化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (7): 2709-2722.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240040
• 材料化学工程与纳米技术 • 上一篇
杜海燕1( ), 朱凯1, 游峰2, 王金凤1, 赵一帆1, 张楠1, 李英3
), 朱凯1, 游峰2, 王金凤1, 赵一帆1, 张楠1, 李英3
收稿日期:2024-01-09
修回日期:2024-04-28
出版日期:2024-07-25
发布日期:2024-08-09
通讯作者:
杜海燕
作者简介:杜海燕(1982—),女,博士,副教授,duhaiyan428@163.com
基金资助:
Haiyan DU1( ), Kai ZHU1, Feng YOU2, Jinfeng WANG1, Yifan ZHAO1, Nan ZHANG1, Ying LI3
), Kai ZHU1, Feng YOU2, Jinfeng WANG1, Yifan ZHAO1, Nan ZHANG1, Ying LI3
Received:2024-01-09
Revised:2024-04-28
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-09
Contact:
Haiyan DU
摘要:
近年来,导电水凝胶在电子驱动器、医疗监测传感器及可穿戴设备等领域的应用备受关注。然而,多数凝胶机械强度低、寿命短、抗冻性能差,从而导致低温下无法使用。为了解决该问题,以聚乙烯醇、离子液体1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑四氟硼酸盐和植酸为原料,在水与二甲基亚砜(DMSO)二元溶液中借助多重氢键及离子基团间的静电作用实现了超分子自组装,制备出一种可用于应变传感的自愈合、耐低温多功能离子水凝胶。研究发现在凝胶中引入DMSO,凝胶表现出优异的抗冻能力;同时,调节DMSO的含量可优化凝胶的强度和韧性,当DMSO体积分数为40%时,最大拉伸强度和断裂伸长率分别可达4.43 MPa和869.1%。该离子水凝胶在低温应变传感器、智能可穿戴响应元件等领域展现出较好的应用潜力。
中图分类号:
杜海燕, 朱凯, 游峰, 王金凤, 赵一帆, 张楠, 李英. 用于应变传感器的自愈合抗冻离子水凝胶[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2709-2722.
Haiyan DU, Kai ZHU, Feng YOU, Jinfeng WANG, Yifan ZHAO, Nan ZHANG, Ying LI. Self-healing anti-freezing ionic hydrogel for strain sensors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2709-2722.
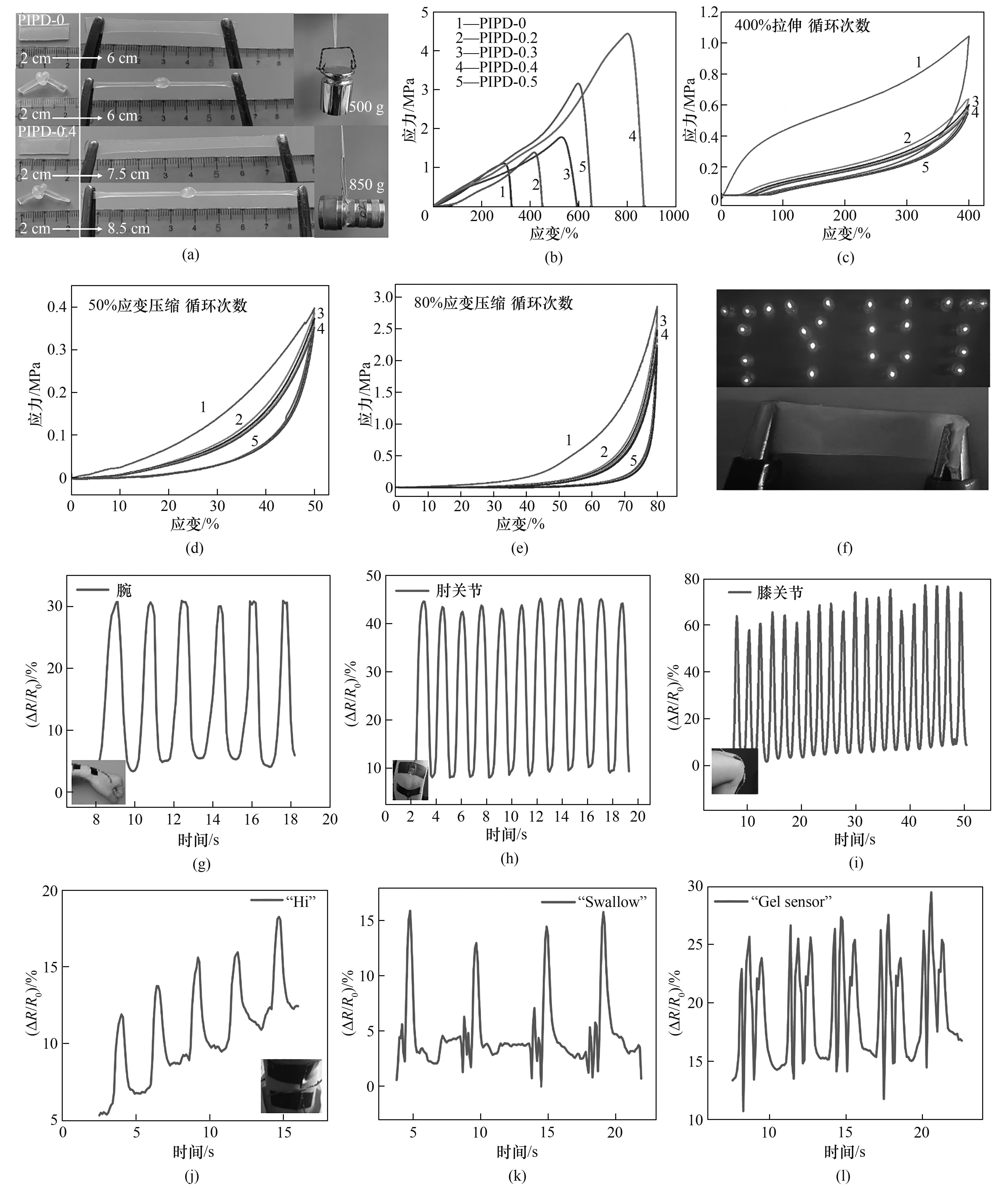
图4 PIPD凝胶的拉伸宏观图(a);PIPD凝胶应力应变曲线(b);PIPD-0.4凝胶循环拉伸和循环压缩测试[(c)~(e)];PIPD凝胶的电导率、应变传感及语音识别测试[(f)~(l)]
Fig.4 Stretched macrograph of PIPD gels (a); Stress-strain curves of PIPD gels (b); Cyclic tensile and cyclic compression test of PIPD-0.4 gel [(c)—(e)]; Electrical conductivity, strain sensing and speech recognition testing of PIPD gels [(f)—(l)]

图6 PIPD凝胶的自愈合宏观图和拉伸曲线[(a)~(f)];自愈合机理(g);愈合前后的凝胶的流变性能曲线[(h)、(i)]
Fig.6 Self-healing macrograph and tensile curves of PIPD gels [(a)—(f)]; Self-healing mechanism (g); The rheological performance curves of original and healed gels [(h),(i)]
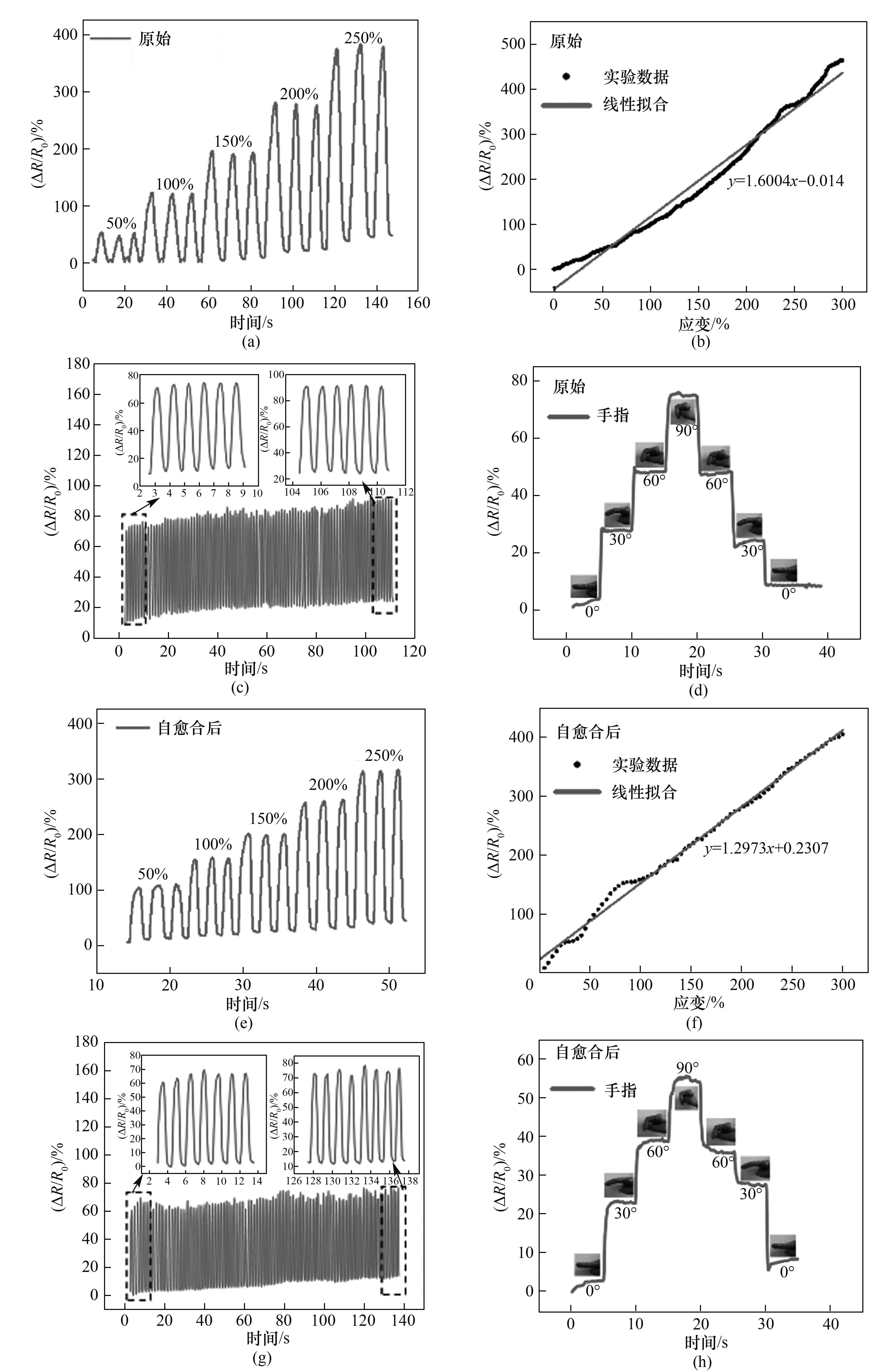
图7 PIPD-0.4凝胶自愈合前后的应变传感响应:应变对电阻的影响[(a)、(e)];灵敏度拟合曲线[(b)、(f)];应变传感稳定性测试[(c)、(g)];对手指关节的实时监测[(d)、(h)]
Fig.7 Strain sensing response of PIPD-0.4 gel before and after self-healing: Impact of strain on resistance [(a),(e)]; Sensitivity fitting curve [(b),(f)]; Strain sensing stability test[(c),(g)]; Real-time detection of finger joints [(d),(h)]

图8 PIPD凝胶在25℃及-25℃下7 d的宏观图及质量损失曲线[(a)~(c)]; PIPD-0和PIPD-0.4的DSC曲线(d);PIPD凝胶在低温下(-25℃)的应变传感[(e)~(h)]
Fig.8 Macrograph and mass loss curve of PIPD gels at 25℃ and -25℃ for 7 days [(a)—(c)]; DSC curves of PIPD-0 and PIPD-0.4 (d); Strain sensing of PIPD gels at low temperature (-25℃) [(e)—(h)]
