CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (3): 1064-1075.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240968
• Catalysis, kinetics and reactors • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jun WAN( ), Jiarui SONG, Chunhuang FAN, Lele WEI, Yina NIE, Lin LIU(
), Jiarui SONG, Chunhuang FAN, Lele WEI, Yina NIE, Lin LIU( )
)
Received:2024-08-28
Revised:2024-09-30
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
Lin LIU
万俊( ), 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳(
), 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳( )
)
通讯作者:
刘琳
作者简介:万俊(1990—),男,博士,副教授,wanjun@yau.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jun WAN, Jiarui SONG, Chunhuang FAN, Lele WEI, Yina NIE, Lin LIU. Highly efficient hole transfer for promoting photocatalytic hydrogen production from alkaline methanol aqueous solution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075.
万俊, 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳. 高效空穴转移助力光催化碱性甲醇-水溶液制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 样品 | Zn含量/% (原子分数) | Cd含量/% (原子分数) | Zn/Cd |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZCS-LNR | 21.83 | 20.55 | 1.06 |
| ZCS-SNR | 23.97 | 21.95 | 1.09 |
| ZCS-NP | 21.10 | 23.16 | 0.91 |
Table 1 Analysis of the XPS content of the different catalysts
| 样品 | Zn含量/% (原子分数) | Cd含量/% (原子分数) | Zn/Cd |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZCS-LNR | 21.83 | 20.55 | 1.06 |
| ZCS-SNR | 23.97 | 21.95 | 1.09 |
| ZCS-NP | 21.10 | 23.16 | 0.91 |
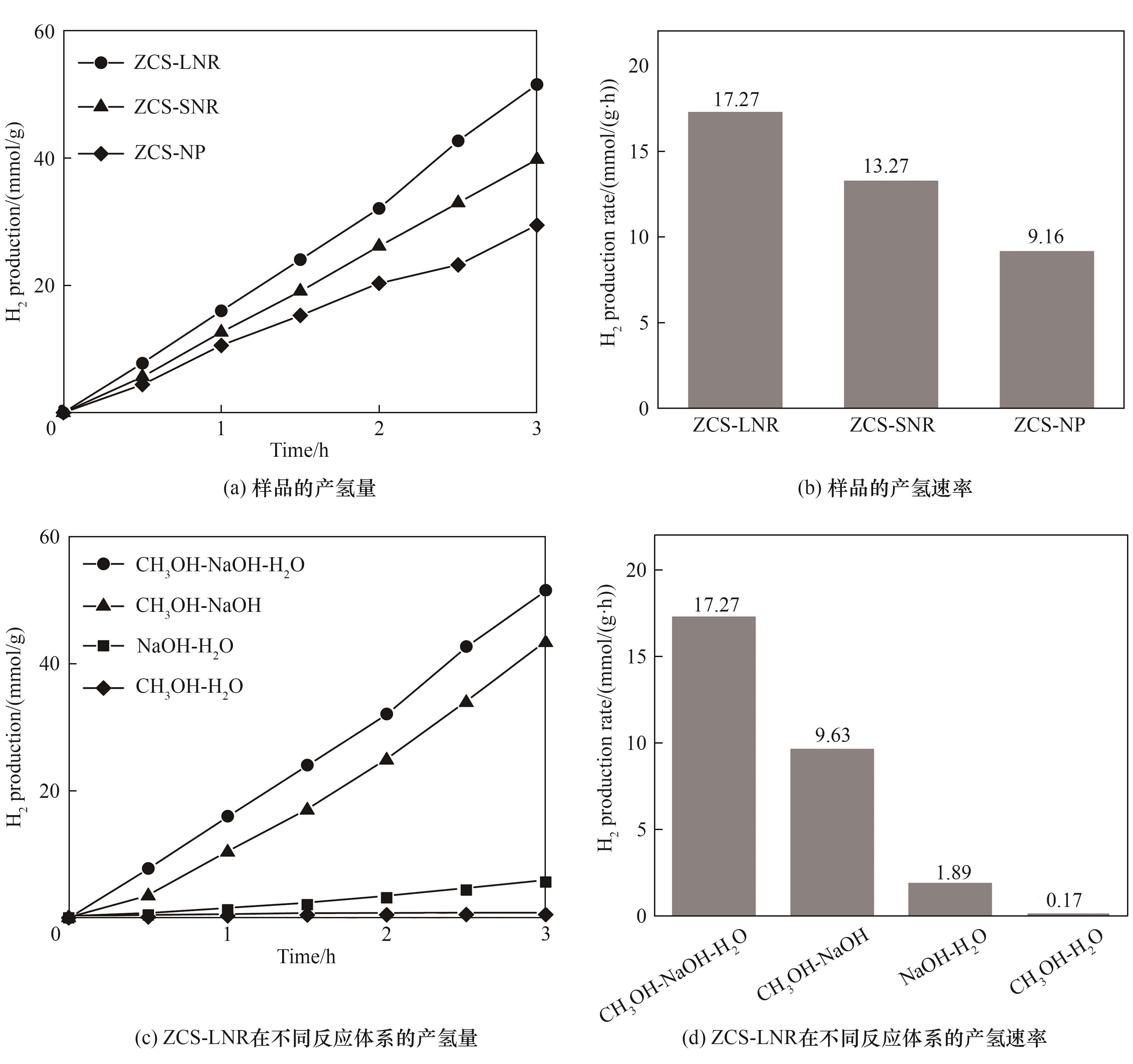
Fig.7 Photocatalytic H2 production of Zn0.5Cd0.5S with different structures in CH3OH-NaOH-H2O system, comparison of H2 production in different reaction systems using ZCS-LNR catalyst
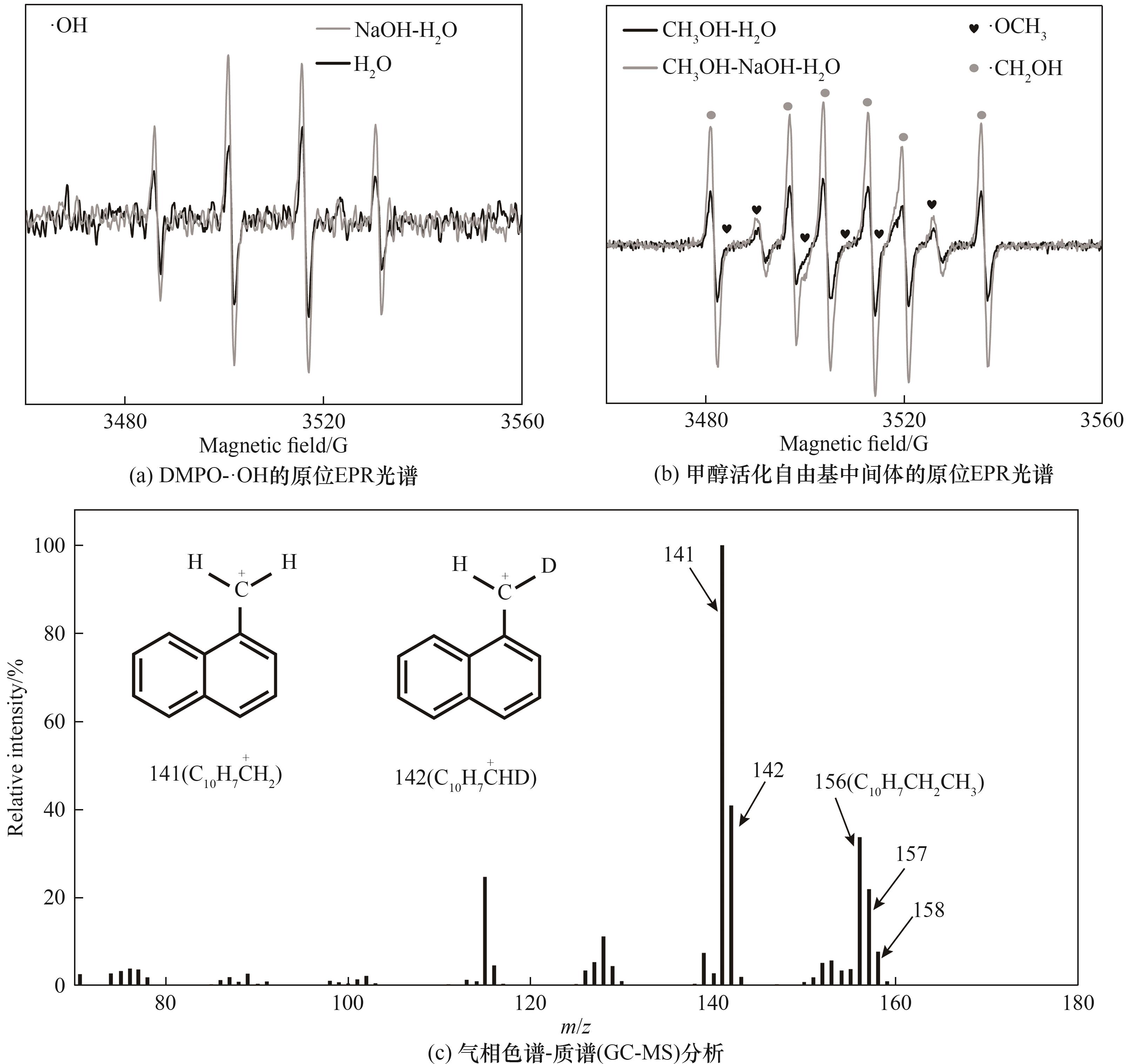
Fig.9 In-situ EPR spectra of ZCS-LNR in different solution systems, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis for deuterium-labeled experiment
| 质荷比(m/z) | 相对丰度/% | rH/D |
|---|---|---|
| 141 | 100 | 2.4 |
| 142 | 41.5 | |
| 156 | 33.7 | 2.4 |
| 157 | 21.9 | |
| 158 | 7.7 |
