CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4737-4751.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250300
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Longyi LYU( ), Minglei TANG, Peng HAO, Minhao WU, Wenfang GAO(
), Minglei TANG, Peng HAO, Minhao WU, Wenfang GAO( ), Guangming ZHANG(
), Guangming ZHANG( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Revised:2025-06-07
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-09-25
Contact:
Wenfang GAO, Guangming ZHANG
吕龙义( ), 唐明磊, 郝鹏, 吴旻昊, 高文芳(
), 唐明磊, 郝鹏, 吴旻昊, 高文芳( ), 张光明(
), 张光明( )
)
通讯作者:
高文芳,张光明
作者简介:吕龙义(1989—),男,博士研究生,副教授,lvlongyi@hebut.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Longyi LYU, Minglei TANG, Peng HAO, Minhao WU, Wenfang GAO, Guangming ZHANG. Progress on the performance and mechanism of high-solids anaerobic digestion enhanced by conductive materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4737-4751.
吕龙义, 唐明磊, 郝鹏, 吴旻昊, 高文芳, 张光明. 导电材料强化高固厌氧消化性能及机制研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4737-4751.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 材料类别 | 导电材料 | 投加量 | 粒径 | 实验体系 | 强化效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铁基 | ZVI | 320 mmol/L | 160 μm | 血清瓶—猪粪 | 反应周期缩短50.6%;CH4产量提高22.2% | [ |
| 铁基 | ZVI | 5 g/L | 300~600 nm | 血清瓶—食物垃圾 | 有机物的转化速率提升18%;CH4产量提高8.5% | [ |
| 铁基 | mZVI | 100 mg/g TS | 150 μm | 血清瓶—废弃活性污泥 | TVFAs浓度下降;CH4产量是对照组的11.9倍 | [ |
| 铁基 | 废铁屑 | 20 g/L | 0.075 mm | 玻璃瓶—城市污泥/餐厨垃圾 | 氨氮浓度降低11%;VFAs含量提高51%;CH4产量提高41.0% | [ |
| 铁基 | 磁铁矿粉 | 3 g/L | 0.5~1.0 mm | 烧瓶—猪粪/小麦秸秆 | 滞后期缩短为14.9 d;CH4产量提高72.1% | [ |
| 铁基 | INPs | 1000 mg/L | <20 μm | 聚丙烯消化器—牛粪 | VS去除率提高109.3%;CH4产量提高77.24% | [ |
| 铁基 | 磁铁矿 | — | 0.2~0.5 mm | 厌氧消化器—废活性污泥 | 有机物的降解速率和VFAs的转化速率加快;CH4产量提高37.4% | [ |
| 铁基 | 针铁矿 | 0.2 g/L | 60~120 μm | 树脂玻璃器—烟草废弃物/剩余污泥 | 酸化代谢及有机物溶解加速;最高产气量提升至359.4 ml/g | [ |
| 碳基 | 活性炭 | 0.8 g/L | — | 血清瓶—食物垃圾 | 滞后期缩短67%;VFAs的降解加速;最大CH4产量提高50% | [ |
| 碳基 | GAC | 27 g/L | 8~12 mm | 血清瓶—废活性污泥 | VFAs平均总浓度下降9.8%;平均CH4产量提高13.1% | [ |
| 碳基 | 碳布 | — | — | 聚碳酸酯消化罐—固体废物 | 滞后期缩短15%;CH4产量提高20% | [ |
| 碳基 | PAC | 10 g/L | — | 消化罐—玉米秸秆 | 纤维素降解率提高6.48%;CH4产量提高17.92% | [ |
| 碳基 | 生物炭 | 8.0 g/L | 150 μm | 锥形瓶—食物垃圾/城市污泥 | 游离铵的积累得到缓解;平均日CH4产量提高46.2% | [ |
| 碳基 | 石墨 | — | 0.16 mm | 血清瓶—脱水污泥 | 促进水解酸化产物的消耗;产气量提高13.8% | [ |
| 碳基 | 石墨烯 | 50 mg/L | 0.5~5 μm | 广口玻璃瓶—食物垃圾/污泥 | 有机物降解率提高23.07%;CH4产量提高36.09% | [ |
| 碳基 | rGO | 20 mg/L | — | 半连续反应器—有机垃圾 | 在OLRs为2.0 gVS/L时,CH4产量提升46% | [ |
| 碳基 | CNTs | 6.5 g/L | 10~30 nm | 批量厌氧反应器—鸡粪 | VFAs的吸收加速;CH4最大产量提高15% | [ |
Table 1 Enhancement effect of a single iron-based/carbon-based conductive material on high-solids anaerobic digestion
| 材料类别 | 导电材料 | 投加量 | 粒径 | 实验体系 | 强化效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铁基 | ZVI | 320 mmol/L | 160 μm | 血清瓶—猪粪 | 反应周期缩短50.6%;CH4产量提高22.2% | [ |
| 铁基 | ZVI | 5 g/L | 300~600 nm | 血清瓶—食物垃圾 | 有机物的转化速率提升18%;CH4产量提高8.5% | [ |
| 铁基 | mZVI | 100 mg/g TS | 150 μm | 血清瓶—废弃活性污泥 | TVFAs浓度下降;CH4产量是对照组的11.9倍 | [ |
| 铁基 | 废铁屑 | 20 g/L | 0.075 mm | 玻璃瓶—城市污泥/餐厨垃圾 | 氨氮浓度降低11%;VFAs含量提高51%;CH4产量提高41.0% | [ |
| 铁基 | 磁铁矿粉 | 3 g/L | 0.5~1.0 mm | 烧瓶—猪粪/小麦秸秆 | 滞后期缩短为14.9 d;CH4产量提高72.1% | [ |
| 铁基 | INPs | 1000 mg/L | <20 μm | 聚丙烯消化器—牛粪 | VS去除率提高109.3%;CH4产量提高77.24% | [ |
| 铁基 | 磁铁矿 | — | 0.2~0.5 mm | 厌氧消化器—废活性污泥 | 有机物的降解速率和VFAs的转化速率加快;CH4产量提高37.4% | [ |
| 铁基 | 针铁矿 | 0.2 g/L | 60~120 μm | 树脂玻璃器—烟草废弃物/剩余污泥 | 酸化代谢及有机物溶解加速;最高产气量提升至359.4 ml/g | [ |
| 碳基 | 活性炭 | 0.8 g/L | — | 血清瓶—食物垃圾 | 滞后期缩短67%;VFAs的降解加速;最大CH4产量提高50% | [ |
| 碳基 | GAC | 27 g/L | 8~12 mm | 血清瓶—废活性污泥 | VFAs平均总浓度下降9.8%;平均CH4产量提高13.1% | [ |
| 碳基 | 碳布 | — | — | 聚碳酸酯消化罐—固体废物 | 滞后期缩短15%;CH4产量提高20% | [ |
| 碳基 | PAC | 10 g/L | — | 消化罐—玉米秸秆 | 纤维素降解率提高6.48%;CH4产量提高17.92% | [ |
| 碳基 | 生物炭 | 8.0 g/L | 150 μm | 锥形瓶—食物垃圾/城市污泥 | 游离铵的积累得到缓解;平均日CH4产量提高46.2% | [ |
| 碳基 | 石墨 | — | 0.16 mm | 血清瓶—脱水污泥 | 促进水解酸化产物的消耗;产气量提高13.8% | [ |
| 碳基 | 石墨烯 | 50 mg/L | 0.5~5 μm | 广口玻璃瓶—食物垃圾/污泥 | 有机物降解率提高23.07%;CH4产量提高36.09% | [ |
| 碳基 | rGO | 20 mg/L | — | 半连续反应器—有机垃圾 | 在OLRs为2.0 gVS/L时,CH4产量提升46% | [ |
| 碳基 | CNTs | 6.5 g/L | 10~30 nm | 批量厌氧反应器—鸡粪 | VFAs的吸收加速;CH4最大产量提高15% | [ |
| 导电材料 | 投加量 | 实验体系 | 强化效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAC-NZVI | 1000 mg/L | 批式反应器—合成啤酒废水 | COD降解率提高9.38%;CH4产量提高14.29% | [ |
| ZVI+AC | 10 g/L | 批式反应器—餐厨垃圾 | 氨抑制得到缓解;CH4产量提高35.0% | [ |
| BC-ZVI | 0.4 g/g VS | 厌氧消化瓶—厨余垃圾 | 缓冲体系pH;促进丁酸向乙酸转化;延滞时间和总反应时间缩短 | [ |
| NZVI-BC | — | 血清瓶—餐厨垃圾 | 缩短滞后时间;加速丙酸降解;CH4产量提高49.87% | [ |
| nFe3O4-CNTs | 6.7 g/L | 批式厌氧反应器—鸡粪 | VFAs更有效地参与甲烷生成;CH4产量提高3.7% | [ |
| Fe0/GO | 1.2 g/L | UASB反应器—清洗废水 | COD去除率提高到91.8%;产气量提高至511 ml/12h | [ |
| RGO-NZVI | 900 mg/L | 硼硅玻璃瓶—乳品废水 | SCOD去除率提高;CH4含量提高至86.27%,COD去除率提高47.37% | [ |
| CTS-Fe | 10 g/L | 玻璃血清瓶—废活性污泥 | 蛋白质和多糖的降解加速;胞外水解酶活性提高 | [ |
| CF@ITO | 5.8 mg/L | 批式反应器—厌氧污泥 | COD去除率提高36.34%;CH4产量提高47.73% | [ |
| Fe3O4-rGO | 0.27 g/L | 厌氧反应器—葡萄糖 | 在高OLR下维持VFA浓度的稳定性;生物气体中CH4含量提高到60%~65% | [ |
