化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (9): 3895-3903.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220539
杜峰( ), 尹思琦, 罗辉, 邓文安(
), 尹思琦, 罗辉, 邓文安( ), 李传, 黄振薇, 王文静
), 李传, 黄振薇, 王文静
收稿日期:2022-04-15
修回日期:2022-06-30
出版日期:2022-09-05
发布日期:2022-10-09
通讯作者:
邓文安
作者简介:杜峰(1972—),男,博士,副教授,Dufeng@upc.edu.cn
基金资助:
Feng DU( ), Siqi YIN, Hui LUO, Wenan DENG(
), Siqi YIN, Hui LUO, Wenan DENG( ), Chuan LI, Zhenwei HUANG, Wenjing WANG
), Chuan LI, Zhenwei HUANG, Wenjing WANG
Received:2022-04-15
Revised:2022-06-30
Online:2022-09-05
Published:2022-10-09
Contact:
Wenan DENG
摘要:
浆态床加氢工艺可以处理不同来源的劣质重油、渣油,氢气的活化是重油加氢处理过程中发生的主要反应之一。钼基催化剂的分散性是影响重油加氢活性的关键因素。构建了Mo7S15、Mo12S26、Mo18S39、Mo25S54和Mo33S71团簇,利用密度泛函理论研究了团簇自身的稳定性、活性以及H2在不同尺寸团簇上的吸附与解离过程。结果发现,在目前所建立的团簇中,其尺寸越小,结合能越低,最高占据分子轨道-最低未占分子轨道(HOMO-LUMO)能隙值越小,团簇稳定性越弱,活性越强。H2在簇上的稳定吸附位点为边缘位点。随团簇尺寸增大,吸附能分别为-64.25、-34.60、-34.14、-7.20、-6.82 kJ/mol,吸附能绝对值减小,氢气分子与团簇的相互作用减弱,并且解离能逐渐增大,分别为13.76、33.14、53.64、60.75、64.47 kJ/mol。目前的结果表明,团簇尺寸越小,氢气的吸附解离越容易,显示出更高的活性。
中图分类号:
杜峰, 尹思琦, 罗辉, 邓文安, 李传, 黄振薇, 王文静. H2在Mo x S y 团簇上吸附解离的尺寸效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3895-3903.
Feng DU, Siqi YIN, Hui LUO, Wenan DENG, Chuan LI, Zhenwei HUANG, Wenjing WANG. Study on size effect of H2 adsorption and dissociation on Mo x S y clusters[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3895-3903.
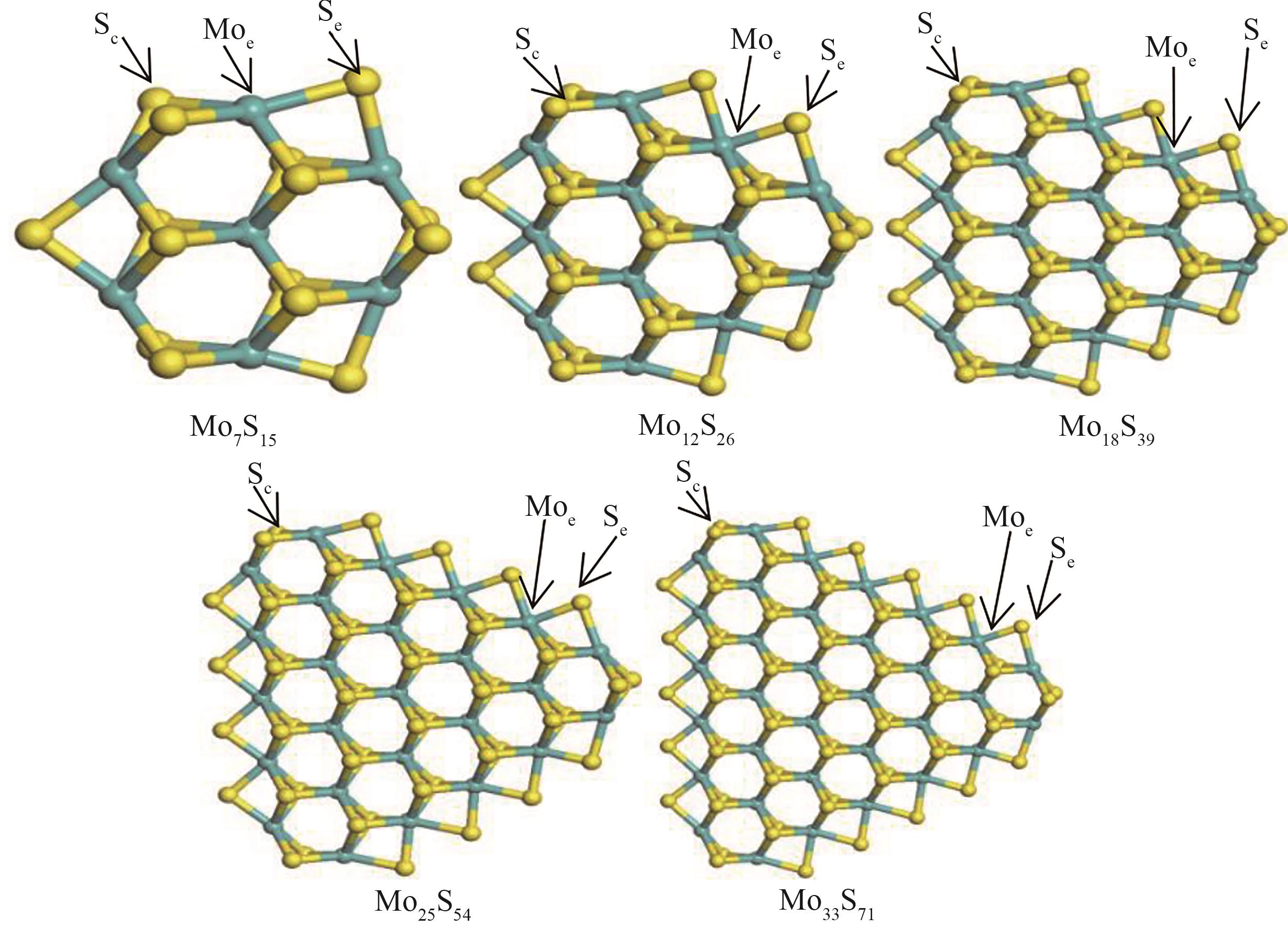
图1 五种不同尺寸的Mo x S y 团簇模型Sc—角硫原子;Moe—边缘钼原子;Se—边缘硫原子
Fig.1 Five different sizes of Mo x S y cluster modelSc—corner sulfur atom; Moe—edge molybdenum atom; Se—edge sulfur atom
| Energy | Mo | S | Mo7S15 | Mo12S26 | Mo18S39 | Mo25S54 | Mo33S71 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E/eV | -1855.00 | -10832.37 | -175589.75 | -304118.30 | -456185.94 | -631793.35 | -830940.07 |
| Eb/eV | — | — | 5.42 | 5.70 | 5.85 | 5.95 | 6.03 |
表1 Mo x S y 团簇、钼原子、硫原子的能量E及不同尺寸Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71)团簇的平均结合能Eb
