CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (11): 4851-4872.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201296
• Celebration Column for School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jie ZHAO1( ),Yue GUO1,Zhen SHEN1,Lijun YANG1,Qiang WU1(
),Yue GUO1,Zhen SHEN1,Lijun YANG1,Qiang WU1( ),Xizhang WANG1,Zheng HU1,2(
),Xizhang WANG1,Zheng HU1,2( )
)
Received:2020-09-09
Revised:2020-09-17
Online:2020-11-05
Published:2020-11-05
Contact:
Qiang WU,Zheng HU
赵杰1( ),郭月1,沈桢1,杨立军1,吴强1(
),郭月1,沈桢1,杨立军1,吴强1( ),王喜章1,胡征1,2(
),王喜章1,胡征1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
吴强,胡征
作者简介:赵杰(1987—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Jie ZHAO,Yue GUO,Zhen SHEN,Lijun YANG,Qiang WU,Xizhang WANG,Zheng HU. Research progress of high-rate capacity layered double hydroxide supercapacitor materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 4851-4872.
赵杰,郭月,沈桢,杨立军,吴强,王喜章,胡征. 高倍率容量层状双金属氢氧化物超级电容材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4851-4872.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.4 Ragone plot for various electrical energy storage devices[126](performances of supercapacitors in Ref. [33-34,46,93,97,106,109,120-123,125] are also provided for comparison, the time constants of the devices are marked in the figure)

Fig.5 Characterization of the monolayer NiTi-LDH nanosheets[36]: TEM image (a); HRTEM image (b); AFM image(c) and the corresponding height profiles (d) (profiles of 1—3 in Fig.(d) correspond to the nanosheets of 1—3 in Fig. (c))

Fig.6 Hierarchical NiAl-LDH and rate capacities[39]: schematic preparation (a), core-shell structure[(b),(c)], yolk-shell structure[(d),(e)], hollow structure[(f),(g)], nanoparticles (h), rate capacities (i)

Fig.7 Influence of hierarchical structure on rate capacity of the CoAl-LDH nanosheet array[43]: schematic diagram of P-CO3-LDH and H-CO3-LDH (a), rate capacities (b) (performance of H-OH-LDH in Fig. (b) is provided for reference)

Fig.8 Electrochemical performances of the CoAl-LDH and the CoAl-LDH/CNTs composite[46]: schematic preparation of the CoAl-LDH/CNTs composite (a), electrochemical impedance spectra (b) (Rs is the intrinsic Ohmic resistance, Rct is the charge transfer resistance), rate capacities(c) ( in Fig. (b),(c) , the data of CNTs are also presented for reference)

Fig.9 Electrochemical performances of the NiAl-LDH and the NiAl-LDH/rGO composite[58]: schematic preparation of the NiAl-LDH/rGO composite (a), electrochemical impedance spectra (b), rate capacities at 3.57—17.86 A·g-1 (c)

Fig.10 Electrochemical performances of CC-LDH and CC-NC-LDH electrodes[93]: schematic preparation of the CC-NC-LDH electrode (a), electrochemical impedance spectra (b), rate capacities (c) (the performance of NiCo-LDH in Fig.(c) is also presented for reference)

Fig.12 Influence of interlayer distance on rate capacity of CoAl-LDH[109]: schematic regulation of the interlayer distance (a), electrochemical impedance spectra (b), rate capacities at 1—32 A·g-1(c) ( DS- is dodecyl sulfate anion in Ref.[109])

Fig.13 Schematic preparation of the LDHs-based composites by exfoliation-self-assembly method: CoAl-LDH/rGO film (a) [120],CoNi-LDH/PEDOT:PSS composite (b) [122]
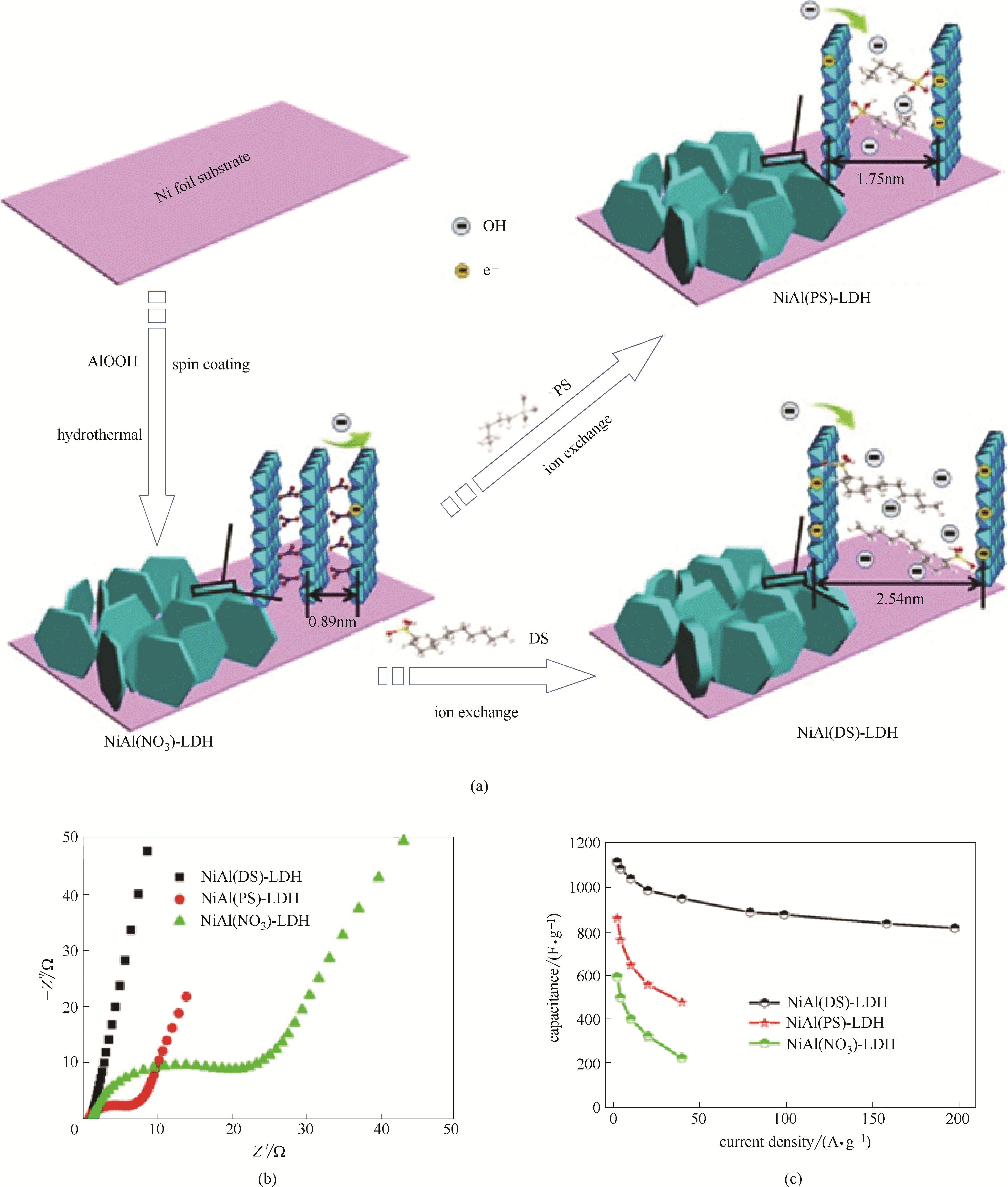
Fig.14 The regulation of interlayer distance of NiAl-LDH nanosheet arrays and the related electrochemical performances[124]: schematic regulation of the interlayer distance(a), electrochemical impedance spectra(b), rate capacities(c)(in Fig.(c), DS is dodecanesulfonate anion. PS is 1-pentanesulfonate anion)

Fig.15 Influences of the interlayer distance on RESR and rate capacity in NiCo-LDH[125]: schematic regulation of interlayer distance(a), RESR(b) and rate capacities(c) of the straight-chain anions intercalated LDHs, RESR (d) and rate capacities(e) of the conjugated-plane anions intercalated LDHs
| Sample | Capacitance/(F·g-1) | Ref. | Sample | Capacitance/(F·g-1) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
at low current (≤ 50 A·g-1) | at high current (> 50 A·g-1) | at low current (≤ 50 A·g-1) | at high current (> 50 A·g-1) | ||||
| regulating compositions | depositing/growing on conductive substrates | ||||||
| NiCoAl-LDH | 2062 (1) 553 (20) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH/CC | 616.9 (1) 454.4 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoNi-LDH | 2614 (5) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/ N-doped CC | 1817 (1) | 1092 (100) | [ |
| CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 715 (0.5) 130 (50) | ― | [ | CoMn-LDH/CC | 1079 (2.1) 891 (42) | ― | [ |
| amorphizating | NiCo-LDH/CC | 1927 (2) 1546 (30) | ― | [ | |||
| NiCoMn-LDHs | 1440 (1) 1104 (50) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/CC | 2105 (2) 1191.3 (20) | ― | [ |
| nanostructuring | NiCo-LDH/NF | 2682 (3) 1706 (20) | ― | [ | |||
| NiTi-LDH | 2310 (1.5) 1206 (30) | ― | [ | MnCo-LDHs@ Ni(OH)2/NF | 2320 (3) 1308 (30) | ― | [ |
| constructing hierarchical structures | NiMn-LDH/NF | 1511 (2.5) 1210 (48) | ― | [ | |||
