化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (8): 3830-3838.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20191568
收稿日期:2019-12-23
修回日期:2020-04-29
出版日期:2020-08-05
发布日期:2020-08-05
通讯作者:
邢杨
作者简介:狄玲(1984—),女,博士,讲师,基金资助:
Ling DI( ),Fang CHEN,Rongrong FU,Chen YANG,Yang XING(
),Fang CHEN,Rongrong FU,Chen YANG,Yang XING( ),Xiaoning WANG
),Xiaoning WANG
Received:2019-12-23
Revised:2020-04-29
Online:2020-08-05
Published:2020-08-05
Contact:
Yang XING
摘要:
利用1例蓝色荧光的富电子金属有机骨架LMOF-a实现对有机农药百菌清、除草醚、氟乐灵及2,6-二氯-4-硝基苯胺快速、高效的发光检测。光谱分析及密度泛函理论计算表明,LMOF-a对除草醚的检测机理为电荷转移机理,而对百菌清、氟乐灵及2,6-二氯-4-硝基苯胺的检测机理同时包含电荷转移机理及荧光共振能量转移机理。经Stern-Volmer方程拟合检测数据,LMOF-a对2,6-二氯-4-硝基苯胺具有最高的检测效率,KSV值达(4.778±0.590) L/mmol,检测限低至0.014 mmol/L。研究为开发快速、高效的有机农药检测技术提供理论参考及技术支持。
中图分类号:
狄玲, 陈放, 付荣荣, 杨辰, 邢杨, 王晓宁. 富电子LMOF对有机农药的检测机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3830-3838.
Ling DI, Fang CHEN, Rongrong FU, Chen YANG, Yang XING, Xiaoning WANG. Mechanism research of organic pesticides detection by rich electronic LMOF[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3830-3838.

图1 有机配体的结构(a); LMOF-a的扫描电镜图(b);LMOF-a中双核Zn(Ⅱ)(c)、有机配体(d)的配位环境;LMOF-a的拓扑结构(e)
Fig.1 Structure of organic ligand(a); SEM image of LMOF-a(b); the coordination environments of binuclear Zn(Ⅱ) center(c) and the organic ligand(d) in LMOF-a; topological structure of LMOF-a(e)

图2 LMOF-a的理论及实测PXRD谱图(a); 有机配体及LMOF-a的红外光谱(b)
Fig. 2 Theoretical and experimental PXRD spectra of LMOF-a(a); FT-IR spectra of organic ligand and LMOF-a(b)
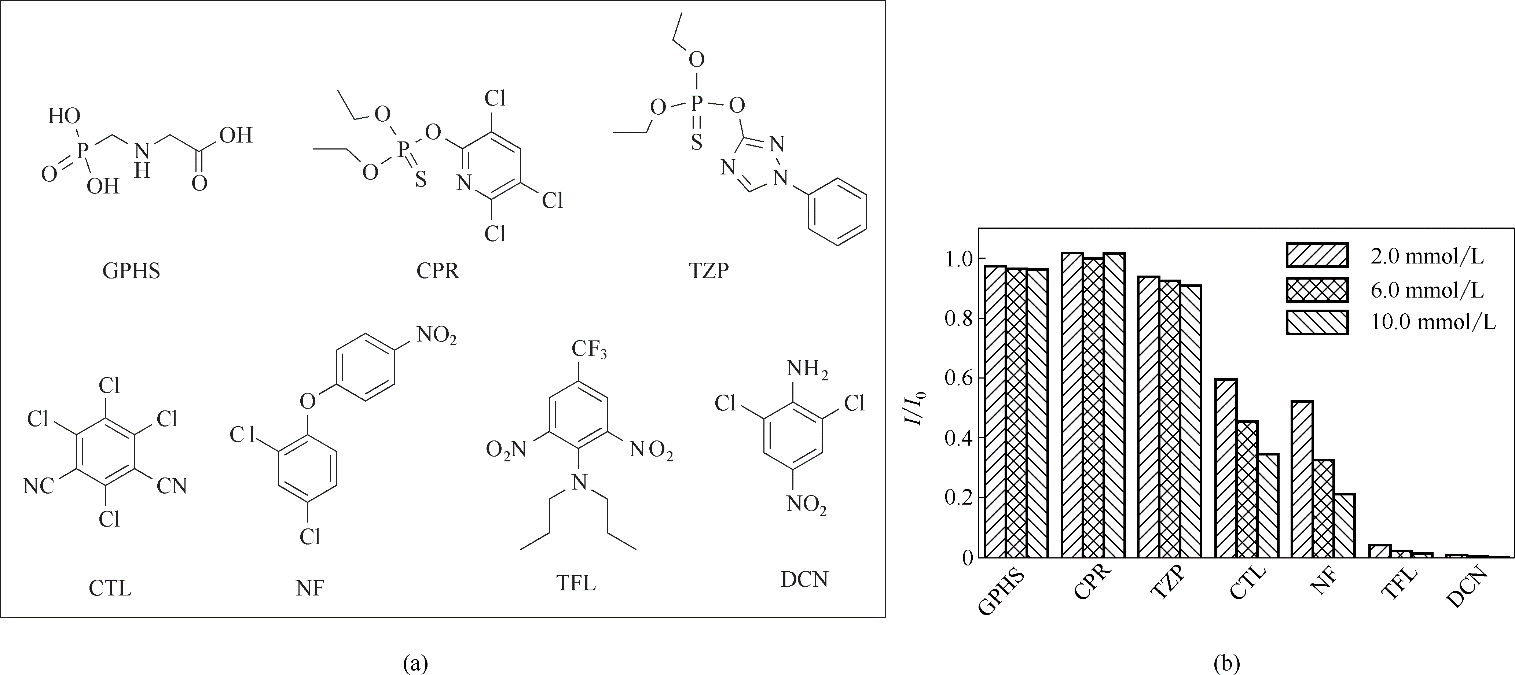
图3 有机农药GPHS、CPR、TZP、CTL、NF、TFL及DCN的结构(a); 2.0、6.0及10.0 mmol/L加入浓度下LMOF-a对7种有机农药的荧光响应(b)
Fig.3 Structures of organic pesticides GPHS, CPR, TZP, CTL, NF, TFL and DCN(a); fluorescent responses of LMOF-a to seven organic pesticides with addition concentration of 2.0, 6.0 and 10.0 mmol/L(b)
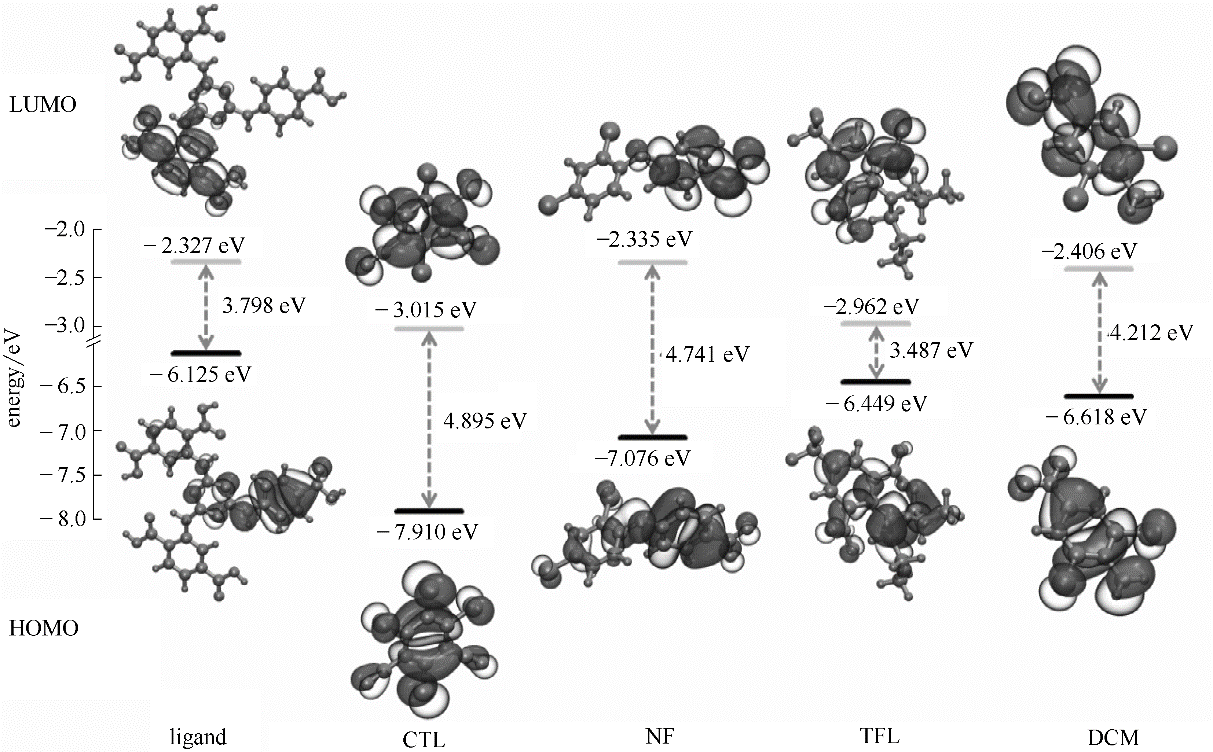
图6 配体及有机农药的电子云等值面分布(0.02 a.u.)及前沿分子轨道能级(1 a.u.= 27.2114 eV)
