化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (12): 4666-4678.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240580
刘思琪1( ), 易智康1, 肖媛1, 段欢欢1,2, 崔国民1(
), 易智康1, 肖媛1, 段欢欢1,2, 崔国民1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-29
修回日期:2024-06-23
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2025-01-03
通讯作者:
崔国民
作者简介:刘思琪(1996—),女,博士研究生,297277707@qq.com
基金资助:
Siqi LIU1( ), Zhikang YI1, Yuan XIAO1, Huanhuan DUAN1,2, Guomin CUI1(
), Zhikang YI1, Yuan XIAO1, Huanhuan DUAN1,2, Guomin CUI1( )
)
Received:2024-05-29
Revised:2024-06-23
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2025-01-03
Contact:
Guomin CUI
摘要:
热-质交换网络是系统工程中的重要领域,对质量交换子网络中贫流股进行处理可以有效回收传质过程中的多余热量,实现高效传质传热。目前的同步优化模型没有考虑到贫流股旁路对热-质交换网络的结构和年度综合费用的影响。因此,通过对质量交换子网络和热交换子网络的耦合关系分析,提出了基于旁路变换的内部贫流股间歇性换热策略来改进节点非结构模型。一方面,将具有单一换热性质的贫流股切割为多重换热流股,从而使热-质交换网络优化具有更丰富的结构;另一方面,贫流股旁路位置的不同也会影响优化效果。此外,由于该数学模型的求解域宽,直接求解的计算难度大,所以强制进化随机游走算法被用以求解该模型,其接受差解机制保证了全局搜索能力。采用所提出的同步优化方法对热-质交换网络算例进行优化,结果表明通过贫流股旁路位置变换获得了新的网络结构,增强了结构多样性;并且通过结构变异带动了年度综合费用的降低。这种方法对于节能减排的进一步推进具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
刘思琪, 易智康, 肖媛, 段欢欢, 崔国民. 考虑贫流股旁路的热-质交换网络同步优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4666-4678.
Siqi LIU, Zhikang YI, Yuan XIAO, Huanhuan DUAN, Guomin CUI. Simultaneous optimization of combined heat and mass exchange network synthesis considering lean stream bypass[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4666-4678.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 运行时长/(h/a) | 8600 |
| 塔板单价/(USD/(stage·a)) | 4552 |
| 塔板效率/% | 20 |
| 换热器费用/(USD/a) | 30000+750A0.81 |
| 年化因子 | 0.2 |
| S2/(USD/kg) | 0.001 |
| 热公用工程费用/(USD·kW/a) | 120 |
| 冷公用工程费用/(USD·kW/a) | 30 |
表1 算例1的费用数据
Table 1 Cost data of example 1
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 运行时长/(h/a) | 8600 |
| 塔板单价/(USD/(stage·a)) | 4552 |
| 塔板效率/% | 20 |
| 换热器费用/(USD/a) | 30000+750A0.81 |
| 年化因子 | 0.2 |
| S2/(USD/kg) | 0.001 |
| 热公用工程费用/(USD·kW/a) | 120 |
| 冷公用工程费用/(USD·kW/a) | 30 |
| R i | Gi /(kg/s) | yiin | yiout | Sj | Ljup/(kg/s) | xjin | xjout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 104 | 8.83×10-4 | 5.00×10-6 | S1 | 40 | 0.07557 | ≤0.115 |
| R2 | 442 | 7.00×10-4 | 5.00×10-6 | S2 | ∞ | 0.00100 | ≤0.010 |
表2 算例1的贫富流股数据
Table 2 Date of the rich/lean streams of example 1
| R i | Gi /(kg/s) | yiin | yiout | Sj | Ljup/(kg/s) | xjin | xjout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 104 | 8.83×10-4 | 5.00×10-6 | S1 | 40 | 0.07557 | ≤0.115 |
| R2 | 442 | 7.00×10-4 | 5.00×10-6 | S2 | ∞ | 0.00100 | ≤0.010 |
| 流股 | Tin/K | Tout/K | Tlo/K | Tup/K | cp /(kJ/(kg·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 298 | 298 | 288 | 313 | 1.00 |
| R2 | 298 | 298 | 288 | 313 | 1.00 |
| S1 | 348 | 368 | 279 | 368 | 2.50 |
| S2 | 310 | — | 280 | 330 | 2.40 |
| HU | 453 | 452 | — | — | — |
| CU | 278 | 283 | — | — | — |
表3 算例1的贫富流股热力学数据
