化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (11): 5118-5127.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221012
顾鋆鋆1,2( ), 黎睿1,2, 吴兴熠1,3, 汤显强1,2(
), 黎睿1,2, 吴兴熠1,3, 汤显强1,2( ), 胡艳平1,2
), 胡艳平1,2
收稿日期:2022-07-20
修回日期:2022-10-12
出版日期:2022-11-05
发布日期:2022-12-06
通讯作者:
汤显强
作者简介:顾鋆鋆(1998—),女,硕士研究生,gujunjun0108@foxmail.com
基金资助:
Junjun GU1,2( ), Rui LI1,2, Xingyi WU1,3, Xianqiang TANG1,2(
), Rui LI1,2, Xingyi WU1,3, Xianqiang TANG1,2( ), Yanping HU1,2
), Yanping HU1,2
Received:2022-07-20
Revised:2022-10-12
Online:2022-11-05
Published:2022-12-06
Contact:
Xianqiang TANG
摘要:
孔隙水是底泥氮素污染的主要载体和释放源头,对富含氮素的孔隙水予以分离和脱除是控制内源氮释放的潜在方案。以富营养化湖泊底泥为研究对象,采用自制底泥孔隙水电动导排装置,在上覆水深度为20 cm的条件下进行底泥孔隙水电动导排,共设置对照、重力排水(0 V/cm电压梯度)和间歇通电(0.5 V/cm电压梯度,4 h On/4 h Off)3组实验,分析了泥-水界面氮浓度及释放通量的变化特征,监测了孔隙水及底泥中氮形态、pH等理化参数,评估了电动导排孔隙水对泥-水界面氮释放通量的控制效果及影响因素。结果表明:电动导排孔隙水可有效降低泥-水界面的氮释放通量,实验进行632 h后,通电实验组泥-水界面累计DTN释放通量为282.28 mg N/m2,与对照组相比氮释放通量削减95.61%。电动导排孔隙水使阳极孔隙水呈酸性,阴极孔隙水呈碱性,pH的改变促进了底泥中可转化态氮(TTN)的活化,与重力排水相比,电动导排孔隙水后底泥离子交换态氮(IEF-N)去除率由11.11%~12.97%提升至12.59%~22.31%。电动导排孔隙水后底泥总氮脱除量为47015.72 mg/m3,累计能耗为162.38 kWh/m3。
中图分类号:
顾鋆鋆, 黎睿, 吴兴熠, 汤显强, 胡艳平. 电动导排孔隙水对泥-水界面氮释放通量的控制效果研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5118-5127.
Junjun GU, Rui LI, Xingyi WU, Xianqiang TANG, Yanping HU. Study on the control effect of electrokinetic drainage of pore water on nitrogen release flux at the mud-water interface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5118-5127.