| FNC | 2 g/L | 血清瓶—偶氮染料废水 | 胞外聚合物的含量和蛋白质比例保持稳定;厌氧颗粒污泥的稳定性增强 | [ |
| Fe3O4-膨润土 | 2 g/g VSS | 厌氧消化器—厨余垃圾 | Fe3O4-膨润土的添加使反应器中累积甲烷产量增加152% | [ |
| g-C3N4/PANI | 1 g/L | 厌氧消化瓶—厌氧污泥 | CH4产量和产生速率分别提高82%和96% | [ |
| TiO2-FNi | 2.82 g/L | 烧瓶—玉米秸秆 | 在11.4 mT的静态磁场下,CH4产量比对照组增加44.71% | [ |
| GAC-MnO2 | 1.5 g/g VSS | 血清瓶—淀粉废水 | COD去除效率提高77%;CH4产量提高36% | [ |
Table 2 Enhancing effect of iron-carbon composite conductive materials on the performance of high-solids anaerobic digestion
| 导电材料 | 投加量 | 实验体系 | 强化效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAC-NZVI | 1000 mg/L | 批式反应器—合成啤酒废水 | COD降解率提高9.38%;CH4产量提高14.29% | [ |
| ZVI+AC | 10 g/L | 批式反应器—餐厨垃圾 | 氨抑制得到缓解;CH4产量提高35.0% | [ |
| BC-ZVI | 0.4 g/g VS | 厌氧消化瓶—厨余垃圾 | 缓冲体系pH;促进丁酸向乙酸转化;延滞时间和总反应时间缩短 | [ |
| NZVI-BC | — | 血清瓶—餐厨垃圾 | 缩短滞后时间;加速丙酸降解;CH4产量提高49.87% | [ |
| nFe3O4-CNTs | 6.7 g/L | 批式厌氧反应器—鸡粪 | VFAs更有效地参与甲烷生成;CH4产量提高3.7% | [ |
| Fe0/GO | 1.2 g/L | UASB反应器—清洗废水 | COD去除率提高到91.8%;产气量提高至511 ml/12h | [ |
| RGO-NZVI | 900 mg/L | 硼硅玻璃瓶—乳品废水 | SCOD去除率提高;CH4含量提高至86.27%,COD去除率提高47.37% | [ |
| CTS-Fe | 10 g/L | 玻璃血清瓶—废活性污泥 | 蛋白质和多糖的降解加速;胞外水解酶活性提高 | [ |
| CF@ITO | 5.8 mg/L | 批式反应器—厌氧污泥 | COD去除率提高36.34%;CH4产量提高47.73% | [ |
| Fe3O4-rGO | 0.27 g/L | 厌氧反应器—葡萄糖 | 在高OLR下维持VFA浓度的稳定性;生物气体中CH4含量提高到60%~65% | [ |
| FNC | 2 g/L | 血清瓶—偶氮染料废水 | 胞外聚合物的含量和蛋白质比例保持稳定;厌氧颗粒污泥的稳定性增强 | [ |
| Fe3O4-膨润土 | 2 g/g VSS | 厌氧消化器—厨余垃圾 | Fe3O4-膨润土的添加使反应器中累积甲烷产量增加152% | [ |
| g-C3N4/PANI | 1 g/L | 厌氧消化瓶—厌氧污泥 | CH4产量和产生速率分别提高82%和96% | [ |
| TiO2-FNi | 2.82 g/L | 烧瓶—玉米秸秆 | 在11.4 mT的静态磁场下,CH4产量比对照组增加44.71% | [ |
| GAC-MnO2 | 1.5 g/g VSS | 血清瓶—淀粉废水 | COD去除效率提高77%;CH4产量提高36% | [ |
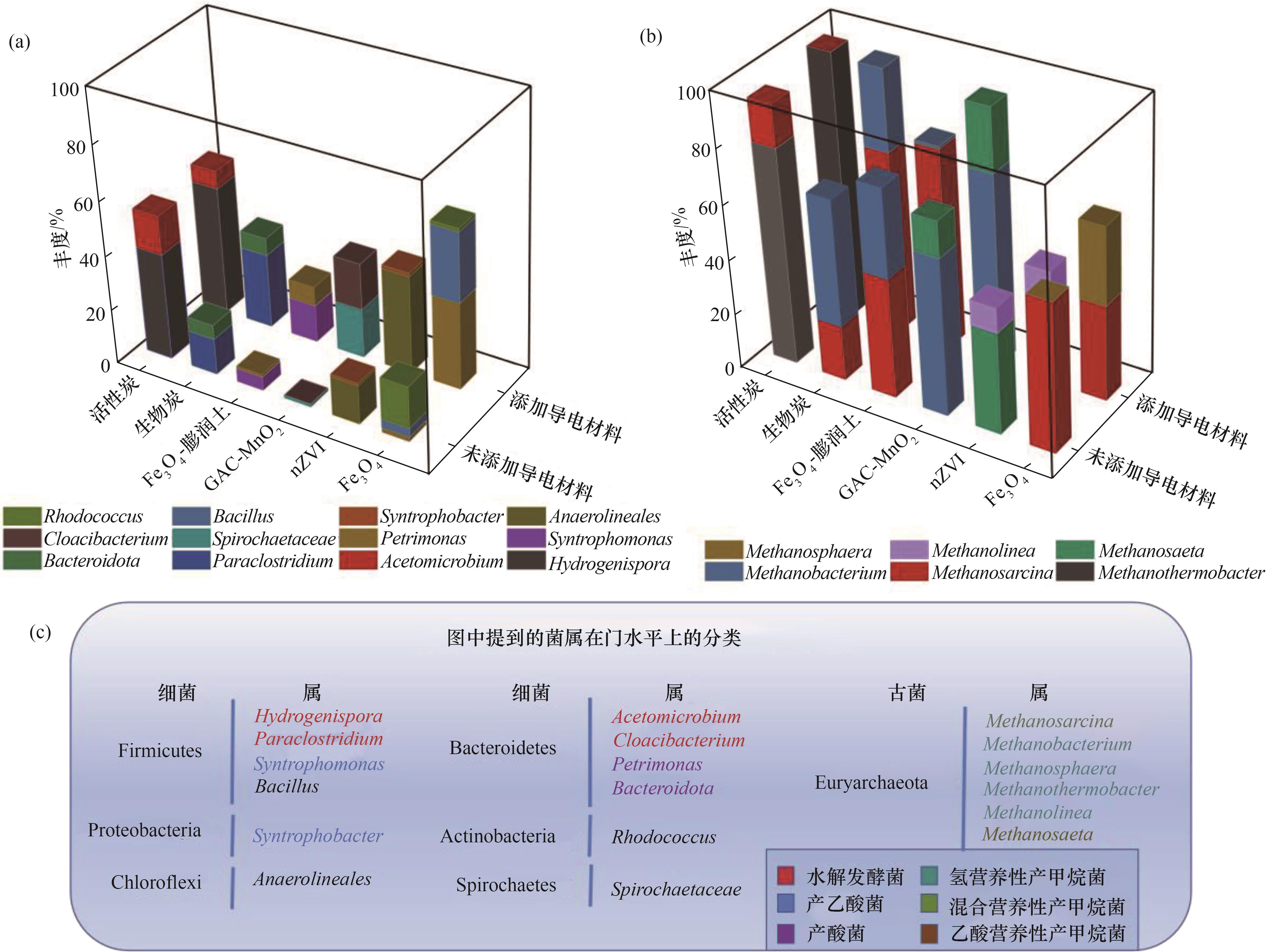
Fig.2 Dynamics of microbial community structure mediated by conductive materials[18,59,62,73-75]: (a) Changes in functional bacterial abundance; (b) Changes in methanogenic archaeal abundance; (c) Systematics at phylum level for key bacterial genera
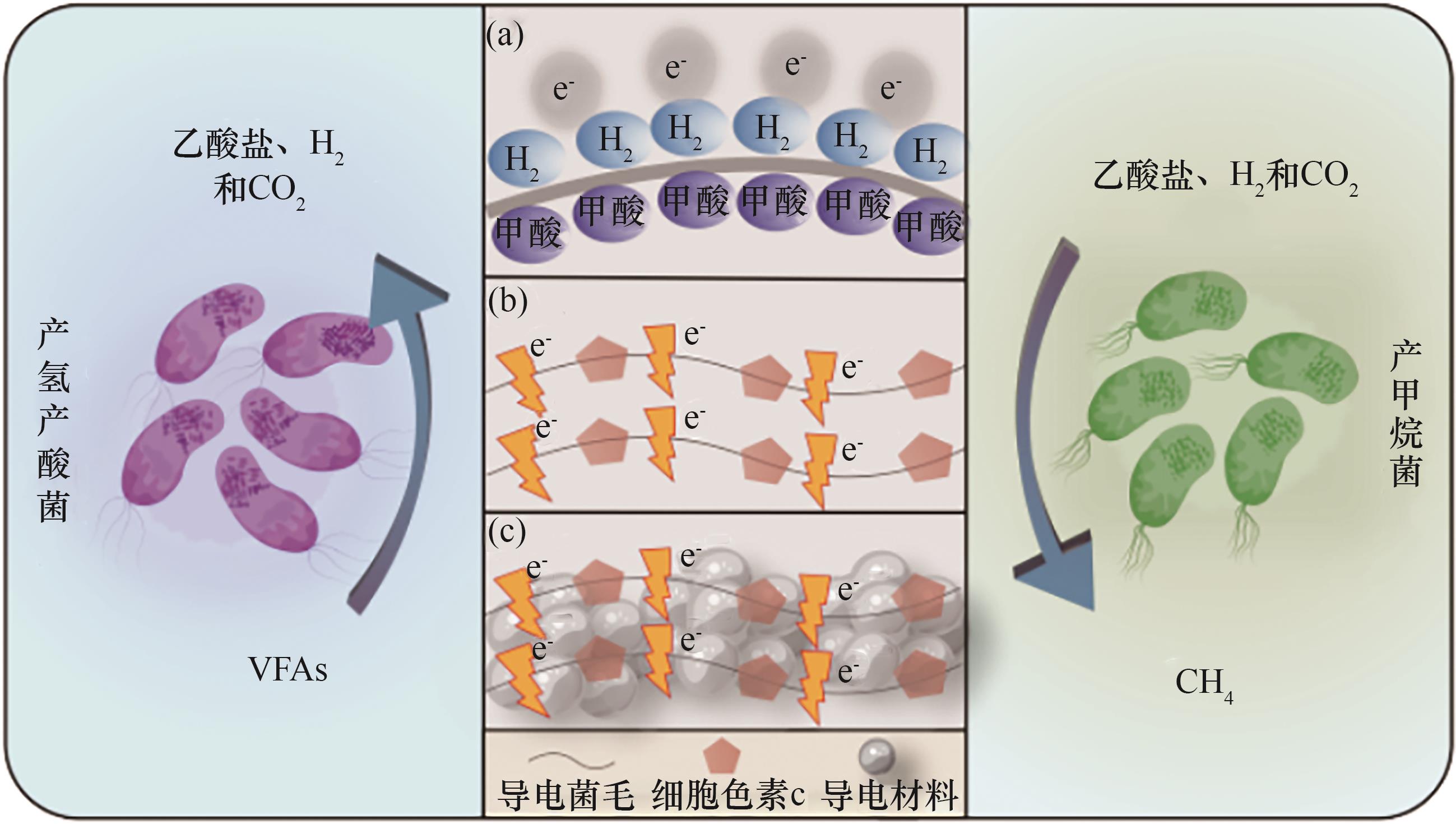
Fig.3 Mechanism shifts in interspecies electron transfer: (a) Interspecies electron transfer mediated by hydrogen/formate carriers; (b) DIET mediated by biological conductive structures (pili/cytochromes); (c) DIET mediated by conductive materials
| 特征类别 | 特征参数 | 重要性排名 | 影响机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 材料本征物性 | 比表面积 | 1 | 促进底物吸附与微生物定殖,提供反应界面 | [ |
| 电导率 | 2 | 直接决定DIET效率,是强化电子传递的核心物性 | [ | |
| 官能团分布 | 3 | 微生物-材料界面电子传递调控,影响表面反应活性和抑制物吸附 | [ | |
| pH缓冲能力 | 4 | 缓解VFAs积累导致的酸化,维持适宜产甲烷环境 | — | |
| 电容特征 | 5 | 在特定条件(低固体系)下依赖高电容材料存储和释放电子 | [ | |
| 工艺参数 | 投加量 | 1 | 存在阈值效应,过量添加易引发团聚、抑制或占据活性位点,抑制活性 | [ |
| 粒径 | 2 | 协同比表面积调控反应效率,较小粒径通常具有更优效果 | [ |
Table 3 Importance ranking and mechanism of machine learning features for HS-AD enhanced by conductive materials
| 特征类别 | 特征参数 | 重要性排名 | 影响机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 材料本征物性 | 比表面积 | 1 | 促进底物吸附与微生物定殖,提供反应界面 | [ |
| 电导率 | 2 | 直接决定DIET效率,是强化电子传递的核心物性 | [ | |
| 官能团分布 | 3 | 微生物-材料界面电子传递调控,影响表面反应活性和抑制物吸附 | [ | |
| pH缓冲能力 | 4 | 缓解VFAs积累导致的酸化,维持适宜产甲烷环境 | — | |
| 电容特征 | 5 | 在特定条件(低固体系)下依赖高电容材料存储和释放电子 | [ | |
| 工艺参数 | 投加量 | 1 | 存在阈值效应,过量添加易引发团聚、抑制或占据活性位点,抑制活性 | [ |
| 粒径 | 2 | 协同比表面积调控反应效率,较小粒径通常具有更优效果 | [ |
| [1] | 周继豪, 沈小东, 张平, 等. 基于好氧堆肥的有机固体废物资源化研究进展[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2017, 34(2): 13-18. |
| Zhou J H, Shen X D, Zhang P, et al. Research progress on recycling of organic solid wastes based on aerobic compost[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2017, 34(2): 13-18. | |
| [2] | 李宵宵, 吴丽杰, 任瑞鹏, 等. 高含固污泥厌氧消化处理技术研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2020, 40(8): 21-25. |
| Li X X, Wu L J, Ren R P, et al. Research progress on anaerobic digestion treatment technology for high-solid sludge[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2020, 40(8): 21-25. | |
| [3] | Wang Y Y, Li G X, Chi M H, et al. Effects of co-digestion of cucumber residues to corn stover and pig manure ratio on methane production in solid state anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 250: 328-336. |
| [4] | Li W L, Gupta R, Zhang Z K, et al. A review of high-solid anaerobic digestion (HSAD): from transport phenomena to process design[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 180: 113305. |
| [5] | Dang Y, Holmes D E, Zhao Z Q, et al. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of complex organic waste with carbon-based conductive materials[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 220: 516-522. |
| [6] | Nabi M, Liang H, Cheng L, et al. A comprehensive review on the use of conductive materials to improve anaerobic digestion: focusing on landfill leachate treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 309: 114540. |
| [7] | 吕龙义, 韩沐达, 马培禹, 等. 强化废水厌氧消化过程的导电材料及其特性影响[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(12): 6957-6967. |