Table 2 Relative abundance and rH/D of molecular ion peak and fragmentation peak of naphthalene ethane
| 质荷比(m/z) | 相对丰度/% | rH/D |
|---|---|---|
| 141 | 100 | 2.4 |
| 142 | 41.5 | |
| 156 | 33.7 | 2.4 |
| 157 | 21.9 | |
| 158 | 7.7 |
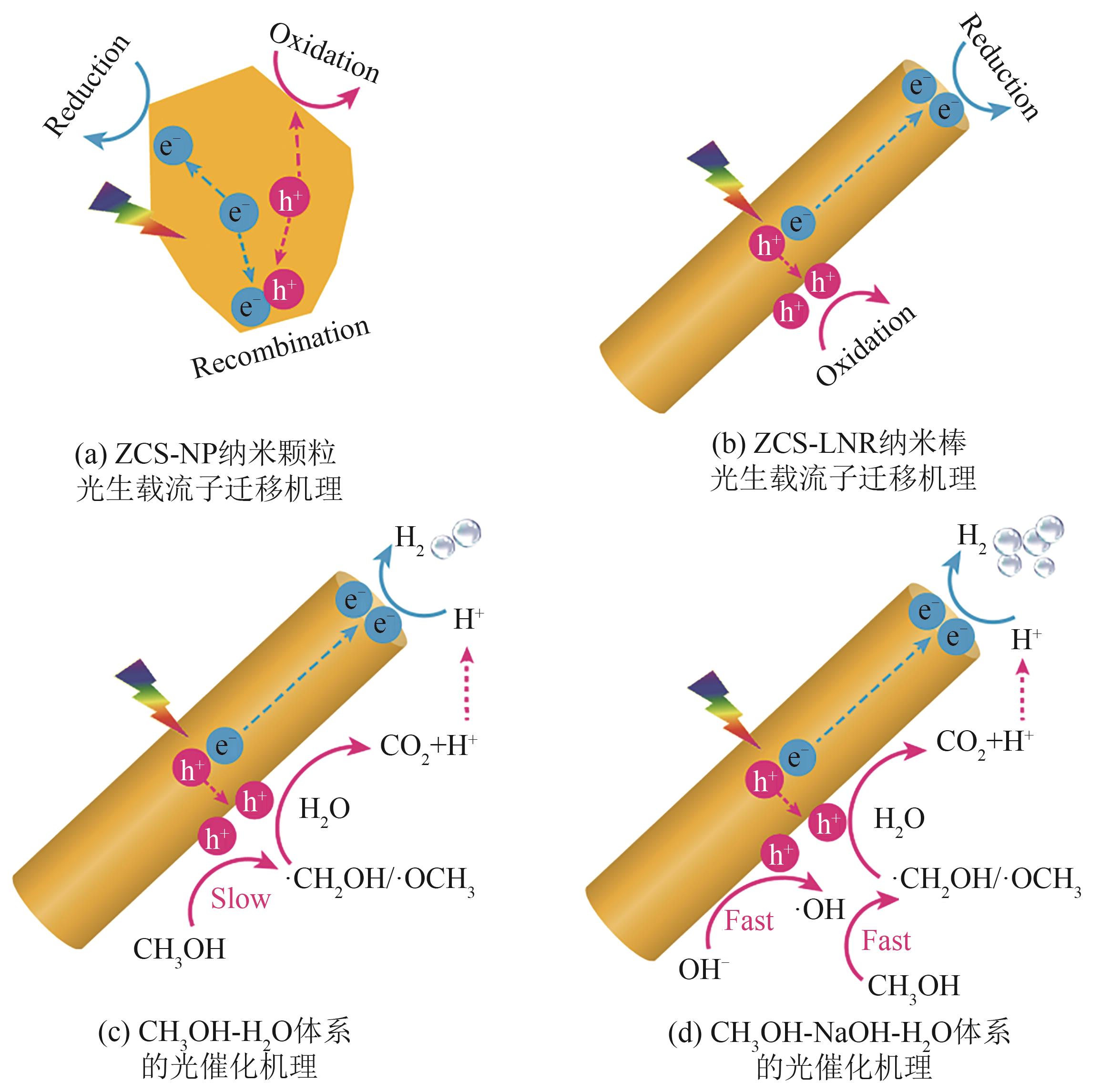
Fig.10 Schematic diagram of the photogenerated charge carrier transfer mechanism for ZCS-NP nanoparticles and ZCS-LNR nanorod catalysts, schematic illustration of the photocatalytic reaction mechanism for ZCS-LNR in CH3OH-H2O and CH3OH-NaOH-H2O systems
| 1 | Yang M, Hunger R, Berrettoni S, et al. A review of hydrogen storage and transport technologies[J]. Clean Energy, 2023, 7(1): 190-216. |
| 2 | Chatterjee S, Parsapur R K, Huang K W. Limitations of ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier for the transportation sector[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(12): 4390-4394. |
| 3 | Zhao J Q, Shi R, Li Z H, et al. How to make use of methanol in green catalytic hydrogen production?[J]. Nano Select, 2020, 1(1): 12-29. |
| 4 | 孙晓明, 沙琪昊, 王陈伟, 等. 用于甲醇重整制氢的铜基催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5975-6001. |
| Sun X M, Sha Q H, Wang C W, et al. Application of copper-based catalysts for hydrogen production in methanol steam reforming[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 5975-6001. | |
| 5 | Nielsen M, Alberico E, Baumann W, et al. Low-temperature aqueous-phase methanol dehydrogenation to hydrogen and carbon dioxide[J]. Nature, 2013, 495: 85-89. |
| 6 | Zhou P, Navid I A, Ma Y J, et al. Solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of more than 9% in photocatalytic water splitting[J]. Nature, 2023, 613: 66-70. |
| 7 | Wang L M, Sun Y, Zhang F Y, et al. Precisely constructed metal sulfides with localized single-atom rhodium for photocatalytic C-H activation and direct methanol coupling to ethylene glycol[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(5): 2205782. |
| 8 | Wang H, Qi H F, Sun X, et al. High quantum efficiency of hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution with PtCu-TiO2 photocatalysts[J]. Nature Materials, 2023, 22(5): 619-626. |
