CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 4318-4330.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250077
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yitong ZHOU1,2( ), Mingxi ZHOU1(
), Mingxi ZHOU1( ), Ruochen LIU1, Shuang YE1, Weiguang HUANG1,2
), Ruochen LIU1, Shuang YE1, Weiguang HUANG1,2
Received:2025-01-17
Revised:2025-04-14
Online:2025-09-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Mingxi ZHOU
周奕彤1,2( ), 周明熙1(
), 周明熙1( ), 刘若晨1, 叶爽1, 黄伟光1,2
), 刘若晨1, 叶爽1, 黄伟光1,2
通讯作者:
周明熙
作者简介:周奕彤(2001—),女,硕士研究生,zhouyt2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yitong ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Ruochen LIU, Shuang YE, Weiguang HUANG. Technical and economic analysis on hydrogen based direct reduction steelmaking co-driven by photovoltaic and power grid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330.
周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 项目 | 数值 | |
|---|---|---|
单晶硅 光伏组件 | 转换效率/% | 20.64 |
| 峰值功率/W | 580.0 | |
| 开路电压/V | 40.9 | |
| 短路电流/A | 18.2 | |
| 工作电压/V | 33.8 | |
| 工作电流/A | 17.2 | |
组串式 逆变器 | 最大输入电压/V | 1500 |
| 额定输入电压/V | 1080 | |
| 最小MPPT电压/V | 600 | |
| 最大MPPT电压/V | 1500 | |
| 额定输出电压/V | 800 | |
| 转换效率/% | 98.43 | |
Table 1 Key component parameters of PV and inverters
| 项目 | 数值 | |
|---|---|---|
单晶硅 光伏组件 | 转换效率/% | 20.64 |
| 峰值功率/W | 580.0 | |
| 开路电压/V | 40.9 | |
| 短路电流/A | 18.2 | |
| 工作电压/V | 33.8 | |
| 工作电流/A | 17.2 | |
组串式 逆变器 | 最大输入电压/V | 1500 |
| 额定输入电压/V | 1080 | |
| 最小MPPT电压/V | 600 | |
| 最大MPPT电压/V | 1500 | |
| 额定输出电压/V | 800 | |
| 转换效率/% | 98.43 | |
| 地区 | 地理位置 | 太阳能年均DNI/(W/m2) | 电力二氧化碳排放因子[ | 电网电力 可再生能源 占比/%[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
新疆 乌鲁木齐 | 43.82°N 87.61°E | 221.65 | 0.6231 | 22.5 |
广东 湛江 | 21.28°N 110.35°E | 127.86 | 0.4403 | 28.1 |
河北 张家口 | 40.82°N 114.87°E | 240.02 | 0.7252 | 24.4 |
| 上海 | 31.24°N 121.47°E | 127.48 | 0.5849 | 30.3 |
Table 2 Annual average direct normal irradiance (DNI) of solar energy, CO2 emission factor of electricity and the proportion of renewable energy in the grid in different geographical locations
| 地区 | 地理位置 | 太阳能年均DNI/(W/m2) | 电力二氧化碳排放因子[ | 电网电力 可再生能源 占比/%[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
新疆 乌鲁木齐 | 43.82°N 87.61°E | 221.65 | 0.6231 | 22.5 |
广东 湛江 | 21.28°N 110.35°E | 127.86 | 0.4403 | 28.1 |
河北 张家口 | 40.82°N 114.87°E | 240.02 | 0.7252 | 24.4 |
| 上海 | 31.24°N 121.47°E | 127.48 | 0.5849 | 30.3 |
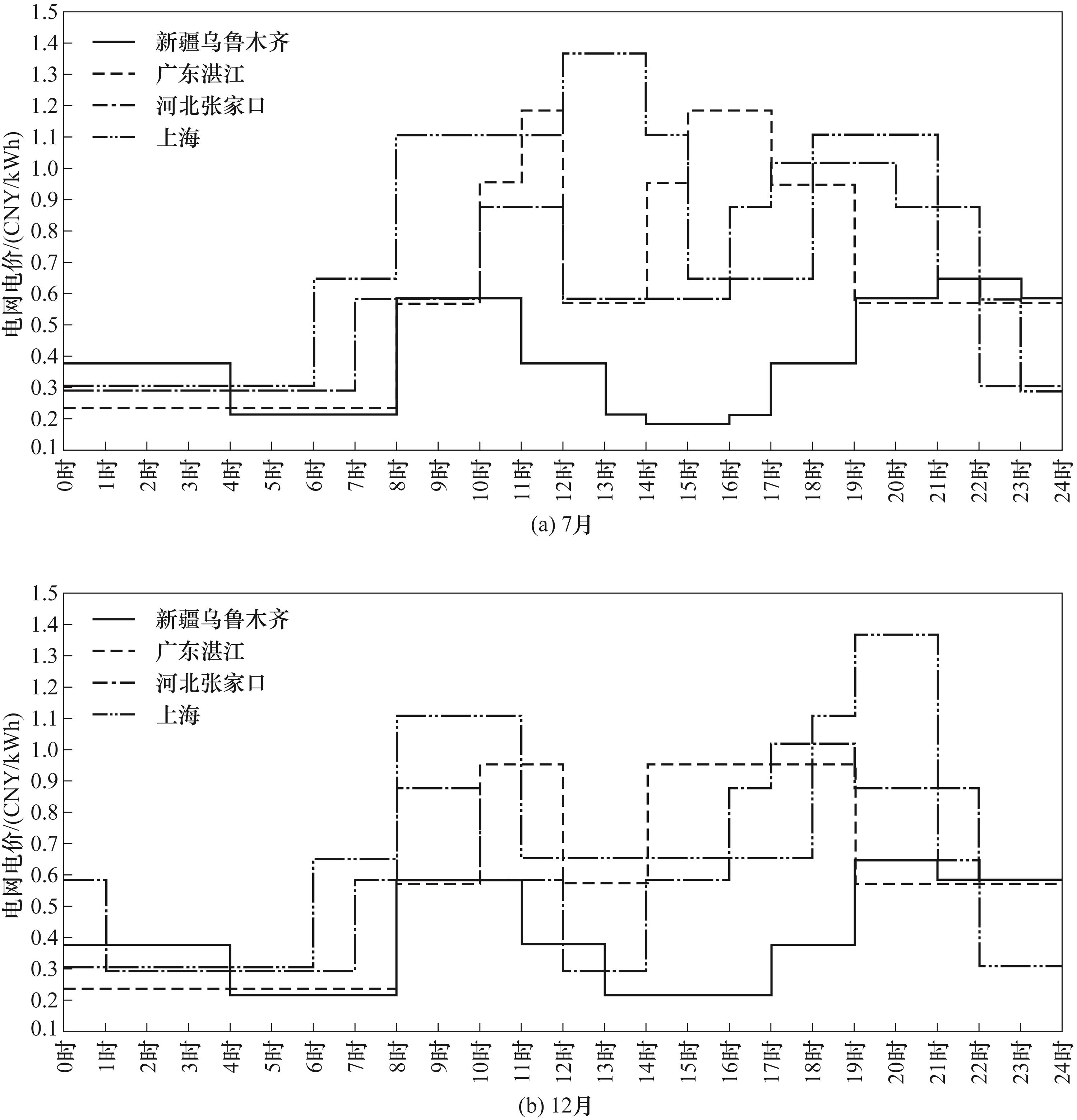