| Lyu L Y, Han M D, Ma P Y, et al. Conductive materials for enhanced anaerobic digestion of wastewater and influence of their properties[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(12): 6957-6967. | |
| [8] | Feng L K, Gao Z L, Hu T Y, et al. A review of application of combined biochar and iron-based materials in anaerobic digestion for enhancing biogas productivity: mechanisms, approaches and performance[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 234: 116589. |
| [9] | Meng X S, Sui Q W, Liu J B, et al. Relieving ammonia inhibition by zero-valent iron (ZVI) dosing to enhance methanogenesis in the high solid anaerobic digestion of swine manure[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 118: 452-462. |
| [10] | Wang P L, Li X N, Li Y, et al. Enhanced anaerobic digestion performance of food waste by zero-valent iron and iron oxides nanoparticles: comparative analyses of microbial community and metabolism[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 371: 128633. |
| [11] | Li W Q, Chen J L, Pang L N, et al. Dosage effect of micron zero-valent iron during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: performance and functional community[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 237: 116997. |
| [12] | 经雪, 程洁红, 孔峰, 等. 外加铁对城市污泥厌氧消化产甲烷的作用[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(2): 125-130. |
| Jing X, Cheng J H, Kong F, et al. Effect of added iron on anaerobic digestion process of municipal sludge in methane production[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(2): 125-130. | |
| [13] | Wang Y Z, Ren G X, Zhang T, et al. Effect of magnetite powder on anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and wheat straw[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 66: 46-52. |
| [14] | Farghali M, Andriamanohiarisoamanana F J, Ahmed M M, et al. Prospects for biogas production and H2S control from the anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: the influence of microscale waste iron powder and iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 101: 141-149. |
| [15] | Jin H Y, Yao X Y, Tang C C, et al. Magnetite modified zeolite as an alternative additive to promote methane production from anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. Renewable Energy, 2024, 224: 120181. |
| [16] | 李小兰, 周芸, 陈志燕, 等. 针铁矿强化剩余污泥与烟草废弃物厌氧发酵的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(6): 2475-2482. |
| Li X L, Zhou Y, Chen Z Y, et al. Enhanced anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge and tobacco waste using Goethite[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(6): 2475-2482. | |
| [17] | Ko J H, Wang N, Yuan T G, et al. Effect of nickel-containing activated carbon on food waste anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 266: 516-523. |
| [18] | Peng H, Zhang Y B, Tan D M, et al. Roles of magnetite and granular activated carbon in improvement of anaerobic sludge digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 666-672. |
| [19] | de Albuquerque F P, Dastyar W, Mirsoleimani Azizi S M, et al. Carbon cloth amendment for boosting high-solids anaerobic digestion with percolate recirculation: spatial patterns of microbial communities[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135606. |
| [20] | Xie Z J, Cao Q, Chen Y C, et al. The biological and abiotic effects of powdered activated carbon on the anaerobic digestion performance of cornstalk[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 343: 126072. |
| [21] | Liu H B, Wang X K, Fang Y Y, et al. Enhancing thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste with biogas residue biochar[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 188: 465-475. |
| [22] | Wu F, Xie J Q, Xin X D, et al. Effect of activated carbon/graphite on enhancing anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 999647. |
| [23] | Wang P, Zheng Y, Lin P R, et al. Effects of graphite, graphene, and graphene oxide on the anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste: attention to methane production and the fate of antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 339: 125585. |
| [24] | Muratçobanoğlu H, Begüm Gökçek Ö, Muratçobanoğlu F, et al. Biomethane enhancement using reduced graphene oxide in anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 354: 127163. |
| [25] | Ziganshina E E, Bulynina S S, Ziganshin A M. Anaerobic digestion of chicken manure assisted by carbon nanotubes: promotion of volatile fatty acids consumption and methane production[J]. Fermentation, 2022, 8(11): 641-651. |
| [26] | Wu Y, Wang S, Liang D H, et al. Conductive materials in anaerobic digestion: from mechanism to application[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 298: 122403. |
| [27] | Yang Z M, Guo R B, Shi X S, et al. Magnetite nanoparticles enable a rapid conversion of volatile fatty acids to methane[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(31): 25662-25668. |