图1 导排水组件结构图及实验装置示意图①导线保护管;②排气管;③橡胶排水管;④上覆水隔绝罩;⑤带孔有机玻璃板;⑥滤布固定条;⑦储水槽;⑧排水管;⑨滤布;⑩EKG电极板
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the structure and experimental set-up of the pore water conductive drainage assembly①wire protection tube; ②exhaust tube; ③rubber drainage tube; ④upper water insulation cover;⑤organic glass plate with holes;⑥filter cloth fixing strip; ⑦water storage tank; ⑧drain pipe;⑨filter cloth; ⑩EKG electrode plate
| 条件 | 通量范围/(mg N/m2) | 释放速率范围/(mg N/(m2·h)) | 平均释放速率/(mg N/(m2·h)) | 累计释放通量/(mg N/ m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 | 79.59~1332.03 | 2.13~26.53 | 9.15 | 6430.85 |
| 0 V/cm | -363.17~513.62 | -5.04~13.48 | 2.08 | 1461.30 |
| 0.5 V/cm | -228.00~216.52 | -9.50~6.81 | 0.45 | 282.28 |
表1 不同条件下上覆水DTN释放通量统计参数
Table 1 Statistical parameters of DTN release flux of overlying water under different conditions
| 条件 | 通量范围/(mg N/m2) | 释放速率范围/(mg N/(m2·h)) | 平均释放速率/(mg N/(m2·h)) | 累计释放通量/(mg N/ m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 | 79.59~1332.03 | 2.13~26.53 | 9.15 | 6430.85 |
| 0 V/cm | -363.17~513.62 | -5.04~13.48 | 2.08 | 1461.30 |
| 0.5 V/cm | -228.00~216.52 | -9.50~6.81 | 0.45 | 282.28 |
| 氮形态 | 去除率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 V/cm | 0.5 V/cm | ||||
| 中部 | 电极 | 阳极 | 中部 | 阴极 | |
| IEF-N | 12.97 | 11.11 | 12.59 | 22.31 | 13.26 |
| WAEF-N | -1.86 | 0.77 | 8.16 | 7.46 | 0.88 |
| SAEF-N | 6.92 | 7.08 | 3.89 | -12.56 | -35.28 |
| SOEF-N | 7.14 | 19.15 | 2.74 | 8.52 | 24.51 |
表2 导排前后底泥各提取态氮平均去除率
Table 2 Average removal rate of extracted nitrogen in sediment before and after drainage
| 氮形态 | 去除率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 V/cm | 0.5 V/cm | ||||
| 中部 | 电极 | 阳极 | 中部 | 阴极 | |
| IEF-N | 12.97 | 11.11 | 12.59 | 22.31 | 13.26 |
| WAEF-N | -1.86 | 0.77 | 8.16 | 7.46 | 0.88 |
| SAEF-N | 6.92 | 7.08 | 3.89 | -12.56 | -35.28 |
| SOEF-N | 7.14 | 19.15 | 2.74 | 8.52 | 24.51 |
| 电压梯度/(V/cm) | 位置 | 导排前有机质含量/% | 导排后有机质 含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 中部 | 9.03 | 8.29 |
| 电极 | 9.03 | 7.46 | |
| 0.5 | 阳极 | 10.96 | 9.22 |
| 中部 | 10.96 | 8.46 | |
| 阴极 | 10.96 | 7.48 |
表3 导排前后底泥有机质含量
Table 3 Organic matter content of sediment before and after drainage
| 电压梯度/(V/cm) | 位置 | 导排前有机质含量/% | 导排后有机质 含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 中部 | 9.03 | 8.29 |
| 电极 | 9.03 | 7.46 | |
| 0.5 | 阳极 | 10.96 | 9.22 |
| 中部 | 10.96 | 8.46 | |
| 阴极 | 10.96 | 7.48 |
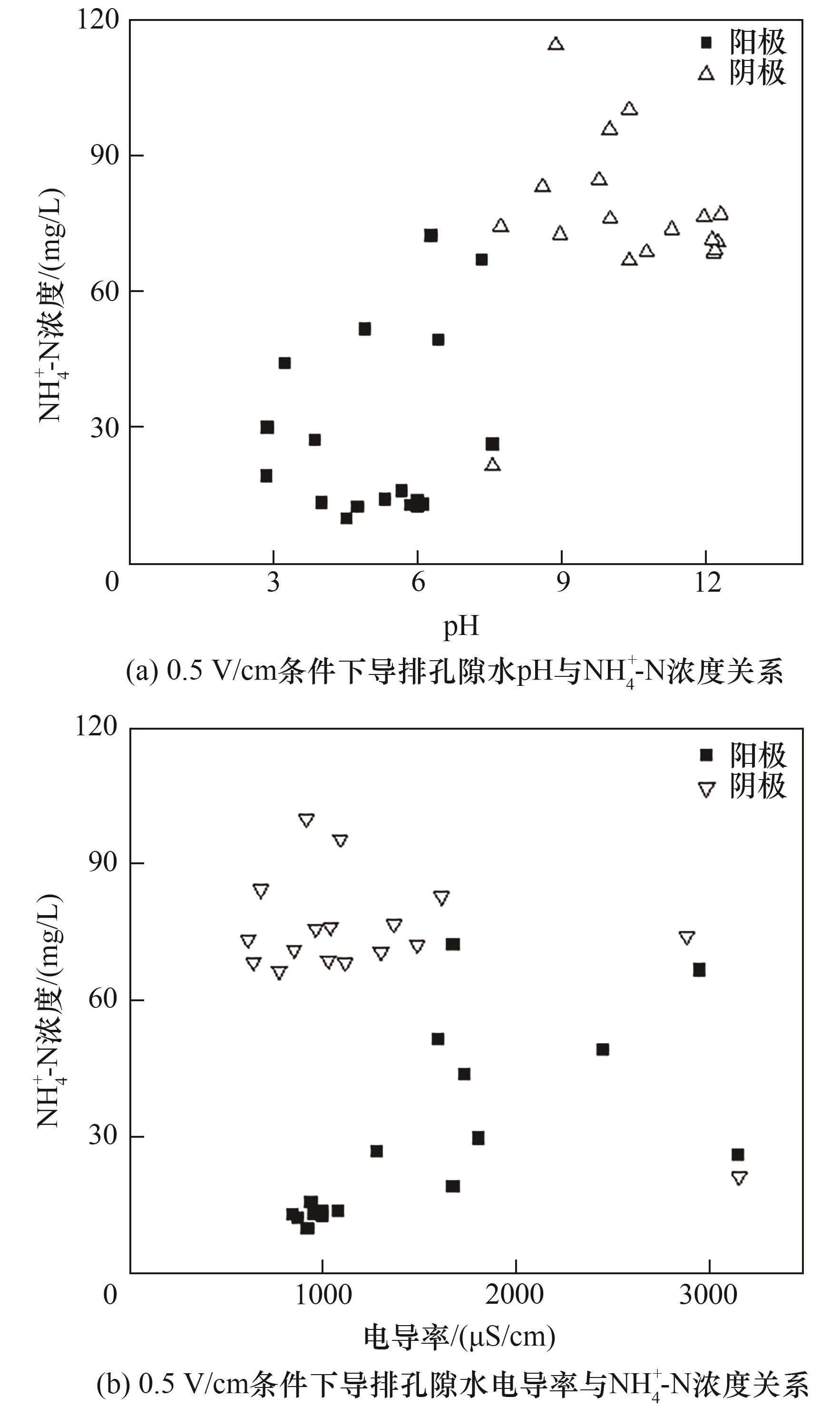
图7 0.5 V/cm条件下导排孔隙水pH、电导率与NH4+-N浓度关系
Fig.7 Relationship between pH value, conductivity and NH4+-N concentration of drainage pore water under 0.5 V/cm voltage gradient