Fig.2 24 h industrial and commercial electricity prices in July and December in Urumqi, Xinjiang; Zhanjiang, Guangdong; Zhangjiakou, Hebei and Shanghai
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 电解槽额定容量/MW | 20[ |
| 电解槽模块数量/套 | 34 |
| 电解槽制氢电耗/(kWh/ | 50 |
| 电解槽设计容量冗余度/% | 50[ |
| 氢气电加热效率/% | 60[ |
Table 3 Parameters of the electrolyser
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 电解槽额定容量/MW | 20[ |
| 电解槽模块数量/套 | 34 |
| 电解槽制氢电耗/(kWh/ | 50 |
| 电解槽设计容量冗余度/% | 50[ |
| 氢气电加热效率/% | 60[ |
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 地下储氢容量/m3 | 32000[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机额定容量/MW | 1.7[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机模块数量 | 1~120 |
| 压缩机/膨胀机电效率/% | 70 |
Table 4 Parameters of the hydrogen storage
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 地下储氢容量/m3 | 32000[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机额定容量/MW | 1.7[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机模块数量 | 1~120 |
| 压缩机/膨胀机电效率/% | 70 |
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| DRI金属化率/% | 94[ |
| 铁矿石电加热效率/% | 85[ |
| 铁矿石杂质SiO2的质量分数/% | 3[ |
| 铁矿石杂质Al2O3的质量分数/% | 2[ |
| 电弧炉电效率/% | 60[ |
| 电弧炉石灰消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 50[ |
| 电弧炉焦炭消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 20[ |
| 电弧炉石墨电极消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 3[ |
Table 5 Parameters of DRI-EAF
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| DRI金属化率/% | 94[ |
| 铁矿石电加热效率/% | 85[ |
| 铁矿石杂质SiO2的质量分数/% | 3[ |
| 铁矿石杂质Al2O3的质量分数/% | 2[ |
| 电弧炉电效率/% | 60[ |
| 电弧炉石灰消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 50[ |
| 电弧炉焦炭消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 20[ |
| 电弧炉石墨电极消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 3[ |
| 参数 | 输入值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 工厂年产能/t | 1×106 | |
| 换热器效率/% | 60[ | |
| 竖炉氢气过量供应与需求量比率 | 1.5[ | |
| 铁矿石价格①/(CNY/t) | 851[ | |
| 工商业用水价格/(CNY/t) | 4.74[ | |
| 焦炭价格②/(CNY/t) | 2004 | |
| 石灰价格③/(CNY/t) | 782[ | |
| 光伏电站 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 3400[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 电解槽 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 2136[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 压缩机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 8546[ |