Table 3 Thermal data of the rich/lean streams of example 1
| 流股 | Tin/K | Tout/K | Tlo/K | Tup/K | cp /(kJ/(kg·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 298 | 298 | 288 | 313 | 1.00 |
| R2 | 298 | 298 | 288 | 313 | 1.00 |
| S1 | 348 | 368 | 279 | 368 | 2.50 |
| S2 | 310 | — | 280 | 330 | 2.40 |
| HU | 453 | 452 | — | — | — |
| CU | 278 | 283 | — | — | — |
| 流股 | FCP/(kW/K) | Tin/K | Tout/K | H/(kW·m2/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 10.0 | 448 | 318 | 0.2 |
| H2 | 40.0 | 398 | 338 | 0.2 |
| C1 | 20.0 | 293 | 428 | 0.2 |
| C2 | 15.0 | 313 | 385 | 0.2 |
表4 算例1的冷热流股数据
Table 4 Data of the hot/cold streams of example 1
| 流股 | FCP/(kW/K) | Tin/K | Tout/K | H/(kW·m2/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 10.0 | 448 | 318 | 0.2 |
| H2 | 40.0 | 398 | 338 | 0.2 |
| C1 | 20.0 | 293 | 428 | 0.2 |
| C2 | 15.0 | 313 | 385 | 0.2 |
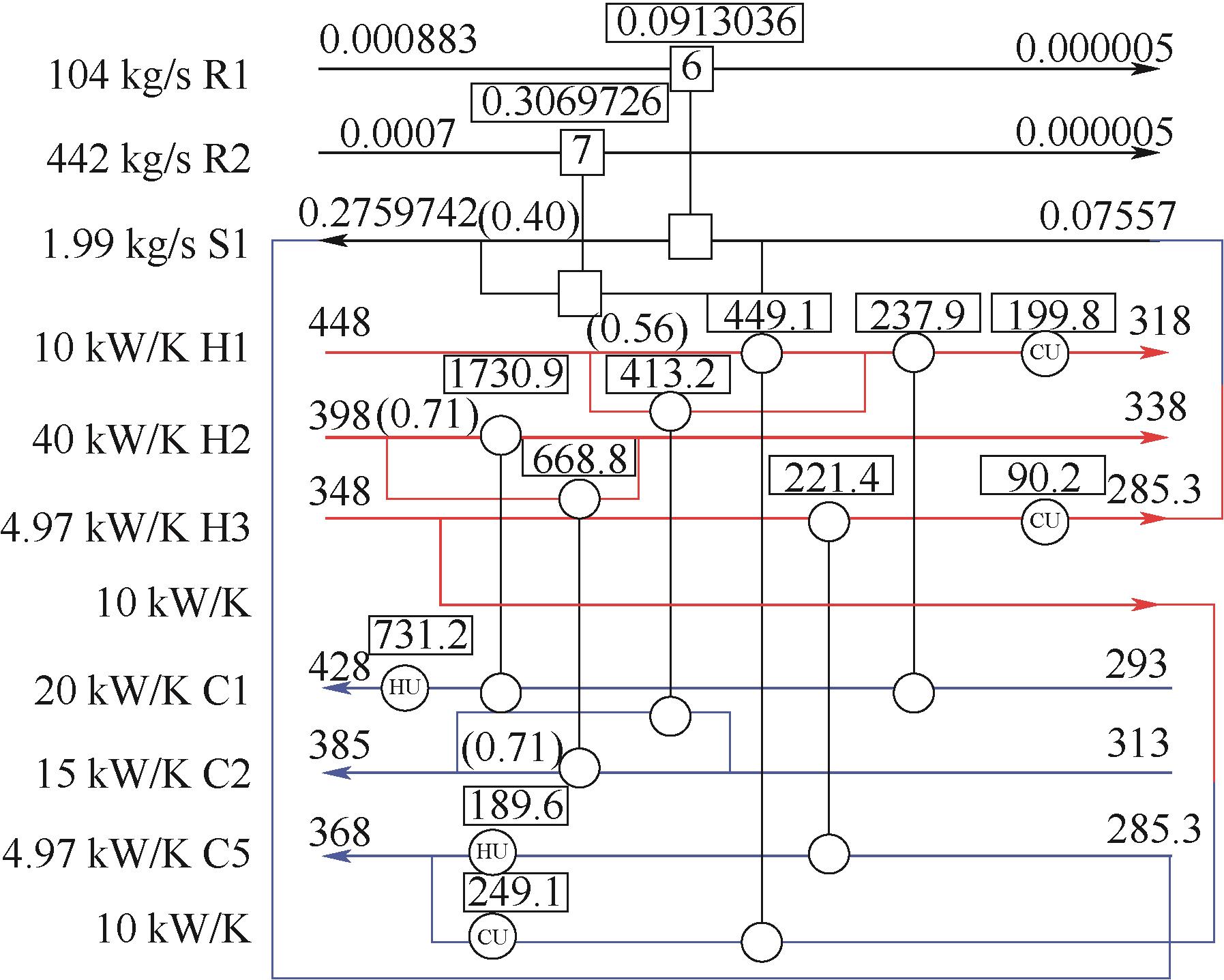
图9 采用本文优化方法求解算例2所得到的优化结果(TAC-HEN为254891 USD/a,TAC-MEN为59176 USD/a,TAC-HMEN为314067 USD/a)
Fig.9 The optimal result of example 2 using the optimization method in this study (TAC-HEN=254891 USD/a,TAC-MEN=59176 USD/a,TAC-HMEN=314067 USD/a)
| 1 | Gatto A. Quantifying management efficiency of energy recovery from waste for the circular economy transition in Europe[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 414: 136948. |
| 2 | Inayat A. Current progress of process integration for waste heat recovery in steel and iron industries[J]. Fuel, 2023, 338: 127237. |
| 3 | Agustina D. The influencing factors in cleaner production adoption on the aluminium processing industry[J]. Journal of Engineering and Management in Industrial System, 2023, 11(1): 14-25. |
| 4 | Isafiade A J, Short M. Review of mass exchanger network synthesis methodologies[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2019, 76: 49-54. |
| 5 | Short M, Isafiade A J. Thirty years of mass exchanger network synthesis—a systematic review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 304: 127112. |
| 6 | Isafiade A, Fraser D. Optimization of combined heat and mass exchanger networks using pinch technology[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2007, 2(6): 554-565. |
| 7 | Bagajewicz M J, Manousiouthakis V. Mass/heat-exchange network representation of distillation networks[J]. AIChE Journal, 1992, 38(11): 1769-1800. |
| 8 | Bagajewicz M J, Pham R, Manousiouthakis V. On the state space approach to mass/heat exchanger network design[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(14): 2595-2621. |
| 9 | Liu L L, Du J, El-Halwagi M M, et al. A simultaneous synthesis method for combined heat and mass exchange networks[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering. Singapore, 2012: 185-189. |
| 10 | Liu L L, Du J, El-Halwagi M M, et al. A systematic approach for synthesizing combined mass and heat exchange networks[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2013, 53: 1-13. |