| 土壤/底泥性质 | 修复目的 | 电极材料及供电方式 | 电压梯度/(V/cm) | 修复时间 | 修复效果 | 能耗/(kWh/m3) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 湖泊沉积物 | 电渗排水除磷 | EKG组件,12 h On/12 h Off间歇通电 | 0.5 | 6 d | 含水率减少4.6%,总磷含量减少112.65 mg/kg | 102.7 | [ |
| 沙壤土,含水率38% | 脱除土壤中的Cr | EKG组件,12 h On/12 h Off间歇通电 | 2 | 7 d | 铬除去率为41.98% | 63.13 | [ |
| 沟渠沉积物,含水率5.8% | 脱除沉积物中六氯苯HCB和锌Zn | 阳极石墨棒,阴极钢管,持续通电 | 0.2~0.4 | 100 d | HCB平均含量由23.6 mg/kg降至21 mg/kg,Zn整体平均含量变化不大 | 563 | [ |
| 疏浚底泥,含水率38.72% | 电渗排水 | 阳极镀锌铁丝,阴极氯化聚丙烯管,持续通电 | 0.3 | 183 h | 含水率下降至33.43% | 7.16 | [ |
表4 电动修复案例
Table 4 Cases of electric remediation of soil
| 土壤/底泥性质 | 修复目的 | 电极材料及供电方式 | 电压梯度/(V/cm) | 修复时间 | 修复效果 | 能耗/(kWh/m3) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 湖泊沉积物 | 电渗排水除磷 | EKG组件,12 h On/12 h Off间歇通电 | 0.5 | 6 d | 含水率减少4.6%,总磷含量减少112.65 mg/kg | 102.7 | [ |
| 沙壤土,含水率38% | 脱除土壤中的Cr | EKG组件,12 h On/12 h Off间歇通电 | 2 | 7 d | 铬除去率为41.98% | 63.13 | [ |
| 沟渠沉积物,含水率5.8% | 脱除沉积物中六氯苯HCB和锌Zn | 阳极石墨棒,阴极钢管,持续通电 | 0.2~0.4 | 100 d | HCB平均含量由23.6 mg/kg降至21 mg/kg,Zn整体平均含量变化不大 | 563 | [ |
| 疏浚底泥,含水率38.72% | 电渗排水 | 阳极镀锌铁丝,阴极氯化聚丙烯管,持续通电 | 0.3 | 183 h | 含水率下降至33.43% | 7.16 | [ |
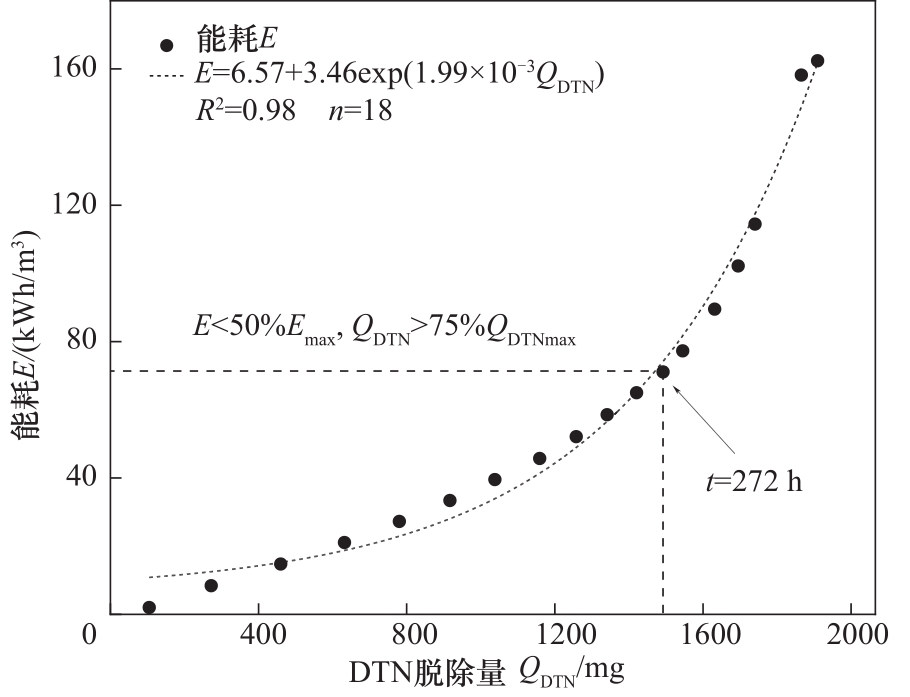
图 8 电动导排孔隙水修复累计能耗与DTN脱除量关系曲线
Fig.8 Relation curve between cumulative energy consumption of electric drainage pore water remediation and DTN removal amount
| 1 | 李宝, 丁士明, 范成新, 等. 滇池福保湾底泥内源氮磷营养盐释放通量估算[J].环境科学,2008, 29(1): 114-120. |
| Li B, Ding S M, Fan C X, et al. Estimation of releasing fluxes of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Fubao Bay in Dianchi Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(1): 114-120. | |
| 2 | Yu J H, Fan C X, Zhong J C, et al. Evaluation of in situ simulated dredging to reduce internal nitrogen flux across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 866-877. |
| 3 | 于飞. 东江(惠州段)及其支流沉积物氮磷分布状况与覆盖修复技术研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2012. |
| Yu F. Distribution characteristics of phosphorus and nitrogen in surface sediments of the Dongjiang River and its tributaries in Huizhou and capping technology for remediation[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2012. | |
| 4 | Kang K, Kim W J, Park S J. Application of activated carbon and crushed concrete as capping material for interrupting the release of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic substance from reservoir sediments[J]. Journal of the Korean Society of Agricultural Engineers, 2016, 58(2): 1-9. |
| 5 | 范成新, 张路, 王建军, 等. 湖泊底泥疏浚对内源释放影响的过程与机理[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(15): 1523-1528. |
| Fan C X, Zhang L, Wang J J, et al. Process and mechanism of the effect of lake sediment dredging on endogenous release [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15): 1523-1528. | |
