化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (1): 543-554.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201045
收稿日期:2020-07-28
修回日期:2020-10-13
出版日期:2021-01-05
发布日期:2021-01-05
通讯作者:
袁珮
作者简介:葛冰青(1995—),女,博士,基金资助:
GE Bingqing( ),YIN Yixuan,WANG Yaxi,ZHANG Hongwei,YUAN Pei(
),YIN Yixuan,WANG Yaxi,ZHANG Hongwei,YUAN Pei( )
)
Received:2020-07-28
Revised:2020-10-13
Online:2021-01-05
Published:2021-01-05
Contact:
YUAN Pei
摘要:
丁腈橡胶(NBR)是由丁二烯和丙烯腈共聚而制得的一种重要的合成橡胶,而由NBR选择性加氢制得的氢化丁腈橡胶(HNBR),不仅保持了NBR原有的耐油和耐磨性,其耐侯性、耐臭氧性等均得到极大改善,被广泛用于武器部件、航天用密封件等领域,是不饱和聚合物化学改性领域的一个重要研究课题。本文采用纳米粒度仪、乌氏黏度计、傅里叶变换红外等表征手段,结合密度泛函理论计算(DFT),系统研究了溶剂性质对NBR在溶剂中的溶解行为、尺寸分布、分子结构及催化加氢性能等的影响。实验结果表明强亲电子溶剂不能溶解NBR,给电子溶剂及部分弱亲电子溶剂能较好地溶解NBR,特别是在酮类溶剂中,NBR粒径小且分布集中。DFT结果表明相比于气相氛围,在所有溶剂氛围中NBR链段里双键的键长均有所增长,且随着溶剂的极性增加而呈增长的趋势,NBR的偶极矩也随着溶剂极性增加而增加。特别是在酮类溶剂中,受溶剂效应的影响NBR分子的HOMO轨道由分子边缘向分子内部移动,表明对链段内部C C双键可能产生积极的影响。加氢结果表明在给电子溶剂中的加氢效果均优于弱亲电子溶剂,但无论选择何种溶剂,对NBR中C
C双键可能产生积极的影响。加氢结果表明在给电子溶剂中的加氢效果均优于弱亲电子溶剂,但无论选择何种溶剂,对NBR中C C双键的加氢选择性均为100%。该研究为NBR非均相溶液加氢体系中溶剂的筛选提供了理论依据。
C双键的加氢选择性均为100%。该研究为NBR非均相溶液加氢体系中溶剂的筛选提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
葛冰青, 阴义轩, 王亚溪, 张宏伟, 袁珮. 溶剂对丁腈橡胶溶解、尺寸、结构和催化加氢的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 543-554.
GE Bingqing, YIN Yixuan, WANG Yaxi, ZHANG Hongwei, YUAN Pei. Study of solvent effect on the dissolution, size, structure and catalytic hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 543-554.
| Structure | Type of H | δ |
|---|---|---|
| 1,4 unit |  CH— CH— | 5.50 |
| —CH2— | 2.15 | |
| —CH(CN)— | 2.65 | |
| —CH2CH(CN)— | 1.70 | |
| 1,2 unit |  CH— and CH— and  CH2 CH2 | 4.90—5.10 |
表1 NBR中不同结构对应的 H 化学位移
Table 1 Chemical shifts of H protons in different microstructures of NBR
| Structure | Type of H | δ |
|---|---|---|
| 1,4 unit |  CH— CH— | 5.50 |
| —CH2— | 2.15 | |
| —CH(CN)— | 2.65 | |
| —CH2CH(CN)— | 1.70 | |
| 1,2 unit |  CH— and CH— and  CH2 CH2 | 4.90—5.10 |
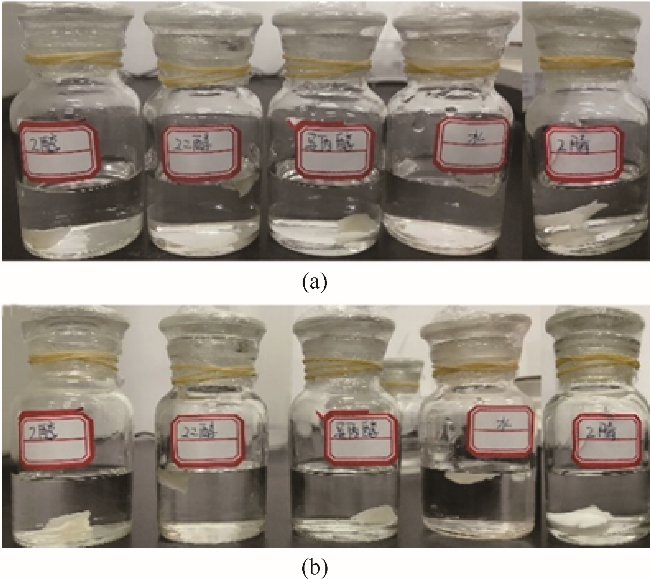
图2 NBR在强亲电子溶剂中放置24 h前(a)、后(b)对比照片(从左至右依次为:EtOH、EG、IPA、水和MeCN)
Fig.2 Pictures for NBR in strong electrophilic solvents before (a) and after (b) 24 h (Solvents from left to right: EtOH, EG, IPA, water and MeCN)