Table 1 Energy E of Mo x S y clusters, molybdenum atoms, sulfur atoms and binding energies Eb of Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71) clusters with different sizes
| Energy | Mo | S | Mo7S15 | Mo12S26 | Mo18S39 | Mo25S54 | Mo33S71 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E/eV | -1855.00 | -10832.37 | -175589.75 | -304118.30 | -456185.94 | -631793.35 | -830940.07 |
| Eb/eV | — | — | 5.42 | 5.70 | 5.85 | 5.95 | 6.03 |
| System | E(HOMO)/eV | E(LUMO)/eV | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo7S15 | -5.539 | -5.431 | 0.108 |
| Mo12S26 | -5.409 | -5.289 | 0.120 |
| Mo18S39 | -5.469 | -5.337 | 0.132 |
| Mo25S54 | -5.612 | -5.266 | 0.346 |
| Mo33S71 | -5.814 | -5.280 | 0.534 |
表2 Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71) 团簇的HOMO-LUMO能隙值Eg
Table 2 HOMO-LUMO energy gap values of Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71) cluster Eg
| System | E(HOMO)/eV | E(LUMO)/eV | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo7S15 | -5.539 | -5.431 | 0.108 |
| Mo12S26 | -5.409 | -5.289 | 0.120 |
| Mo18S39 | -5.469 | -5.337 | 0.132 |
| Mo25S54 | -5.612 | -5.266 | 0.346 |
| Mo33S71 | -5.814 | -5.280 | 0.534 |
| Species | Corners | Edges | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r(H—H)/nm | r(H—S)/nm | Eads/(kJ/mol) | r(H—H)/nm | r(H—Mo)/nm | r(H—S)/nm | Eads/(kJ/mol) | |
| Mo7S15H2 | 0.0772 | 0.292 | -48.58 | 0.0773 | 0.220 | 0.271 | -64.25 |
| Mo12S26H2 | 0.0749 | 0.359 | -14.62 | 0.0769 | 0.228 | 0.273 | -34.60 |
| Mo18S39H2 | 0.0748 | 0.362 | -14.26 | 0.0763 | 0.231 | 0.275 | -34.14 |
| Mo25S54H2 | 0.0748 | 0.365 | -7.13 | 0.0750 | 0.311 | 0.297 | -7.20 |
| Mo33S71H2 | 0.0748 | 0.370 | -5.59 | 0.0748 | 0.332 | 0.319 | -6.82 |
表3 氢气在不同尺寸团簇边缘位和角位的吸附结构参数、吸附能(Eads)
Table 3 Adsorption structure parameters and adsorption energy (Eads) of hydrogen at the edges and corners of clusters with different sizes
| Species | Corners | Edges | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r(H—H)/nm | r(H—S)/nm | Eads/(kJ/mol) | r(H—H)/nm | r(H—Mo)/nm | r(H—S)/nm | Eads/(kJ/mol) | |