Fig.6 Electron density isosurfaces (0.02 a.u.) and energy levels of frontier molecular orbitals of the ligand and organic pesticides
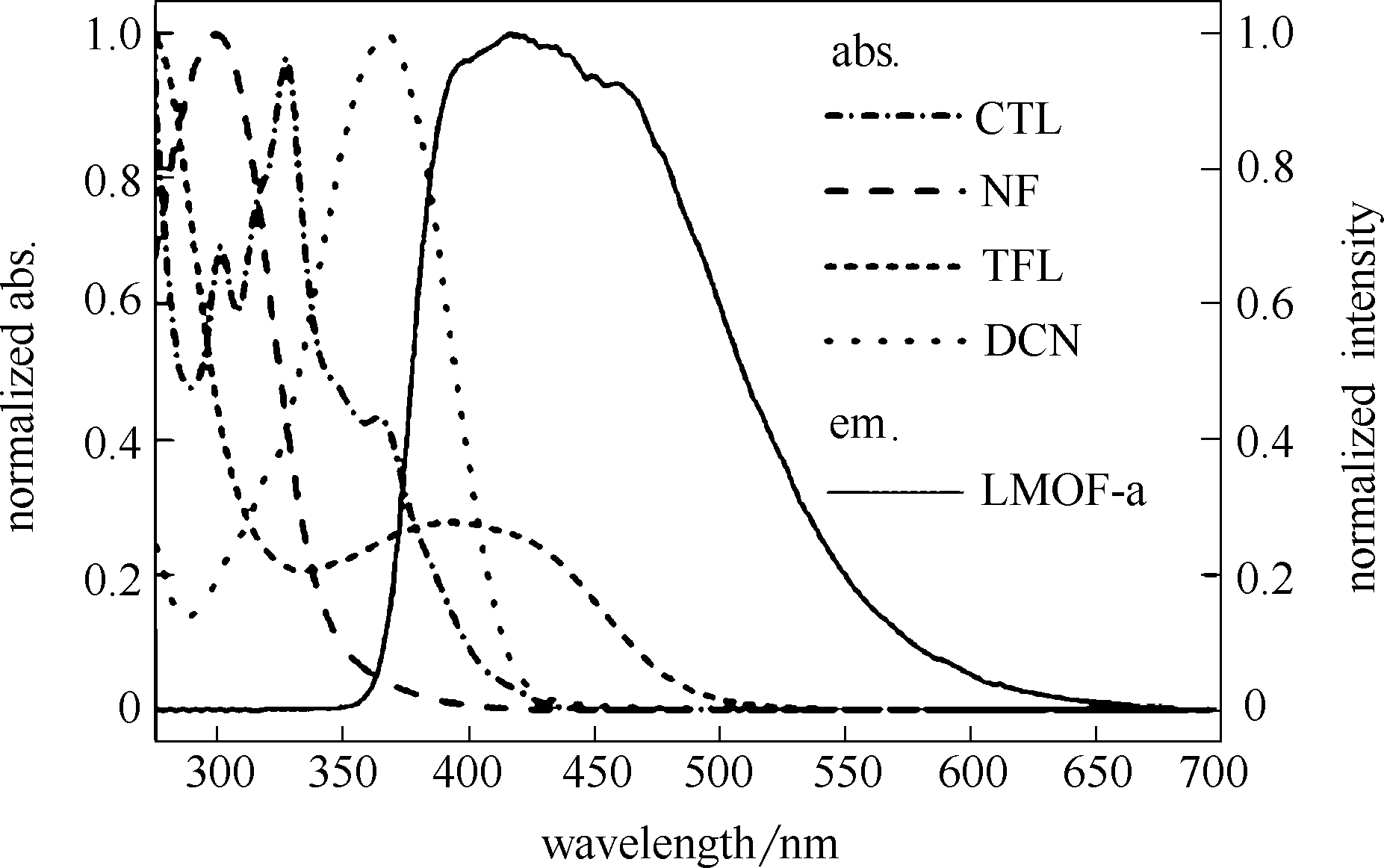
图7 有机农药CTL、NF、TFL及DCN的紫外可见光谱与LMOF-a的荧光光谱的交叠
Fig.7 Overlaps between UV-vis spectra of organic pesticides CTL, NF, TFL, DCN and fluorescent spectrum of LMOF-a
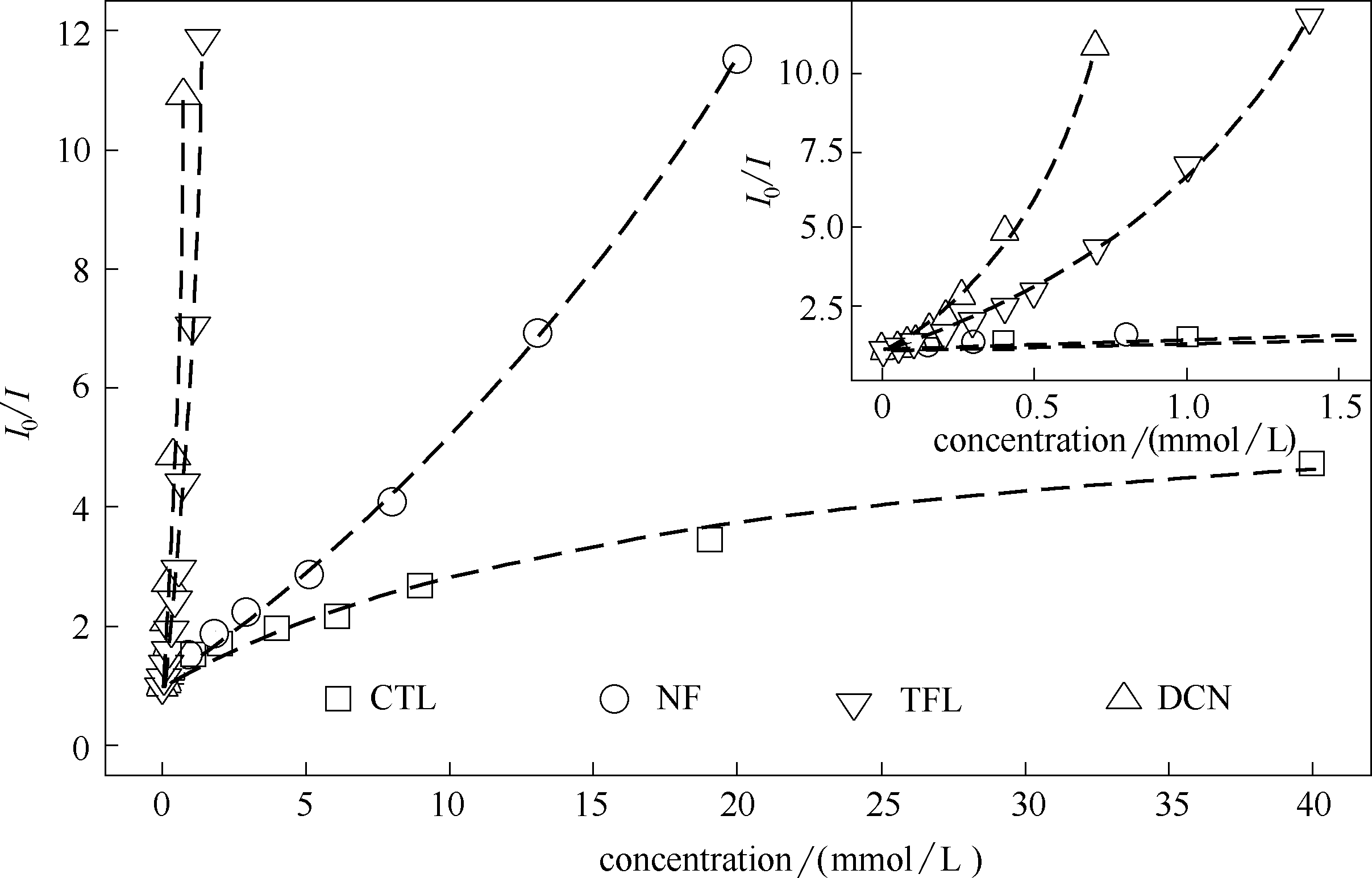
图8 LMOF-a荧光检测有机农药NF、CTL、TFL及DCN的Stern-Volmer曲线
Fig.8 Stern-Volmer plots of LMOF-a for fluorescent detection of organic pesticides NF, CTL, TFL and DCN
| Pesticides | KSV/(L/mmol) | Standard | f1 | f2 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL | 0.322 | 0.035 | 0.845 | 0.155 | 0.993 |
| NF | 0.335 | 0.015 | 1.049 | -0.049 | 0.998 |
| TFL | 3.025 | 0.156 | 1.133 | -0.133 | 0.997 |
| DCN | 4.778 | 0.590 | 1.181 | -0.181 | 0.991 |
表1 LMOF-a检测有机农药的拟合参数
Table 1 Fitting parameters for organic pesticides detection by LMOF-a
| Pesticides | KSV/(L/mmol) | Standard | f1 | f2 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL | 0.322 | 0.035 | 0.845 | 0.155 | 0.993 |
| NF | 0.335 | 0.015 | 1.049 | -0.049 | 0.998 |
| TFL | 3.025 | 0.156 | 1.133 | -0.133 | 0.997 |
| DCN | 4.778 | 0.590 | 1.181 | -0.181 | 0.991 |
| 1 | Kim K H, Kabir E, Jahan S A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 575: 525-535. |
| 2 | Chen J, Huang Y, Kannan P, et al. Flexible and adhesive surface enhance Raman scattering active tape for rapid detection of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(4): 2149-2155. |
| 3 | Andreu V, Picó Y. Determination of currently used pesticides in biota[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 404(9): 2659-2681. |
| 4 | Inglezakis V J, Moustakas K. Household hazardous waste management: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 150: 310-321. |
