CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (2): 429-438.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230955
• Thermodynamics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yongjun XIAO( ), Zhaochong SHI, Ren WAN, Fan SONG, Changjun PENG(
), Zhaochong SHI, Ren WAN, Fan SONG, Changjun PENG( ), Honglai LIU
), Honglai LIU
Received:2023-09-13
Revised:2024-01-09
Online:2024-04-10
Published:2024-02-25
Contact:
Changjun PENG
肖拥君( ), 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军(
), 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军( ), 刘洪来
), 刘洪来
通讯作者:
彭昌军
作者简介:肖拥君(1998—),女,硕士研究生,xiaoyongjun00@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yongjun XIAO, Zhaochong SHI, Ren WAN, Fan SONG, Changjun PENG, Honglai LIU. Prediction of self-diffusion coefficients of ionic liquids using back-propagation neural networks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 429-438.
肖拥君, 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军, 刘洪来. 反向传播神经网络用于预测离子液体的自扩散系数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 429-438.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 折数 | MSEcation×104 | MSEanion×104 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 验证集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 验证集 | 测试集 | |
| 1 | 3.19 | 6.05 | 8.78 | 5.36 | 22.1 | 38.3 |
| 2 | 2.26 | 4.47 | 11.8 | 3.09 | 4.46 | 11.2 |
| 3 | 7.52 | 8.66 | 17.3 | 1.93 | 3.16 | 14.4 |
| 4 | 4.00 | 15.0 | 9.73 | 2.33 | 6.27 | 13.4 |
| 5 | 2.39 | 8.50 | 5.90 | 13.2 | 16.3 | 15.6 |
| 6 | 12.0 | 9.96 | 18.0 | 8.25 | 9.79 | 39.1 |
| 7 | 1.88 | 4.27 | 6.90 | 5.71 | 63.5 | 12.8 |
| 8 | 10.6 | 34.8 | 21.3 | 4.77 | 2.92 | 13.0 |
| 9 | 1.12 | 2.28 | 9.08 | 41.9 | 109 | 36.6 |
| MSE | 5.02 | 10.4 | 12.1 | 9.62 | 26.4 | 21.6 |
Table 1 Summary of MSE between experimental and calculated values
| 折数 | MSEcation×104 | MSEanion×104 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 验证集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 验证集 | 测试集 | |
| 1 | 3.19 | 6.05 | 8.78 | 5.36 | 22.1 | 38.3 |
| 2 | 2.26 | 4.47 | 11.8 | 3.09 | 4.46 | 11.2 |
| 3 | 7.52 | 8.66 | 17.3 | 1.93 | 3.16 | 14.4 |
| 4 | 4.00 | 15.0 | 9.73 | 2.33 | 6.27 | 13.4 |
| 5 | 2.39 | 8.50 | 5.90 | 13.2 | 16.3 | 15.6 |
| 6 | 12.0 | 9.96 | 18.0 | 8.25 | 9.79 | 39.1 |
| 7 | 1.88 | 4.27 | 6.90 | 5.71 | 63.5 | 12.8 |
| 8 | 10.6 | 34.8 | 21.3 | 4.77 | 2.92 | 13.0 |
| 9 | 1.12 | 2.28 | 9.08 | 41.9 | 109 | 36.6 |
| MSE | 5.02 | 10.4 | 12.1 | 9.62 | 26.4 | 21.6 |
| 项目 | R2 (lnD) | 数据点 | RMSE | AARD /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳离子 | 训练集 | 0.9988 | 864 | 0.23 | 2.5 |
| 验证集 | 0.9978 | 108 | 0.45 | 3.3 | |
| 测试集 | 0.9943 | 111 | 0.54 | 4.4 | |
| 总集 | 0.9982 | 1083 | 0.30 | 2.8 | |
| 阴离子 | 训练集 | 0.9974 | 728 | 0.30 | 3.4 |
| 验证集 | 0.9965 | 91 | 0.39 | 4.2 | |
| 测试集 | 0.9853 | 92 | 0.88 | 5.0 | |
| 总集 | 0.9966 | 911 | 0.41 | 3.7 | |
Table 2 Statistical parameters of BP-ANN model
| 项目 | R2 (lnD) | 数据点 | RMSE | AARD /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳离子 | 训练集 | 0.9988 | 864 | 0.23 | 2.5 |
| 验证集 | 0.9978 | 108 | 0.45 | 3.3 | |
| 测试集 | 0.9943 | 111 | 0.54 | 4.4 | |
| 总集 | 0.9982 | 1083 | 0.30 | 2.8 | |
| 阴离子 | 训练集 | 0.9974 | 728 | 0.30 | 3.4 |
| 验证集 | 0.9965 | 91 | 0.39 | 4.2 | |
| 测试集 | 0.9853 | 92 | 0.88 | 5.0 | |
| 总集 | 0.9966 | 911 | 0.41 | 3.7 | |