| 1 | Amoli V, Kim J S, Kim S Y, et al. Ionic tactile sensors for emerging human-interactive technologies: a review of recent progress[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(20): 4532-4563. |
| 2 | Li P J, Yang X T, Chen F X, et al. Confined water dominates ion/molecule transport in hydrogel nanochannels[J]. Nano Letters, 2024, 24(3): 897-904. |
| 3 | Lee J H, Cho K, Kim J K. Age of flexible electronics: emerging trends in soft multifunctional sensors[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(16): 505-536. |
| 4 | Chu Z M, Jiao W C, Huang Y F, et al. Superhydrophobic gradient wrinkle strain sensor with ultra-high sensitivity and broad strain range for motion monitoring[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(15): 9634-9643. |
| 5 | Ma L L, Wang J X, He J M, et al. Ultra-sensitive, durable and stretchable ionic skins with biomimetic micronanostructures for multi-signal detection, high-precision motion monitoring, and underwater sensing[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(47): 26949-26962. |
| 6 | Jiang C C, Lai X J, Wu Z Z, et al. A high-thermopower ionic hydrogel for intelligent fire protection[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(40): 21368-21378. |
| 7 | 王雨柔, 王国琪, 李想, 等. 溶液法制备柔性压阻式传感器的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 214-228. |
| Wang Y R, Wang G Q, Li X, et al. Research progress of flexible piezoresistive sensors prepared by solution-based processing[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(2): 214-228. | |
| 8 | Sher M, Shah L A, Ara L, et al. Xanthan gum toughen ionically conductive hydrogels for flexible and artificial epidermis sensors with multifunctionality and self-healability[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2024, 370: 199-209. |
| 9 | Rong Q F, Lei W W, Huang J, et al. Low temperature tolerant organohydrogel electrolytes for flexible solid‐state supercapacitors[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(31): 1967-1973. |
| 10 | Wei P L, Chen T, Chen G Y, et al. Conductive self-healing nanocomposite hydrogel skin sensors with antifreezing and thermoresponsive properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(2): 3068-3079. |
| 11 | Yu J, Feng Y F, Sun D, et al. Highly conductive and mechanically robust cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels with antifreezing and antidehydration performances for flexible humidity sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(8): 10886-10897. |
| 12 | Pan S X, Xia M, Li H H, et al. Transparent, high-strength, stretchable, sensitive and anti-freezing poly(vinyl alcohol) ionic hydrogel strain sensors for human motion monitoring[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(8): 2827-2837. |
