CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (12): 5615-5624.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220692
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wei YANG( ), Yujie WANG, Kaibin FANG, Hanbo ZOU, Shengzhou CHEN(
), Yujie WANG, Kaibin FANG, Hanbo ZOU, Shengzhou CHEN( ), Zili LIU
), Zili LIU
Received:2022-05-06
Revised:2022-10-21
Online:2023-01-17
Published:2022-12-05
Contact:
Shengzhou CHEN
杨伟( ), 王昱杰, 方凯斌, 邹汉波, 陈胜洲(
), 王昱杰, 方凯斌, 邹汉波, 陈胜洲( ), 刘自力
), 刘自力
通讯作者:
陈胜洲
作者简介:杨伟(1982—),男,博士,高级工程师,wyang@gzhu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Wei YANG, Yujie WANG, Kaibin FANG, Hanbo ZOU, Shengzhou CHEN, Zili LIU. Influence of cobalt-manganese ratio adjustment on the properties of LiNi0.8Co0.10-y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5615-5624.
杨伟, 王昱杰, 方凯斌, 邹汉波, 陈胜洲, 刘自力. Co-Mn比例调控对LiNi0.8Co0.10-y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2材料性能影响探究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5615-5624.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.1 Full XRD patterns (a), expanded views of (003) peaks (b), expanded views of (101), (006)/(012) peaks (c) and expanded views of (018)/(110) peaks (d) of LiNi0.8Co0.10-y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 (y=0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04)
| 样品 | a/Å | c/Å | c/a | v/Å3 | I(003)/I(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiNi0.8Co0.09Mn0.06Al0.05O2 | 2.8717 | 14.1813 | 4.9383 | 101.28 | 1.5408 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.08Mn0.07Al0.05O2 | 2.8748 | 14.1944 | 4.9376 | 101.59 | 1.5674 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.07Mn0.08Al0.05O2 | 2.8743 | 14.1844 | 4.9349 | 101.49 | 1.4205 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.06Mn0.09Al0.05O2 | 2.8735 | 14.1910 | 4.9385 | 101.48 | 1.3298 |
Table 1 Cell parameter of LiNi0.8Co0.10–y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 (y=0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04) samples
| 样品 | a/Å | c/Å | c/a | v/Å3 | I(003)/I(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiNi0.8Co0.09Mn0.06Al0.05O2 | 2.8717 | 14.1813 | 4.9383 | 101.28 | 1.5408 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.08Mn0.07Al0.05O2 | 2.8748 | 14.1944 | 4.9376 | 101.59 | 1.5674 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.07Mn0.08Al0.05O2 | 2.8743 | 14.1844 | 4.9349 | 101.49 | 1.4205 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.06Mn0.09Al0.05O2 | 2.8735 | 14.1910 | 4.9385 | 101.48 | 1.3298 |
| 样品 | 含量/% (mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(理论含量/实际含量) | Co(理论含量/实际含量) | Mn(理论含量/实际含量) | Al(理论含量/实际含量) | |