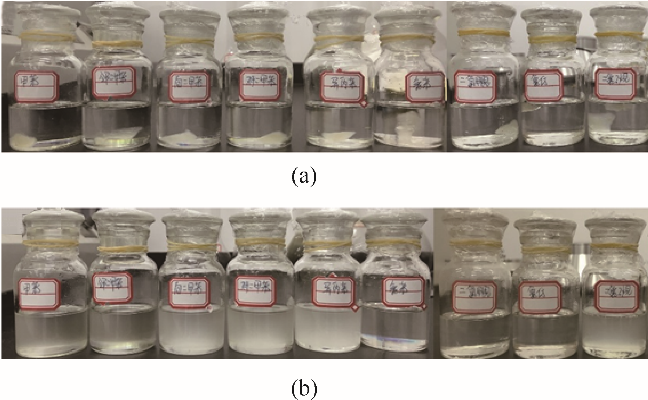
图3 NBR在弱亲电子溶剂中放置24 h前(a)、后(b)对比照片(从左至右溶剂依次为:TOL、OX、MX、PX、TIPB、MCB、DCM、TCM和EDC)
Fig.3 Pictures for NBR in weak electrophilic solvents before (a) and after (b) 24 h (Solvents from left to right: TOL,OX,MX,PX,TIPB,MCB,DCM,TCM and EDC)

图4 NBR在给电子溶剂中放置24 h前(a)、后(b)对比照片(从左至右溶剂依次为:ACE、MEK、MIBK、CYC、NMP、MAC、EA、IBAC和DMF)
Fig.4 Pictures for NBR in electron donating solvents before (a) and after (b) 24 h (Solvents from left to right: ACE,MEK,MIBK,CYC,NMP,MAC,EA,IBAC and DMF)
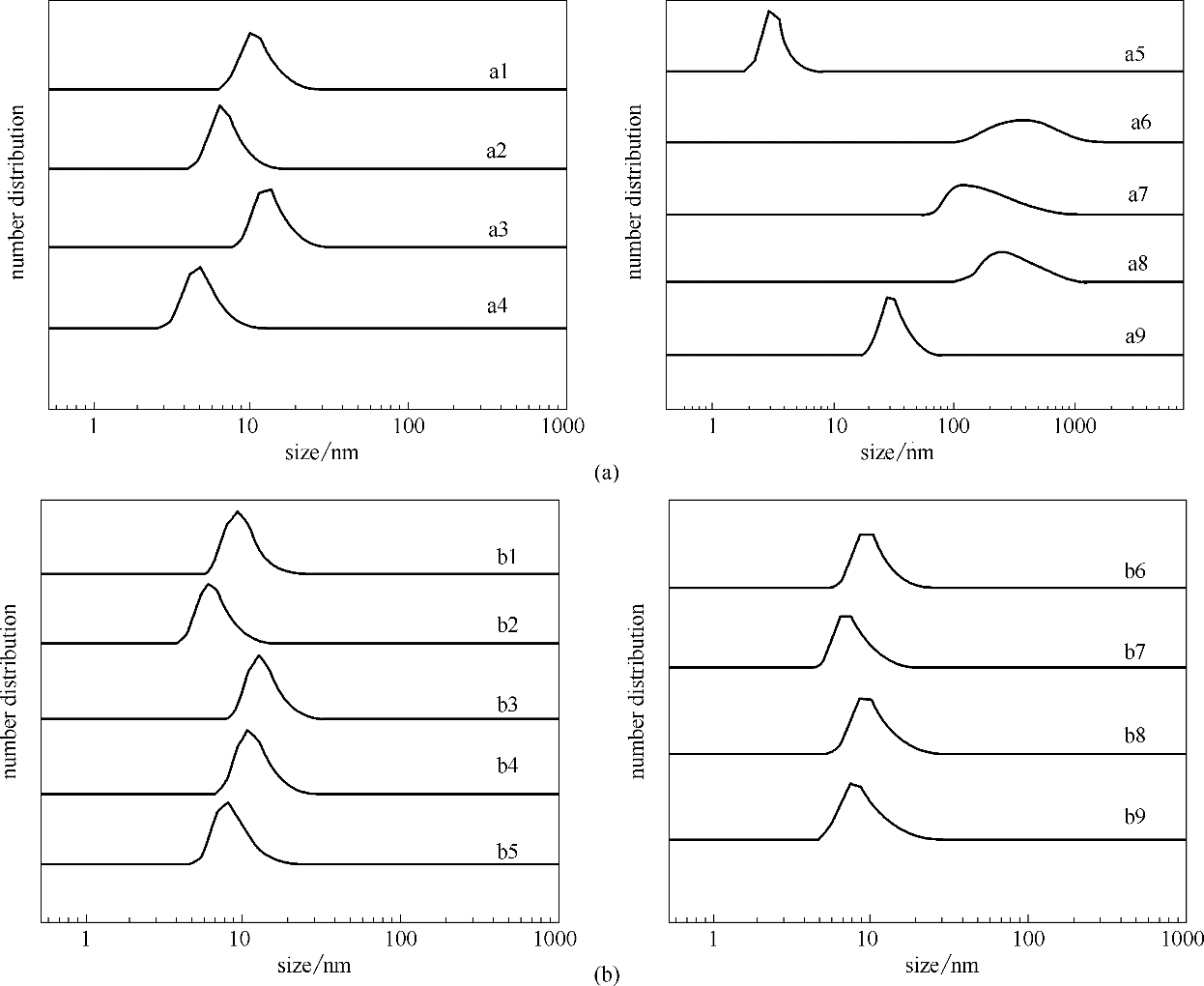
图5 弱亲电子溶剂(a)和给电子溶剂(b)中NBR的尺寸分布(a1~a9分别为:DCM、TCM、EDC、MCB、TOL、OX、MX、PX和TIPB; b1~b9分别为:ACE、MEK、MIBK、CYC、NMP、MAC、EA、IBAC和DMF)(Solvents a1—a9: DCM, TCM, EDC, MCB, TOL, OX, MX, PX and TIPB; solvents b1—b9: ACE,MEK,MIBK,CYC,NMP,MAC,EA,IBAC and DMF)
Fig.5 The size distribution of NBR in weak electrophilic solvents (a) and electron donating solvents (b)
| 编号 | 溶剂 | [η]/(L/g) | ηsp | 编号 | 溶剂 | [η]/(L/g) | ηsp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | DCM | 1.84×10-1 | 2.55 | b1 | ACE | 6.88×10-2 | 1.13 |
| a2 | TCM | 1.32×10-1 | 2.17 | b2 | MEK | 6.17×10-2 | 0.92 |
| a3 | EDC | 1.13×10-1 | 2.00 | b3 | MIBK | 5.68×10-2 | 0.97 |
| a4 | MCB | 1.03×10-1 | 1.48 | b4 | CYC | 1.21×10-1 | 1.63 |
| a5 | TOL | 4.90×10-2 | 0.61 | b5 | NMP | 1.35×10-1 | 1.68 |
| a6 | OX | 4.91×10-2 | 0.60 | b6 | MAC | 6.59×10-2 | 1.06 |
| a7 | MX | 2.72×10-2 | 0.38 | b7 | EA | 6.85×10-2 | 1.07 |
| a8 | PX | 3.83×10-2 | 0.41 | b8 | IBAC | 5.13×10-2 | 0.78 |
| a9 | TIPB | 2.31×10-2 | 0.24 | b9 | DMF | 9.56×10-2 | 1.38 |
表2 弱亲电子(a1~a9)和给电子溶剂(b1~b9)中NBR溶液的黏度
Table 2 Viscosity of NBR solutions in weak electrophilic solvents (a1—a9) and electron donating solvents (b1—b9)
| 编号 | 溶剂 | [η]/(L/g) | ηsp | 编号 | 溶剂 | [η]/(L/g) | ηsp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | DCM | 1.84×10-1 | 2.55 | b1 | ACE | 6.88×10-2 | 1.13 |
| a2 | TCM | 1.32×10-1 | 2.17 | b2 | MEK | 6.17×10-2 | 0.92 |
| a3 | EDC | 1.13×10-1 | 2.00 | b3 | MIBK | 5.68×10-2 | 0.97 |
| a4 | MCB | 1.03×10-1 | 1.48 | b4 | CYC | 1.21×10-1 | 1.63 |
| a5 | TOL | 4.90×10-2 | 0.61 | b5 | NMP | 1.35×10-1 | 1.68 |
| a6 | OX | 4.91×10-2 | 0.60 | b6 | MAC | 6.59×10-2 | 1.06 |