| 13 | Yiming B, Guo X, Ali N, et al. Ambiently and mechanically stable ionogels for soft ionotronics[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(33): 2102773. |
| 14 | Vishnyakov A, Lyubartsev A P, Laaksonen A. Molecular dynamics simulations of dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl sulfoxide- water mixture[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001, 105(10): 1702-1710. |
| 15 | Wong D B, Sokolowsky K P, El-Barghouthi M I, et al. Water dynamics in water/DMSO binary mixtures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2012, 116(18): 5479-5490. |
| 16 | 郑夏, 刘建亭, 刘樟, 等. 仿生控冰材料用于细胞及组织的冷冻保存[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 729-741. |
| Zheng X, Liu J T, Liu Z, et al. Bio-inspired ice-controlling materials for cryopreservation of cells and tissues[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 729-741. | |
| 17 | Ye Y H, Zhang Y F, Chen Y, et al. Cellulose nanofibrils enhanced, strong, stretchable, freezing‐tolerant ionic conductive organohydrogel for multi-functional sensors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(35): 3430-3441. |
| 18 | Sebastian S, Rohila Y, Yadav E, et al. Supramolecular organo/hydrogel-fabricated long alkyl chain α-amidoamides as a smart soft material for pH-responsive curcumin release[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2024, 25(2): 975-989. |
| 19 | Nita L E, Chiriac A P, Ghilan A, et al. Alginate enriched with phytic acid for hydrogels preparation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 181: 561-571. |
| 20 | Zhang S, Zhang Y H, Li B, et al. One-step preparation of a highly stretchable, conductive, and transparent poly(vinyl alcohol)-phytic acid hydrogel for casual writing circuits[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(35): 32441-32448. |
| 21 | Zhao Y Z, Liang Q D, Mugo S M, et al. Self‐healing and shape‐editable wearable supercapacitors based on highly stretchable hydrogel electrolytes[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(24): 39-51. |
| 22 | Gu C N, Wang M K, Zhang K H, et al. A full‐device autonomous self‐healing stretchable soft battery from self‐bonded eutectogels[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(6): 8392-8404. |
| 23 | Marolt G, Šala M, Pihlar B. Voltammetric investigation of iron(Ⅲ) interactions with phytate[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 176: 1116-1125. |
| 24 | Dang D Q, Park N, Kim J, et al. Dual‐crosslinked hydrogels with metal coordination from novel co‐polyaspartamide containing 1,2‐dihydroxy and imidazole pendant groups[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2021, 138(43): 51278-51290. |