| 5 | Koureas M, Tsakalof A, Tsatsakis A, et al. Systematic review of biomonitoring studies to determine the association between exposure to organophosphorus and pyrethroid insecticides and human health outcomes[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2012, 210(2): 155-168. |
| 6 | Odukkathil G, Vasudevan N. Toxicity and bioremediation of pesticides in agricultural soil[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2013, 12(4): 421-444. |
| 7 | Rodrigo M, Oturan N, Oturan M A. Electrochemically assisted remediation of pesticides in soils and water: a review[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(17): 8720-8745. |
| 8 | Handford C E, Elliott C T, Campbell K. A review of the global pesticide legislation and the scale of challenge in reaching the global harmonization of food safety standards[J]. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 2015, 11(4): 525-536. |
| 9 | Pateiro-Moure M, Arias-EstéVez M, Simal-GáNdara J S. Critical review on the environmental fate of quaternary ammonium herbicides in soils devoted to vineyards[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(10): 4984-4998. |
| 10 | Bruzzoniti M C, Checchini L, de Carlo R M, et al. QuEChERS sample preparation for the determination of pesticides and other organic residues in environmental matrices: a critical review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 406(17): 4089-4116. |
| 11 | Rojano-Delgado A M, Luque de Castro M D. Capillary electrophoresis and herbicide analysis: present and future perspectives[J]. Electrophoresis, 2014, 35(17): 2509-2519. |
| 12 | Elbashir A A, Aboul-Enein H Y. Separation and analysis of triazine herbcide residues by capillary electrophoresis[J]. Biomedical Chromatography, 2015, 29(6): 835-842. |
| 13 | Singha D K, Majee P, Mondal S K, et al. Highly selective aqueous phase detection of azinphos-methyl pesticide in ppb level using a cage-connected 3D MOF[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2017, 2(20): 5760-5768. |