| Mo7S15H2 | 0.0772 | 0.292 | -48.58 | 0.0773 | 0.220 | 0.271 | -64.25 |
| Mo12S26H2 | 0.0749 | 0.359 | -14.62 | 0.0769 | 0.228 | 0.273 | -34.60 |
| Mo18S39H2 | 0.0748 | 0.362 | -14.26 | 0.0763 | 0.231 | 0.275 | -34.14 |
| Mo25S54H2 | 0.0748 | 0.365 | -7.13 | 0.0750 | 0.311 | 0.297 | -7.20 |
| Mo33S71H2 | 0.0748 | 0.370 | -5.59 | 0.0748 | 0.332 | 0.319 | -6.82 |

图2 不同尺寸Mo x S y 团簇边缘位点处Mo 4d、S 3p与H 1s轨道投影态密度图:(a) Mo7S15团簇; (b) Mo12S26团簇; (c) Mo18S39团簇; (d) Mo25S54团簇; (e) Mo33S71团簇
Fig.2 PDOS of Mo 4d, S 3p and H 1s orbitals at edge sites of Mo x S y clusters with different sizes:(a) Mo7S15 clusters; (b) Mo12S26 clusters; (c) Mo18S39 clusters; (d) Mo25S54 clusters; (e) Mo33S71 clusters
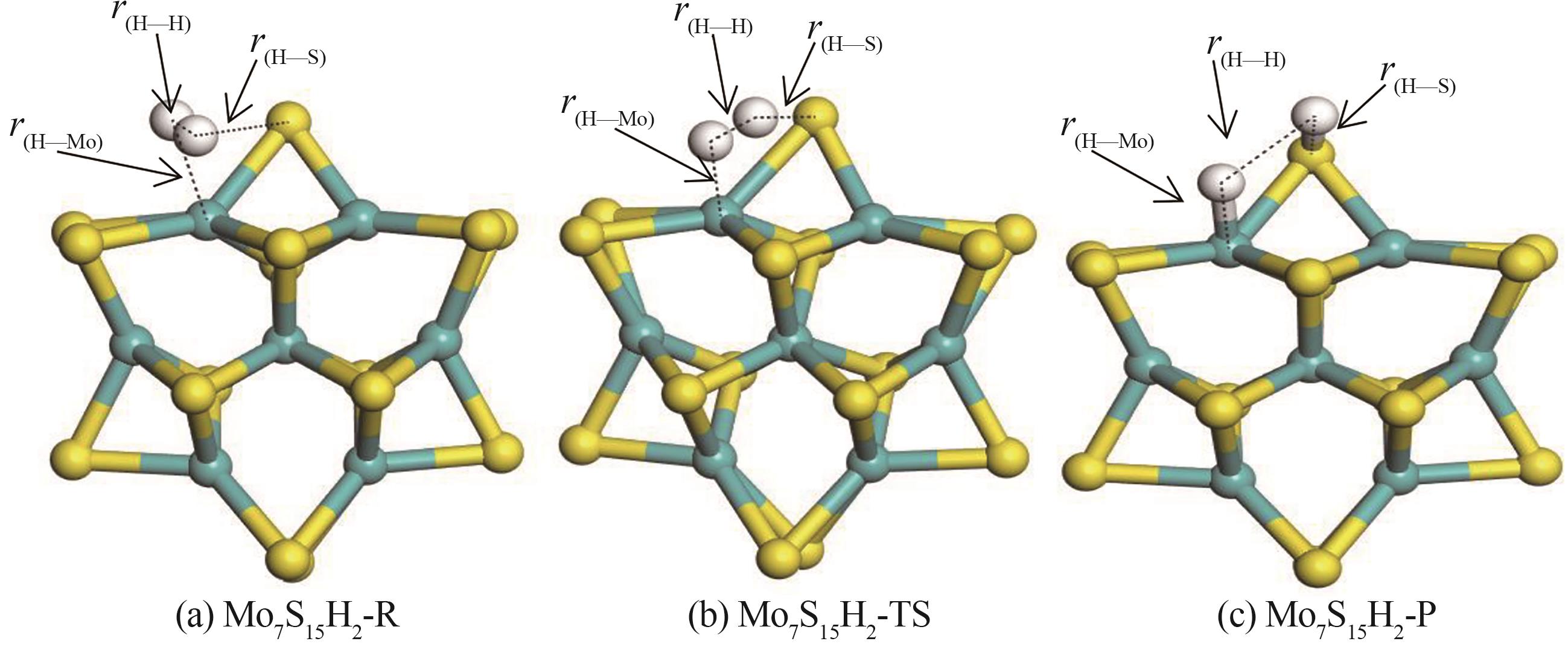
图3 H2在Mo7S15团簇上解离的初态(Mo7S15H2-R)、过渡态(Mo7S15H2-TS)及末态(Mo7S15H2-P)的优化构型
Fig.3 The optimized configuration of initial state (Mo7S15H2-R), transition state (Mo7S15H2-TS) and final state (Mo7S15H2-P) of H2 dissociation on Mo7S15 clusters
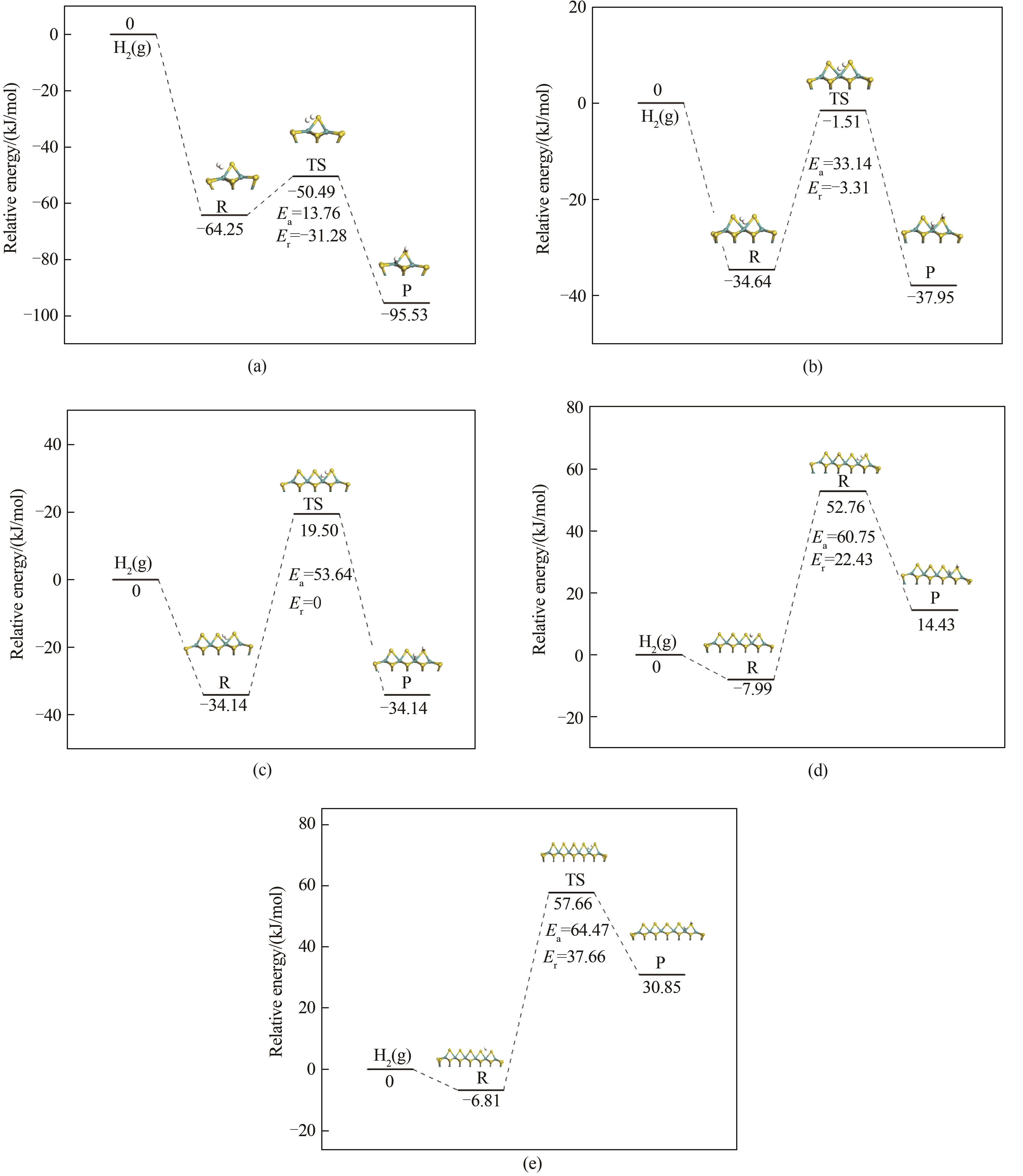
图4 氢气分子在Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71)团簇上的吸附解离过程:(a) Mo7S15团簇; (b) Mo12S26团簇; (c) Mo18S39团簇; (d) Mo25S54团簇; (e) Mo33S71团簇
Fig.4 Adsorption and dissociation process of hydrogen molecules on Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71) clusters:(a) Mo7S15 clusters; (b) Mo12S26 clusters; (c) Mo18S39 clusters; (d) Mo25S54 clusters; (e) Mo33S71 clusters
| Species | r(H—H) /nm | r(H—Mo)/nm | r(H—S) /nm | Ea/ (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo7S15H2-R | 0.0773 | 0.2200 | 0.2710 | 13.76 |
| Mo7S15H2-TS | 0.1084 | 0.1824 | 0.2553 | |
| Mo7S15H2-P | 0.2241 | 0.1693 | 0.1362 | |
| Mo12S26H2-R | 0.0769 | 0.2280 | 0.2730 | 33.14 |
| Mo12S26H2-TS | 0.1035 | 0.1828 | 0.1593 | |
| Mo12S26H2-P | 0.2310 | 0.1690 | 0.1364 | |
| Mo18S39H2-R | 0.0763 | 0.2310 | 0.2750 | 53.64 |
| Mo18S39H2-TS | 0.1102 | 0.1809 | 0.1517 | |
| Mo18S39H2-P | 0.2252 | 0.1685 | 0.1362 | |