| 9 | Xiao M, Baktash A, Lyu M Q, et al. Unveiling the role of water in heterogeneous photocatalysis of methanol conversion for efficient hydrogen production[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(21): e202402004. |
| 10 | Huang H M, Garduño-Castro M H, Morrill C, et al. Catalytic cascade reactions by radical relay[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(17): 4626-4638. |
| 11 | Shatskiy A, Alvey G R, Kärkäs M D. Chemodivergent difunctionalization of alkenes through base-controlled radical relay[J]. Chem, 2022, 8(1): 12-14. |
| 12 | Zhao L M, Meng Q Y, Fan X B, et al. Photocatalysis with quantum dots and visible light: selective and efficient oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds through a radical relay process in water[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(11): 3020-3024. |
| 13 | Ren W, Si R R, Wang J H, et al. Study of the different morphologies of Zn0.5Cd0.5S for photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Environmental Science: Advances, 2023, 2(5): 721-730. |
| 14 | He K, Chen N F, Wang C J, et al. Method for determining crystal grain size by X-ray diffraction[J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2018, 53(2): 1700157. |
| 15 | Sun R H, Zhang J, Jing B Y, et al. CoP3 quantum dots decorated on CdZnS nanorods as Z-scheme p-n heterojunctions for photocatalytic H2 production[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2024, 7(7): 7122-7131. |
| 16 | Li H Q, Wang X, Xu J Q, et al. One-dimensional CdS nanostructures: a promising candidate for optoelectronics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(22): 3017-3037. |
| 17 | Ganesh R S, Durgadevi E, Silambarasan K, et al. Effect of ethylenediamine on morphology of 2D Co-Mo-S@NG hybrids and their enhanced electrocatalytic activity for DSSCs application[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2020, 105: 104725. |
| 18 | Liang Q, Jin J, Liu C H, et al. Fabrication of the ternary heterojunction Cd0.5Zn0.5S@UIO-66@g-C3N4 for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2018, 5(2): 335-343. |