| 运营成本/% | 4[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 地下储氢 | 建设成本/(CNY/m3) | 359[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 膨胀机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 4409[ |
| 运营成本④/% | 4 | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 竖炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tDRI) | 1780[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 电弧炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tLS) | 1638[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 劳动力成本/(CNY/(人·a)) | 9.76万[ | |
| 粗钢售价⑤/(CNY/t) | 4629[ | |
| 碳市场碳价⑥/(CNY/t) | 90 | |
| 税率⑦/% | 25 | |
| 折现率/% | 7[ | |
| 残值率⑧/% | 5 | |
Table 6 Technical and economic parameters of hydrogen-based DRI-EAF plant
| 参数 | 输入值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 工厂年产能/t | 1×106 | |
| 换热器效率/% | 60[ | |
| 竖炉氢气过量供应与需求量比率 | 1.5[ | |
| 铁矿石价格①/(CNY/t) | 851[ | |
| 工商业用水价格/(CNY/t) | 4.74[ | |
| 焦炭价格②/(CNY/t) | 2004 | |
| 石灰价格③/(CNY/t) | 782[ | |
| 光伏电站 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 3400[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 电解槽 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 2136[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 压缩机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 8546[ |
| 运营成本/% | 4[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 地下储氢 | 建设成本/(CNY/m3) | 359[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 膨胀机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 4409[ |
| 运营成本④/% | 4 | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 竖炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tDRI) | 1780[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 电弧炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tLS) | 1638[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 劳动力成本/(CNY/(人·a)) | 9.76万[ | |
| 粗钢售价⑤/(CNY/t) | 4629[ | |
| 碳市场碳价⑥/(CNY/t) | 90 | |
| 税率⑦/% | 25 | |
| 折现率/% | 7[ | |
| 残值率⑧/% | 5 | |
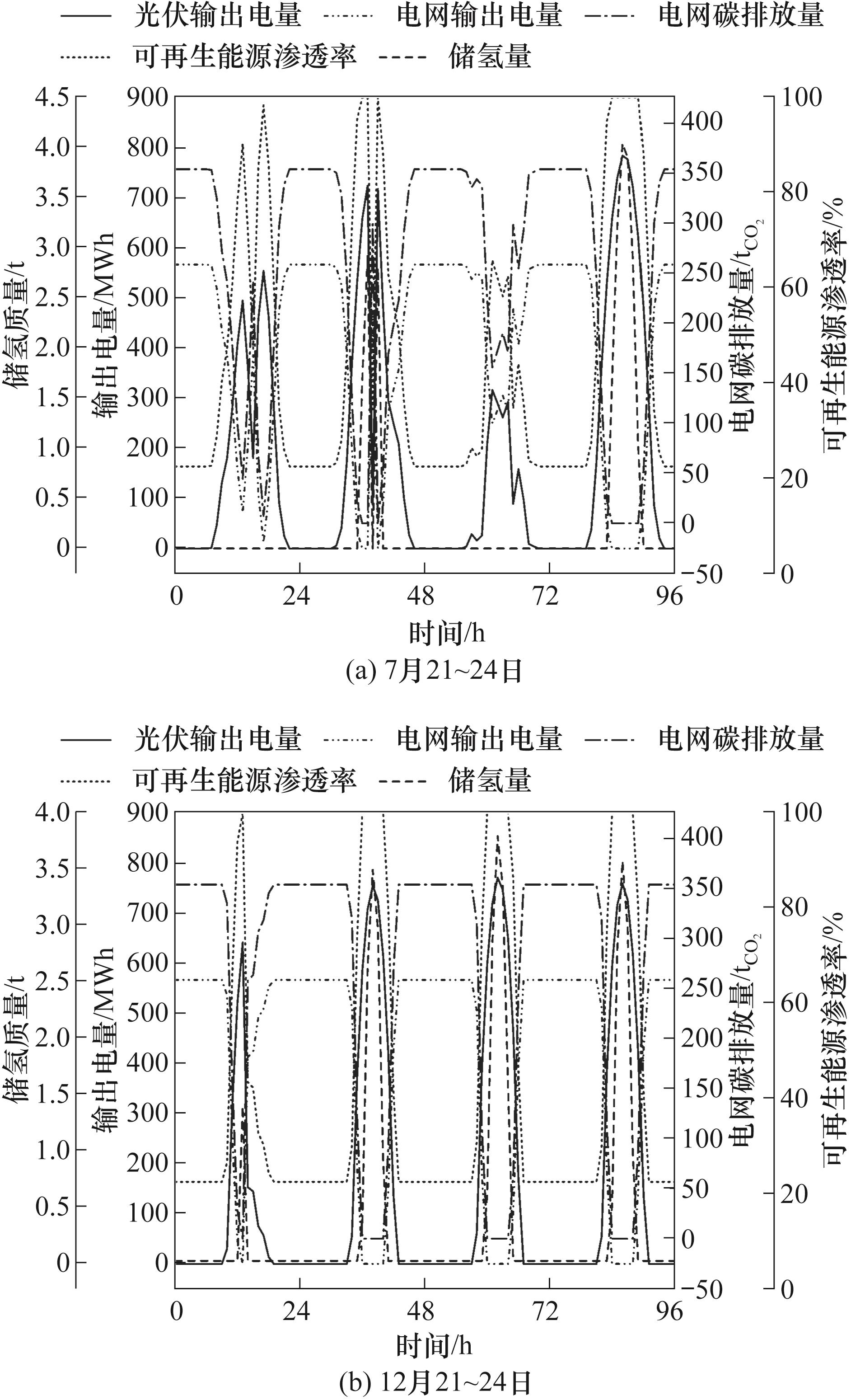
Fig.4 Hourly PV power generation, grid output power and carbon emissions, excess renewable energy hydrogen storage capacity and renewable energy share ratio of the 1000 MW PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
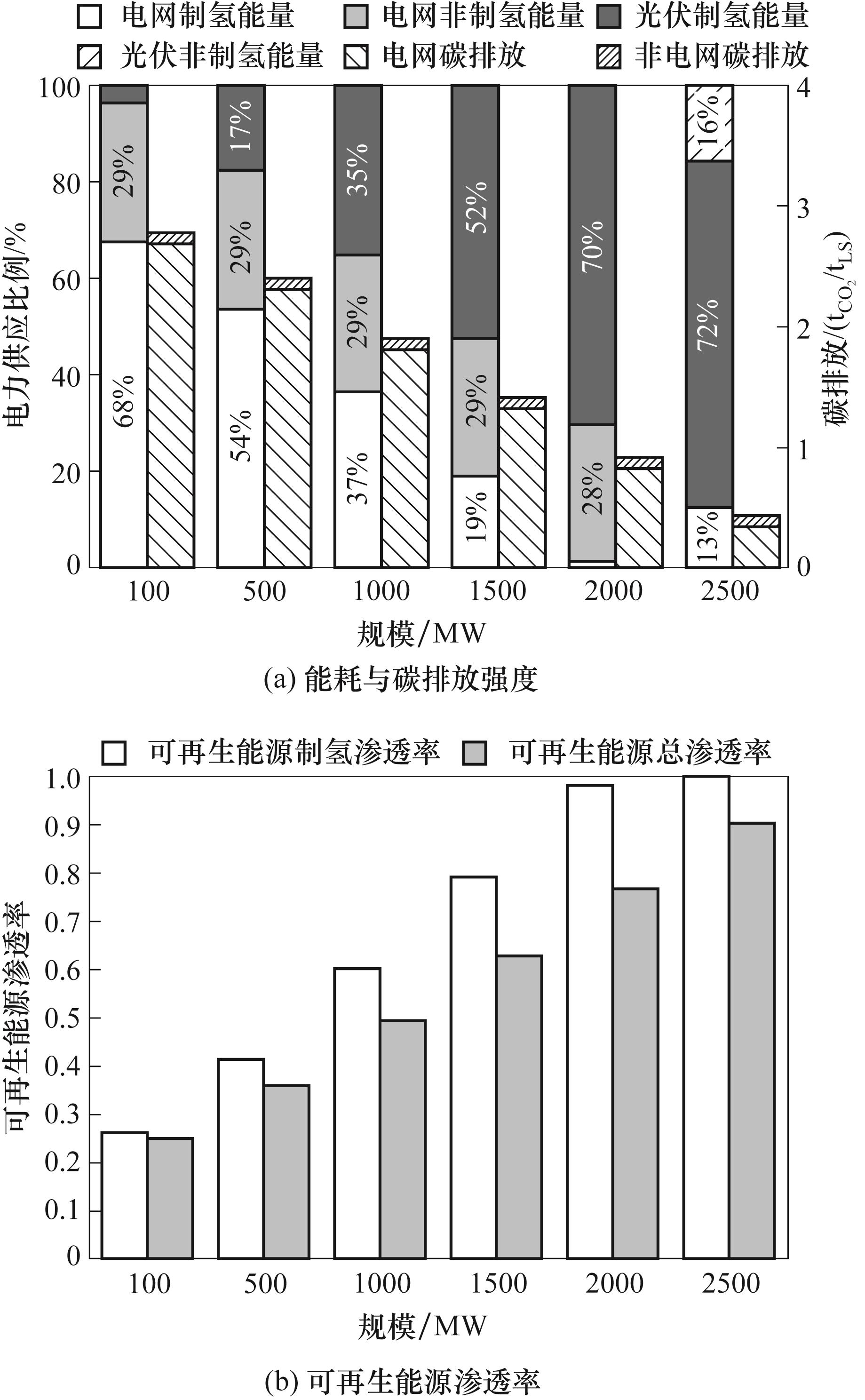
Fig.5 Energy consumption, carbon emission intensity, and renewable energy share ratio of the DRI-EAF plant under different scales of the PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
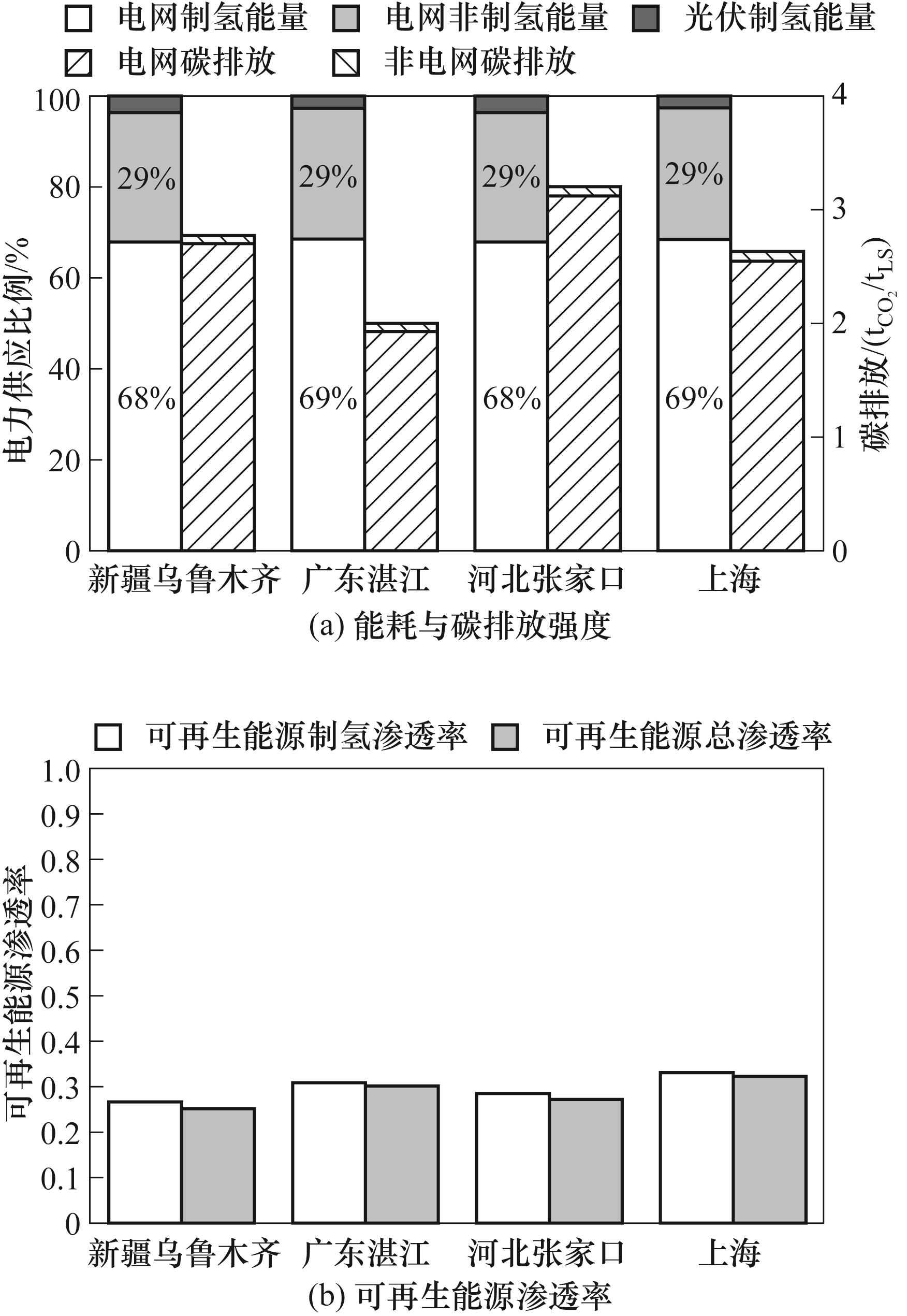