| Mo25S54H2-R | 0.0750 | 0.3110 | 0.2970 | 60.75 |
| Mo25S54H2-TS | 0.1096 | 0.1807 | 0.1531 | |
| Mo25S54H2-P | 0.2252 | 0.1688 | 0.1361 | |
| Mo33S71H2-R | 0.0748 | 0.3320 | 0.3190 | 64.47 |
| Mo33S71H2-TS | 0.1045 | 0.1827 | 0.1576 | |
| Mo33S71H2-P | 0.2292 | 0.1690 | 0.1364 |
表4 氢气在Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71)团簇上的解离能垒Ea以及初态(R)、过渡态(TS)、末态(P)的构型参数
Table 4 Dissociation barriers Ea of hydrogen on Mo x S y (x=7,12,18,25,33; y=15,26,39,54,71) clusters and configuration parameters of initial state(R), transition states(TS) and final state(P)
| Species | r(H—H) /nm | r(H—Mo)/nm | r(H—S) /nm | Ea/ (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo7S15H2-R | 0.0773 | 0.2200 | 0.2710 | 13.76 |
| Mo7S15H2-TS | 0.1084 | 0.1824 | 0.2553 | |
| Mo7S15H2-P | 0.2241 | 0.1693 | 0.1362 | |
| Mo12S26H2-R | 0.0769 | 0.2280 | 0.2730 | 33.14 |
| Mo12S26H2-TS | 0.1035 | 0.1828 | 0.1593 | |
| Mo12S26H2-P | 0.2310 | 0.1690 | 0.1364 | |
| Mo18S39H2-R | 0.0763 | 0.2310 | 0.2750 | 53.64 |
| Mo18S39H2-TS | 0.1102 | 0.1809 | 0.1517 | |
| Mo18S39H2-P | 0.2252 | 0.1685 | 0.1362 | |
| Mo25S54H2-R | 0.0750 | 0.3110 | 0.2970 | 60.75 |
| Mo25S54H2-TS | 0.1096 | 0.1807 | 0.1531 | |
| Mo25S54H2-P | 0.2252 | 0.1688 | 0.1361 | |
| Mo33S71H2-R | 0.0748 | 0.3320 | 0.3190 | 64.47 |
| Mo33S71H2-TS | 0.1045 | 0.1827 | 0.1576 | |
| Mo33S71H2-P | 0.2292 | 0.1690 | 0.1364 |
| 31 | Bacaud R. Dispersed phase catalysis: past and future. Celebrating one century of industrial development[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 624-632. |
| 32 | Kim K D, Lee Y K. Active phase of dispersed MoS2 catalysts for slurry phase hydrocracking of vacuum residue[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 369: 111-121. |
| 1 | Energy Information Administration U.S.. Annual energy outlook 2020 with projections to 2050[R]. U. S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, 2020. |
| 2 | 刘美, 刘金东, 张树广, 等. 悬浮床重油加氢裂化技术进展[J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(12): 2435-2440. |