| a7 | MX | 2.72×10-2 | 0.38 | b7 | EA | 6.85×10-2 | 1.07 |
| a8 | PX | 3.83×10-2 | 0.41 | b8 | IBAC | 5.13×10-2 | 0.78 |
| a9 | TIPB | 2.31×10-2 | 0.24 | b9 | DMF | 9.56×10-2 | 1.38 |
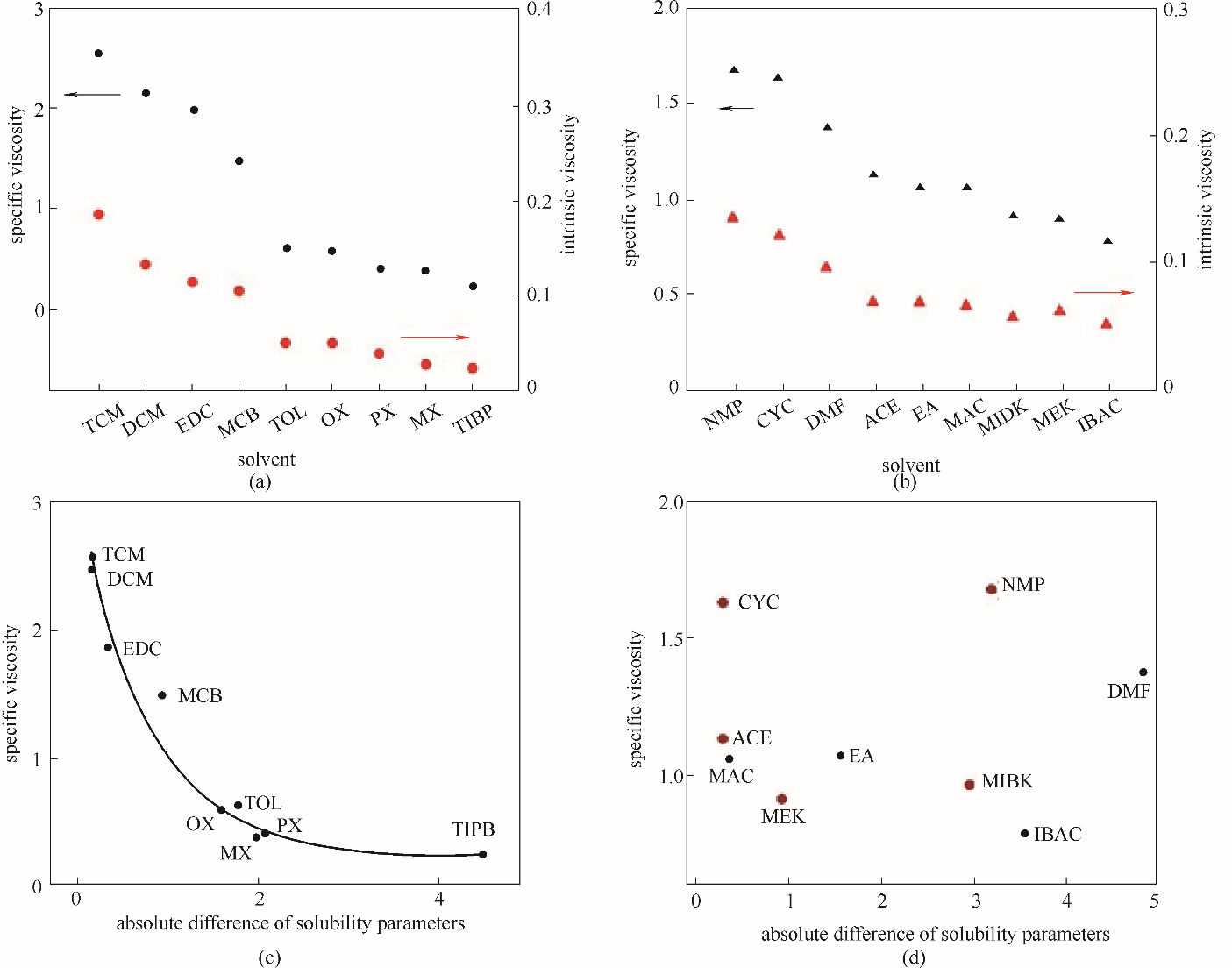
图6 弱亲电子溶剂(a)和给电子溶剂(b)中NBR溶液特性黏度和增比黏度之间的关系;弱亲电子溶剂(c)和给电子溶剂(d)中NBR溶液增比黏度与溶解度参数的绝对差值的关系(溶解度参数的绝对差值?δ=|δNBR-δsolvent|)
Fig.6 The relationship between the characteristic viscosity and the specific viscosity of NBR solutions in weak electrophilic solvents (a) and electron donating solvents (b); the relationship between specific viscosity of NBR solutions and absolute difference of solubility parameters in weak electrophilic solvents (c) and electron donating solvents (d) (absolute difference of solubility parameters ?δ=|δNBR-δsolvent|)
溶剂 种类 | 溶剂 | Bond length/? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1,4-C C— C— | 1,2-C C— C— | ||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |||
弱亲 电子 溶剂 | TOL | 1.3391 | 1.3355 | 1.3400 | 1.3370 | 1.3371 | 1.3348 |
| OX | 1.3391 | 1.3355 | 1.3401 | 1.3371 | 1.3371 | 1.3348 | |
| TCM | 1.3395 | 1.3359 | 1.3405 | 1.3375 | 1.3376 | 1.3351 | |
| MCB | 1.3397 | 1.3359 | 1.3406 | 1.3376 | 1.3376 | 1.3351 | |
给电子 溶剂 | EA | 1.3396 | 1.3359 | 1.3406 | 1.3376 | 1.3376 | 1.3352 |
| MAC | 1.3397 | 1.3360 | 1.3407 | 1.3376 | 1.3377 | 1.3352 | |
| CYC | 1.3398 | 1.3362 | 1.3409 | 1.3378 | 1.3379 | 1.3354 | |
| MEK | 1.4000 | 1.3364 | 1.3411 | 1.3379 | 1.3381 | 1.3356 | |
| ACE | 1.3399 | 1.3363 | 1.3410 | 1.3378 | 1.3380 | 1.3355 | |
| 气相 | NBR | 1.3384 | 1.3348 | 1.3392 | 1.3365 | 1.3365 | 1.3346 |
表3 不同溶剂中NBR链段里不同位置CC双键键长
Table 3 The length of CC double bonds at different positions of NBR molecule in different solvents
溶剂 种类 | 溶剂 | Bond length/? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1,4-C C— C— | 1,2-C C— C— | ||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |||
弱亲 电子 溶剂 | TOL | 1.3391 | 1.3355 | 1.3400 | 1.3370 | 1.3371 | 1.3348 |
| OX | 1.3391 | 1.3355 | 1.3401 | 1.3371 | 1.3371 | 1.3348 | |
| TCM | 1.3395 | 1.3359 | 1.3405 | 1.3375 | 1.3376 | 1.3351 | |
| MCB | 1.3397 | 1.3359 | 1.3406 | 1.3376 | 1.3376 | 1.3351 | |
给电子 溶剂 | EA | 1.3396 | 1.3359 | 1.3406 | 1.3376 | 1.3376 | 1.3352 |