| [28] | Wang Y Y, Wang D L, Fang H Y. Comparison of enhancement of anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge through adding nano-zero valent iron and zero valent iron[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(48): 27181-27190. |
| [29] | Kong X, Wei Y H, Xu S, et al. Inhibiting excessive acidification using zero-valent iron in anaerobic digestion of food waste at high organic load rates[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 211: 65-71. |
| [30] | Velimirovic M, Carniato L, Simons Q, et al. Corrosion rate estimations of microscale zerovalent iron particles via direct hydrogen production measurements[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 270: 18-26. |
| [31] | Zheng Y, Quan X C, Zhuo M H, et al. In-situ formation and self-immobilization of biogenic Fe oxides in anaerobic granular sludge for enhanced performance of acidogenesis and methanogenesis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 787: 147400. |
| [32] | Fu L, Zhou T, Wang J Y, et al. NanoFe3O4 as solid electron shuttles to accelerate acetotrophic methanogenesis by Methanosarcina barkeri [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 388. |
| [33] | 高雪濛, 周丽丽, 秦杰, 等. 氧化铁投加方式对餐厨垃圾厌氧消化产气的影响[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(4): 101-105. |
| Gao X M, Zhou L L, Qin J, et al. Effect of iron dioxide addition modes on methane generation in food waste anaerobic digestion[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(4): 101-105. | |
| [34] | Lü C X, Shen Y W, Li C, et al. Redox-active biochar and conductive graphite stimulate methanogenic metabolism in anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge: beyond direct interspecies electron transfer[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(33): 12626-12636. |
| [35] | Zhang M, Li J H, Wang Y C, et al. Impacts of different biochar types on the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(72): 42375-42386. |
| [36] | Ambaye T G, Rene E R, Dupont C, et al. Anaerobic digestion of fruit waste mixed with sewage sludge digestate biochar: influence on biomethane production[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2020, 8: 31. |
| [37] | 张福贵, 叶东旭, 刘鹏程, 等. 不同碳氮比对中温和高温厌氧消化的影响研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2020, 45(7): 108-114. |
| Zhang F G, Ye D X, Liu P C, et al. Effect of different carbon nitrogen ratio on medium and high temperature anaerobic digestion[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2020, 45(7): 108-114. | |
| [38] | Wang S Y, Ai S Y, Nzediegwu C, et al. Carboxyl and hydroxyl groups enhance ammonium adsorption capacity of iron (Ⅲ) chloride and hydrochloric acid modified biochars[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 309: 123390. |
| [39] | 王彦朝, 吴瑒, 刘一苇, 等. 碳基导电材料促进有机固废厌氧消化产甲烷的研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(9): 146-155. |
| Wang Y Z, Wu Y, Liu Y W, et al. Research progress of carbon-based conductive materials to promote methane production from anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(9): 146-155. | |
| [40] | Zhang L, Zhang J X, Loh K C. Activated carbon enhanced anaerobic digestion of food waste—laboratory-scale and pilot-scale operation[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 75: 270-279. |
| [41] | 罗景阳, 邵钱祺, 王凤, 等. 碳基材料对有机废弃物厌氧消化的影响及作用机制研究进展[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(12): 1701-1709. |
| Luo J Y, Shao Q Q, Wang F, et al. Research progress on effects of carbonaceous materials on anaerobic digestion of organic wastes and underlying mechanisms[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2021, 49(12): 1701-1709. | |
| [42] | Yan W W, Zhang L, Wijaya S M, et al. Unveiling the role of activated carbon on hydrolysis process in anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 296: 122366. |
| [43] | Florentino A P, Xu R, Zhang L, et al. Anaerobic digestion of blackwater assisted by granular activated carbon: from digestion inhibition to methanogenesis enhancement[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 233: 462-471. |
| [44] | Jeyakumar R B, Vincent G S. Recent advances and perspectives of nanotechnology in anaerobic digestion: a new paradigm towards sludge biodegradability[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(12): 7191. |
| [45] | Hao Y, Wang Y Y, Ma C X, et al. Carbon nanomaterials induce residue degradation and increase methane production from livestock manure in an anaerobic digestion system[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 240: 118257. |
| [46] | François M, Lin K S, Rachmadona N, et al. Utilization of carbon-based nanomaterials for wastewater treatment and biogas enhancement: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Chemosphere, 2024, 350: 141008. |