| LiNi0.8Co0.09Mn0.06Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.8028 | 0.09/0.0851 | 0.06/0.0572 | 0.05/0.0549 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.08Mn0.07Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.8074 | 0.08/0.0833 | 0.07/0.0726 | 0.05/0.0367 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.07Mn0.08Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.7992 | 0.07/0.0728 | 0.08/0.0829 | 0.05/0.0451 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.06Mn0.09Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.7927 | 0.06/0.0624 | 0.09/0.0909 | 0.05/0.054 |
Table 2 Content of the quaternary metal of as-prepared LiNi0.8Co0.10-y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 (y=0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04) samples
| 样品 | 含量/% (mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(理论含量/实际含量) | Co(理论含量/实际含量) | Mn(理论含量/实际含量) | Al(理论含量/实际含量) | |
| LiNi0.8Co0.09Mn0.06Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.8028 | 0.09/0.0851 | 0.06/0.0572 | 0.05/0.0549 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.08Mn0.07Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.8074 | 0.08/0.0833 | 0.07/0.0726 | 0.05/0.0367 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.07Mn0.08Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.7992 | 0.07/0.0728 | 0.08/0.0829 | 0.05/0.0451 |
| LiNi0.8Co0.06Mn0.09Al0.05O2 | 0.80/0.7927 | 0.06/0.0624 | 0.09/0.0909 | 0.05/0.054 |
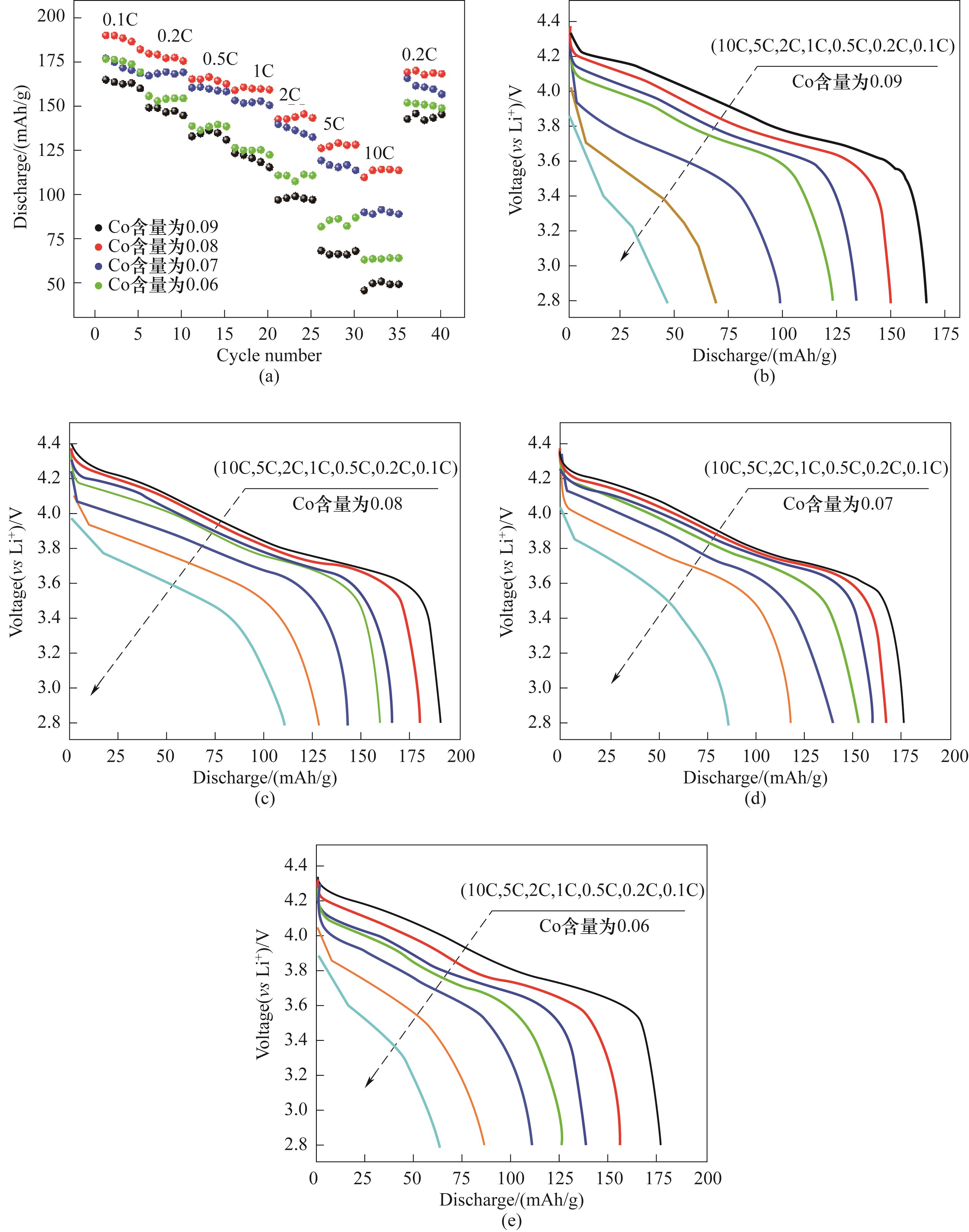
Fig.4 The rate performances of LiNi0.8Co0.10-y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 (y=0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04) cathode materials (a) and the corresponding discharge curves: y=0.01 (b), y=0.02 (c), y=0.03 (d), y=0.04 (e)
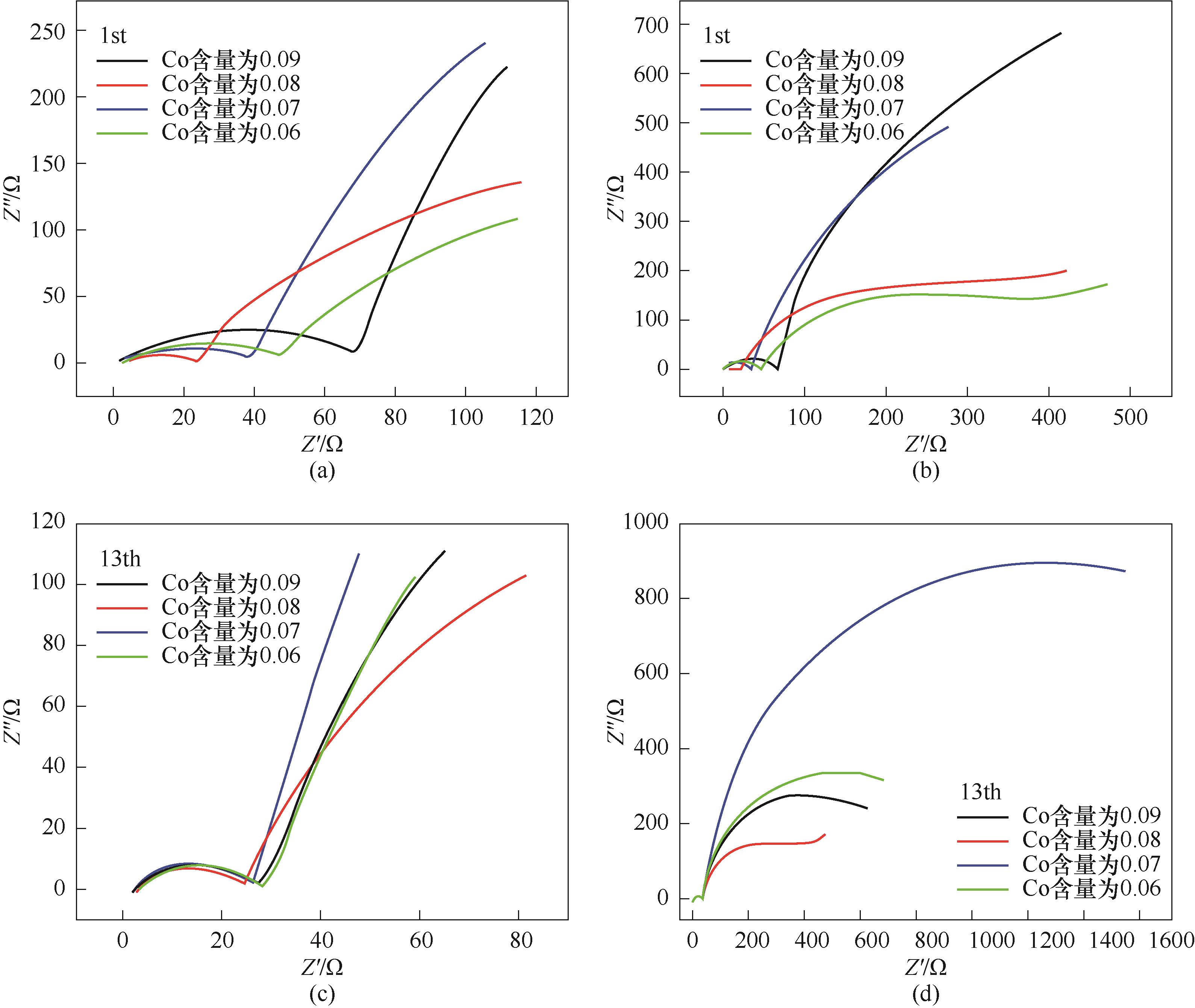
Fig.6 The high frequency region of the Nyquist plots for the first cycle 0.1C rate (a), Nyquist plots for the first cycle at 0.1C rate (b), the high frequency region of the Nyquist plots for the 13th cycle at 1C rate (c) and Nyquist plots for the 13th cycle at 1C rate (d) of LiNi0.8Co0.10–y Mn0.05+y Al0.05O2 (y=0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04)
| 1 | Yang C K, Shao R W, Mi Y Y, et al. Stable interstitial layer to alleviate fatigue fracture of high nickel cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 376: 200-206. |
| 2 | Kong F T, Liang C P, Wang L H, et al. Kinetic stability of bulk LiNiO2 and surface degradation by oxygen evolution in LiNiO2-based cathode materials[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(2): 1802586. |