| 14 | Vikrant K, Tsang D C W, Raza N, et al. Potential utility of metal-organic framework-based platform for sensing pesticides[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(10): 8797-8817. |
| 15 | Yi F Y, Chen D, Wu M K, et al. Chemical sensors based on metal-organic frameworks[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2016, 81(8): 675-690. |
| 16 | Zhao M, Huang Y, Peng Y, et al. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets: synthesis and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(16): 6267-6295. |
| 17 | Jayaramulu K, Kanoo P, George S J, et al. Tunable emission from a porous metal-organic framework by employing an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer responsive ligand[J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(42): 7906-7908. |
| 18 | Zhang C, Che Y, Zhang Z, et al. Fluorescent nanoscale zinc (Ⅱ)-carboxylate coordination polymers for explosive sensing[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(8): 2336-2338. |
| 19 | Wang R, Dong X Y, Xu H, et al. A super water-stable europium-organic framework: guests inducing low-humidity proton conduction and sensing of metal ions[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(65): 9153-9156. |
| 20 | Kumar P, Paul A K, Deep A. A luminescent nanocrystal metal organic framework for chemosensing of nitro group containing organophosphate pesticides[J]. Analytical Methods, 2014, 6(12): 4095-4101. |
| 21 | Deep A, Bhardwaj S K, Paul A K, et al. Surface assembly of nano-metal organic framework on amine functionalized indium tin oxide substrate for impedimetric sensing of parathion[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 65: 226-231. |
| 22 | Bhardwaj S K, Bhardwaj N, Mohanta G C, et al. Immunosensing of atrazine with antibody-functionalized Cu-MOF conducting thin films[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(47): 26124-26130. |