| 25 | Yang H C, Guo X J, Chen R R, et al. A hybrid sponge with guanidine and phytic acid enriched surface for integration of antibiofouling and uranium uptake from seawater[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 525: 146611-146622. |
| 26 | Feng E K, Li X, Li J J, et al. Stretchable, healable, adhesive, transparent, anti-drying and anti-freezing organohydrogels toward multi-functional sensors and information platforms[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(43): 15530-15541. |
| 27 | Xia Y L, He Y, Zhang F H, et al. A review of shape memory polymers and composites: mechanisms, materials, and applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(6): 713-745. |
| 28 | Hu L X, Chee P L, Sugiarto S, et al. Hydrogel‐based flexible electronics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(14): 5326-5357. |
| 29 | Liu Y Z, Wang W Q, Gu K, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with integrated toughness, conductivity, and freezing tolerance based on ionic liquid/water binary solvent systems[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(24): 29008-29020. |
| 30 | 刘玲玲, 丁蕾, 徐莉, 等. 化学交联聚乙烯醇改性纤维素碱性阴离子交换复合膜的制备与性能[J]. 物理化学学报, 2011, 27(11): 2665-2670. |
| Liu L L, Ding L, Xu L, et al. Synthesis and properties of chemically cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) modified quaterized hydroxyethylcellulose ethoxylate as novel alkaline anion-exchange membrane[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2011, 27(11): 2665-2670. | |
| 31 | 陈玉娟, 王燕鸿, 樊栓狮, 等. 不同浓度聚乙烯醇对甲烷水合物分解作用的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(22): 2253-2258. |
| Chen Y J, Wang Y H, Fan S S., et al. Molecular dynamic simulation of methane hydrate decomposition with polyvinyl alcohol at different concentrations[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(22): 2253-2258. | |
| 32 | Xu L J, Gao S, Guo Q R, et al. A solvent‐exchange strategy to regulate noncovalent interactions for strong and antiswelling hydrogels[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(52): 4579-4585. |
| 33 | Hu R F, Zhao J, Wang Y H, et al. A highly stretchable, self-healing, recyclable and interfacial adhesion gel: preparation, characterization and applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 334-341. |
| 34 | Liu Y N, Li H L, Wang X, et al. Flexible supercapacitors with high capacitance retention at temperatures from -20 to 100℃ based on DMSO-doped polymer hydrogel electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(20): 12051-12059. |
| 35 | Thakur K, Rajhans A, Kandasubramanian B. Starch/PVA hydrogels for oil/water separation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(31): 32013-32028. |