| NiAl-LDH | 735 (2) 548 (25) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/NF | 2184 (1) 1494 (20) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH | 2275.5 (1) 1007.8 (25) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/SS | 2104 (1) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH | 1887.5 (1) 1187.5 (10) | ― | [ | expanding interlayer distance | |||
| NiFe-LDH | 1061 (1) 598 (10) | ― | [ | CoFe-LDH | 456 (2) 337 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoAl-LDH | 1031 (1) 763 (40) | 680 (100) | [ | CoAl-LDH | 1481.7 (1) 856.7 (32) | ― | [ |
| compositing with carbon | NiCo-LDH | 1646 (3) 680 (10) | ― | [ | |||
| NiCo-LDH/CNTs | 1843 (0.5) 1231 (10) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH | 1100 (1) 750 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiAl-LDH/CNTs | 2034 (1) 1729 (10) | ― | [ | CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 1055 (1) 300 (15) | ― | [ |
| NiMn-LDH/CNTs | 2960 (1.5) 2353 (30) | ― | [ | NiMn-LDH | 1881 (1) 649 (10) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH/CNTs | 1896 (1) 1479 (40) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH | 1580 (10) | ― | [ |
| CoAl-LDH/CNTs | 1949.5 (1) 1066.4 (10) | ― | [ | CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 590 (10) | ― | [ |
| NiCoAl-LDH/rGO | 1866 (1) 1360 (10) | ― | [ | selective etching | |||
| NiAl-LDH/rGO | 2712.7 (1) 1174 (50) | ― | [ | NiCoAl-LDH | 1289 (1) 738 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH/rGO | 1911.1 (2) 1469.8 (20) | ― | [ | exfoliation-self-assembly | |||
| MgAl-LDH/rGO | 1334 (1) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH/rGO | 1043 (1) 912 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoMn-LDH/rGO | 1635 (1) 1161 (10) | ― | [ | CoNi-LDH/ PEDOT:PSS | 960 (2) 804 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiCoAl-LDH/rGO | 1544 (1) 1081 (40) | ― | [ | depositing/growing on conductive substrates+ expanding interlayer distance | |||
| NiAl-LDH/NF | 1125 (1) | 819 (200) | [ | ||||
| NiFe-LDH/rGO | 1196 (1) 861 (10) | ― | [ | sub-nanometer-scale fine regulation of interlayer distance | |||
| NiCo-LDH/C | 2558 (1) 1916 (20) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH | 2115 (1) 949 (50) | 626 (100) 410 (150) | [ |
Table 1 Rate capacities of LDHs-based electrode materials in each strategy (three-electrode test system)
| Sample | Capacitance/(F·g-1) | Ref. | Sample | Capacitance/(F·g-1) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
at low current (≤ 50 A·g-1) | at high current (> 50 A·g-1) | at low current (≤ 50 A·g-1) | at high current (> 50 A·g-1) | ||||
| regulating compositions | depositing/growing on conductive substrates | ||||||
| NiCoAl-LDH | 2062 (1) 553 (20) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH/CC | 616.9 (1) 454.4 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoNi-LDH | 2614 (5) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/ N-doped CC | 1817 (1) | 1092 (100) | [ |
| CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 715 (0.5) 130 (50) | ― | [ | CoMn-LDH/CC | 1079 (2.1) 891 (42) | ― | [ |
| amorphizating | NiCo-LDH/CC | 1927 (2) 1546 (30) | ― | [ | |||
| NiCoMn-LDHs | 1440 (1) 1104 (50) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/CC | 2105 (2) 1191.3 (20) | ― | [ |
| nanostructuring | NiCo-LDH/NF | 2682 (3) 1706 (20) | ― | [ | |||
| NiTi-LDH | 2310 (1.5) 1206 (30) | ― | [ | MnCo-LDHs@ Ni(OH)2/NF | 2320 (3) 1308 (30) | ― | [ |
| constructing hierarchical structures | NiMn-LDH/NF | 1511 (2.5) 1210 (48) | ― | [ | |||
| NiAl-LDH | 735 (2) 548 (25) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/NF | 2184 (1) 1494 (20) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH | 2275.5 (1) 1007.8 (25) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH/SS | 2104 (1) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH | 1887.5 (1) 1187.5 (10) | ― | [ | expanding interlayer distance | |||
| NiFe-LDH | 1061 (1) 598 (10) | ― | [ | CoFe-LDH | 456 (2) 337 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoAl-LDH | 1031 (1) 763 (40) | 680 (100) | [ | CoAl-LDH | 1481.7 (1) 856.7 (32) | ― | [ |
| compositing with carbon | NiCo-LDH | 1646 (3) 680 (10) | ― | [ | |||
| NiCo-LDH/CNTs | 1843 (0.5) 1231 (10) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH | 1100 (1) 750 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiAl-LDH/CNTs | 2034 (1) 1729 (10) | ― | [ | CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 1055 (1) 300 (15) | ― | [ |
| NiMn-LDH/CNTs | 2960 (1.5) 2353 (30) | ― | [ | NiMn-LDH | 1881 (1) 649 (10) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH/CNTs | 1896 (1) 1479 (40) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH | 1580 (10) | ― | [ |
| CoAl-LDH/CNTs | 1949.5 (1) 1066.4 (10) | ― | [ | CoⅡCoⅢ-LDH | 590 (10) | ― | [ |
| NiCoAl-LDH/rGO | 1866 (1) 1360 (10) | ― | [ | selective etching | |||
| NiAl-LDH/rGO | 2712.7 (1) 1174 (50) | ― | [ | NiCoAl-LDH | 1289 (1) 738 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiCo-LDH/rGO | 1911.1 (2) 1469.8 (20) | ― | [ | exfoliation-self-assembly | |||