| [47] | Zhang J Y, Wang Z Y, Wang Y W, et al. Effects of graphene oxide on the performance, microbial community dynamics and antibiotic resistance genes reduction during anaerobic digestion of swine manure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 850-859. |
| [48] | Sun M C, Zhang Z H, Liu G H, et al. Enhancing methane production of synthetic brewery water with granular activated carbon modified with nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) in anaerobic system[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 760: 143933. |
| [49] | Zhang S, Ma X X, Xie D, et al. Adding activated carbon to the system with added zero-valent iron further improves anaerobic digestion performance by alleviating ammonia inhibition and promoting DIET[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106616. |
| [50] | 赵光琪, 刘建国, 孔鑫, 等. 碳热还原铁基生物炭材料(BC-ZVI)对厨余垃圾厌氧消化的影响研究[J]. 环境卫生工程, 2022, 30(3): 1-7. |
| Zhao G Q, Liu J G, Kong X, et al. Effect of zero-valent iron laden biochar obtained from carbothermal reduction on anaerobic digestion of food waste[J]. Environmental Sanitation Engineering, 2022, 30(3): 1-7. | |
| [51] | Zhang M, Wang Y C. Impact of biochar supported nano zero-valent iron on anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste: methane production, performance stability and microbial community structure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 340: 125715. |
| [52] | Ziganshina E E, Ziganshin A M. Magnetite nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes for improving the operation of mesophilic anaerobic digesters[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(4): 938. |
| [53] | Lan H X, Ji L Y, Li K, et al. Mediated anaerobic system performance, co-metabolizing flora and electron transfer by graphene oxide supported zero-valent iron composite[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(2): 109631. |
| [54] | Sasidharan R, Kumar A, Paramasivan B, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-nano zerovalent iron assisted anaerobic digestion of dairy wastewater: a potential strategy for CH4 enrichment[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 110035. |
| [55] | Zhang B, Zhao Z W, Ma R, et al. Unveiling the mechanisms of Fe(Ⅲ)-loaded chitosan composite (CTS-Fe) in enhancing anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 138: 200-211. |
| [56] | Wang Z W, Wei C H, Yu H R, et al. Preparation and mechanism of carbon felt supported iron trioxide and zero-valent iron for enhancing anaerobic digestion performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 468: 143565. |
| [57] | Barrena R, del Carmen Vargas-García M, Catacora-Padilla P, et al. Magnetite-based nanoparticles and nanocomposites for recovery of overloaded anaerobic digesters[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 372: 128632. |
| [58] | Lv L Y, Yin B B, Zhang D Y, et al. Synchronous reinforcement azo dyes decolorization and anaerobic granular sludge stability by Fe, N co-modified biochar: enhancement based on extracellular electron transfer[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 480: 135836. |
| [59] | Zhu R L, Chen Y D, Huang Y R, et al. Improving anaerobic digestion performance after severe acidification: unveiling the impacts of Fe3O4-bentonite composites in co-digestion of waste activated sludge and food waste[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 402: 130775. |
| [60] | Lu Q L, Li X Y, Rene E R, et al. Heterogeneous g-C3N4/polyaniline composites enhanced the conversion of organics into methane during anaerobic wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 258: 119480. |
| [61] | Zhao B, Zheng P F, Yang Y Y, et al. Enhanced anaerobic digestion under medium temperature conditions: augmentation effect of magnetic field and composites formed by titanium dioxide on the foamed nickel[J]. Energy, 2022, 257: 124791. |
| [62] | Yang B, Xu H, Liu Y B, et al. Role of GAC-MnO2 catalyst for triggering the extracellular electron transfer and boosting CH4 production in syntrophic methanogenesis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383: 123211. |
| [63] | 黄雯雯. 纳米零价铁型生物炭介导猪场废水厌氧消化特性及机理研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2022. |
| Huang W W. Characteristics and mechanism of anaerobic digestion of pig wastewater mediated by zero-valent iron biochar[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2022. | |
| [64] | Li P F, Wang Q, He X M, et al. Investigation on the effect of different additives on anaerobic co-digestion of corn straw and sewage sludge: comparison of biochar, Fe3O4, and magnetic biochar[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 345: 126532. |