| Liu M, Liu J D, Zhang S G, et al. Advances of heavy oil hydrocracking in suspended bed[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(12): 2435-2440. | |
| 3 | Angeles M J, Leyva C, Ancheyta J, et al. A review of experimental procedures for heavy oil hydrocracking with dispersed catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2014, 220: 274-294. |
| 4 | Al-Attas T A, Ali S A, Zahir M H, et al. Recent advances in heavy oil upgrading using dispersed catalysts[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(9): 7917-7949. |
| 5 | Nguyen M T, Nguyen N T, Cho J, et al. A review on the oil-soluble dispersed catalyst for slurry-phase hydrocracking of heavy oil[J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2016,43(25): 1-12. |
| 6 | Varakin A N, Mozhaev A V, Pimerzin A A, et al. Toward HYD/DEC selectivity control in hydrodeoxygenation over supported and unsupported Co(Ni)-MoS2 catalysts. A key to effective dual-bed catalyst reactor for co-hydroprocessing of diesel and vegetable oil[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 357: 556-564. |
| 7 | Vutolkina A, Glotov A, Baygildin I, et al. Ni-Mo sulfide nanosized catalysts from water-soluble precursors for hydrogenation of aromatics under water gas shift conditions[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry 2020, 92: 949-966. |
| 8 | 屈丹龙, 李毅. 含油污泥高值转化过程Mo基负载催化剂的研究[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(2): 383-387. |
| Qu D L, Li Y. The preparation of Mo based catalysts for high value catalytic pyrolysis of oily sludge[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021,50(2): 383-387. | |
| 9 | Cai Z P, Ma Y D, Zhang J Y, et al. Tunable ionic liquids as oil-soluble precursors of dispersed catalysts for suspended-bed hydrocracking of heavy residues[J]. Fuel, 2022, 313: 122-130. |
| 10 | 戴咏川, 赵德智. 石油化学基础[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2009: 248. |