| MgAl-LDH/rGO | 1334 (1) | ― | [ | CoAl-LDH/rGO | 1043 (1) 912 (20) | ― | [ |
| CoMn-LDH/rGO | 1635 (1) 1161 (10) | ― | [ | CoNi-LDH/ PEDOT:PSS | 960 (2) 804 (30) | ― | [ |
| NiCoAl-LDH/rGO | 1544 (1) 1081 (40) | ― | [ | depositing/growing on conductive substrates+ expanding interlayer distance | |||
| NiAl-LDH/NF | 1125 (1) | 819 (200) | [ | ||||
| NiFe-LDH/rGO | 1196 (1) 861 (10) | ― | [ | sub-nanometer-scale fine regulation of interlayer distance | |||
| NiCo-LDH/C | 2558 (1) 1916 (20) | ― | [ | NiCo-LDH | 2115 (1) 949 (50) | 626 (100) 410 (150) | [ |
| 33 | Chen H C, Qin Y, Cao H, et al. Synthesis of amorphous nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxides for supercapacitor-battery hybrid energy storage system[J]. Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 17: 194-203. |
| 34 | Li H B, Yu M H, Wang F X, et al. Amorphous nickel hydroxide nanospheres with ultrahigh capacitance and energy density as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials[J]. Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 1894. |
| 35 | Li S, Zhang Y, Liu N, et al. Operando revealing dynamic reconstruction of NiCo carbonate hydroxide for high-rate energy storage[J]. Joule, 2020, 4: 1-15. |
| 36 | Zhao Y, Wang Q, Bian T, et al. Ni3+ doped monolayer layered double hydroxide nanosheets as efficient electrodes for supercapacitors[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(16): 7168-7173. |
| 37 | Yang J, Yu C, Hu C, et al. Surface-confined fabrication of ultrathin nickel cobalt-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(44): 1803272. |
| 38 | Gu Z, Atherton J J, Xu Z P. Hierarchical layered double hydroxide nanocomposites: structure, synthesis and applications[J]. Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(15): 3024-3036. |
| 39 | Shao M, Ning F, Zhao Y, et al. Core-shell layered double hydroxide microspheres with tunable interior architecture for supercapacitors[J]. Chem. Mater., 2012, 24(6): 1192-1197. |
| 40 | Yan T, Li Z, Li R, et al. Nickel-cobalt double hydroxides microspheres with hollow interior and hedgehog-like exterior structures for supercapacitors[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(44): 23587-23592. |
| 41 | Yan T, Zhu H, Li R, et al. Microwave synthesis of nickel/cobalt double hydroxide ultrathin flowerclusters with three-dimensional structures for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 111: 71-79. |
| 42 | Li X, Zai J, Liu Y, et al. Atomically thin layered NiFe double hydroxides assembled 3D microspheres with promoted electrochemical performances[J]. J. Power Sources, 2016, 325: 675-681. |
| 43 | Liu X, Zhou A, Pan T, et al. Ultrahigh-rate-capability of a layered double hydroxide supercapacitor based on a self-generated electrolyte reservoir[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(21): 8421-8427. |
| 44 | Yang J, Yu C, Fan X, et al. 3D architecture materials made of NiCoAl-LDH nanoplates coupled with NiCo-carbonate hydroxide nanowires grown on flexible graphite paper for asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4(18): 1400761. |
| 1 | Miller J R, Simon P. Electrochemical capacitors for energy management[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5889): 651-652. |
| 2 | Wang Y, Song Y, Xia Y. Electrochemical capacitors: mechanism, materials, systems, characterization and applications[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(21): 5925-5950. |
| 3 | Zhu Q, Zhao D, Cheng M, et al. A new view of supercapacitors: integrated supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(36): 1901081. |
| 4 | Gao Q, Demarconnay L, Raymundo-Piñero E, et al. Exploring the large voltage range of carbon/carbon supercapacitors in aqueous lithium sulfate electrolyte[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(11): 9611-9617. |
| 5 | Wu T H, Hsu C T, Hu C C, et al. Important parameters affecting the cell voltage of aqueous electrical double-layer capacitors[J]. J. Power Sources, 2013, 242: 289-298. |
| 6 | Xia J, Chen F, Li J, et al. Measurement of the quantum capacitance of graphene[J]. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4(8): 505-509. |
| 7 | Xiang K, Xu Z, Qu T, et al. Two dimensional oxygen-vacancy-rich Co3O4 nanosheets with excellent supercapacitor performances[J]. Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(92): 12410-12413. |
| 8 | Ma Q, Yao Y, Yan M, et al. Effective enhancement of electrochemical energy storage of cobalt-based nanocrystals by hybridization with nitrogen-doped carbon nanocages[J]. Sci. China Mater., 2019, 62(10): 1393-1402. |
| 9 | Lai H, Shang L, Wu Q, et al. Spinel nickel cobaltite mesostructures assembled from ultrathin nanosheets for high-performance electrochemical energy storage[J]. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(2): 684-691. |
| 10 | Lai H, Wu Q, Zhao J, et al. Mesostructured NiO/Ni composites for high-performance electrochemical energy storage[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(6): 2053-2060. |