| [65] | Lim E Y, Lee J T E, Zhang L, et al. Abrogating the inhibitory effects of volatile fatty acids and ammonia in overloaded food waste anaerobic digesters via the supplementation of nano-zero valent iron modified biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152968. |
| [66] | Zhang M, Li J H, Wang Y C. Impact of biochar-supported zerovalent iron nanocomposite on the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(10): 10292-10305. |
| [67] | Liu H Y, Xu Y, Li L, et al. A review on application of single and composite conductive additives for anaerobic digestion: advances, challenges and prospects[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 174: 105844. |
| [68] | Wang M W, Zhao Z Q, Zhang Y B. Magnetite-contained biochar derived from Fenton sludge modulated electron transfer of microorganisms in anaerobic digestion[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123972. |
| [69] | Liang J L, Luo L W, Li D Y, et al. Promoting anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste with different types of conductive materials: performance, stability, and underlying mechanism[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125384. |
| [70] | Shakoor M B, Ye Z L, Chen S H. Engineered biochars for recovering phosphate and ammonium from wastewater: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 779: 146240. |
| [71] | Duan X, Chen Y Z, Yan Y Y, et al. New method for algae comprehensive utilization: algae-derived biochar enhances algae anaerobic fermentation for short-chain fatty acids production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121637. |
| [72] | Li X J, Qin R H, Yang W J, et al. Effect of asparagine, corncob biochar and Fe(Ⅱ) on anaerobic biological treatment under low temperature: enhanced performance and microbial community dynamic[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 317: 115348. |
| [73] | Jin H Y, Ren Y X, Tang C C, et al. Biomethane production enhancement from waste activated sludge with recycled magnetic biochar: insights into the recycled strategies and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 434: 139835. |
| [74] | Wang R N, Abdullah Al-Dhabi N, Jiang Y F, et al. Effect of nano zero-valent iron on the anaerobic digestion of food waste: performance and mechanism[J]. Fuel, 2024, 366: 131342. |
| [75] | Yang Y F, Cheng X, Rene E R, et al. Effect of iron sources on methane production and phosphorous transformation in an anaerobic digestion system of waste activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 395: 130315. |
| [76] | Liang J L, Luo L W, Wong J W C, et al. Recent advances in conductive materials amended anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and municipal organic solid waste: roles, mechanisms, and potential application[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 360: 127613. |
| [77] | Gao M X, Du P F, Zhi B Y, et al. Magnetic biochar affects the metabolic pathway in methanogenesis of anaerobic digestion of food waste[J]. GCB Bioenergy, 2022, 14(5): 572-584. |
| [78] | Wang G J, Li Q, Li Y, et al. Redox-active biochar facilitates potential electron tranfer between syntrophic partners to enhance anaerobic digestion under high organic loading rate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 298: 122524. |
| [79] | Baek G, Kim J, Lee C. A review of the effects of iron compounds on methanogenesis in anaerobic environments[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 113: 109282. |
| [80] | Gahlot P, Ahmed B, Tiwari S B, et al. Conductive material engineered direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) in anaerobic digestion: mechanism and application[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 20: 101056. |
| [81] | Wu L J, Jin T, Chen H, et al. Conductive materials as fantastic toolkits to stimulate direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic digestion: new insights into methanogenesis contribution, characterization technology, and downstream treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 326: 116732. |
| [82] | 张万里, 刘平, 王志康, 等. 碳材料增强微生物种间电子传递强化餐厨垃圾厌氧消化产甲烷研究综述[J]. 可再生能源, 2023, 41(5): 586-596. |
| Zhang W L, Liu P, Wang Z K, et al. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of food waste by carbon materials via mediating microorganisms interspecific electron transport[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2023, 41(5): 586-596. | |
| [83] | Yin Q D, Wu G X. Advances in direct interspecies electron transfer and conductive materials: electron flux, organic degradation and microbial interaction[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(8): 107443. |
| [84] | Zhuo M H, Quan X C, Yin R Y, et al. Enhancing methane production and interspecies electron transfer of anaerobic granular sludge by the immobilization of magnetic biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 2024, 352: 141332. |