| Dai Y C, Zhao D Z. Fundamentals of Petrochemical[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2009: 248. | |
| 11 | Zhou X D, Ma F Y, Wu H, et al. The effects of Fe2O3 and MoS2 on the catalytic activation pathway of hydrogen sources during direct coal liquefaction[J]. Energy, 2021, 234: 121-129. |
| 12 | Travert A, Nakamura H, van Santen R A, et al. Hydrogen activation on Mo-based sulfide catalysts, a periodic DFT study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(24): 7084-7095. |
| 13 | Kadiev K M, Maximov A L, Kadieva M K. The effect of MoS2 active site dispersion on suppression of polycondensation reactions during heavy oil hydroconversion[J]. Catalysts, 2021, 11(6): 676-693. |
| 14 | Zheng A D, Wang D, Wang L, et al. Highly efficient MoS2 nanocatalysts for slurry-phase hydrogenation of unconventional feedstocks into fuels[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(3): 2590-2601. |
| 15 | 梁瑜, 赵彤, 赵斌彬, 等. WO3对Pt/α-Al2O3催化萘深度加氢的促进作用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5643-5652. |
| Liang Y, Zhao T, Zhao B B, et al. Promotion of WO3 species on Pt/α-Al2O3 for the deep hydrogenation of naphthalene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5643-5652 | |
| 16 | Ding S J, Peng S Z, Yan Z J, et al. Charge effects on quinoline hydrodenitrogenation catalyzed by Ni-Mo-S active sites—a theoretical study by DFT calculation[J]. Petroleum Science, 2022, 19(1): 339-344. |
| 17 | 魏淑贤, 李阳, 葛少辉,等. MoS2催化剂活性位形成及甲硫醇脱硫机理的研究[J].高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(4): 956-962. |
| Wei S X, Li Y, Ge S H, et al. Study on active site formation of MoS2 catalysts and their desulfurization mechanism of CH3SH[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(4): 956-962. | |
| 18 | Delley B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1990, 92(1): 508-517. |
| 19 | Delley B. Fast calculation of electrostatics in crystals and large molecules[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(15): 6107-6110. |