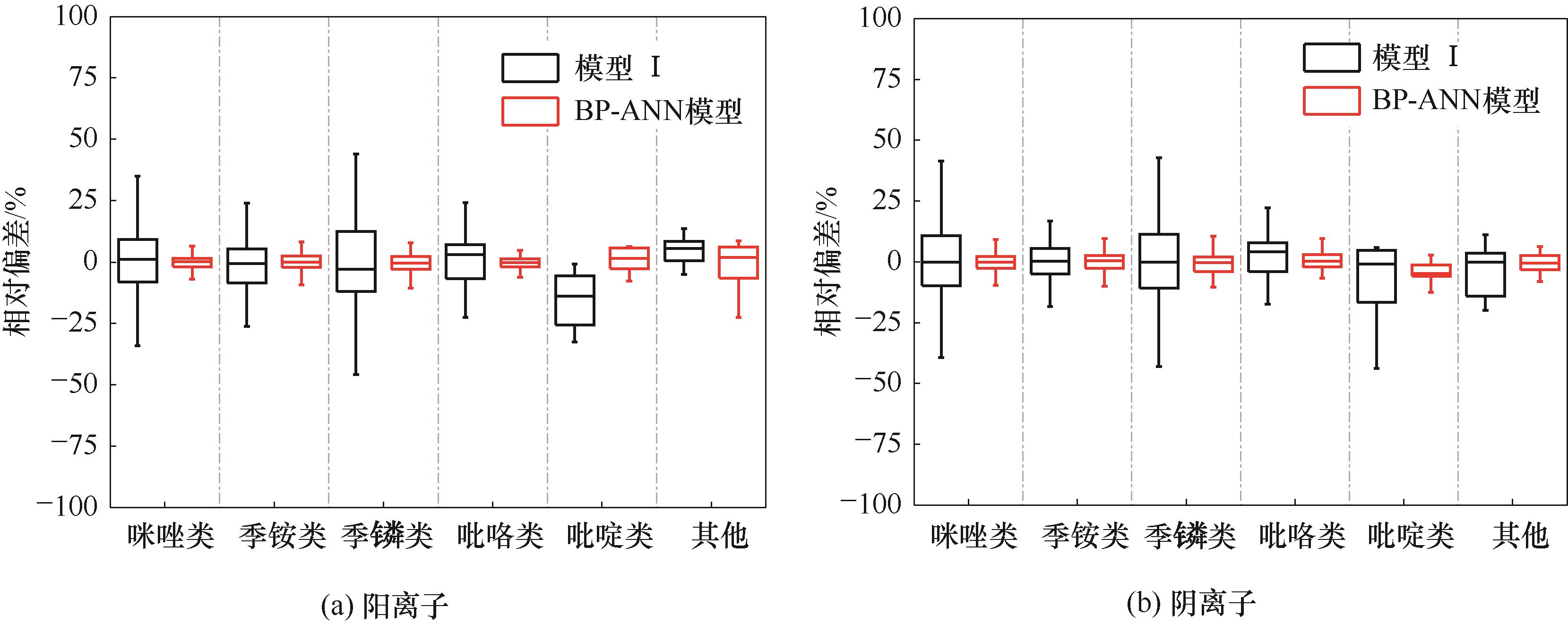
Fig.7 Box plot representing distributions of relative deviations between experimental self-diffusion coefficients of ILs and the calculated values of two models
| IL类型 | 数据点 | 模型Ⅰ[ | BP-ANN 模型 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | AARD/% | RMSE | AARD/% | |||
| 阳离子 | 咪唑类 | 690 | 2.4 | 15 | 0.33 | 2.3 |
| 季铵类 | 184 | 0.61 | 9.5 | 0.20 | 2.9 | |
季 类 类 | 109 | 0.90 | 20 | 0.22 | 4.0 | |
| 吡咯类 | 62 | 1.7 | 13 | 0.24 | 3.1 | |
| 吡啶类 | 8 | 0.93 | 19 | 0.33 | 4.2 | |
| 其他 | 30 | 0.45 | 8.3 | 0.39 | 7.3 | |
| 阴离子 | 咪唑类 | 561 | 1.6 | 16 | 0.49 | 3.7 |
| 季铵类 | 146 | 0.71 | 7.9 | 0.23 | 3.1 | |
季 类 类 | 109 | 1.1 | 19 | 0.27 | 4.2 | |
| 吡咯类 | 60 | 2.5 | 14 | 0.24 | 3.7 | |
| 吡啶类 | 8 | 0.53 | 12 | 0.087 | 4.9 | |
| 其他 | 27 | 0.24 | 8.6 | 0.15 | 3.2 | |
Table 3 Summary of RMSE and AARD between the experimental self-diffusion coefficients of different ILs and the calculated values of two models
| IL类型 | 数据点 | 模型Ⅰ[ | BP-ANN 模型 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | AARD/% | RMSE | AARD/% | |||
| 阳离子 | 咪唑类 | 690 | 2.4 | 15 | 0.33 | 2.3 |
| 季铵类 | 184 | 0.61 | 9.5 | 0.20 | 2.9 | |
季 类 类 | 109 | 0.90 | 20 | 0.22 | 4.0 | |
| 吡咯类 | 62 | 1.7 | 13 | 0.24 | 3.1 | |
| 吡啶类 | 8 | 0.93 | 19 | 0.33 | 4.2 | |
| 其他 | 30 | 0.45 | 8.3 | 0.39 | 7.3 | |
| 阴离子 | 咪唑类 | 561 | 1.6 | 16 | 0.49 | 3.7 |
| 季铵类 | 146 | 0.71 | 7.9 | 0.23 | 3.1 | |
季 类 类 | 109 | 1.1 | 19 | 0.27 | 4.2 | |
| 吡咯类 | 60 | 2.5 | 14 | 0.24 | 3.7 | |
| 吡啶类 | 8 | 0.53 | 12 | 0.087 | 4.9 | |
| 其他 | 27 | 0.24 | 8.6 | 0.15 | 3.2 | |
| 1 | Ohno H. Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2011. |
| 2 | Nordness O, Brennecke J F. Ion dissociation in ionic liquids and ionic liquid solutions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(23): 12873-12902. |
| 3 | Sun L Y, Morales-Collazo O, Xia H, et al. Effect of structure on transport properties (viscosity, ionic conductivity, and self-diffusion coefficient) of aprotic heterocyclic anion (AHA) room temperature ionic liquids(2): Variation of alkyl chain length in the phosphonium cation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2016, 120(25): 5767-5776. |
| 4 | Zmpitas J, Gross J. Modified Stokes-Einstein equation for molecular self-diffusion based on entropy scaling[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(11): 4453-4459. |
| 5 | Overbeck V, Schröder H, Bonsa A M, et al. Insights into the translational and rotational dynamics of cations and anions in protic ionic liquids by means of NMR fast-field-cycling relaxometry[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(4): 2663-2675. |
| 6 | Morris D C, Morris A R, Price W S, et al. Diffusion measurements to understand dynamics and structuring in solutions involving a homologous series of ionic liquids[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2023, 24(11): e202300015. |
| 7 | 辛绪亮, 张晓冬, 赵宗昌, 等. 离子液体[BMIM]Br的水溶液VLE与扩散系数的分子模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(S2): 16-20. |
| Xin X L, Zhang X D, Zhao Z C, et al. Molecular simulation of VLE and diffusion coefficient for aqueous solutions of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(S2): 16-20. | |
| 8 | Kowsari M H, Alavi S, Ashrafizaadeh M, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids(Ⅰ): Dynamics and diffusion coefficient[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 129(22): 224508. |