| [85] | Park J H, Park J H, Seong H J, et al. Metagenomic insight into methanogenic reactors promoting direct interspecies electron transfer via granular activated carbon[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 259: 414-422. |
| [86] | 安彤, 吴宗林, 庞悦, 等. 导电材料强化挥发性脂肪酸互营氧化产甲烷菌群的种间直接电子传递研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021, 27(3): 800-807. |
| An T, Wu Z L, Pang Y, et al. Direct interspecies electron transfer strengthened by conductive materials between syntrophic methanogenic communities of volatile fatty acids[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2021, 27(3): 800-807. | |
| [87] | 于亚梅, 沈雁文, 朱南文, 等. 生物炭和石墨的电化学性质对剩余污泥厌氧消化产甲烷的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 807-820. |
| Yu Y M, Shen Y W, Zhu N W, et al. Effect of electrochemical properties of biochar and graphite on methane production in anaerobic digestion of excess activated sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(3): 807-820. | |
| [88] | Liu L, Yun S N, Ke T, et al. Dual utilization of aloe peel: aloe peel-derived carbon quantum dots enhanced anaerobic co-digestion of aloe peel[J]. Waste Management, 2023, 159: 163-173. |
| [89] | 吕龙义, 靳梦婷, 魏子茵, 等. 铁基材料强化市政污泥厌氧消化效能及机制的研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(11): 6713-6722. |
| Lyu L Y, Jin M T, Wei Z Y, et al. Research progress on the efficiency and mechanism of iron-based materials for enhancing anaerobic digestion of municipal sludge[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(11): 6713-6722. | |
| [90] | Liu F H, Rotaru A E, Shrestha P M, et al. Magnetite compensates for the lack of a pilin-associated c-type cytochrome in extracellular electron exchange[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(3): 648-655. |
| [91] | Wang J, Zhong C, Zhang X, et al. Quantitative analysis of acetate oxidation in the presence of iron in a thermophilic methanogenic reactor[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 149: 928-932. |
| [92] | Zhu Y H, Zhao Z Q, Yang Y F, et al. Dual roles of zero-valent iron in dry anaerobic digestion: enhancing interspecies hydrogen transfer and direct interspecies electron transfer[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 118: 481-490. |
| [93] | Wang D X, Han Y X, Han H J, et al. New insights into enhanced anaerobic degradation of Fischer-Tropsch wastewater with the assistance of magnetite[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 257: 147-156. |
| [94] | Liu H Y, Xu Y, Li L, et al. A novel green composite conductive material enhancing anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge via improving electron transfer and metabolic activity[J]. Water Research, 2022, 220: 118687. |
| [95] | Song Y F, Zhang Z H, Liu Y B, et al. Enhancement of anaerobic treatment of antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater through the development of iron-based and carbon-based materials: a critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 479: 135514. |
| [96] | Gao Z H, Cui T Y, Qian H, et al. Can wood waste be a feedstock for anaerobic digestion? A machine learning assisted meta-analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 487: 150496. |
| [97] | Xu W C, Long F, Zhao H, et al. Performance prediction of ZVI-based anaerobic digestion reactor using machine learning algorithms[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 121: 59-66. |
| [98] | Gupta R, Zhang L, Hou J Y, et al. Review of explainable machine learning for anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 369: 128468. |
| [99] | Wang Y, Huntington T, Scown C D. Tree-based automated machine learning to predict biogas production for anaerobic co-digestion of organic waste[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(38): 12990-13000. |
| [100] | Andrade Cruz I, Chuenchart W, Long F, et al. Application of machine learning in anaerobic digestion: perspectives and challenges[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 345: 126433. |
| [101] | Wang L G, Long F, Liao W, et al. Prediction of anaerobic digestion performance and identification of critical operational parameters using machine learning algorithms[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 298: 122495. |
| [102] | Yildirim O, Ozkaya B. Prediction of biogas production of industrial scale anaerobic digestion plant by machine learning algorithms[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 335: 138976. |
| [103] | Zhang Y, Yang X R, Feng Y J, et al. Accelerating integrated prediction, analysis and targeted optimization for anaerobic digestion of biomass after hydrothermal pretreatment using automated machine learning[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 202: 114688. |
| [104] | Zhang Y, Feng Y J, Ren Z H, et al. Tree-based machine learning model for visualizing complex relationships between biochar properties and anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 374: 128746. |