| 20 | Delley B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2000, 113(18): 7756-7764. |
| 21 | Perdew J P. Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas[J]. Physical Review. B, 1986, 33(12): 8822-8824. |
| 22 | Delley B. Efficient and accurate expansion methods for molecules in local density models[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1982, 76(4): 1949-1960. |
| 23 | Perdew J P, Wang Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy[J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 45(23): 13244-13249. |
| 24 | Moses P G, Hinnemann B, Topsøe H, et al. The hydrogenation and direct desulfurization reaction pathway in thiophene hydrodesulfurization over MoS2 catalysts at realistic conditions: a density functional study[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 248(2): 188-203. |
| 25 | Schweiger H, Raybaud P, Kresse G, et al. Shape and edge sites modifications of MoS2 catalytic nanoparticles induced by working conditions: a theoretical study[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 207(1): 76-87. |
| 26 | Joo P H, Cheng J L, Yang K S. Size effects and odd-even effects in MoS2 nanosheets: first-principles studies[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(44): 29927-29933. |
| 27 | Mcbride K L, Head J D. DFT investigation of MoS2 nanoclusters used as desulfurization catalysts[J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2009, 109(15): 3570-3582. |
| 28 | Govind N, Petersen M, Fitzgerald G, et al. A generalized synchronous transit method for transition state location[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2003, 28(2): 250-258 |
| 29 | Raybaud P, Hafner J, Kresse G, et al. Ab initio study of the H2-H2S/MoS2 gas-solid interface: the nature of the catalytically active sites[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2000, 189(1): 129-146. |
| 30 | Wang W, Zhao X G, Li H F, et al. DFT study of H2 dissociation on Mo x S y clusters[J]. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2015, 17(1): 16-23. |