Fig.7 Energy consumption, carbon emission intensity and renewable energy share ratio of the DRI-EAF plant with 100 MW PV power station at different locations
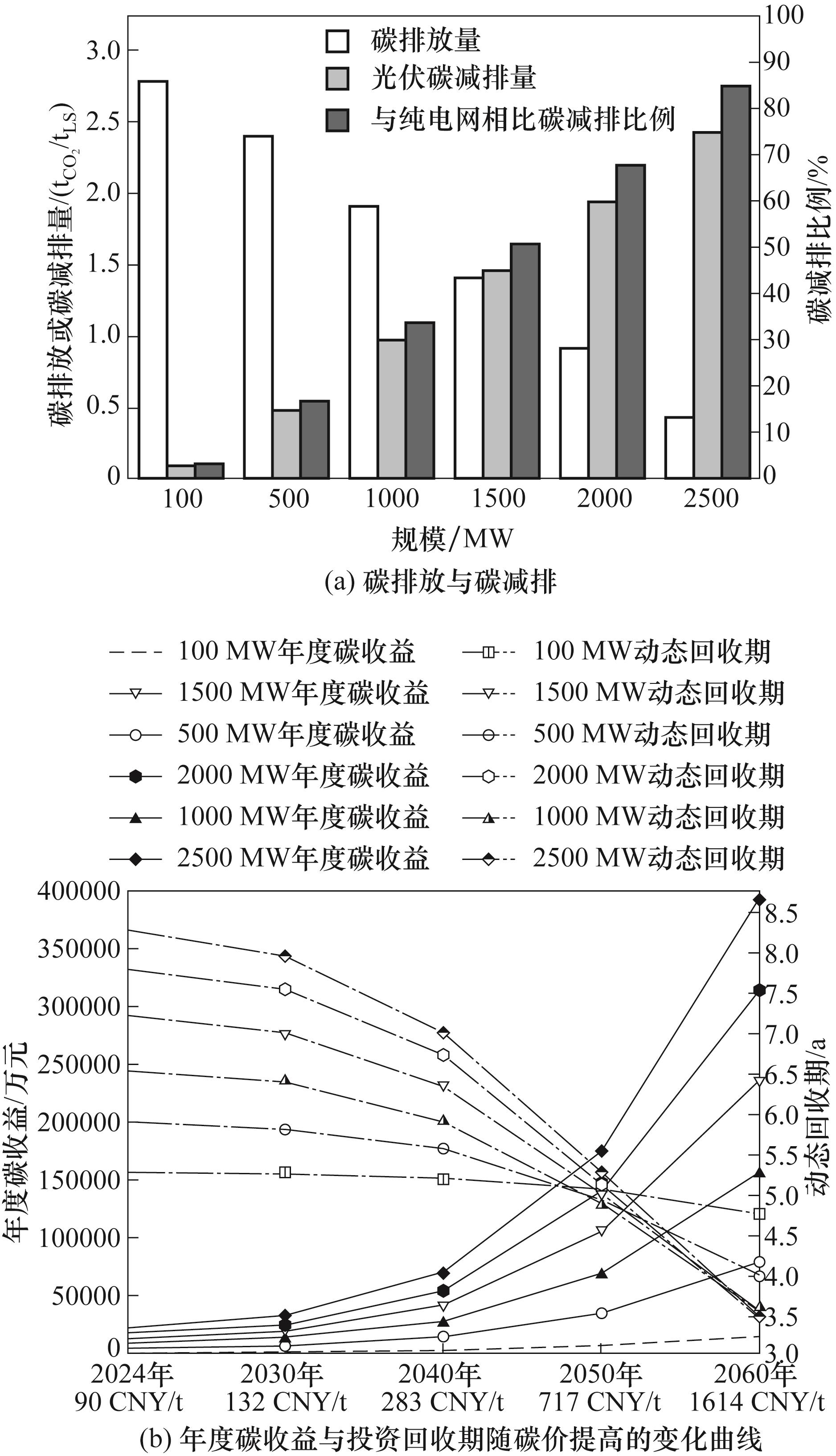
Fig.10 Carbon emission reduction intensity and effects of carbon price of the DRI-EAF plant under different scales of the PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
| [1] | International Energy Agency. Iron and steel technology roadmap[R]. Paris: IEA, 2020. |
| [2] | Zhang J S, Shen J L, Xu L S, et al. The CO2 emission reduction path towards carbon neutrality in the Chinese steel industry: a review[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 2023, 99: 107017. |
| [3] | Perpiñán J, Peña B, Bailera M, et al. Integration of carbon capture technologies in blast furnace based steel making: a comprehensive and systematic review[J]. Fuel, 2023, 336: 127074. |
| [4] | World Steel Association. Sustainability indicators 2023 report[R]. Brussels: WSA, 2023. |
| [5] | Wang Y X, Liu J, Tang X L, et al. Decarbonization pathways of C h i n a ' s iron and steel industry toward carbon neutrality[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 194: 106994. |
| [6] | Seker M, Memmedov A, Huseyinov R, et al. Power quality measurement and analysis in electric arc furnace for Turkish electricity transmission system[J]. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika, 2017, 23(6): 25-33. |
| [7] | Fan Z Y, Friedmann S J. Low-carbon production of iron and steel: technology options, economic assessment, and policy[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(4): 829-862. |
| [8] | Kodgire P. Hydrogen — imminent clean and green energy: hydrogen production technologies life cycle assessment review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2025, 193: 483-500. |
| [9] | Hasnain S M W U, Farooqi A S, Ayodele B V, et al. Advancements in Ni and Co-based catalysts for sustainable syngas production via Bi-reforming of methane: a review of recent advances[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 434: 139904. |
| [10] | Shen J L, Zhang Q, Tian S S, et al. The role of hydrogen in iron and steel production: development trends, decarbonization potentials, and economic impacts[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 92: 1409-1422. |
| [11] | Lan C C, Hao Y J, Shao J N, et al. Effect of H2 on blast furnace ironmaking: a review[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(11): 1864. |