| [105] | Khashaba N H, Ettouney R S, Abdelaal M M, et al. Artificial neural network modeling of biochar enhanced anaerobic sewage sludge digestion[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(4): 107988. |
| [106] | Deng Y, Zhang Y F, Zhao Z Q. A data-driven approach for revealing the linkages between differences in electrochemical properties of biochar during anaerobic digestion using automated machine learning[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 927: 172291. |
| [107] | He X M, Guo J Y, Kang X H, et al. Facilitating renewable natural gas production for a circular bioeconomy: AI-driven process visualization and data augmentation on biochar-mediated anaerobic digestion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 516: 164179. |
| [108] | Long F, Wang L G, Cai W F, et al. Predicting the performance of anaerobic digestion using machine learning algorithms and genomic data[J]. Water Research, 2021, 199: 117182. |
| [109] | Pei Z J, Liu S J, Jing Z M, et al. Understanding of the interrelationship between methane production and microorganisms in high-solid anaerobic co-digestion using microbial analysis and machine learning[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 373: 133848. |
| [110] | Adeleke A A, Okolie J A, Ogbaga C C, et al. Machine learning model for the evaluation of biomethane potential based on the biochemical composition of biomass[J]. BioEnergy Research, 2024, 17(1): 731-743. |
| [1] | Zheng GAO, Hui WANG, Zhiguo QU. Data-driven high-throughput screening of anion-pillared metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272. |
| [2] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [3] | Zhihong CHEN, Jiawei WU, Xiaoling LOU, Junxian YUN. Recent advances in machine learning for biomanufacturing of chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [4] | Jialang HU, Mingyuan JIANG, Lyuming JIN, Yonggang ZHANG, Peng HU, Hongbing JI. Machine learning-assisted high-throughput computational screening of MOFs and advances in gas separation research [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1973-1996. |
| [5] | Yinjie ZHOU, Sibei JI, Songyang HE, Xu JI, Ge HE. Machine learning-assisted high-throughput screening approach for CO2 separation from CO2-rich natural gas using metal-organic frameworks [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1093-1101. |
| [6] | Yaqi HOU, Wei ZHANG, Hong ZHANG, Feiyu GAO, Jiahua HU. Optimization of LBM multiphase flow models based on machine learning and particle swarm algorithm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1120-1132. |
| [7] | Haijun FENG, Bingxuan ZHANG, Jian ZHOU. Predicting and interpreting the toxicity of ionic liquids using graph neural network [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 93-106. |
| [8] | Yiru WEN, Jia FU, Dahuan LIU. Advances in machine learning-based materials research for MOFs: energy gas adsorption separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1370-1381. |
| [9] | Dongfei LIU, Fan ZHANG, Zheng LIU, Diannan LU. A review of machine learning potentials and their applications to molecular simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1241-1255. |
| [10] | Yuxiang CHEN, Chuanlei LIU, Zijun GONG, Qiyue ZHAO, Guanchu GUO, Hao JIANG, Hui SUN, Benxian SHEN. Machine learning-assisted solvent molecule design for efficient absorption of ethanethiol [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 914-923. |
| [11] | Yujiao ZENG, Xin XIAO, Gang YANG, Yibo ZHANG, Guangming ZHENG, Fang LI, Fengling WANG. Surrogate modeling and optimization of wet phosphoric acid production process based on mechanism and data hybrid driven [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 936-944. |
| [12] | Gen LIU, Zhongshun SUN, Bo ZHANG, Rongjiang ZHANG, Zhiqiang WU, Bolun YANG. Establishment of machine learning-driven biomass pyrolysis model and optimization of volatiles chemical looping reforming hydrogen production process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4333-4347. |
| [13] | Yewei DING, Wenbo KANG, Yutong SONG, Qinxi FAN, Yuanhui JI. Mechanism and screening of indomethacin self-assembled nanomedical drugs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4141-4151. |
| [14] | Maoxian WANG, Qidian SUN, Zhe FU, Fang HUA, Ye JI, Yi CHENG. Understanding pyrolysis process of polyethylene by combined method of molecular-level kinetic model with machine learning [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4320-4332. |
| [15] | Jian RUAN, Shuang LI, Zhenghui WEN. Application of automation and artificial intelligence in flow chemistry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4120-4140. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||