| 9 | Harris K R, Kanakubo M. Self-diffusion, velocity cross-correlation, distinct diffusion and resistance coefficients of the ionic liquid [BMIM][Tf 2N] at high pressure[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(37): 23977-23993. |
| 10 | Harris K R. Relations between the fractional Stokes-Einstein and Nernst-Einstein equations and velocity correlation coefficients in ionic liquids and molten salts[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2010, 114(29): 9572-9577. |
| 11 | 张先明, 胡玉峰, 杨振钰, 等. 离子液体的黏度与其扩散系数和电导率的新型关系方程[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2014, 44(6): 1034-1040. |
| Zhang X M, Hu Y F, Yang Z Y, et al. New relations between viscosity and self-diffusion coefficient or conductivity of ionic liquids[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2014, 44(6): 1034-1040. | |
| 12 | Rosenfeld Y. Relation between the transport coefficients and the internal entropy of simple systems[J]. Physical Review A, 1977, 15(6): 2545-2549. |
| 13 | Malvaldi M, Chiappe C. Excess entropy scaling of diffusion in room-temperature ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(24): 244502. |
| 14 | Hopp M, Mele J L, Gross J. Self-diffusion coefficients from entropy scaling using the PCP-SAFT equation of state[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(38): 12942-12950. |
| 15 | Dehlouz A, Jaubert J N, Galliero G, et al. Entropy scaling-based correlation for estimating the self-diffusion coefficients of pure fluids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(37): 14033-14050. |
| 16 | Dyre J C. Perspective: excess-entropy scaling[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2018, 149(21): 210901. |
| 17 | Gharagheizi F, Eslamimanesh A, Mohammadi A H, et al. Group contribution model for determination of molecular diffusivity of non-electrolyte organic compounds in air at ambient conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 68(1): 290-304. |
| 18 | Safi A, Nicolas C, Neau E, et al. Diffusion coefficients of organic compounds at infinite dilution in mixtures involving associating compounds. experimental determination and modeling by group contribution methods[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2008, 53(2): 444-448. |
| 19 | Zhou J, Chupradit S, Ershov K, et al. Prediction of molecular diffusivity of organic molecules based on group contribution with tree optimization and SVM models[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 353: 118808. |
| 20 | Das R N, Roy K. Advances in QSPR/QSTR models of ionic liquids for the design of greener solvents of the future[J]. Molecular Diversity, 2013, 17(1): 151-196. |
| 21 | Mirkhani S A, Gharagheizi F, Sattari M. A QSPR model for prediction of diffusion coefficient of non-electrolyte organic compounds in air at ambient condition[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(9): 959-966. |
| 22 | Nordness O, Kelkar P, Lyu Y Y, et al. Predicting thermophysical properties of dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids from sigma profiles[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 334: 116019. |
| 23 | Allers J P, Garzon F H, Alam T M. Artificial neural network prediction of self-diffusion in pure compounds over multiple phase regimes[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(8): 4615-4623. |