| [12] | Rechberger K, Spanlang A, Conde A S, et al. Green hydrogen-based direct reduction for low-carbon steelmaking[J]. Steel Research International, 2020, 91(11): 2000110. |
| [13] | Müller N, Herz G, Reichelt E, et al. Assessment of fossil-free steelmaking based on direct reduction applying high-temperature electrolysis[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2021, 4: 100158. |
| [14] | Elsheikh H, Eveloy V. Assessment of variable solar- and grid electricity-driven power-to-hydrogen integration with direct iron ore reduction for low-carbon steel making[J]. Fuel, 2022, 324: 124758. |
| [15] | 李峰, 储满生, 唐珏, 等. 中国氢冶金工艺现状、挑战及发展对策[J]. 前瞻科技, 2024, 3(4): 44-57. |
| Li F, Chu M S, Tang J, et al. Current status, challenges, and development strategies of hydrogen metallurgy technologies in China[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2024, 3(4): 44-57. | |
| [16] | Bhaskar A, Assadi M, Nikpey Somehsaraei H. Decarbonization of the iron and steel industry with direct reduction of iron ore with green hydrogen[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(3): 758. |
| [17] | Jacobasch E, Herz G, Rix C, et al. Economic evaluation of low-carbon steelmaking via coupling of electrolysis and direct reduction[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 328: 129502. |
| [18] | Vogl V, Max Å, Nilsson L J. Assessment of hydrogen direct reduction for fossil-free steelmaking[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 203: 736-745. |
| [19] | Home-System Advisor Model[Z]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| [20] | 生态环境部. 关于发布2022年电力二氧化碳排放因子的公告[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Announcement on the release of 2022 electricity carbon dioxide emission factors[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [21] | 国家能源局. 国家能源局关于印发2023年度全国可再生能源电力发展监测评价结果的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| National Energy Administration. Notice of the national energy administration on issuing the monitoring and evaluation results of national renewable energy power development in 2023[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [22] | Bhaskar A. HDRI-EAF-Technoeconomic-model[CP/OL]. Zenodo, 2020[2025-01-07]. . |
| [23] | Bade S O, Taiwo K, Ndulue U F, et al. A review of underground hydrogen storage systems: current status, modeling approaches, challenges, and future prospective[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 80: 449-474. |