| [1] | 俞夏琪, 冯格, 赵金燕, 李嘉远, 邓声威, 郑靖楠, 李雯雯, 王亚秋, 沈榄, 刘旭, 徐威威, 王建国, 王式彬, 姚子豪, 毛成立. 基体(TDI-TMP-T313)与氧化剂(AP)相互作用的第一性原理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3511-3517. |
| [2] | 赵继昊, 唐伟强, 徐小飞, 赵双良, 贺炅皓. 高分子复合材料中键合剂在不同纳米填料表面的吸附能计算[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3174-3181. |
| [3] | 罗小松, 黄金保, 周梅, 牟鑫, 徐伟伟, 吴雷. 对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯二聚体水/醇/氨解机理的理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 4859-4871. |
| [4] | 龚翔, 李林森, 姜召. PdCo/SiO2双金属催化剂用于杂环储氢载体的高效脱氢[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4448-4460. |
| [5] | 朱先会, 王甫, 夏杰成, 袁金良. 功能型离子液体协同吸收NH3和CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4324-4334. |
| [6] | 马生贵, 田博文, 周雨薇, 陈琳, 江霞, 高涛. 氮掺杂Stone-Wales缺陷石墨烯吸附H2S的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. |
| [7] | 张芳芳, 韩敏, 赵娟, 凌丽霞, 章日光, 王宝俊. 单空缺石墨烯负载的Pd单原子催化剂上NO还原的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1382-1391. |
| [8] | 唐伟强, 谢鹏, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 反应密度泛函理论的构建与初步应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 633-652. |
| [9] | 葛冰青, 阴义轩, 王亚溪, 张宏伟, 袁珮. 溶剂对丁腈橡胶溶解、尺寸、结构和催化加氢的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 543-554. |
| [10] | 刘佳鑫, 徐宇, 花儿. 异辛基乙二胺-酰基丙氨酸型质子化离子液体的分子间氢键相互作用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 15-22. |
| [11] | 狄玲, 陈放, 付荣荣, 杨辰, 邢杨, 王晓宁. 富电子LMOF对有机农药的检测机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3830-3838. |
| [12] | 孙巍, 左然. MMAl在NH2与H混合覆盖的AlN(0001)-Al表面的吸附与扩散研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3213-3219. |
| [13] | 张红, 唐留. p型掺杂剂Cp2Mg在MOCVD气相中的反应机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3000-3008. |
| [14] | 宫梦, 方阳, 陈伟, 陈应泉, 陆强, 杨海平, 陈汉平. 纤维素组分对氨基酸热解的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2312-2319. |
| [15] | 朱晓蓉, 李亚飞. 二维AuP2材料电催化固氮性能的理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4820-4825. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号