| 11 | 陈子禾, 崔国民, 徐玥, 等. 基于控制参数动态协调策略的换热网络优化研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2020, 41(4): 957-965. |
| Chen Z H, Cui G M, Xu Y, et al. Study of heat exchanger network optimization based on dynamic coordination strategy of control parameters[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2020, 41(4): 957-965. | |
| 12 | 薛东峰, 陈理, 袁一, 等. 质量交换网络综合[J]. 现代化工, 2001, 21(6): 16-19, 21. |
| Xue D F, Chen L, Yuan Y, et al. Synthesis of mass exchange network[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2001, 21(6): 16-19, 21. | |
| 13 | Dong H G, Lin C Y, Chang C T. Simultaneous optimization approach for integrated water-allocation and heat-exchange networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(14): 3664-3678. |
| 14 | Kamat S, Bandyopadhyay S. Optimization of regeneration temperature for energy integrated water allocation networks[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2022, 8: 100490. |
| 15 | 彭肖祎, 董轩, 廖祖维, 等. 数学规划与图形方法相结合设计热集成用水网络[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 1047-1058. |
| Peng X Y, Dong X, Liao Z W, et al. Optimal design of heat integrated water allocation networks combining mathematical programming with graphical tools[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 1047-1058. | |
| 16 | Boix M, Pibouleau L, Montastruc L, et al. Minimizing water and energy consumptions in water and heat exchange networks[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 36: 442-455. |
| 17 | Kim J, Kim J, Kim J, et al. A simultaneous optimization approach for the design of wastewater and heat exchange networks based on cost estimation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2009, 17(2): 162-171. |
| 18 | Drobež R, Pintarič Z N, Pahor B, et al. Simultaneous synthesis of a biogas process and heat exchanger network[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 43: 91-100. |
| 19 | Isafiade A J, Fraser D M. Interval based MINLP superstructure synthesis of combined heat and mass exchanger networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2009, 87(11): 1536-1542. |
| 20 | Ghazouani S, Zoughaib A, Le Bourdiec S. An MILP model for simultaneous mass allocation and heat exchange networks design[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 158: 411-428. |
| 21 | Dong X, Zhang C J, Peng X Y, et al. Simultaneous design of heat integrated water allocation networks considering all possible splitters and mixers[J]. Energy, 2022, 238: 121916. |
| 22 | 刘薇薇, 崔国民, 张璐, 等. 一种应用于换热网络综合的阻尼优化方法[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2060-2072. |
| Liu W W, Cui G M, Zhang L, et al. Damping optimization method for heat exchange network synthesis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2060-2072. | |
| 23 | Srinivas B K, El-Halwagi M M. Synthesis of combined heat and reactive mass-exchange networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1994, 49(13): 2059-2074. |