| 11 | Song W, Wu J, Wang G, et al. Rich-mixed-valence NixCo3-xPy porous nanowires interwelded junction-free 3D network architectures for ultrahigh areal energy density supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(46): 1804620. |
| 12 | Chen L Y, Hou Y, Kang J L, et al. Toward the theoretical capacitance of RuO2 reinforced by highly conductive nanoporous gold[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2013, 3(7): 851-856. |
| 13 | Zhao M, Zhao Q, Li B, et al. Recent progress in layered double hydroxide based materials for electrochemical capacitors: design, synthesis and performance[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(40): 15206-15225. |
| 14 | Zhou G, Xu L, Hu G, et al. Nanowires for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Chem. Rev., 2019, 119: 11042-11109. |
| 15 | Shao Y, El-Kady M F, Sun J, et al. Design and mechanisms of asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Chem. Rev., 2018, 118: 9233-9280. |
| 16 | Yin H, Tang Z. Ultrathin two-dimensional layered metal hydroxides: an emerging platform for advanced catalysis, energy conversion and storage[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(18): 4873-4891. |
| 17 | Gao X, Wang P, Pan Z, et al. Recent progress in two-dimensional layered double hydroxides and their derivatives for supercapacitors[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(6): 1226-1254. |
| 18 | 孟格, 刘军枫, 孙晓明, 等. 水滑石纳米阵列电极在能量储存和转化中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2017, 47(4): 408-419. |
| Meng G, Liu J F, Sun X M, et al. Layered double hydroxide nanoarrays toward electrochemical energy storage and conversion[J]. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2017, 47(4): 408-419. | |
| 19 | 安哲, 何静, 段雪. 基于层状前体制备活性位高分散催化材料[J]. 催化学报, 2013, 34(1): 225-234. |
| An Z, He J, Duan X. Catalysts with catalytic sites highly dispersed from layered double hydroxide as precursors[J]. Chin. J. Catal., 2013, 34(1): 225-234. | |
| 20 | 闫东鹏, 陆军, 段雪. 层状复合金属氢氧化物: 主客体结构研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2013, 43(1): 1-14. |
| Yan D P, Lu J, Duan X. Layered double hydroxide: research progress of host-guest structure[J]. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2013, 43(1): 1-14. | |
| 21 | 陈艳, 王丽秋, 王晨晔, 等. 以钢渣为原料合成层状双氢氧化物及其结构表征[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(12): 5149-5156. |
| Chen Y, Wang L Q, Wang C Y, et al. Synthesis and structural characterization of layered double hydroxide using steel slag as raw material[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(12): 5149-5156. | |
| 22 | 王瑞瑞, 赵有璟, 邵明飞, 等. 层状双金属氢氧化物用于催化水氧化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(1): 54-72. |
| Wang R R, Zhao Y J, Shao M F, et al. Recent progresses in water oxidation over layered double hydroxide catalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(1): 54-72. | |
| 23 | Li X, Du D, Zhang Y, et al. Layered double hydroxides toward high-performance supercapacitors[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(30): 15460-15485. |
| 24 | Yu J, Wang Q, O’Hare D, et al. Preparation of two dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheets and their applications[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(19): 5950-5974. |
| 25 | Wang Q, O’Hare D. Recent advances in the synthesis and application of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheets[J]. Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(7): 4124-4155. |
| 26 | Chen J, Wang X, Wang J, et al. Sulfidation of NiMn-layered double hydroxides/graphene oxide composites toward supercapacitor electrodes with enhanced performance[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(5): 1501745. |
| 27 | Quan W, Tang Z, Hong Y, et al. Hydroxyl compensation effects on the cycle stability of nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxides synthesized via solvothermal method[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 182: 445-451. |
| 28 | Wang X, Lin Y, Su Y, et al. Design and synthesis of ternary-component layered double hydroxides for high-performance supercapacitors: understanding the role of trivalent metal ions[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 225: 263-271. |
| 29 | Li Z, Duan H, Shao M, et al. Ordered-vacancy-induced cation intercalation into layered double hydroxides: a general approach for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Chem, 2018, 4(9): 2168-2179. |
| 30 | Xie L, Hu Z, Lv C, et al. CoxNi1-x double hydroxide nanoparticles with ultrahigh specific capacitances as supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 78: 205-211. |
| 31 | Vialat P, Mousty C, Taviot-Gueho C, et al. High-performing monometallic cobalt layered double hydroxide supercapacitor with defined local structure[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(30): 4831-4842. |
| 32 | Vialat P, Rabu P, Mousty C, et al. Insight of an easy topochemical oxidative reaction in obtaining high performance electrochemical capacitor based on CoⅡCoⅢ monometallic cobalt layered double hydroxide[J]. J. Power Sources, 2015, 293: 1-10. |