| [24] | Daraei M, Campana P E, Thorin E. Power-to-hydrogen storage integrated with rooftop photovoltaic systems and combined heat and power plants[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 276: 115499. |
| [25] | Germeshuizen L M, Blom P W E. A techno-economic evaluation of the use of hydrogen in a steel production process, utilizing nuclear process heat[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(25): 10671-10682. |
| [26] | Pfeifer H, Kirschen M. Thermodynamic analysis of EAF energy efficiency and comparison with a statistical model of electric energy demand[R]. Venice: Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, 2002. |
| [27] | 百川盈孚. 2023年中国铁矿石市场报告[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Bainfo. 2023 China iron ore market report[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [28] | 乌鲁木齐市人民政府. 乌鲁木齐市城市供水价格标准及依据[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Urumqi Municipal People's Government. Price standards and basis for urban water supply in Urumqi city[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [29] | Yang L Z, Hu H, Wang M X, et al. Comparative life cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis of electric arc furnace steelmaking processes integrated with solar energy system[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 425: 138868. |
| [30] | 中国光伏行业协会. 中国光伏产业发展路线图(2023—2024年)[EB/OL]. [2025-01-06]. . |
| China Photovoltaic Industry Association. Roadmap for the development of China's photovoltaic industry (2023—2024)[EB/OL]. [2025-01-06]. . | |
| [31] | Sheng K L, Wang X J, Si F Y, et al. Rational capacity investment for renewable hydrogen-based steelmaking systems: a multi-stage expansion planning strategy[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 372: 123746. |
| [32] | International Energy Agency. Global hydrogen review 2022[R]. Paris: OECD, 2022. |
| [33] | Tebibel H. Dual-objective optimization of solar driven alkaline electrolyzer system for on-site hydrogen production and storage: current and future scenarios[J]. Renewable Energy, 2024, 237: 121784. |
| [34] | Jindal A, Shrimali G, Tiwary N. At scale adoption of green hydrogen in Indian industry: costs, subsidies and policies[J]. Energy for Sustainable Development, 2024, 83, 101549. |
| [35] | Chen Y Z, Hill D, Billings B, et al. Hydrogen underground storage for grid electricity storage: an optimization study on techno-economic analysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 322: 119115. |