| 24 | 刘琳琳. 多组分体系质量-热量联合交换网络综合研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013. |
| Liu L L. Study on combined mass and heat exchange networks synthesis for multi-component systems[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2013. | |
| 25 | 孙琳, 赵野, 罗雄麟. 基于夹点技术与超结构模型的多程换热网络最优综合[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(3): 967-975. |
| Sun L, Zhao Y, Luo X L. Synthesis of multi-pass heat exchanger network based on pinch technology and superstructure model[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(3): 967-975. | |
| 26 | Liu L L, Du J, Yang F L. Combined mass and heat exchange network synthesis based on stage-wise superstructure model[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 23(9): 1502-1508. |
| 27 | Zhou Z Q, Cui G M, Xiao Y. A novel node-based non-structural model for mass exchanger network synthesis using a stochastic algorithm[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 376: 134227. |
| 28 | Shenoy U V. Heat Exchanger Network Synthesis: Process Optimization by Energy and Resource Analysis[M]. Houston: Gulf Pub., 1995. |
| [1] | 李焱, 郑利军, 张恩勇, 王云飞. 深水海底管道软管内部流体渗透特性模型与试验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 118-125. |
| [2] | 孙娜娜, 董红妹, 郭文豪, 柳健, 胡建波, 靳爽. 改性磁性纳米粒子稳定的稠油O/W型乳状液的流变性影响因素及管输压降预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 143-157. |
| [3] | 杜得辉, 冯威, 张江辉, 项燕龙, 乔高攀, 李蔚. 微型翅片疏水复合强化管管内流动沸腾换热预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 95-107. |
| [4] | 李季, 王建林, 何睿, 周新杰, 王雯, 赵利强. 基于DBSVDD-RVR的多模态间歇过程质量变量在线软测量[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3231-3241. |
| [5] | 赵武灵, 满奕. 基于变分编码器的纳米纤维素分子结构预测模型框架研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3221-3230. |
| [6] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [7] | 朱子良, 王爽, 姜宇昂, 林梅, 王秋旺. 欧拉-拉格朗日迭代固-液相变算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [8] | 王倩倩, 李冰, 郑伟波, 崔国民, 赵兵涛, 明平文. 氢燃料电池局部动态特征三维模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [9] | 金虎, 杨帆, 戴梦瑶. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的液滴在圆柱壁面上运动过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2897-2908. |
| [10] | 杨明军, 巩广军, 郑嘉男, 宋永臣. 泥质低渗水合物降压开采特性与模型研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2909-2916. |
| [11] | 童永祺, 程杰, 林海, 陈曦, 赵海波. 10 MWth化学链燃烧反应装置的CPFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2949-2959. |
| [12] | 李洪瑞, 黄纯西, 洪小东, 廖祖维, 王靖岱, 阳永荣. 基于自适应变步长同伦法的循环流程收敛算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2604-2612. |
| [13] | 黄静茹, 陈佳轩, 张群锋, 阮晋, 朱来, 叶光华, 周兴贵. ZSM-5分子筛结构对苯烷基化反应性能影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2544-2555. |
| [14] | 马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| [15] | 李子扬, 郑楠, 方嘉宾, 魏进家. 再压缩S-CO2布雷顿循环性能分析及多目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2143-2156. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号