| 36 | Zhu B D, Ma D Z, Wang J, et al. Structure and properties of semi-interpenetrating network hydrogel based on starch[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 133: 448-455. |
| 37 | Heimer N E, Del Sesto R E, Meng Z Z, et al. Vibrational spectra of imidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2006, 124(1/2/3): 84-95. |
| 38 | Feng W Q, Lu Y H, Chen Y, et al. Thermal stability of imidazolium-based ionic liquids investigated by TG and FTIR techniques[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 125(1): 143-154. |
| 39 | Sakai H, Ikemoto Y, Kinoshita T, et al. Fourier-transform spectra of metal salts of phytic acid in the mid- to far-infrared spectral range[J]. Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2017, 92: 215-219. |
| 40 | Klemenkova Z S, Kononova E G. Elucidation of the water-DMSO mixing process based on an IR study[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 2015, 44(2): 280-292. |
| 41 | Kannan P P, Karthick N K, Mahendraprabu A, et al. Red/blue shifting hydrogen bonds in acetonitrile-dimethyl sulphoxide solutions: FTIR and theoretical studies[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2017, 1139: 196-201. |
| 42 | Deyab M A, Zaky M T, Nessim M I. Inhibition of acid corrosion of carbon steel using four imidazolium tetrafluoroborates ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 229: 396-404. |
| 43 | Wang B X, Xu W, Yang Z C, et al. An overview on recent progress of the hydrogels: from material resources, properties, to functional applications[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2022, 43(6): 785-806. |
| 44 | Bai R B, Yang J W, Morelle X P, et al. Fatigue fracture of self-recovery hydrogels[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2018, 7(3): 312-317. |
| 45 | Fu D, Huang G Q, Xie Y, et al. Novel uracil-functionalized poly(ionic liquid) hydrogel: highly stretchable and sensitive as a direct wearable ionic skin for human motion detection[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(8): 11062-11075. |
| 46 | He W D, Guo X C, Xia P, et al. Temperature and pressure sensitive ionic conductive triple-network hydrogel for high-durability dual signal sensors[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 647: 456-466. |
| 47 | Wu J T, Xia G J, Li S B, et al. A flexible and self-healable gelled polymer electrolyte based on a dynamically cross-linked PVA ionogel for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(52): 22509-22519. |
| 48 | Peng F, Li G Z, Liu X X, et al. Redox-responsive gel-sol/sol-gel transition in poly(acrylic acid) aqueous solution containing Fe(Ⅲ) ions switched by light[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(48): 16166-16167. |