| [36] | Singer G, Köll R, Aichhorn L, et al. Utilizing hydrogen pressure energy by expansion machines — PEM fuel cells in mobile and other potential applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 343: 121056. |
| [37] | Eveloy V, Kannan P, Romeo L M. Comparative energy, emissions and economic assessment of low-carbon iron and steel making processes using imported liquid organic hydrogen carrier options[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 89: 1321-1341. |
| [38] | 我的钢铁网. Mysteel年报:2023年国内钢铁市场回顾与2024年展望[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Mysteel. Mysteel annual report: review of domestic steel market in 2023 and outlook for 2024[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [39] | Bhaskar A, Assadi M, Somehsaraei H N. Can methane pyrolysis based hydrogen production lead to the decarbonisation of iron and steel industry?[J]. Energy Conversion and Management: X, 2021, 10: 100079. |
| [40] | Qi S Z, Cheng S H, Tan X J, et al. Predicting China's carbon price based on a multi-scale integrated model[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 324: 119784. |
| [1] | Yufeng WANG, Xiaoxue LUO, Hongliang FAN, Baijing WU, Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI. Green organic electrosynthesis coupled with water electrolysis to produce hydrogen—overview of electrode interface regulation strategies [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [2] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [3] | Ning YANG, Haonan LI, Xiao LIN, Stella GEORGIADOU, Wen-Feng LIN. Application of plastic-derived carbon@CoMoO4 composites as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [4] | Jiaxiang CHEN, Wei ZHOU, Xuewei ZHANG, Lijie WANG, Yuming HUANG, Yang YU, Miaoting SUN, Wanjing LI, Junshu YUAN, Hongbo ZHANG, Xiaoxiao MENG, Jihui GAO, Guangbo ZHAO. Simulation study on the hydrogen production performance of a two-dimensional PEMWE model under pulsed voltage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [5] | Tianhao WU, Tingwei YE, Yan LIN, Zhen HUANG. In-situ hydrogen supplementation of biomass chemical looping gasification to produce syngas with controllable H2/CO [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [6] | Pengwei LIAO, Qinghui LIU, An PAN, Jiayue WANG, Xiaogui FU, Siyu YANG, Hao YU. Wind power hydrogen production systems considering uncertainty: multi-time scale operation strategy [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [7] | Fenhong SONG, Wenguang WANG, Liang GUO, Jing FAN. Modulation of TiO2 by C-element modified g-C3N4 and photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of composites [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [8] | Haiyan JI, Jiayin LIU, Haijun WU, Jinglin HE, Ziheng JIN, Dianhang WEI, Xia JIANG. Research progress on the application of low-temperature plasma in biomass gasification to produce hydrogen [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [9] | Pengfei ZHAO, Ruomei QI, Xinfeng GUO, Hu FANG, Lufei XU, Xiao LI, Jin LIN. Analysis of hydrogen-to-oxygen impurities in a 1000 m3/h alkaline water electrolysis system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1765-1778. |
| [10] | Zhineng TAO, Tong QIU, Baoguo WANG. Steady-state modeling on hydrogen production by anion exchange membrane water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1711-1721. |
| [11] | Jingrun LI, Siyu YANG, Qinghui LIU, An PAN, Jiayue WANG, Xiaogui FU, Hao YU. Analysis of multiple operating strategies for large-scale wind power coupled with thermal power for hydrogen production under various scenarios [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1191-1206. |
| [12] | Jun WAN, Jiarui SONG, Chunhuang FAN, Lele WEI, Yina NIE, Lin LIU. Highly efficient hole transfer for promoting photocatalytic hydrogen production from alkaline methanol aqueous solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075. |
| [13] | Xiaohang ZHONG, Wei XU, Wen ZHANG, Li XU, Yuxin WANG. A critical review on the effects of Fe impurity on H2 production via alkaline water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 519-531. |
| [14] | Ke ZHANG, Weijie REN, Mengna WANG, Kaifeng FAN, Liping CHANG, Jiabin LI, Tao MA, Jinping TIAN. Liquid-liquid mixing characteristics of Bunsen reaction products in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 623-636. |
| [15] | Mengfan YIN, Qian WANG, Tao ZHENG, Kui JI, Shaogui WANG, Hui GUO, Zhiqiang LIN, Rui ZHANG, Hui SUN, Haiyan LIU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU, Xianghai MENG, Yueping WANG. Process design of 10000 t industrial demonstration of hydrogen production from renewable energy electrolytic water - low temperature and low pressure ammonia synthesis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 825-834. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||