| 19 | Tang Z R, Han B, Han C, et al. One dimensional CdS based materials for artificial photoredox reactions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(6): 2387-2410. |
| 20 | Liu S Q, Tang Z R, Sun Y G, et al. One-dimension-based spatially ordered architectures for solar energy conversion[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(15): 5053-5075. |
| 21 | Tang Z R, Yin X, Zhang Y H, et al. Synthesis of titanate nanotube-CdS nanocomposites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(20): 11758-11766. |
| 22 | Chen M X, Umer K, Li B N, et al. Metalloporphyrin based MOF-545 coupled with solid solution Zn x Cd1- x S for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 653: 380-389. |
| 23 | Fan Y, Hao X Q, Yi N X, et al. Strong electronic coupling of Mo2TiC2 MXene/ZnCdS ohmic junction for boosting photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 357: 124313. |
| 24 | Zhang Z J, Yin Q, Xu L L, et al. Potassium-doped-C3N4/Cd0.5Zn0.5S photocatalysts toward the enhancement of photocatalytic activity under visible-light[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 816: 152654. |
| 25 | Wang X, Liu B Y, Ma S Q, et al. Induced dipole moments in amorphous ZnCdS catalysts facilitate photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 2600. |
| 26 | Khan K, Tao X P, Zhao Y, et al. Spatial separation of dual-cocatalysts on one-dimensional semiconductors for photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(26): 15607-15614. |
| 27 | Lu X X, Chen W J, Yao Y, et al. Photogenerated charge dynamics of CdS nanorods with spatially distributed MoS2 for photocatalytic hydrogen generation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 127709. |
| 28 | Nakibli Y, Amirav L. Selective growth of Ni tips on nanorod photocatalysts[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(13): 4524-4527. |
| 29 | Wan J, Wang Y, Liu J Q, et al. Full-space electric field in Mo-decorated Zn2In2S5 polarization photocatalyst for oriented charge flow and efficient hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(31): 2405060. |