| 45 | Li Z, Shao M, Zhou L, et al. A flexible all-solid-state micro-supercapacitor based on hierarchical CuO@layered double hydroxide core–shell nanoarrays[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 20: 294-304. |
| 46 | Yu L, Shi N, Liu Q, et al. Facile synthesis of exfoliated Co-Al LDH-carbon nanotube composites with high performance as supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(33): 17936-17942. |
| 47 | Chen H, Cai F, Kang Y, et al. Facile assembly of Ni-Co hydroxide nanoflakes on carbon nanotube network with highly electrochemical capacitive performance[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(22): 19630-19637. |
| 48 | Wang Y, Chen Z, Li H, et al. The synthesis and electrochemical performance of core-shell structured Ni-Al layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotubes composites[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 222: 185-193. |
| 49 | Zhao J, Chen J, Xu S, et al. Hierarchical NiMn layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotubes architecture with superb energy density for flexible supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(20): 2938-2946. |
| 50 | Liu C G, Lee Y S, Kim Y J, et al. Electrochemical characteristics of hydrothermally deposited nickel hydroxide on multi-walled carbon nanotube for supercapacitor electrode[J]. Synthetic Met., 2009, 159: 2009-2012. |
| 51 | Yang W, Gao Z, Wang J, et al. Solvothermal one-step synthesis of Ni-Al layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide sheet ternary nanocomposite with ultrahigh capacitance for supercapacitors[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(12): 5443-5454. |
| 52 | Zhou Q, Fan T, Li Y, et al. Hollow-structure NiCo hydroxide/carbon nanotube composite for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. J. Power Sources, 2019, 426: 111-115. |
| 53 | Yu C, Yang J, Zhao C, et al. Nanohybrids from NiCoAl-LDH coupled with carbon for pseudocapacitors: understanding the role of nano-structured carbon[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(6): 3097-3104. |
| 54 | Bai C, Sun S, Xu Y, et al. Facile one-step synthesis of nanocomposite based on carbon nanotubes and Nickel-Aluminum layered double hydroxides with high cycling stability for supercapacitors[J]. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2016, 480: 57-62. |
| 55 | Li M, Liu F, Zhang X B, et al. A comparative study of Ni-Mn layered double hydroxide/carbon composites with different morphologies for supercapacitors[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(43): 30068-30078. |
| 56 | Su L, Zhang X, Yuan C, et al. Symmetric self-hybrid supercapacitor consisting of multiwall carbon nanotubes and Co-Al layered double hydroxides[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155(2): A110-A114. |
| 57 | Lai F, Miao Y E, Zuo L, et al. Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber network: a facile template for decoration of ultrathin nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide nanosheets as high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor electrode[J]. Small, 2016, 12(24): 3235-3244. |
| 58 | Xu J, Gai S, He F, et al. A sandwich-type three-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheet array/graphene composite: fabrication and high supercapacitor performance[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(4): 1022-1031. |
| 59 | Gao Z, Wang J, Li Z, et al. Graphene nanosheet/Ni2+/Al3+ layered double-hydroxide composite as a novel electrode for a supercapacitor[J]. Chem. Mater., 2011, 23(15): 3509-3516. |
| 60 | Zhang L, Wang J, Zhu J, et al. 3D porous layered double hydroxides grown on graphene as advanced electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(32): 9046-9053. |
| 61 | Wimalasiri Y, Fan R, Zhao X S, et al. Assembly of Ni-Al layered double hydroxide and graphene electrodes for supercapacitors[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 134: 127-135. |
| 62 | Yan L, Li R, Li Z, et al. Three-dimensional activated reduced graphene oxide nanocup/nickel aluminum layered double hydroxides composite with super high electrochemical and capacitance performances[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 95: 146-154. |
| 63 | Huang P, Cao C, Sun Y, et al. One-pot synthesis of sandwich-like reduced graphene oxide@CoNiAl layered double hydroxide with excellent pseudocapacitive properties[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(20): 10858-10863. |
| 64 | Cai X, Shen X, Ma L, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of NiCo-layered double hydroxide nanosheets decorated on RGO sheets for high performance supercapacitor[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 268: 251-259. |
| 65 | Zhong Y, Liao Y, Gao A, et al. Supercapacitive behavior of electrostatic self-assembly reduced graphene oxide/CoAl-layered double hydroxides nanocomposites[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 669: 146-155. |