| MAC | 1.3397 | 1.3360 | 1.3407 | 1.3376 | 1.3377 | 1.3352 | |
| CYC | 1.3398 | 1.3362 | 1.3409 | 1.3378 | 1.3379 | 1.3354 | |
| MEK | 1.4000 | 1.3364 | 1.3411 | 1.3379 | 1.3381 | 1.3356 | |
| ACE | 1.3399 | 1.3363 | 1.3410 | 1.3378 | 1.3380 | 1.3355 | |
| 气相 | NBR | 1.3384 | 1.3348 | 1.3392 | 1.3365 | 1.3365 | 1.3346 |

图9 弱亲电子溶剂(a)和给电子溶剂(b)中NBR链段不同位置的CC双键的键长
Fig.9 The bond length of the CC double bonds at different positions of NBR molecule in weak electrophilic solvents (a) and electron donating solvents (b)
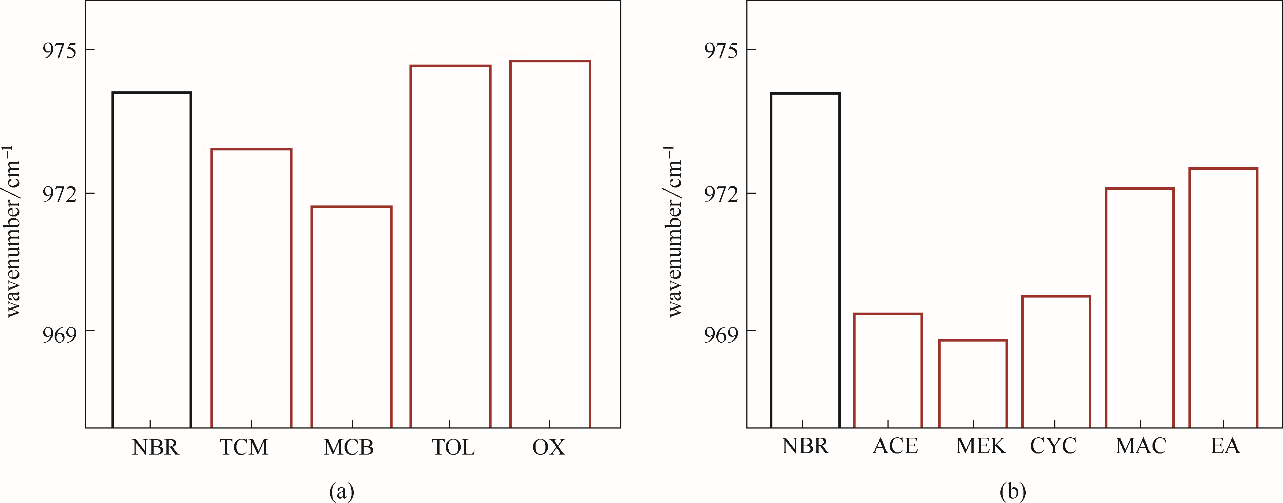
图10 弱亲电子溶剂(a)和给电子溶剂(b)中NBR链段里1,4-CC—双键红外伸缩振动峰位置
Fig.10 The stretching vibration peak position of the 1, 4-CC— double bond of NBR chain in weak electrophilic solvents (a) and electron donating solvents (b)
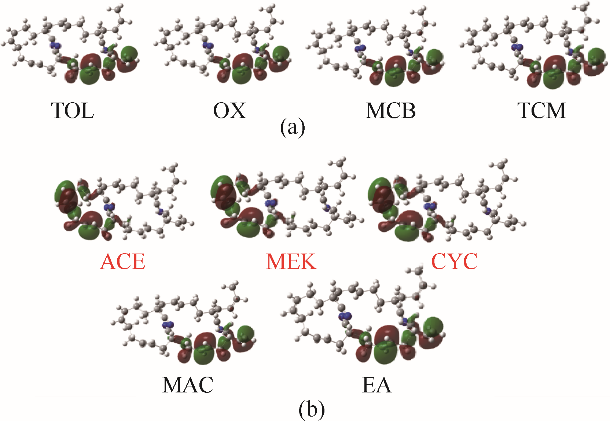
图12 NBR在弱亲电子溶剂(a)和给电子溶剂(b)中HOMO轨道分布图
Fig.12 The HOMO orbital distribution of the NBR molecule in weak electrophilic solvents (a) and electron donating solvents (b)
溶剂 类型 | 溶剂 | 介电 常数 | ELUMO/ a.u. | EHOMO/a.u. | ?Egap/a.u. | ?G/(kcal/mol) | 偶极矩/D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
弱亲 电子 溶剂 | TOL | 2.24 | 0.01201 | -0.22966 | 0.24167 | -19.14 | 5.99 |
| OX | 2.27 | 0.01264 | -0.23036 | 0.24300 | -18.69 | 6.07 | |
| TCM | 4.90 | 0.01176 | -0.22935 | 0.24111 | -25.87 | 6.62 | |
| MCB | 5.65 | 0.00988 | -0.22837 | 0.23825 | -24.77 | 6.79 | |
给电子 溶剂 | EA | 6.02 | 0.01037 | -0.22847 | 0.23884 | -22.19 | 6.80 |
| MAC | 6.68 | 0.00996 | -0.22838 | 0.23834 | -22.29 | 6.89 | |
| CYC | 18.30 | 0.01206 | -0.22974 | 0.24180 | -22.20 | 7.35 | |
| MEK | 18.51 | 0.01245 | -0.23065 | 0.24310 | -26.31 | 7.50 | |
| ACE | 20.49 | 0.01226 | -0.23006 | 0.24232 | -25.47 | 7.42 | |
| 气相 | NBR | 0 | 0.00420 | -0.22990 | 0.23410 | 0 | 5.01 |
表4 不同溶剂中NBR前线轨道能量、能隙值、溶剂化能及偶极矩
Table 4 Frontier orbit energy, energy gap, solvation energy and dipole moments of NBR in different solvents
溶剂 类型 | 溶剂 | 介电 常数 | ELUMO/ a.u. | EHOMO/a.u. | ?Egap/a.u. | ?G/(kcal/mol) | 偶极矩/D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
弱亲 电子 溶剂 | TOL | 2.24 | 0.01201 | -0.22966 | 0.24167 | -19.14 | 5.99 |
| OX | 2.27 | 0.01264 | -0.23036 | 0.24300 | -18.69 | 6.07 | |