| 30 | Wolff C M, Frischmann P D, Schulze M, et al. All-in-one visible-light-driven water splitting by combining nanoparticulate and molecular co-catalysts on CdS nanorods[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3: 862-869. |
| 31 | Khan K, Tao X P, Shi M, et al. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production on Cd0.9Zn0.1S nanorods with an apparent quantum efficiency exceeding 80%[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(7): 2003731. |
| [1] | Bo GAO, Jiaqi WANG, Zhiliang LIU, Xuanlie ZHAO, Kun GE. Modeling and thermodynamic and economic analysis of offshore wind power-based hydrogen production systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1207-1220. |
| [2] | Jingrun LI, Siyu YANG, Qinghui LIU, An PAN, Jiayue WANG, Xiaogui FU, Hao YU. Analysis of multiple operating strategies for large-scale wind power coupled with thermal power for hydrogen production under various scenarios [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1191-1206. |
| [3] | Liwen ZHAO, Guilian LIU. Performance enhancement and parameter optimization of complex catalytic reaction system based on system integration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1111-1119. |
| [4] | Chuanchao HE, Jinghong ZHOU, Yueqiang CAO, Yao SHI, Xinggui ZHOU. Bed-particle dual scale coupled simulation on Ag/SiO2 catalyzed hydrogenation of oxalate to methyl glycolate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 654-666. |
| [5] | Ke ZHANG, Weijie REN, Mengna WANG, Kaifeng FAN, Liping CHANG, Jiabin LI, Tao MA, Jinping TIAN. Liquid-liquid mixing characteristics of Bunsen reaction products in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 623-636. |
| [6] | Mengfan YIN, Qian WANG, Tao ZHENG, Kui JI, Shaogui WANG, Hui GUO, Zhiqiang LIN, Rui ZHANG, Hui SUN, Haiyan LIU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU, Xianghai MENG, Yueping WANG. Process design of 10000 t industrial demonstration of hydrogen production from renewable energy electrolytic water - low temperature and low pressure ammonia synthesis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 825-834. |