| 23 | Wang J, He C, Wu P, et al. An amide-containing metal-organic tetrahedron responding to a spin-trapping reaction in a fluorescent enhancement manner for biological imaging of NO in living cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(32): 12402-12405. |
| 24 | Hu Z, Deibert B J, Li J. Luminescent metal-organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(16): 5815-5840. |
| 25 | Kumar P, Paul A K, Deep A. Sensitive chemosensing of nitro group containing organophosphate pesticides with MOF-5[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014, 195: 60-66. |
| 26 | Ghosh P, Saha S K, Roychowdhury A, et al. Recognition of an explosive and mutagenic water pollutant, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, by cost-effective luminescent MOFs[J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 2015(17): 2851-2857. |
| 27 | Helal A, Qamaruddin M, Aziz M A, et al. MB-UiO-66-NH2 metal-organic framework as chromogenic and fluorogenic sensor for hydrazine hydrate in aqueous solution[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2017, 2(25): 7630-7636. |
| 28 | Jin D, Gong A, Zhou H. Visible-light-activated photoelectrochemical biosensor for the detection of the pesticide acetochlor in vegetables and fruit based on its inhibition of glucose oxidase[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(28): 17489-17496. |
| 29 | Smith J V. Topochemistry of zeolites and related materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1988, 88(1): 149-182. |
| 30 | Cundy C S, Cox P A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: history and development from the earliest days to the present time[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2003, 103(3): 663-701. |
| 31 | Farahani Y D, Safarifard V. Highly selective detection of Fe3+, Cd2+ and CH2Cl2 based on a fluorescent Zn-MOF with azine-decorated pores[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2019, 275: 131-140. |