| TCM | 4.90 | 0.01176 | -0.22935 | 0.24111 | -25.87 | 6.62 | |
| MCB | 5.65 | 0.00988 | -0.22837 | 0.23825 | -24.77 | 6.79 | |
给电子 溶剂 | EA | 6.02 | 0.01037 | -0.22847 | 0.23884 | -22.19 | 6.80 |
| MAC | 6.68 | 0.00996 | -0.22838 | 0.23834 | -22.29 | 6.89 | |
| CYC | 18.30 | 0.01206 | -0.22974 | 0.24180 | -22.20 | 7.35 | |
| MEK | 18.51 | 0.01245 | -0.23065 | 0.24310 | -26.31 | 7.50 | |
| ACE | 20.49 | 0.01226 | -0.23006 | 0.24232 | -25.47 | 7.42 | |
| 气相 | NBR | 0 | 0.00420 | -0.22990 | 0.23410 | 0 | 5.01 |
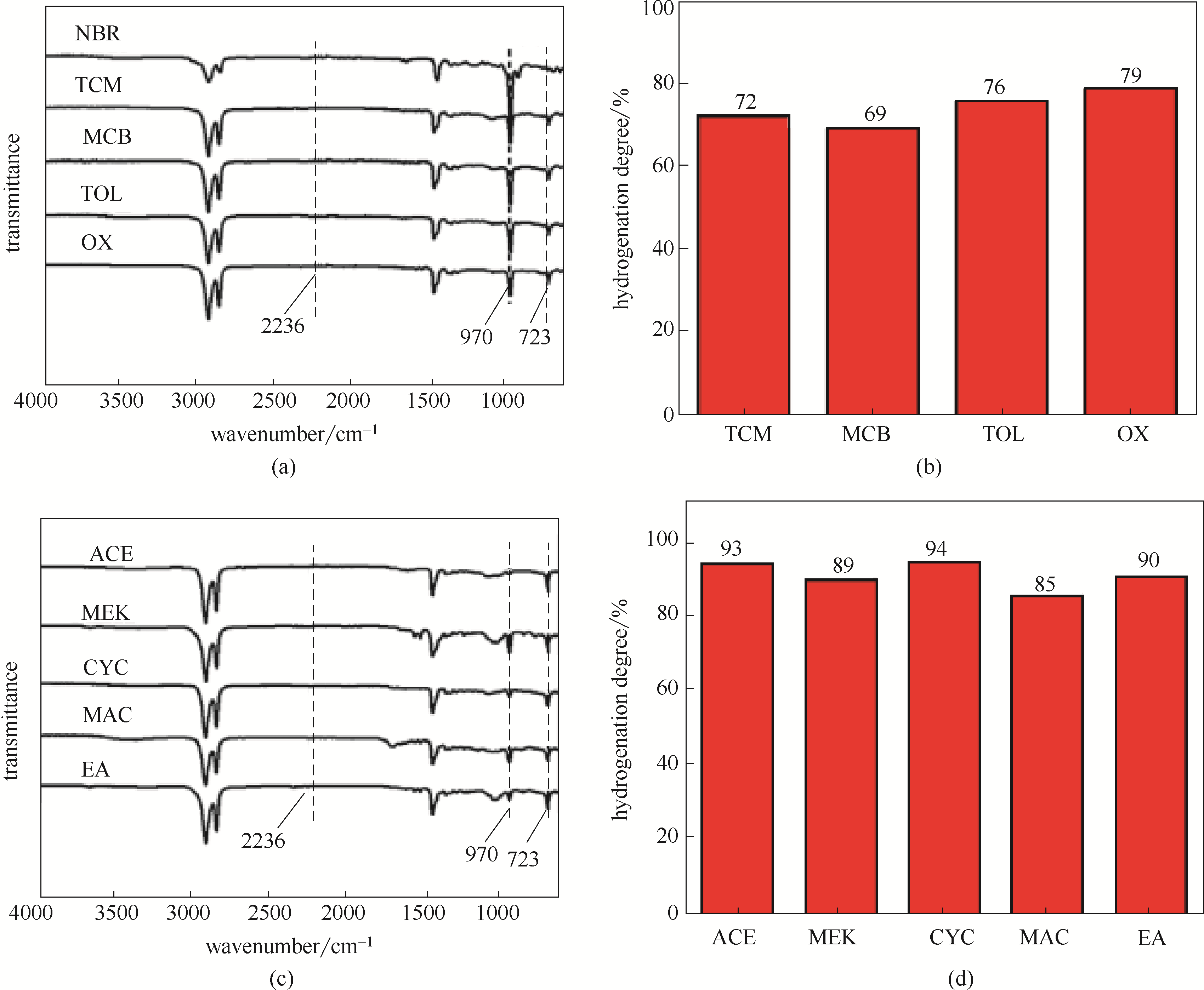
图13 在弱亲电子溶剂[(a), (b)]和给电子溶剂[(c), (d)]中得到的HNBR红外谱图及其加氢度
Fig.13 FT-IR spectra and hydrogenation degree of HNBR obtained in weak electrophilic solvents [(a), (b)] and electron donating solvents [(c), (d)]
| 1 | 孙黎, 毕忠华, 高梅, 等. 氢化丁腈橡胶的研究进展[J]. 特种橡胶制品, 2020, 41(1): 60-64. |
| Sun L, Bi Z H, Gao M, et al. Research progress of hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber[J]. Special Purpose Rubber Products, 2020, 41(1): 60-64. | |
| 2 | Budrugeac P. Thermooxidative degradation of some nitrile-butadiene rubbers[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 1992, 38(2): 165-172. |
| 3 | Zhao J, Yang R, Iervolino R, et al. Investigation of crosslinking in the thermooxidative aging of nitrile–butadiene rubber[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(3): 41319. |
| 4 | Ciesielski A. An Introduction to Rubber Technology[M]. Smithers Rapra Technology, 1999. |
| 5 | Zhou W, Peng X. Preparation of a novel homogeneous bimetallic Rhodium/Palladium ionic catalyst and its application for the catalytic hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber[J]. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2016, 823: 76-82. |
| 6 | Ning S, Yang S, Wei X, et al. Selective hydrogenation of nitrile-butadiene rubber catalyzed by thermoregulated phase transfer phosphine rhodium complex[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 123(2): 1040-1046. |
| 7 | Zhou W, Peng X. Preparation and catalytic application of Rh3+/Ru3+ bimetallic catalyst stabilized by triolefinic macrocycle-terminated poly (propylene imine) dendrimer[J]. Macromolecular Research, 2016, 24(11): 1024-1029. |