| 6 | Liu C, Zhong J C, Wang J J, et al. Fifteen-year study of environmental dredging effect on variation of nitrogen and phosphorus exchange across the sediment-water interface of an urban lake[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 639-648. |
| 7 | 陈重军, 潘钰伟, 谢嘉玮, 等. 河流污染底泥原位覆盖材料及其应用研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(1): 100-109. |
| Chen C J, Pan Y W, Xie J W, et al. Research progress of in situ covering materials for river polluted sediment and their applications [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2022, 12(1): 100-109. | |
| 8 | Booij K, Hoedemaker J R, Bakker J F. Dissolved PCBs, PAHs, and HCB in pore waters and overlying waters of contaminated harbor sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(18): 4213-4220. |
| 9 | 胡俊, 刘永定, 刘剑彤. 滇池沉积物间隙水中氮、磷形态及相关性的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005, 25(10): 1391-1396. |
| Hu J, Liu Y D, Liu J T. Studying on the form and the relativity of nitrogen and phosphorus in the pore water of sediment in Dianchi Lake[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(10): 1391-1396. | |
| 10 | Li S S, Zheng C Q, Yang S Q, et al. Reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus loading from polluted sediment by electrolysis[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2021, 159: 106088. |
| 11 | 罗启仕, 王慧, 张锡辉, 等. 土壤中硝酸盐在非均匀电动力学作用下的迁移与转化[J]. 环境科学, 2004, 25(2): 98-103. |
| Luo Q S, Wang H, Zhang X H, et al. Movement and transformation of nitrate in soil by non-uniform electrokinetics[J]. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(2): 98-103. | |
| 12 | 吴兴熠, 黎睿, 汤显强, 等. 电动导排间隙水脱除底泥内源氮的性能[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(3): 1208-1218. |
| Wu X Y, Li R, Tang X Q, et al. Performance of separating sediment endogenous nitrogen via electrokinetic drainage of pore water[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(3): 1208-1218. | |
| 13 | 胡天怡, 胡悦, 赵立坤, 等. 黑臭底泥的电渗脱水特性及污染物迁移规律[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(10): 103-110. |
| Hu T Y, Hu Y, Zhao L K, et al. Study on dewatering characteristics and pollutant migration of black-odorous river sediments during electroosmotic operation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(10): 103-110. | |
| 14 | 赖江钿, 程明双, 余光伟, 等. 利用电动修复技术原位氧化去除黑臭底泥还原性污染物的室内模拟实验[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(7): 1779-1788. |
| Lai J T, Cheng M S, Yu G W, et al. Indoor simulation experiment of in situ oxidation removing the reductive pollutants in black-odorous river sediment with electrokinetic remediation[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(7): 1779-1788. | |