| 66 | Fang J, Li M, Li Q, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of CoAl-layered double hydroxide/graphene oxide composite and its application in supercapacitors[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 85: 248-255. |
| 67 | Zhang L, Zhang X, Shen L, et al. Enhanced high-current capacitive behavior of graphene/CoAl-layered double hydroxide composites as electrode material for supercapacitors[J]. J. Power Sources, 2012, 199: 395-401. |
| 68 | Dong X, Wang L, Wang D, et al. Layer-by-layer engineered Co-Al hydroxide nanosheets/graphene multilayer films as flexible electrode for supercapacitor[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(1): 293-298. |
| 69 | Zhang W, Ma C, Fang J, et al. Asymmetric electrochemical capacitors with high energy and power density based on graphene/CoAl-LDH and activated carbon electrodes[J]. RSC Adv., 2013, 3(7): 2483-2490. |
| 70 | Yan T, Li R, Li Z. Nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide ultrathin nanoflakes decorated on graphene sheets with a 3D nanonetwork structure as supercapacitive materials[J]. Mater. Res. Bull., 2014, 51: 97-104. |
| 71 | Wan H, Liu J, Ruan Y, et al. Hierarchical configuration of NiCo2S4 nanotube@Ni-Mn layered double hydroxide arrays/three-dimensional graphene sponge as electrode materials for high-capacitance supercapacitors[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(29): 15840-15847. |
| 72 | Li M, Cheng J P, Liu F, et al. 3D-Architectured nickel-cobalt-manganese layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide composite for high-performance supercapacitor[J]. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2015, 640: 5-10. |
| 73 | Zhang L, Hui K N, Hui K S, et al. Facile synthesis of porous CoAl-layered double hydroxide/graphene composite with enhanced capacitive performance for supercapacitors[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 186: 522-529. |
| 74 | Hatui G, Nayak G C, Udayabhanu G. One pot solvothermal synthesis of sandwich-like Mg Al layered double hydroxide anchored reduced graphene oxide: an excellent electrode material for supercapacitor[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 219: 214-226. |
| 75 | Li M, Cheng J P, Wang J, et al. The growth of nickel-manganese and cobalt-manganese layered double hydroxides on reduced graphene oxide for supercapacitor[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 206: 108-115. |
| 76 | Zheng C H, Yao T, Xu T R, et al. Growth of ultrathin Ni-Co-Al layered double hydroxide on reduced graphene oxide and superb supercapacitive performance of the resulting composite[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 678: 93-101. |
| 77 | 严琳, 孔惠, 李在均. 3D石墨烯/镍铝层状双金属氢氧化物的制备及超级电容性能[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(5): 822-828. |
| Yan L, Kong H, Li Z J. Synthesis and supercapacitor property of three-dimensional graphene/Ni-Al layered double hydroxide composite[J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2013, 71(5): 822-828. | |
| 78 | Gao X, Lv H, Li Z, et al. Low-cost and high-performance of a vertically grown 3D Ni-Fe layered double hydroxide/graphene aerogel supercapacitor electrode material[J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(109): 107278-107285. |
| 79 | Peng W, Li H, Song S. Synthesis of fluorinated graphene/CoAl-layered double hydroxide composites as electrode materials for supercapacitors[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(6): 5204-5212. |
| 80 | Daud M, Kamal M S, Shehzad F, et al. Graphene/layered double hydroxides nanocomposites: a review of recent progress in synthesis and applications[J]. Carbon, 2016, 104: 241-252. |
| 81 | Gu T H, Gunjakar J L, Kim I Y, et al. Porous hybrid network of graphene and metal oxide nanosheets as useful matrix for improving the electrode performance of layered double hydroxides[J]. Small, 2015, 11(32): 3921-3931. |
| 82 | Wei Y, Zhang X, Wu X, et al. Carbon quantum dots/Ni-Al layered double hydroxide composite for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(45): 39317-39322. |
| 83 | Xiong G, He P, Wang D, et al. Hierarchical Ni-Co hydroxide petals on mechanically robust graphene petal foam for high-energy asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(30): 5460-5470. |
| 84 | Malak-Polaczyk A, Vix-Guterl C, Frackowiak E. Carbon/layered double hydroxide (LDH) composites for supercapacitor application[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(6): 3346-3351. |
| 85 | Yang Q, Li Z, Zhang R, et al. Carbon modified transition metal oxides/hydroxides nanoarrays toward high-performance flexible all-solid-state supercapacitors[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 41: 408-416. |
| 86 | Wei J, Wang J, Song Y, et al. Synthesis of self-assembled layered double hydroxides/carbon composites by in situ solvothermal method and their application in capacitors[J]. J. Solid State Chem., 2012, 196: 175-181. |
| 87 | Zhang L, Ou M, Yao H, et al. Enhanced supercapacitive performance of graphite-like C3N4 assembled with NiAl-layered double hydroxide[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 186: 292-301. |