| 3 | Bai X T, Ban L Q, Zhuang W D. Research progress on coating and doping modification of nickel rich ternary cathode materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 972. |
| 4 | Zhu L, Liu Y, Wu W Y, et al. Surface fluorinated LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 as a positive electrode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(29): 15156-15162. |
| 5 | Yang W, Xie Q, Fang K B, et al. Inhibition of adverse phase transition at 4.2 V via increasing cobalt content on Ni-rich layered cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(7): 7365-7375. |
| 6 | Aishova A, Park G T, Yoon C S, et al. Cobalt-free high-capacity Ni-rich layered Li[Ni0.9Mn0.1]O2 cathode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(4): 1903179. |
| 7 | Muralidharan N, Essehli R, Hermann R P, et al. LiNi x Fe y Al z O2, a new cobalt-free layered cathode material for advanced Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 471: 228389. |
| 8 | Muto S, Tatsumi K, Kojima Y, et al. Effect of Mg-doping on the degradation of LiNiO2-based cathode materials by combined spectroscopic methods[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 205: 449-455. |
| 9 | Li W D, Lee S, Manthiram A. High-nickel NMA: a cobalt-free alternative to NMC and NCA cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(33): 2002718. |
| 10 | Fang K, Xie Q, Wang C, et al. Understanding the feasibility of manganese substitution for cobalt in the synthesis of nickel-rich and cobalt-free cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(7): 7190-7200. |
| 11 | Park S H, Park K S, Sun Y K, et al. Structural and electrochemical characterization of lithium excess and Al-doped nickel oxides synthesized by the sol-gel method[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46(8): 1215-1222. |
| 12 | Guilmard M, Croguennec L, Denux D, et al. Thermal stability of lithium nickel oxide derivatives(1): Li x Ni1.02O2 and Li x Ni0.89Al0.16O2 (x = 0.50 and 0.30)[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2003, 15(23): 4476-4483. |
| 13 | Bai G L, Wang C H, Luo J J, et al. High-capacity spherical LiNi0.82Co0.15Al0.03O2 cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2019, 4(31): 9050-9054. |
| 14 | Vadivel S, Phattharasupakun N, Wutthiprom J, et al. High-performance Li-ion batteries using nickel-rich lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxide-nanocarbon core-shell cathode: in operando X-ray diffraction[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(34): 30719-30727. |
| 15 | Lin S P, Fung K Z, Hon Y M, et al. Effect of Al addition on formation of layer-structured LiNiO2 [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2002, 167(1): 97-106. |