| 15 | 汤显强, 李青云, 胡艳平, 等. 一种基于孔隙水导排的河湖污染底泥原位减量除污装置: 207671889U[P]. 2018-07-31. |
| Tang X Q, Li Q Y, Hu Y P, et al. Bed mud normal position decrement scrubbing device is polluted in river lake based on hole water drainage guide: 207671889U[P]. 2018-07-31. | |
| 16 | 王圣瑞. 湖泊沉积物—水界面过程——基本理论与常用测定方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. |
| Wang S R. Sediment-water Interface Process of Lakes: Basic Theory and Common Measurement Methods [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. | |
| 17 | 蔡传伦. 电动修复技术去除太湖沉积物中氮磷污染的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018. |
| Cai C L. Study on electrokinetic remediation technology to remove N and P pollution from sediments in Taihu Lake[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 18 | 黄琨, 万军伟, 陈刚, 等. 非饱和土的抗剪强度与含水率关系的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(9): 2600-2604. |
| Huang K, Wan J W, Chen G, et al. Testing study of relationship between water content and shear strength of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 2600-2604. | |
| 19 | 吴辉, 胡黎明. 考虑电导率变化的电渗固结模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(4): 734-738. |
| Wu H, Hu L M. Numerical simulation of electro-osmosis consolidation considering variation of electrical conductivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(4): 734-738. | |
| 20 | Wen D D, Fu R B, Li Q. Removal of inorganic contaminants in soil by electrokinetic remediation technologies: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123345. |
| 21 | Virkutyte J, Sillanpää M, Latostenmaa P. Electrokinetic soil remediation—critical overview[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 289(1/2/3): 97-121. |
| 22 | Kim K W, Kim Y J, Kim I T, et al. Electrochemical conversion characteristics of ammonia to nitrogen[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(7): 1431-1441. |
| 23 | 周睿, 袁旭音, Marip Ja Bawk, 等. 不同湖泊入湖河流沉积物可转化态氮的空间分布及其影响因素[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 1122-1128. |
| Zhou R, Yuan X Y, Bawk M, et al. Spatial distributions of transferable nitrogen forms and influencing factors in sediments from inflow rivers in different lake basins[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(3): 1122-1128. | |
| 24 | 吕晓霞, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 南黄海表层沉积物中氮的潜在生态学功能[J]. 生态学报, 2004(8): 1635-1643. |
| Lü X X, Song J M, Yuan H M, et al. The potential ecological roles of nitrogen in the surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(8): 1635-1643. | |
| 25 | Garcia-Segura S, Lanzarini-Lopes M, Hristovski K, et al. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate: fundamentals to full-scale water treatment applications[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 236: 546-568. |