| 88 | Xu J, Ma C, Cao J, et al. Facile synthesis of core-shell nanostructured hollow carbon nanospheres@nickel cobalt double hydroxide as high-performance electrode materials for supercapacitors[J]. Dalton Trans., 2017, 46(10): 3276-3283. |
| 89 | Wang Y, Dou H, Wang J, et al. Three-dimensional porous MXene/layered double hydroxide composite for high performance supercapacitors[J]. J. Power Sources, 2016, 327: 221-228. |
| 90 | Zhang D, Cao J, Zhang X, et al. NiMn layered double hydroxide nanosheets in-situ anchored on Ti3C2 MXene via chemical bonds for superior supercapacitors[J]. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3(6): 5949-5964. |
| 91 | Li S, Cheng P, Luo J, et al. High-performance flexible asymmetric supercapacitor based on CoAl-LDH and rGO electrodes[J]. Nano-Micro Lett., 2017, 9(3): 31. |
| 92 | Shi L, Sun P, Du L, et al. Flexible honeycomb-like NiMn layered double hydroxide/carbon cloth architecture for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Mater. Lett., 2016, 175: 275-278. |
| 93 | Li S, Yu C, Yang J, et al. A superhydrophilic “nanoglue” for stabilizing metal hydroxides onto carbon materials for high-energy and ultralong-life asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10(9): 1958-1965. |
| 94 | Zhao J, Chen J, Xu S, et al. CoMn-layered double hydroxide nanowalls supported on carbon fibers for high-performance flexible energy storage devices[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(31): 8836-8843. |
| 95 | Shakir I, Shahid M, Rana U A, et al. Nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide anchored zinc oxide nanowires grown on carbon fiber cloth for high-performance flexible pseudocapacitive energy storage devices[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 129: 28-32. |
| 96 | Nagaraju G, Raju G S R, Ko Y H, et al. Hierarchical Ni-Co layered double hydroxide nanosheets entrapped on conductive textile fibers: a cost-effective and flexible electrode for high-performance pseudocapacitors[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(2): 812-825. |
| 97 | Chen H, Hu L, Chen M, et al. Nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide nanosheets for high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(7): 934-942. |
| 98 | Liu S, Lee S C, Patil U, et al. Hierarchical MnCo-layered double hydroxides@Ni(OH)2 core-shell heterostructures as advanced electrodes for supercapacitors[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(3): 1043-1049. |
| 99 | Gu Y, Lu Z, Chang Z, et al. NiTi layered double hydroxide thin films for advanced pseudocapacitor electrodes[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(36): 10655-10661. |
| 100 | Guo X L, Liu X Y, Hao X D, et al. Nickel-manganese layered double hydroxide nanosheets supported on nickel foam for high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 194: 179-186. |
| 101 | Zheng X, Gu Z, Hu Q, et al. Ultrathin porous nickel-cobalt hydroxide nanosheets for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes[J]. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(22): 17007-17013. |
| 102 | Han J, Dou Y, Zhao J, et al. Flexible CoAl LDH@PEDOT core/shell nanoplatelet array for high-performance energy storage[J]. Small, 2013, 9(1): 98-106. |
| 103 | Abushrenta N, Wu X, Wang J, et al. Hierarchical Co-based porous layered double hydroxide arrays derived via alkali etching for highperformance supercapacitors[J]. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 13082. |
| 104 | Adhikari S P, Awasthi G P, Kim K S, et al. Synthesis of three-dimensional mesoporous Cu-Al layered double hydroxide/g-C3N4 nanocomposites on Ni-foam for enhanced supercapacitors with excellent long-term cycling stability[J]. Dalton Trans., 2018, 47(13): 4455-4466. |
| 105 | Wang J, Song Y, Li Z, et al. In situ Ni/Al layered double hydroxide and its electrochemical capacitance performance[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(12): 6463-6467. |
| 106 | Guo W, Yu C, Li S, et al. High-stacking-density, superior-roughness LDH bridged with vertically aligned graphene for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Small, 2017, 13(37): 1701288. |
| 107 | Gupta V, Gupta S, Miura N. Potentiostatically deposited nanostructured CoxNi1-x layered double hydroxides as electrode materials for redox-supercapacitors[J]. J. Power Sources, 2008, 175(1): 680-685. |
| 108 | Ge X, Gu C D, Wang X L, et al. Ionothermal synthesis of cobalt iron layered double hydroxides (LDHs) with expanded interlayer spacing as advanced electrochemical materials[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(40): 17066-17076. |
| 109 | Xiao Y, Su D, Wang X, et al. Layered double hydroxides with larger interlayer distance for enhanced pseudocapacitance[J]. Sci. China Mater., 2018, 61(2): 263-272. |
| 110 | Lin Y, Xie X, Wang X, et al. Understanding the enhancement of electrochemical properties of NiCo layered double hydroxides via functional pillared effect: an insight into dual charge storage mechanisms[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 246: 406-414. |