| 32 | Jensen S, Tan K, Lustig W, et al. Quenching of photoluminescence in a Zn-MOF sensor by nitroaromatic molecules[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(9): 2625-2632. |
| 33 | Di L, Zhang J J, Liu S Q, et al. Two dynamic abw-type metal organic frameworks built of pentacarboxylate and Zn2+ as photoluminescent probes of nitroaromatics[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(8): 4539-4546. |
| 34 | Zhao G J, Han K L. Hydrogen bonding in the electronic excited state[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2012, 45(3): 404-413. |
| 35 | Singha D K, Majee P, Mandal S, et al. Detection of pesticides in aqueous medium and in fruit extracts using a three-dimensional metal-organic framework: experimental and computational study[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 57(19): 12155-12165. |
| 36 | Nagarkar S S, Joarder B, Chaudhari A K, et al. Highly selective detection of nitro explosives by a luminescent metal-organic framework[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(10): 2881-2885. |
| 37 | Dai Y, Zhou H, Song X D, et al. Two (5,5)-connected isomeric frameworks as highly selective and sensitive photoluminescent probes of nitroaromatics[J]. CrystEngComm, 2017, 19(20): 2786-2794. |
| 38 | Xing Y, Qiao C, Li X, et al. The dependence of oxygen sensitivity on molecular structures of Ir(Ⅲ) complexes and application for photostable and reversible luminescent oxygen sensing[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(27): 15370-15380. |
| 39 | Wang X D, Wolfbeis O S. Optical methods for sensing and imaging oxygen: materials, spectroscopies and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(10): 3666-3761. |
| [1] | 杜峰, 尹思琦, 罗辉, 邓文安, 李传, 黄振薇, 王文静. H2在Mo x S y 团簇上吸附解离的尺寸效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3895-3903. |