| 16 | Jo M, Noh M, Oh P, et al. A new high power LiNi0.81Co0.1Al0.09O2 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(13): 1301583. |
| 17 | Xia Y, Zheng J M, Wang C M, et al. Designing principle for Ni-rich cathode materials with high energy density for practical applications[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 49: 434-452. |
| 18 | Yang K. Influence of Al and Mn on the electrochemical performance of LiNi x Co y Mn1- x- y O2 as a cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2019, 14(9): 9007-9016. |
| 19 | Yudha C S, Muzayanha S U, Widiyandari H, et al. Synthesis of LiNi0.85Co0.14Al0.01O2 cathode material and its performance in an NCA/graphite full-battery[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(10): 1886. |
| 20 | Yan P F, Zheng J M, Gu M, et al. Intragranular cracking as a critical barrier for high-voltage usage of layer-structured cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14101. |
| 21 | Xu C L, Xiang W, Wu Z G, et al. Constructing a protective pillaring layer by incorporating gradient Mn4+ to stabilize the surface/interfacial structure of LiNi0.815Co0.15Al0.035O2 cathode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(33): 27821-27830. |
| 22 | Yang W, Qiu X L, Wang C Y, et al. Controllable morphology tailoring with solvothermal method toward LiMnPO4/C cathode materials for improved performance and favorable thermostability[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022, 35(5): 790-800. |
| 23 | Cao C H, Zhang J, Xie X H, et al. Composition, structure, and performance of Ni-based cathodes in lithium ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2017, 23(6): 1337-1356. |
| 24 | Liu Q, Du K, Guo H W, et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of Co-Mn-Mg multi-doped nickel based cathode materials LiNi0.9Co0.1- x [Mn1/2Mg1/2] x O2 for secondary lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 90: 350-357. |
| 25 | 叶乃清, 刘长久, 沈上越. 锂离子电池正极材料LiNiO2存在的问题与解决办法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(6): 1217-1224. |
| Ye N Q, Liu C J, Shen S Y. Drawbacks and improve ways of LiNiO2 as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(6): 1217-1224. | |
| 26 | Myung S T, Maglia F, Park K J, et al. Nickel-rich layered cathode materials for automotive lithium-ion batteries: achievements and perspectives[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(1): 196-223. |
| 27 | Liu L L, Wang S L, Zhang Z Y, et al. Fluoroethylene carbonate as an electrolyte additive for improving interfacial stability of high-voltage LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode[J]. Ionics, 2019, 25(3): 1035-1043. |