| 24 | Allers J P, Priest C W, Greathouse J A, et al. Using computationally-determined properties for machine learning prediction of self-diffusion coefficients in pure liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2021, 125(47): 12990-13002. |
| 25 | Xiao Y J, Song F, An S H, et al. Quantitative structure-property relationship for predicting the diffusion coefficient of ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 349: 118476. |
| 26 | Agatonovic-Kustrin S, Beresford R. Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2000, 22(5): 717-727. |
| 27 | Nami F, Deyhimi F. Prediction of activity coefficients at infinite dilution for organic solutes in ionic liquids by artificial neural network[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2011, 43(1): 22-27. |
| 28 | Paduszyński K. In silico calculation of infinite dilution activity coefficients of molecular solutes in ionic liquids: critical review of current methods and new models based on three machine learning algorithms[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2016, 56(8): 1420-1437. |
| 29 | Hakim M, Behmardikalantari G, Abedini Najafabadi H, et al. Prediction of liquid-liquid equilibrium behavior for aliphatic + aromatic + ionic liquid using two different neural network-based models[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2015, 394: 140-147. |
| 30 | Delley B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2000, 113(18): 7756-7764. |
| 31 | Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15): 154104. |
| 32 | 霍猛, 彭晓婉, 赵金, 等. 基于COSMO-RS的离子液体吸收CO的溶剂筛选及H2/CO分离实验[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5305-5313. |
| Huo M, Peng X W, Zhao J, et al. COSMO-RS based solvent screening and H2/CO separation experiments for CO absorption by ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5305-5313. | |
| 33 | 李明宴, 李进龙, 彭昌军, 等. 基于COSMO-SAC模型研究离子液体对氨水溶液汽液平衡的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1044-1053. |
| Li M Y, Li J L, Peng C J, et al. The effect of ionic liquids on the vapor-liquid equilibrium of ammonia-water solution by the COSMO-SAC[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1044-1053. | |
| 34 | Mao Y G, Damodaran K. Ionization dynamics in ionic liquids probed via self-diffusion coefficient measurements[J]. Chemical Physics, 2014, 440: 87-93. |
| 35 | Fernández A, García J, Torrecilla J S, et al. Volumetric, transport and surface properties of [bmim][MeSO4] and [emim][EtSO4] ionic liquids as a function of temperature[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2008, 53(7): 1518-1522. |
| 36 | Lemaoui T, Darwish A S, Attoui A, et al. Predicting the density and viscosity of hydrophobic eutectic solvents: towards the development of sustainable solvents[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(23): 8511-8530. |
| 37 | Lemaoui T, Darwish A S, El Houda Hammoudi N, et al. Prediction of electrical conductivity of deep eutectic solvents using COSMO-RS sigma profiles as molecular descriptors: a quantitative structure-property relationship study[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(29): 13343-13354. |