| 8 | Zhou W, Zhang D, Wang Y, et al. Preparation of Rh metallic nanoparticle stabilized by 15-membered nitrogen-containing triolefinic macrocycle-ended poly (propylene imine) dendrimer and its catalytic hydrogenation for nitrile-butadiene rubber[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2017, 295(5): 767-772. |
| 9 | Kubo Y, Ohura K. Process for hydrogenation of conjugated diene polymers: US4337329[P]. 1982-06-29. |
| 10 | Kubo Y, Ohura K. Process for hydrogenating conjugated diene polymers: US4452951[P]. 1984-04-09. |
| 11 | Zou R, Li C, Zhang L, et al. Selective hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) with rhodium nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes at room temperature[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 81: 4-9. |
| 12 | Cao P, Wu M, Zou R, et al. A ternary Rh complex catalyst highly active and stable in the hydrogenation of acrylonitrile–butadiene rubber[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39: 1583-1586. |
| 13 | Cao P, Huang C, Zhang L, et al. One-step fabrication of RGO/HNBR composites via selective hydrogenation of NBR with graphene-based catalyst[J]. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 2015, 5(51): 41098-41102. |
| 14 | Chen J, Ma L, Cheng T, et al. [J]. Stable and recyclable Pd catalyst supported on modified silica hollow microspheres with macroporous shells for enhanced catalytic hydrogenation of NBR[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 53: 15064-15080. |
| 15 | Chen J, Wu Z, Liu H, et al. A surface-cofunctionalized silica supported palladium catalyst for selective hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber with enhanced catalytic activity and recycling performance[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(27): 11821-11830. |
| 16 | Dyson P J, Jessop P G. Solvent effects in catalysis: rational improvements of catalysts via manipulation of solvent interactions[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6: 3302-3316. |
| 17 | Li Y, Cheng H, Lin W, et al. Solvent effects on heterogeneous catalysis in the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over a conventional Pd/C catalyst[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2018, 8: 3580-3589. |