| [2] | 裴仁花, 王永洪, 张新儒, 李晋平. 碳纳米管/环糊精金属有机骨架协同强化混合基质膜的CO2分离[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3904-3914. |
| [3] | 俞夏琪, 冯格, 赵金燕, 李嘉远, 邓声威, 郑靖楠, 李雯雯, 王亚秋, 沈榄, 刘旭, 徐威威, 王建国, 王式彬, 姚子豪, 毛成立. 基体(TDI-TMP-T313)与氧化剂(AP)相互作用的第一性原理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3511-3517. |
| [4] | 赵继昊, 唐伟强, 徐小飞, 赵双良, 贺炅皓. 高分子复合材料中键合剂在不同纳米填料表面的吸附能计算[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3174-3181. |
| [5] | 王毅, 熊启钊, 陈杨, 杨江峰, 李立博, 李晋平. 锆基金属有机骨架材料用于氨吸附性能的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1772-1780. |
| [6] | 罗小松, 黄金保, 周梅, 牟鑫, 徐伟伟, 吴雷. 对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯二聚体水/醇/氨解机理的理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 4859-4871. |
| [7] | 龚翔, 李林森, 姜召. PdCo/SiO2双金属催化剂用于杂环储氢载体的高效脱氢[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4448-4460. |
| [8] | 朱先会, 王甫, 夏杰成, 袁金良. 功能型离子液体协同吸收NH3和CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4324-4334. |
| [9] | 马生贵, 田博文, 周雨薇, 陈琳, 江霞, 高涛. 氮掺杂Stone-Wales缺陷石墨烯吸附H2S的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. |
| [10] | 王结祥, 李洪国, 叶松寿, 郑进保, 陈秉辉. 卤素负载锌-腺嘌呤骨架材料的构建及无助剂催化CO2环加成反应[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3686-3695. |
| [11] | 王莹, 郑柏树, 王刘盛, 汪冠宇, 曾文江, 汪朝旭, 阳庆元. 锆基金属-有机骨架材料分离放射性气体Rn的计算筛选研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2688-2696. |
| [12] | 张芳芳, 韩敏, 赵娟, 凌丽霞, 章日光, 王宝俊. 单空缺石墨烯负载的Pd单原子催化剂上NO还原的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1382-1391. |
| [13] | 唐伟强, 谢鹏, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 反应密度泛函理论的构建与初步应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 633-652. |
| [14] | 李建惠, 兰天昊, 陈杨, 杨江峰, 李立博, 李晋平. MOF复合材料在气体吸附分离中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 167-179. |
| [15] | 葛冰青, 阴义轩, 王亚溪, 张宏伟, 袁珮. 溶剂对丁腈橡胶溶解、尺寸、结构和催化加氢的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 543-554. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号