIU, Yingying ZHAO, Junsheng YUAN. Simulation and optimization of selective electrodialysis magnesium and lithium separation process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2477-2485. |
| [15] | Zhen LONG, Jinhang WANG, Junjie REN, Yong HE, Xuebing ZHOU, Deqing LIANG. Experimental study on inhibition effect of natural gas hydrate formation by mixing ionic liquid with PVCap [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||