| 18 | Linda N, Elena S, Alexey B, et al. Selective hydrogenation of 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol over Pd-nanoparticles stabilized in hypercrosslinked polystyrene: solvent effect[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 241:179-188. |
| 19 | 刘卅, 贾德民. 贮氢合金催化丁腈橡胶溶液加氢反应工艺条件的研究[J]. 弹性体, 2006, 16(2): 19-23. |
| Liu S, Jia D M. Hydrogenation conditions of nitrile rubber solution catalyzed by hydrogen storage alloy[J]. China Elastomerics, 2006, 16(2): 19-23. | |
| 20 | Shirai M, Torii K, Arai M. Hydrogenation of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubbers with palladium loaded mesopore-size controlled clay materials[J]. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 2000, 130: 2105-2110. |
| 21 | Wang S, Ge B, Yin Y, et al. Solvent effect in heterogeneous catalytic selective hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber: relationship between reaction activity and solvents with density functional theory analysis[J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(2): 663-672. |
| 22 | Liu B, Zhang H, Ren J, et al. Effect of solvent aromaticity on poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene)(PFO) chain solution behavior and film condensed state structure[J]. Polymer, 2019, 185: 121986. |
| 23 | Dickson R M, Becke A D. Basis-set-free local density-functional calculations of geometries of polyatomic molecules[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 99(5): 3898-3905. |
| 24 | Fokin A A, Gerbig D, Schreiner P R. σ/σ- and π/π-interactions are equally important: multilayered graphanes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(50):20036-20039. |
| 25 | Orio M, Pantazis D A, Neese F. Density functional theory[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2009, 102(2/3): 443-453. |
| 26 | 阴义轩, 成婷婷, 袁珮, 等. 丁腈橡胶非均相加氢催化剂失活原因及再生性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2528-2539. |
| Yin Y X, Cheng T T, Yuan P, et al. Deactivation and regeneration of heterogeneous hydrogenation catalyst for nitrile butadiene rubber[J]. CISEC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2528-2539. | |