| 111 | Zhang H, Tahir M U, Yan X, et al. Ni-Al layered double hydroxide with regulated interlayer spacing as electrode for aqueous asymmetric supercapacitor[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 368: 905-913. |
| 112 | Silva A S, Sanchis-Gual R, Carrasco J A, et al. Boosting the supercapacitive behavior of CoAl layered double hydroxides via tuning the metal composition and interlayer space[J]. Batter. Supercaps, 2020, 3(6): 499-509. |
| 113 | Wang L, Dong Z H, Wang Z G, et al. Layered α-Co(OH)2 nanocones as electrode materials for pseudocapacitors: understanding the effect of interlayer space on electrochemical activity[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(21): 2758-2764. |
| 114 | Wang X, Zhang J, Yang S, et al. Interlayer space regulating of NiMn layered double hydroxides for supercapacitors by controlling hydrothermal reaction time[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2019, 295: 1-6. |
| 115 | Liu X, Ma R, Bando Y, et al. A general strategy to layered transition-metal hydroxide nanocones: tuning the composition for high electrochemical performance[J]. Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(16): 2148-2153. |
| 116 | Liu X, Ma R, Bando Y, et al. High-yield preparation, versatile structural modification, and properties of layered cobalt hydroxide nanocones[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(27): 4292-4302. |
| 117 | Wang X, Yan C, Sumboja A, et al. Achieving high rate performance in layered hydroxide supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4(6): 1301240. |
| 118 | Ge X, Gu C, Yin Z, et al. Periodic stacking of 2D charged sheets: self-assembled superlattice of Ni-Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) and reduced graphene oxide[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 20: 185-193. |
| 119 | Ma R, Liu X, Liang J, et al. Molecular-scale heteroassembly of redoxable hydroxide nanosheets and conductive graphene into superlattice composites for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(24): 4173-4178. |
| 120 | Zhang R, An H, Li Z, et al. Mesoporous graphene-layered double hydroxides free-standing films for enhanced flexible supercapacitors[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 289: 85-92. |
| 121 | Wu X, Jiang L, Long C, et al. Dual support system ensuring porous Co-Al hydroxide nanosheets with ultrahigh rate performance and high energy density for supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(11): 1648-1655. |
| 122 | Zhao J, Xu S, Tschulik K, et al. Molecular-scale hybridization of clay monolayers and conducting polymer for thin-film supercapacitors[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(18): 2745-2753. |
| 123 | Lan Y, Li M, Fan W, et al. Functional molecules regulated and intercalated nickel-cobalt LDH nano-sheets on carbon fiber cloths as an advanced free-standing electrode for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2019, 321: 134708. |
| 124 | Yin Q, Zhang J, Liu X, et al. Pillaring-effect induced ultrahigh-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage based on layered double hydroxide nanoplate arrays[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58(27): 11954-11963. |
| 125 | Zhao J, Ge C, Zhao Z, et al. Sub-nanometer-scale fine regulation of interlayer distance in Ni-Co layered double hydroxides leading to high-rate supercapacitors[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 76: 105026. |
| 126 | Simon P, Gogotsi Y. Perspectives for electrochemical capacitors and related devices [J]. Nat. Mater., 2020, . |
| [1] | Cheng CHENG, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Haitao HU, Hongxiang XUE. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of surface microstructure effect on crystallization fouling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [3] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [5] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [7] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [9] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [10] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [11] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [12] | Jipeng ZHOU, Wenjun HE, Tao LI. Reaction engineering calculation of deactivation kinetics for ethylene catalytic oxidation over irregular-shaped catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [13] | Guangyu WANG, Kai ZHANG, Kaihua ZHANG, Dongke ZHANG. Heat and mass transfer and energy consumption for microwave drying of coal slime [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2382-2390. |
| [14] | Jing LI, Conghao SHEN, Daliang GUO, Jing LI, Lizheng SHA, Xin TONG. Research progress in the application of lignin-based carbon fiber composite materials in energy storage components [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2322-2334. |
| [15] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||