| 26 | 赵宝刚, 张夏彬, 昝逢宇, 等. 不同湖泊表层沉积物氮形态的分布特征与影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(2): 837-847. |
| Zhao B G, Zhang X B, Zan F Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen forms in surface sediments of different lakes[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(2): 837-847. | |
| 27 | 李俊国, 王凡, 冯艳平, 等. 氢气还原海绵铁去除水体中硝酸盐的研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(12): 76-80. |
| Li J G, Wang F, Feng Y P, et al. Nitrate removal from water by spherical sponge iron prepared by H2 reduction[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 33(12): 76-80. | |
| 28 | 姜人源, 朱顺妮, 王忠铭, 等. 不同pH条件下小球藻氨氮处理及生物质生产能力[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(9): 42-47. |
| Jiang R Y, Zhu S N, Wang Z M, et al. Research on Chlorella’s ammonia nitrogen treatment ability and biomass production under different pH conditions[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(9): 42-47. | |
| 29 | Zhao X C, Tan X B, Yang L B, et al. Cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa in anaerobic wastewater: the coupled effects of ammonium, temperature and pH conditions on lipids compositions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 284: 90-97. |
| 30 | 任丽娟, 林敏, 董仁杰, 等. 厌氧消化灭活畜禽粪污中病原菌的研究进展[J]. 中国沼气, 2021, 39(6): 22-31. |
| Ren L J, Lin M, Dong R J, et al. Pathogen inactivation of livestock and poultry manure through anaerobic digestion: a review[J]. China Biogas, 2021, 39(6): 22-31. | |
| 31 | Reyter D, Bélanger D, Roué L. Nitrate removal by a paired electrolysis on copper and Ti/IrO2 coupled electrodes - Influence of the anode/cathode surface area ratio[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(6): 1918-1926. |
| 32 | 庄源益, 戴树桂, 张明顺. 水中氨氮挥发影响因素探讨[J]. 环境化学, 1995, 14(4): 343-346. |
| Zhuang Y Y, Dai S G, Zhang M S. A preliminary study on factors influened the volatilization of ammonia from water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1995, 14(4): 343-346. | |
| 33 | 沈叔云, 何岩, 黄民生, 等. 曝气扰动对泥水界面硝化-反硝化性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(10): 4153-4158. |
| Shen S Y, He Y, Huang M S, et al. Effects of aerating disturbances on nitrification-denitrification at sediment-water interface[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(10): 4153-4158. | |
| 34 | Kim W S, Jeon E K, Jung J M, et al. Field application of electrokinetic remediation for multi-metal contaminated paddy soil using two-dimensional electrode configuration[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2014, 21(6): 4482-4491. |