| 27 | Fukui K,Yonezawa T, Shingu H. A molecular orbital theory of reactivity in aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2004, 20(10): 722-725. |
| 28 | Fukui K. Theory of orientation and stereoselection[J]. Reactivity & Structure Concepts in Organic Chemistry, 1975, 15: 1-85. |
| 29 | 周公度, 段连云. 结构化学基础[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2002: 11-22. |
| Zhou G D, Duan L Y. Fundamentals of Structural Chemistry [M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2002: 11-22. | |
| 30 | 付新梅, 李燕, 王景辉. 有机小分子偶极矩影响因素研究[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2015, (4): 408-412. |
| Fu X M, Li Y, Wang J H. Influencing factors of organic small molecule Dipole moment[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2015, (4): 408-412. |
| [1] | 胡超, 董玉明, 张伟, 张红玲, 周鹏, 徐红彬. 浓硫酸活化五氧化二钒制备高浓度全钒液流电池正极电解液[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [2] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [3] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [4] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [5] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [6] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [7] | 于旭东, 李琪, 陈念粗, 杜理, 任思颖, 曾英. 三元体系KCl + CaCl2 + H2O 298.2、323.2及348.2 K相平衡研究及计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3256-3265. |
| [8] | 陈天华, 刘兆轩, 韩群, 张程宾, 李文明. 喷雾冷却换热强化研究进展及影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3149-3170. |
| [9] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [10] | 王海, 林宏, 王晨, 许浩洁, 左磊, 王军锋. 高压静电场强化多孔介质表面沸腾传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2869-2879. |
| [11] | 刘春雨, 周桓宇, 马跃, 岳长涛. CaO调质含油污泥干燥特性及数学模型[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3018-3027. |
| [12] | 李勇, 高佳琦, 杜超, 赵亚丽, 李伯琼, 申倩倩, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Ni@C@TiO2核壳双重异质结的构筑及光热催化分解水产氢[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [13] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [14] | 刘道银, 陈柄岐, 张祖扬, 吴琰. 颗粒聚团结构对曳力特性影响的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2351-2362. |
| [15] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号