| [1] | Xi MENG, Yan WANG, Zijian SUN, Junfei QIAO. Prediction of NO x emissions for municipal solid waste incineration processes using attention modular neural network [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 593-603. |
| [2] | Lin WANG, Rongding JIANG, Chunxiao ZHANG, Xiuzhen LI, Yingying TAN. Evaluation and predictive study of the mixing rules for vapor-liquid equilibrium of R1234yf mixtures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 475-483. |
| [3] | Qichao LIU, Shibo ZHANG, Yunlong ZHOU, Yuqing LI, Cong CHEN, Yiwen RAN. Gas-liquid two-phase flow regimes and transformation mechanism in horizontal tube under fluctuating vibration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 493-504. |
| [4] | Gang YIN, Zhongyou QIAN, Wenqi CAO, Pengcheng QUAN, Hengquan XU, Feiya YAN, Min WANG, Yu XIANG, Dongmei XIANG, Jian LU, Yuhai ZUO, Wen HE, Runting LU. Health state diagnosis of aluminum electrolytic cells based on Adaboost-PSO-SVM [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 354-365. |
| [5] | Qi WANG, Bin ZHANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Hujian WU, Haitao ZHAN, Tao WANG. Synthesis of isoxepac and 2-ethylanthraquinone catalyzed by chloroaluminate-triethylamine ionic liquid/P2O5 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [6] | Ruimin CHE, Wenqiu ZHENG, Xiaoyu WANG, Xin LI, Feng XU. Research progress on homogeneous processing of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [7] | Zehao MI, Er HUA. DFT and COSMO-RS theoretical analysis of SO2 absorption by polyamines type ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [8] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [9] | Shaoqi YANG, Shuheng ZHAO, Lungang CHEN, Chenguang WANG, Jianjun HU, Qing ZHOU, Longlong MA. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived compounds to alkanes in Raney Ni-protic ionic liquid system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [10] | Meisi CHEN, Weida CHEN, Xinyao LI, Shangyu LI, Youting WU, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Advances in silicon-based ionic liquid microparticle enhanced gas capture and conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [11] | Lizhi WANG, Qiancheng HANG, Yeling ZHENG, Yan DING, Jiaji CHEN, Qing YE, Jinlong LI. Separation of methyl propionate + methanol azeotrope using ionic liquid entrainers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741. |
| [12] | Jie CHEN, Yongsheng LIN, Kai XIAO, Chen YANG, Ting QIU. Study on catalytic synthesis of sec-butanol by tunable choline-based basic ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [13] | Gang YIN, Yihui LI, Fei HE, Wenqi CAO, Min WANG, Feiya YAN, Yu XIANG, Jian LU, Bin LUO, Runting LU. Early warning method of aluminum reduction cell leakage accident based on KPCA and SVM [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3419-3428. |
| [14] | Linqi YAN, Zhenlei WANG. Multi-step predictive soft sensor modeling based on STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM combined model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [15] | Yuanliang ZHANG, Xinqi LUAN, Weige SU, Changhao LI, Zhongxing ZHAO, Liqin ZHOU, Jianmin CHEN, Yan HUANG, Zhenxia ZHAO. Study on selective extraction of nicotine by ionic liquids composite extractant and DFT calculation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2947-2956. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||