| [7] | Xiaohang ZHONG, Wei XU, Wen ZHANG, Li XU, Yuxin WANG. A critical review on the effects of Fe impurity on H2 production via alkaline water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 519-531. |
| [8] | Fan LI, Yanjun YIN, Junchao XU, Liqiao JIANG, Xiaohan WANG, Huaqiang CHU. Enhancing the flame stability in a flat plate burner using catalytic coating of CeO2-ZrO2 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 394-404. |
| [9] | Jijun ZOU, Baohong LIU, Chengxiang SHI, Lun PAN, Xiangwen ZHANG. Research progress of heterogeneous catalysts for conversion of holocellulose derivatives into bio-aviation fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 1-17. |
| [10] | Chen YANG, Wei MAO, Xingzong DONG, Song TIAN, Fengwei ZHAO, Jian LYU. Research progress in the synthesis of olefins by selective hydrodechlorination [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 53-70. |
| [11] | Zhijiao JI, Xiaofang ZHANG, Wen GAN, Yunpeng XUE. Influence of support on the performance of single atom electrocatalyst for ammonia synthesis and the control strategy [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 18-39. |
| [12] | Shan GUO, Yu TIAN, Yongbin XU, Peng WANG, Zhiming LIU. Synthesis of a high-efficacy medium-entropy alloy catalyst via the recycling of spent batteries and its subsequent performance evaluation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 231-240. |
| [13] | Meilin SHI, Lianda ZHAO, Xingjian DENG, Jingsong WANG, Haibin ZUO, Qingguo XUE. Research progress on catalytic methane reforming process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 25-39. |
| [14] | Yachao LIU, Xiaojie TAN, Xudong LI, Rui WANG, Hui WANG, Xuan HAN, Qingshan ZHAO. Synthesis of efficient cobalt carbonate nanosheets based on DES for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3320-3328. |
| [15] | Mengting ZHANG, Shulin WANG, Xi SANG, Xinghao YUAN, Gang XU. Artificial Cu-TM1459 metalloenzyme catalyzes asymmetric Michael addition reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3255-3265. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||