| 28 | Janssen P, Kasnatscheew J, Streipert B, et al. Fluorinated electrolyte compound as a bi-functional interphase additive for both anodes and cathodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(14): A3525-A3530. |
| 29 | Liu Y D, Xie J. Failure study of commercial LiFePO4 cells in overcharge conditions using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(10): A2208-A2217. |
| 30 | Huang B, Li X H, Wang Z X, et al. Synthesis of Mg-doped LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 oxide and its electrochemical behavior in high-voltage lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(8): 13223-13230. |
| 31 | Zhao D N, Wang P, Cui X L, et al. Robust and sulfur-containing ingredient surface film to improve the electrochemical performance of LiDFOB-based high-voltage electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 260: 536-548. |
| 32 | Yang J, Xia Y Y. Suppressing the phase transition of the layered Ni-rich oxide cathode during high-voltage cycling by introducing low-content Li2MnO3 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(2): 1297-1308. |
| 33 | Weber R, Louli A J, Plucknett K P, et al. Resistance growth in lithium-ion pouch cells with LiNi0.80Co0.15Al0.05O2 positive electrodes and proposed mechanism for voltage dependent charge-transfer resistance[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166(10): A1779-A1784. |
| [1] | Qi WANG, Bin ZHANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Hujian WU, Haitao ZHAN, Tao WANG. Synthesis of isoxepac and 2-ethylanthraquinone catalyzed by chloroaluminate-triethylamine ionic liquid/P2O5 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [2] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [3] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [5] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | Yuming TU, Gaoyan SHAO, Jianjie CHEN, Feng LIU, Shichao TIAN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of calcium-based catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [7] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [8] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [9] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [10] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [11] | Bin LI, Zhenghu XU, Shuang JIANG, Tianyong ZHANG. Clean and efficient synthesis of accelerator CBS by hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2919-2925. |
| [12] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [13] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [14] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [15] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||