| 35 | Tang X Q, Li R, Han D, et al. Impacts of electrokinetic isolation of phosphorus through pore water drainage on sediment phosphorus storage dynamics[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 115210. |
| 36 | 刘欢, 孔维苇, 王晓锋, 等. 重庆梁滩河表层沉积物氮形态时空特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6): 332-341. |
| Liu H, Kong W W, Wang X F, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen morphology in surface sediments of Liangtan river,Chongqing[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 332-341. | |
| 37 | 李泰平, 袁松虎, 林莉, 等. 电动力学修复对沉积物理化性质的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(2): 57-60, 67. |
| Li T P, Yuan S H, Lin L, et al. Examining changes of physico-chemical characteristics of contaminated sediment after electrokinetic remediation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 33(2): 57-60, 67. | |
| 38 | Mohamedelhassan E, Shang J Q. Effects of electrode materials and current intermittence in electro-osmosis[J]. Ground Improvement, 2001, 5(1): 3-11. |
| 39 | Tang X Q, Li Q Y, Wang Z H, et al. In situ electrokinetic isolation of cadmium from paddy soil through pore water drainage: effects of voltage gradient and soil moisture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 337: 210-219. |
| 40 | Li T P, Yuan S H, Wan J Z, et al. Pilot-scale electrokinetic movement of HCB and Zn in real contaminated sediments enhanced with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 76(9): 1226-1232. |
| 41 | 陈雄峰, 荆一凤, 吕鑑, 等. 电渗法对太湖环保疏浚底泥脱水干化研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2006, 19(5): 54-58. |
| Chen X F, Jing Y F, Lü J, et al. The research of environmental dredged sludge dewatering in Taihu Lake by electro-osmotic[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(5): 54-58. |
| [1] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [5] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [6] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [7] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [9] | 朱理想, 罗默也, 张晓东, 龙涛, 余冉. 醌指纹法指示三氯乙烯污染土功能微生物活性应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2647-2654. |
| [10] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| [11] | 胡南, 陶德敏, 杨照岚, 王学兵, 张向旭, 刘玉龙, 丁德馨. 铁炭微电解与硫酸盐还原菌耦合修复铀尾矿库渗滤水的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2655-2667. |
| [12] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [13] | 黄磊, 孔令学, 白进, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 李平, 李文. 油页岩添加对准东高钠煤灰熔融行为影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2123-2135. |
| [14] | 郭旭, 张永政, 夏厚兵, 杨娜, 朱真珍, 齐晶瑶. 碳基材料电氧化去除水体污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [15] | 张正, 何永平, 孙海东, 张荣子, 孙正平, 陈金兰, 郑一璇, 杜晓, 郝晓刚. 蛇形流场电控离子交换装置用于选择性提锂[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号