| 49 | 王姣, 姚虹, 周琦, 等. 基于柱[5]芳烃主客体包结构筑分子响应型超分子水凝胶[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(1): 175-180. |
| Wang J, Yao H, Zhou Q, et al. Molecule-responsive supramolecular hydrogel constructed from pillar[5]arene based on host-guest system[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(1): 175-180. | |
| 50 | Zhang Y P, Xu J H, Wang H B. Bio-based, self-adhesive, and self-healing ionogel with excellent mechanical properties for flexible strain sensor[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(59): 37661-37666. |
| 51 | Lan J, Li Y S, Yan B, et al. Transparent stretchable dual-network ionogel with temperature tolerance for high-performance flexible strain sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(33): 37597-37606. |
| [1] | 贾娟, 杨扬, 朱恂, 叶丁丁, 陈蓉, 廖强. 用于伤口敷料的水凝胶电刺激释药性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2700-2708. |
| [2] | 张广宇, 付然飞, 孙冰, 袁俊聪, 冯翔, 杨朝合, 徐伟. CO2-环氧丙烷合成碳酸丙烯酯:氢键供体效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2243-2251. |
| [3] | 武颖韬, 费立涵, 孔祥东, 王帜, 汤成龙, 黄佐华. 咪唑二氰胺离子液体掺混糠醇的自燃及推进性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2017-2025. |
| [4] | 张文惠, 唐茹意, 崔希利, 邢华斌. 羧酸端基Y型全氟聚醚的氟谱解析及结构表征[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1718-1723. |
| [5] | 蒋方涛, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志, 张晶. 基于[bmim][BF4]相转移催化的氟代碳酸乙烯酯高效合成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1543-1551. |
| [6] | 王瑞瑞, 金颖, 刘玉梅, 李梦悦, 朱胜文, 闫瑞一, 刘瑞霞. 聚合离子液体设计及催化环己烷选择性氧化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1552-1564. |
| [7] | 肖扬可, 常印龙, 李平, 王文俊, 李伯耿, 刘平伟. 动态化学交联聚烯烃类弹性体研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1394-1413. |
| [8] | 刘静, 杨文博, 吕英迪, 陶胜洋. 喷雾-反溶剂结晶法制备掺杂铝粉的复合微球[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1724-1734. |
| [9] | 吴立盛, 刘杰, 王添添, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 开环易位烯烃聚合物的动态交联改性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1118-1136. |
| [10] | 成文凯, 颜金钰, 王嘉骏, 冯连芳. 卧式捏合反应器及其在聚合工业中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 768-781. |
| [11] | 肖拥君, 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军, 刘洪来. 反向传播神经网络用于预测离子液体的自扩散系数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 429-438. |
| [12] | 麻雪怡, 刘克勤, 胡激江, 姚臻. POE溶液聚合反应器内混合与反应过程的CFD研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 322-337. |
| [13] | 朱娇, 栾丽萍, 从深震, 刘新磊. 氢气分离有机膜[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 138-158. |
| [14] | 王琪, 张斌, 张晓昕, 武虎建, 战海涛, 王涛. 氯铝酸-三乙胺离子液体/P2O5催化合成伊索克酸和2-乙基蒽醌[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [15] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号